事件分发机制分析
从源码中分析Android的事件分发机制,看懂了源码就知道了整个事件分发机制的流程,看事件分发机制之前我们要知道几个相关事件处理的方法,Android主要就是通过这几个方法对事件进行分发拦截处理的:
(一)dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) 该方法用于事件分发
(二)onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) 该方法可拦截事件ViewGroup中才会有此方法
(三)onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) 该方法用于处理事件
其中几个方法中的参数都是MotionEvent类型,MotionEvent类中封装了事件的类型和事件触摸点位置等信息
下面我们通过一个实例进行对事件日志打印来看一下事件执行的顺序
1.自定义ViewGroup 实现dispatchTouchEvent和onInterceptTouchEvent,onTouchEvent方法并添加相应日志打印
public class MyViewGroup extends RelativeLayout {
private static final String TAG = "MyViewGroup";
public MyViewGroup(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public MyViewGroup(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public MyViewGroup(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
@Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
Log.i(TAG, "dispatchTouchEvent: action="+ev.getAction());
return super.dispatchTouchEvent(ev);
}
@Override
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
Log.i(TAG, "onInterceptTouchEvent: action="+ev.getAction());
return super.onInterceptTouchEvent(ev);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
Log.i(TAG, "onTouchEvent: action="+event.getAction());
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}
}
2.自定义View 实现dispatchTouchEvent和onTouchEvent方法并添加相应日志打印
public class MyView extends View implements View.OnTouchListener, View.OnClickListener {
private static final String TAG = "MyView";
public MyView(Context context) {
this(context,null);
}
public MyView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs,0);
}
public MyView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
setOnTouchListener(this);
setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
Log.i(TAG, "dispatchTouchEvent: action="+event.getAction());
return super.dispatchTouchEvent(event);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
Log.i(TAG, "onTouchEvent: action="+event.getAction());
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
Log.i(TAG, "onTouch: action="+event.getAction());
return false;
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Log.i(TAG, "onClick");
}
}
3.创建一个Activty 实现dispatchTouchEvent和onTouchEvent方法并添加相应日志打印
public class Main2Activity extends AppCompatActivity {
private static final String TAG = "Main2Activity";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main2);
}
@Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
Log.i(TAG, "dispatchTouchEvent: action="+ev.getAction());
return super.dispatchTouchEvent(ev);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
Log.i(TAG, "onTouchEvent: action="+event.getAction());
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}
}
4.将自定义View和ViewGroup添加到activity的布局文件中
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<com.example.test.MyViewGroup xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".Main2Activity">
<com.example.test.MyView
android:id="@+id/child_view"
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_height="300dp"
android:background="@color/colorAccent"/>
</com.example.test.MyViewGroup>
5.运行app,点击屏幕上的MyView查看打印日志
ACTION_DOWN = 0 表示手指按下事件
ACTION_UP = 1 表示手指抬起事件
ACTION_MOVE = 2 表示手指滑动事件
2020-02-16 19:37:08.640 6532-6532/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: dispatchTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 19:37:08.642 6532-6532/com.example.test I/MyViewGroup: dispatchTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 19:37:08.642 6532-6532/com.example.test I/MyViewGroup: onInterceptTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 19:37:08.642 6532-6532/com.example.test I/MyView: dispatchTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 19:37:08.643 6532-6532/com.example.test I/MyView: onTouch: action=0
2020-02-16 19:37:08.643 6532-6532/com.example.test I/MyView: onTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 19:37:08.695 6532-6532/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: dispatchTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 19:37:08.696 6532-6532/com.example.test I/MyViewGroup: dispatchTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 19:37:08.696 6532-6532/com.example.test I/MyViewGroup: onInterceptTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 19:37:08.696 6532-6532/com.example.test I/MyView: dispatchTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 19:37:08.697 6532-6532/com.example.test I/MyView: onTouch: action=2
2020-02-16 19:37:08.697 6532-6532/com.example.test I/MyView: onTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 19:37:08.764 6532-6532/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: dispatchTouchEvent: action=1
2020-02-16 19:37:08.765 6532-6532/com.example.test I/MyViewGroup: dispatchTouchEvent: action=1
2020-02-16 19:37:08.765 6532-6532/com.example.test I/MyViewGroup: onInterceptTouchEvent: action=1
2020-02-16 19:37:08.765 6532-6532/com.example.test I/MyView: dispatchTouchEvent: action=1
2020-02-16 19:37:08.766 6532-6532/com.example.test I/MyView: onTouch: action=1
2020-02-16 19:37:08.766 6532-6532/com.example.test I/MyView: onTouchEvent: action=1
2020-02-16 19:37:08.779 6532-6532/com.example.test I/MyView: onClick
从上面日志可以看出事件先调用Activity的dispatchTouchEvent()方法进行分发DOWN事件,紧接着调用ViewGroup的dispatchTouchEvent()方法进行分发DOWN事件,那么事件到底是怎么分发的呢?怎么从Activity的事件传到ViewGroup的呢?这里我们从Activity的dispatchTouchEvent()方法源码开始进行分析;
Activity中的dispatchTouchEvent()方法源码如下
/**
* Called to process touch screen events. You can override this to
* intercept all touch screen events before they are dispatched to the
* window. Be sure to call this implementation for touch screen events
* that should be handled normally.
