驱动浅析(观看韦东山视频)
第12课第1节+字符设备驱动程序之概念介绍.WMV
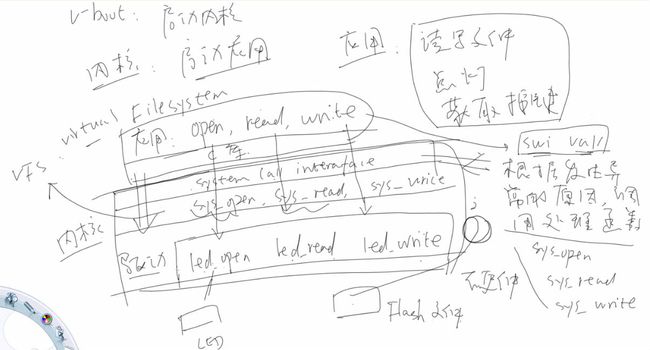
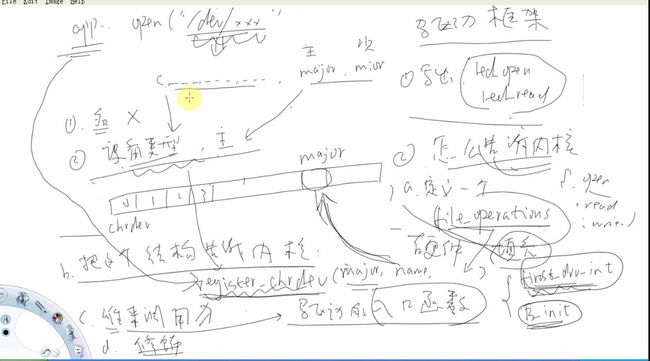
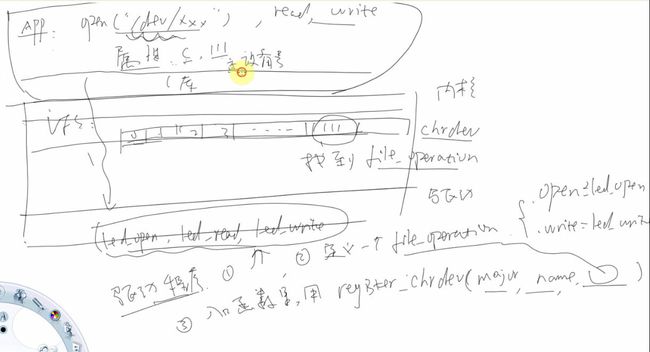
应用程序调用open,read,write等C库函数的时候,会进入内核空间。那么它是怎么进入内核空间的呢?
其实调用open,read,write等C库函数的实现,实质上会执行一条swi val指令,这条汇编指令就会引发
一个异常,就像中断一样,随之进入内核的异常处理函数当中;然后,system call interface(系统调用接口)
会在异常处理函数中根据发生中断的原因,调用不同的处理函数,比如用open的时候,传递进来的是val1,
用read的时候,传进来的是val2,用write的时候,传进来的是val3, 如open--->sys_open,read--->sys_read,
write--->sys_write(sys_open,sys_read,sys_write对应的那一层叫做VFS(虚拟文件系统)) ,这些sys_open,
sys_read,sys_write会根据打开的不同文件(如open(“/dev/leds”,O_RDWR),open("hello.txt",O_RDWR)),
调用不同的底层驱动程序(如led_open(),file_open())来实现不同的功能。
第12课第2.1节+字符设备驱动程序之LED驱动程序_编写编译
第一个驱动程序代码:first_drv.c
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
static struct class *firstdrv_class;
static struct class_device *firstdrv_class_dev;
volatile unsigned long *gpfcon = NULL;
volatile unsigned long *gpfdat = NULL;
static int first_drv_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
//printk("first_drv_open\n");
/* 配置GPF4,5,6为输出 */
*gpfcon &= ~((0x3<<(4*2)) | (0x3<<(5*2)) | (0x3<<(6*2)));
*gpfcon |= ((0x1<<(4*2)) | (0x1<<(5*2)) | (0x1<<(6*2)));
return 0;
}
static ssize_t first_drv_write(struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t * ppos)
{
int val;
//printk("first_drv_write\n");
copy_from_user(&val, buf, count); // copy_to_user();
if (val == 1)
{
// 点灯
*gpfdat &= ~((1<<4) | (1<<5) | (1<<6));
}
else
{
// 灭灯
*gpfdat |= (1<<4) | (1<<5) | (1<<6);
}
return 0;
}
static struct file_operations first_drv_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE, /* 这是一个宏,推向编译模块时自动创建的__this_module变量 */
.open = first_drv_open,
.write = first_drv_write,
};
int major;
static int first_drv_init(void)
{
major = register_chrdev(0, "first_drv", &first_drv_fops); // 注册, 告诉内核
firstdrv_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "firstdrv");
firstdrv_class_dev = class_device_create(firstdrv_class, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "xyz"); /* /dev/xyz */
gpfcon = (volatile unsigned long *)ioremap(0x56000050, 16);
gpfdat = gpfcon + 1;
return 0;
}
static void first_drv_exit(void)
{
unregister_chrdev(major, "first_drv"); // 卸载
class_device_unregister(firstdrv_class_dev);
class_destroy(firstdrv_class);
iounmap(gpfcon);
}
module_init(first_drv_init);
module_exit(first_drv_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
KERN_DIR = /work/system/linux-2.6.22.6
all:
make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules
clean:
make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules clean
rm -rf modules.order
第一个应用程序firstdrvtest.c
#include
#include
#include
#include
/* firstdrvtest on
* firstdrvtest off
*/
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd;
int val = 1;
fd = open("/dev/xyz", O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0)
{
printf("can't open!\n");
}
if (argc != 2)
{
printf("Usage :\n");
printf("%s \n", argv[0]);
return 0;
}
if (strcmp(argv[1], "on") == 0)
{
val = 1;
}
else
{
val = 0;
}
write(fd, &val, 4);
return 0;
}
可以用cat /proc/devices查看目前内核支持的设备,可以再其中查看目前内核中拥有的设备及其主设备号,以及设备文件名。
使用mknod /dev/xxx c major minor来手动创建设备文件。
使用insmod first_drv.ko来加载驱动。
使用rmmod first_drv来卸载驱动。
使用lsmod来查看目前拥有的模块驱动。
first_drv.c中
firstdrv_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "firstdrv"); //当加载驱动的时候,它会在/sys/class/下创建一个firstdrv类信息
firstdrv_class_dev = class_device_create(firstdrv_class, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "xyz"); //它会在/sys/class/firstdrv类下创建一个xyz设备,在xyz设备下有一个dev文件,可以通过cat dev命令查看其内容为252:0,其中252为主设备号,0为次设备号。而mdev会根据这这些内容自行创建设备节点,此处为/dev/xyz c 252 0。
mdev为何能够完成这些功能呢?
应为我们在制作根文件系统时,在/etc/init.d/rcS文件中加入echo /sbin/mdev > /proc/sys/kernel/hotplug,用来设置内核当有设备拔插时,调用/sbin/mdev