*
* @param ev The touch screen event.
*
* @return boolean Return true if this event was consumed.
*/
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
if (ev.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
//当前分发的事件为DOWN事件 该方法是一个空方法 当activity的事件分发就会调用
onUserInteraction();
}
//这里调用了Window的superDispatchTouchEvent,由Window的实现了PhoneWindow来实现这个方法
if (getWindow().superDispatchTouchEvent(ev)) {
return true;
}
//这里调用Activity自身的onTouchEvent方法
//当getWindow().superDispatchTouchEvent(ev)返回true,onTouchEvent将不会调用
return onTouchEvent(ev);
}
下面我们接着来看PhoneWindow的superDispatchTouchEvent()方法
// This is the top-level view of the window, containing the window decor.
private DecorView mDecor;
....................................................
@Override
public boolean superDispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
//这里又调用了DecorView的superDispatchTouchEvent
return mDecor.superDispatchTouchEvent(event);
}
DecorView 中的superDispatchTouchEvent方法,当前DecorView extends FrameLayout ,而FramLayout中并没有dispatchTouchEvent方法,FrameLayout extends ViewGroup,最终这里是调用了ViewGroup的dispatchTouchEvent方法
public boolean superDispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
//调用了ViewGroup的dispatchTouchEvent方法
return super.dispatchTouchEvent(event);
}
这里我们重点来分析一下ViewGroup的dispatchTouchEvent()方法
@Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
.......................................................
//handled该值代表该方法最终的返回值
boolean handled = false;
//onFilterTouchEventForSecurity方法 Filter the touch event to apply security policies.
//过滤事件运用于安全策略 判断该事件是被分发还是被放弃 比如:当前视图被遮挡则会放弃事件
if (onFilterTouchEventForSecurity(ev)) {
final int action = ev.getAction();
final int actionMasked = action & MotionEvent.ACTION_MASK;
// Handle an initial down.
if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
// Throw away all previous state when starting a new touch gesture.
// The framework may have dropped the up or cancel event for the previous gesture
// due to an app switch, ANR, or some other state change.
//清除和取消所有之前的事件状态 以开启一个新的事件
cancelAndClearTouchTargets(ev);
//resets all touch state in preparation for a new cycle.
resetTouchState();
}
// Check for interception.
//检查当前事件是否发生拦截
final boolean intercepted;
if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN
|| mFirstTouchTarget != null) {
//这里disallowIntercept值取决于子View是否调用了requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent方法来请求父类不拦截事件
final boolean disallowIntercept = (mGroupFlags & FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT) != 0;
//当disallowIntercept为false表示要执行父类ViewGroup的onInterceptTouchEvent方法
//当disallowIntercept为true则不会执行父类ViewGroup的onInterceptTouchEvent方法
if (!disallowIntercept) {
intercepted = onInterceptTouchEvent(ev);
ev.setAction(action); // restore action in case it was changed
} else {
intercepted = false;
}
} else {
// There are no touch targets and this action is not an initial down
// so this view group continues to intercept touches.
intercepted = true;
}
// Check for cancelation.
final boolean canceled = resetCancelNextUpFlag(this)
|| actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL;
TouchTarget newTouchTarget = null;
//如果当前事件没有被取消和被拦截
if (!canceled && !intercepted) {
if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN
|| (split && actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_DOWN)
|| actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_HOVER_MOVE) {
final int actionIndex = ev.getActionIndex(); // always 0 for down
final int idBitsToAssign = split ? 1 << ev.getPointerId(actionIndex)
: TouchTarget.ALL_POINTER_IDS;
// Clean up earlier touch targets for this pointer id in case they
// have become out of sync.
removePointersFromTouchTargets(idBitsToAssign);
final int childrenCount = mChildrenCount;
if (newTouchTarget == null && childrenCount != 0) {
final float x = ev.getX(actionIndex);
final float y = ev.getY(actionIndex);
// Find a child that can receive the event.
// Scan children from front to back.
//buildTouchDispatchChildList对子View根据Z值进行排序 例如,重叠的View
final ArrayList<View> preorderedList = buildTouchDispatchChildList();
final boolean customOrder = preorderedList == null
&& isChildrenDrawingOrderEnabled();
final View[] children = mChildren;
for (int i = childrenCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final int childIndex = getAndVerifyPreorderedIndex(
childrenCount, i, customOrder);
final View child = getAndVerifyPreorderedView(
preorderedList, children, childIndex);
//这里canViewReceivePointerEvents方法判断当前子View是否能接收到事件
//isTransformedTouchPointInView方法用于判断当前事件是否在子View的视图上
//不满足则不做操作,执行下一个View的处理
if (!canViewReceivePointerEvents(child)
|| !isTransformedTouchPointInView(x, y, child, null)) {
ev.setTargetAccessibilityFocus(false);
continue;
}
}
}
}
}
// Dispatch to touch targets.
//这里mFirstTouchTarget为空
if (mFirstTouchTarget == null) {
// No touch targets so treat this as an ordinary view.
//这里dispatchTransformedTouchEvent中第三个参数child为null 会调用自己的dispatchTouchEvent方法去分发事件
handled = dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, canceled, null,
TouchTarget.ALL_POINTER_IDS);
} else {
// Dispatch to touch targets, excluding the new touch target if we already
// dispatched to it. Cancel touch targets if necessary.
TouchTarget predecessor = null;
TouchTarget target = mFirstTouchTarget;
//TouchTarget 是一个单链表结构,封装着触摸事件信息,包含当前接收事件的View和下一个接收事件的TouchTarget
//这里遍历所有能接收到事件的View
while (target != null) {
final TouchTarget next = target.next;
if (alreadyDispatchedToNewTouchTarget && target == newTouchTarget) {
handled = true;
} else {
final boolean cancelChild = resetCancelNextUpFlag(target.child)
|| intercepted;
//dispatchTransformedTouchEvent方法中会调用子View的dispatchTouchEvent分发事件
if (dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, cancelChild,
target.child, target.pointerIdBits)) {
handled = true;
}
if (cancelChild) {
if (predecessor == null) {
//mFirstTouchTarget赋值
mFirstTouchTarget = next;
} else {
predecessor.next = next;
}
target.recycle();
target = next;
continue;
}
}
predecessor = target;
target = next;
}
}
}
return handled;
}
接下来看一下ViewGroup的dispatchTransformedTouchEvent()方法做了什么
/**
* Transforms a motion event into the coordinate space of a particular child view,
* filters out irrelevant pointer ids, and overrides its action if necessary.
* If child is null, assumes the MotionEvent will be sent to this ViewGroup instead.
*/
private boolean dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(MotionEvent event, boolean cancel,
View child, int desiredPointerIdBits) {
final boolean handled;
// Perform any necessary transformations and dispatch.
//当child为null时会调用自己的dispatchTouchEvent方法分发事件
if (child == null) {
handled = super.dispatchTouchEvent(transformedEvent);
} else {
final float offsetX = mScrollX - child.mLeft;
final float offsetY = mScrollY - child.mTop;
transformedEvent.offsetLocation(offsetX, offsetY);
if (! child.hasIdentityMatrix()) {
transformedEvent.transform(child.getInverseMatrix());
}
//调用子View的dispatchTouchEvent方法来分发事件
handled = child.dispatchTouchEvent(transformedEvent);
}
// Done.
transformedEvent.recycle();
return handled;
}
以上我们已经对getWindow().superDispatchTouchEvent(ev)即ViewGroup的dispatchTouchEvent方法进行分析,接下来我们对View的dispatchTouchEvent()方法进行分析
/**
* Pass the touch screen motion event down to the target view, or this
* view if it is the target.
*
* @param event The motion event to be dispatched.
* @return True if the event was handled by the view, false otherwise.
*/
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
boolean result = false;
//onFilterTouchEventForSecurity与上面ViewGroup中使用到的方法一样,对事件进行过滤,过滤掉被遮挡的事件等
if (onFilterTouchEventForSecurity(event)) {
if ((mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED && handleScrollBarDragging(event)) {
result = true;
}
//noinspection SimplifiableIfStatement
ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
//这里可以看到我们平常使用的OnTouchListener监听事件
//mOnTouchListener.onTouch()这个监听方法返回值直接影响了onTouchEvent()方法是否被调用
//当返回值为true时onTouchEvent()方法将不会被调用
if (li != null && li.mOnTouchListener != null
&& (mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED
&& li.mOnTouchListener.onTouch(this, event)) {
result = true;
}
//这里调用了我们的onTouchEvent()方法
if (!result && onTouchEvent(event)) {
result = true;
}
}
return result;
}
跟着源码继续分析View的onTouchEvent()方法
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
final float x = event.getX();
final float y = event.getY();
final int viewFlags = mViewFlags;
final int action = event.getAction();
final boolean clickable = ((viewFlags & CLICKABLE) == CLICKABLE
|| (viewFlags & LONG_CLICKABLE) == LONG_CLICKABLE)
|| (viewFlags & CONTEXT_CLICKABLE) == CONTEXT_CLICKABLE;
if (mTouchDelegate != null) {
if (mTouchDelegate.onTouchEvent(event)) {
return true;
}
}
if (clickable || (viewFlags & TOOLTIP) == TOOLTIP) {
switch (action) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
boolean prepressed = (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PREPRESSED) != 0;
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PRESSED) != 0 || prepressed) {
// take focus if we don't have it already and we should in
// touch mode.
boolean focusTaken = false;
if (isFocusable() && isFocusableInTouchMode() && !isFocused()) {
focusTaken = requestFocus();
}
if (!mHasPerformedLongPress && !mIgnoreNextUpEvent) {
// This is a tap, so remove the longpress check
removeLongPressCallback();
// Only perform take click actions if we were in the pressed state
if (!focusTaken) {
// Use a Runnable and post this rather than calling
// performClick directly. This lets other visual state
// of the view update before click actions start.
if (mPerformClick == null) {
mPerformClick = new PerformClick();
}
//在这里最终调用了performClick()方法
if (!post(mPerformClick)) {
performClickInternal();
}
}
}
}
mIgnoreNextUpEvent = false;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
......................................................
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL:
...........................................................................
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
...............................................
break;
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
View的performClick()方法中调用了我们平常使用的OnClickListener监听
public boolean performClick() {
final boolean result;
final ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnClickListener != null) {
playSoundEffect(SoundEffectConstants.CLICK);
//调用了OnClickListener监听的回调方法
li.mOnClickListener.onClick(this);
result = true;
} else {
result = false;
}
return result;
}
从以上源码分析可以看出一次Down事件的正常分发流程如下图所示
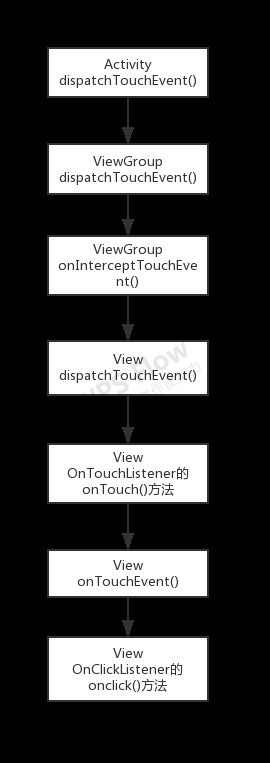
整个事件的分发流程大体是这样的,事件主要有3种类型,ACTION_DOWN按下,ACTION_MOVE移动,ACTION_UP抬起等事件,而事件分发需要一个一个的分发,先分发ACTION_DOWN事件,其后可能会分发ACTION_MOVE事件,最后分发ACTION_UP事件;事件从Activity的dispatchTouchEvent开始分发,紧接着调用了ViewGroup的dispatchTouchEvent方法进行分发事件,在分发Down事件的过程中ViewGroup可以通过onInterceptTouchEvent方法来拦截事件,如果拦截后,将不会再往下分发事件;如果没有拦截,ViewGroup会调用它的子View去调用dispatchTouchEvent继续分发事件,如果子View为ViewGroup又会让它的子View调用dispatchTouchEvent继续分发事件,直到最后一个子View执行事件分发,接着执行该子View的onTouchEvent方法,如果当前子View不处理事件会返回到它的父View处理,依次类推,最后返回给Activity的OnTouchEvent方法执行。
当处理事件冲突的时候,子类可以请求父类不拦截事件即不走父类的onInterceptTouchEvent方法,用到的方法为getParent().requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent(true); true表示子类不让父类拦截事件
问题1:将当前Activity中的dispatchTouchEvent()方法返回true或者为false,上面的案例的打印日志是什么?
2020-02-16 17:16:11.017 27877-27877/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: dispatchTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 17:16:11.068 27877-27877/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: dispatchTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 17:16:11.075 27877-27877/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: dispatchTouchEvent: action=1
问题2:将MyViewGroup中的dispatchTouchEvent()方法返回true或者为false,上面的案例的打印日志是什么?
返回true
2020-02-16 18:58:08.788 2314-2314/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: dispatchTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 18:58:08.789 2314-2314/com.example.test I/MyViewGroup: dispatchTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 18:58:08.826 2314-2314/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: dispatchTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 18:58:08.827 2314-2314/com.example.test I/MyViewGroup: dispatchTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 18:58:08.843 2314-2314/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: dispatchTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 18:58:08.844 2314-2314/com.example.test I/MyViewGroup: dispatchTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 18:58:08.846 2314-2314/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: dispatchTouchEvent: action=1
2020-02-16 18:58:08.846 2314-2314/com.example.test I/MyViewGroup: dispatchTouchEvent: action=1
返回false
2020-02-16 18:59:16.403 2837-2837/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: dispatchTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 18:59:16.405 2837-2837/com.example.test I/MyViewGroup: dispatchTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 18:59:16.405 2837-2837/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: onTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 18:59:16.409 2837-2837/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: dispatchTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 18:59:16.409 2837-2837/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: onTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 18:59:16.449 2837-2837/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: dispatchTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 18:59:16.449 2837-2837/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: onTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 18:59:16.466 2837-2837/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: dispatchTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 18:59:16.466 2837-2837/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: onTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 18:59:16.468 2837-2837/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: dispatchTouchEvent: action=1
2020-02-16 18:59:16.468 2837-2837/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: onTouchEvent: action=1
问题3:将MyViewGroup中的onInterceptTouchEvent()方法返回true,上面的案例的打印日志是什么?
2020-02-16 19:13:00.492 3274-3274/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: dispatchTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 19:13:00.493 3274-3274/com.example.test I/MyViewGroup: dispatchTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 19:13:00.493 3274-3274/com.example.test I/MyViewGroup: onInterceptTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 19:13:00.493 3274-3274/com.example.test I/MyViewGroup: onTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 19:13:00.494 3274-3274/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: onTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 19:13:00.508 3274-3274/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: dispatchTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 19:13:00.508 3274-3274/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: onTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 19:13:00.525 3274-3274/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: dispatchTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 19:13:00.525 3274-3274/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: onTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 19:13:00.542 3274-3274/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: dispatchTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 19:13:00.542 3274-3274/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: onTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 19:13:00.546 3274-3274/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: dispatchTouchEvent: action=1
2020-02-16 19:13:00.547 3274-3274/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: onTouchEvent: action=1
问题4:给MyView设置的OnTouchListener和OnClickListener,与自身的onTouchEvent()方法,执行顺序是什么?
2020-02-16 17:56:50.590 29801-29801/com.example.test I/MyView: dispatchTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 17:56:50.590 29801-29801/com.example.test I/MyView: onTouch: action=0
2020-02-16 17:56:50.590 29801-29801/com.example.test I/MyView: onTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 17:56:50.635 29801-29801/com.example.test I/MyView: dispatchTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 17:56:50.635 29801-29801/com.example.test I/MyView: onTouch: action=2
2020-02-16 17:56:50.635 29801-29801/com.example.test I/MyView: onTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 17:56:50.651 29801-29801/com.example.test I/MyView: dispatchTouchEvent: action=1
2020-02-16 17:56:50.651 29801-29801/com.example.test I/MyView: onTouch: action=1
2020-02-16 17:56:50.651 29801-29801/com.example.test I/MyView: onTouchEvent: action=1
2020-02-16 17:56:50.662 29801-29801/com.example.test I/MyView: onClick
可以看到OnTouchListener的onTouch()方法执行后,再执行onTouchEvent()方法,当整个事件DOWN,MOVE事件执行完成后手指离开屏幕时执行UP事件后,执行了OnClickListener的onClick()方法,因为performClick()方法在事件UP中执行的;
注意:当OnTouchListener的onTouch()方法返回值为true的时候不会执行onTouchEvent方法和OnClickListener的onClick()方法
问题5:将MyView中的dispatchTouchEvent()方法返回false,上面的案例的打印日志是什么?
2020-02-16 19:25:51.762 5233-5233/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: dispatchTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 19:25:51.763 5233-5233/com.example.test I/MyViewGroup: dispatchTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 19:25:51.763 5233-5233/com.example.test I/MyViewGroup: onInterceptTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 19:25:51.763 5233-5233/com.example.test I/MyView: dispatchTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 19:25:51.763 5233-5233/com.example.test I/MyViewGroup: onTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 19:25:51.765 5233-5233/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: onTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 19:25:51.817 5233-5233/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: dispatchTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 19:25:51.817 5233-5233/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: onTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 19:25:51.852 5233-5233/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: dispatchTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 19:25:51.852 5233-5233/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: onTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 19:25:51.857 5233-5233/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: dispatchTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 19:25:51.858 5233-5233/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: onTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 19:25:51.859 5233-5233/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: dispatchTouchEvent: action=1
2020-02-16 19:25:51.860 5233-5233/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: onTouchEvent: action=1
问题5:将MyView中的dispatchTouchEvent()方法返回true,上面的案例的打印日志是什么?
2020-02-16 19:28:44.983 5564-5564/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: dispatchTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 19:28:44.984 5564-5564/com.example.test I/MyViewGroup: dispatchTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 19:28:44.984 5564-5564/com.example.test I/MyViewGroup: onInterceptTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 19:28:44.984 5564-5564/com.example.test I/MyView: dispatchTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 19:28:45.029 5564-5564/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: dispatchTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 19:28:45.029 5564-5564/com.example.test I/MyViewGroup: dispatchTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 19:28:45.030 5564-5564/com.example.test I/MyViewGroup: onInterceptTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 19:28:45.030 5564-5564/com.example.test I/MyView: dispatchTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 19:28:45.044 5564-5564/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: dispatchTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 19:28:45.045 5564-5564/com.example.test I/MyViewGroup: dispatchTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 19:28:45.045 5564-5564/com.example.test I/MyViewGroup: onInterceptTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 19:28:45.045 5564-5564/com.example.test I/MyView: dispatchTouchEvent: action=2
2020-02-16 19:28:45.046 5564-5564/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: dispatchTouchEvent: action=1
2020-02-16 19:28:45.047 5564-5564/com.example.test I/MyViewGroup: dispatchTouchEvent: action=1
2020-02-16 19:28:45.047 5564-5564/com.example.test I/MyViewGroup: onInterceptTouchEvent: action=1
2020-02-16 19:28:45.047 5564-5564/com.example.test I/MyView: dispatchTouchEvent: action=1
问题6:将MyView中的onTouchEvent()方法返回false,上面的案例的打印日志是什么?
2020-02-16 19:31:59.576 5883-5883/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: dispatchTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 19:31:59.577 5883-5883/com.example.test I/MyViewGroup: dispatchTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 19:31:59.577 5883-5883/com.example.test I/MyViewGroup: onInterceptTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 19:31:59.577 5883-5883/com.example.test I/MyView: dispatchTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 19:31:59.577 5883-5883/com.example.test I/MyView: onTouch: action=0
2020-02-16 19:31:59.577 5883-5883/com.example.test I/MyView: onTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 19:31:59.577 5883-5883/com.example.test I/MyViewGroup: onTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 19:31:59.578 5883-5883/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: onTouchEvent: action=0
2020-02-16 19:31:59.665 5883-5883/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: dispatchTouchEvent: action=1
2020-02-16 19:31:59.665 5883-5883/com.example.test I/Main2Activity: onTouchEvent: action=1