Java集合:LinkedList详解
概述
本文就LinkedList的几个主要方法展开介绍,并结合几个图片来介绍几个重要操作。
基础属性
transient int size = 0; // 节点数量
/**
* Pointer to first node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (first.prev == null && first.item != null)
*/
transient Node first; // 第一个节点(头结点)
/**
* Pointer to last node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (last.next == null && last.item != null)
*/
transient Node last; // 最后一个节点(尾节点)
//...
private static class Node { // Node的数据结构
E item; // 存放的对象
Node next; // 下一个节点
Node prev; // 上一个节点
Node(Node prev, E element, Node next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
} 基本数据结构图如下:
add方法
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e); // 调用linkLast方法, 将节点添加到尾部
return true;
}
public void add(int index, E element) { // 在index位置插入节点,节点值为element
checkPositionIndex(index);
if (index == size) // 如果索引为size,即将element插入链表尾部
linkLast(element);
else // 否则,将element插入原index位置节点的前面,即:将element插入index位置,将原index位置节点移到index+1的位置
linkBefore(element, node(index)); // 将element插入index位置
}add(int index, E element):
- 检查index是否越界
- 比较index与size,如果index==size,则代表插入位置为链表尾部,调用linkLast方法(linkLast方法详解见下文),否则调用linkBefore方法(LinkBefore方法详解见下文)
get方法
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index); // 校验index是否越界
return node(index).item; // 根据index, 调用node方法寻找目标节点,返回目标节点的item
}- 校验index是否越界
- 调用node方法寻找目标节点,并返回目标节点的item(node方法详解见下文)
set方法
public E set(int index, E element) { // 替换index位置节点的值为element
checkElementIndex(index); // 检查index是否越界
Node x = node(index); // 根据index, 调用node方法寻找到目标节点
E oldVal = x.item; // 节点的原值
x.item = element; // 将节点的item属性设为element
return oldVal; //返回节点原值
} - 检查index是否越界
- 调用node方法寻找目标节点(node方法详解见下文)
- 将目标节点的item属性设为element
remove方法
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) { // 如果o为空, 则遍历链表寻找item属性为空的节点, 并调用unlink方法将该节点移除
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else { // 如果o不为空, 则遍历链表寻找item属性跟o相同的节点, 并调用unlink方法将该节点移除
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
public E remove(int index) { // 移除index位置的节点
checkElementIndex(index); // 检查index是否越界
return unlink(node(index)); // 移除index位置的节点
} - 判断o是否为null,如果o为null,则遍历链表寻找item属性为空的节点,并调用unlink方法将该节点移除(unlink方法详解见下文)
- 如果o不为null, 则遍历链表寻找item属性跟o相同的节点,并调用unlink方法将该节点移除(unlink方法详解见下文)
remove(int index):
- 检查index是否越界
- 调用unlink方法,移除index位置的节点(unlink方法详解见下文)
clear方法
public void clear() { // 清除链表的所有节点
// Clearing all of the links between nodes is "unnecessary", but:
// - helps a generational GC if the discarded nodes inhabit
// more than one generation
// - is sure to free memory even if there is a reachable Iterator
for (Node x = first; x != null; ) { // 从头结点开始遍历将所有节点的属性清空
Node next = x.next;
x.item = null;
x.next = null;
x.prev = null;
x = next;
}
first = last = null; // 将头结点和尾节点设为null
size = 0;
modCount++;
} - 从first节点开始,遍历将所有节点的属性清空
- 将first节点和last节点设为null
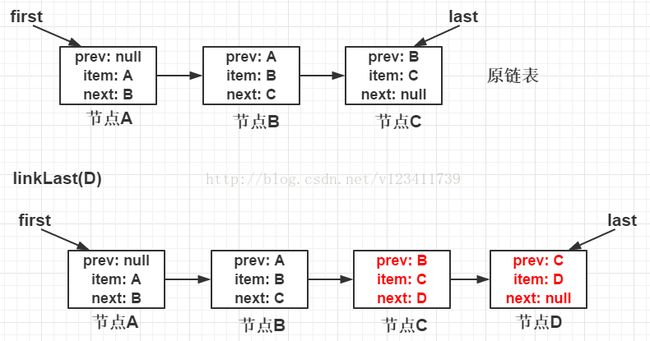
linkLast方法
void linkLast(E e) { // 将e放到链表的最后一个节点
final Node l = last; // 拿到当前的尾节点l节点
final Node newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); // 使用e创建一个新的节点newNode, prev属性为l节点, next属性为null
last = newNode; // 将当前尾节点设置为上面新创建的节点newNode
if (l == null) // 如果l节点为空则代表当前链表为空, 将newNode设置为头结点
first = newNode;
else // 否则将l节点的next属性设置为newNode
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
} - 拿到当前的尾节点l节点
- 使用e创建一个新的节点newNode,prev属性为l节点,next属性为null
- 将当前尾节点设置为上面新创建的节点newNode
- 如果l节点为空则代表当前链表为空, 将newNode设置为头结点,否则将l节点的next属性设置为newNode
linkBefore方法
void linkBefore(E e, Node succ) { // 将e插入succ节点前面
// assert succ != null;
final Node pred = succ.prev; // 拿到succ节点的prev节点
final Node newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ); // 使用e创建一个新的节点newNode,其中prev属性为pred节点,next属性为succ节点
succ.prev = newNode; // 将succ节点的prev属性设置为newNode
if (pred == null) // 如果pred节点为null,则代表succ节点为头结点,要把e插入succ前面,因此将first设置为newNode
first = newNode;
else // 否则将pred节点的next属性设为newNode
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
} - 拿到succ节点的prev节点
- 使用e创建一个新的节点newNode,其中prev属性为pred节点,next属性为succ节点
- 将succ节点的prev属性设置为newNode
- 如果pred节点为null,则代表succ节点为头结点,要把e插入succ前面,因此将first设置为newNode,否则将pred节点的next属性设为newNode
unlink方法
E unlink(Node x) { // 移除链表上的x节点
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item; // x节点的值
final Node next = x.next; // x节点的下一个节点
final Node prev = x.prev; // x节点的上一个节点
if (prev == null) { // 如果prev为空,则代表x节点为头结点,则将first指向next即可
first = next;
} else { // 否则,x节点不为头结点,
prev.next = next; // 将prev节点的next属性指向x节点的next属性
x.prev = null; // 将x的prev属性清空
}
if (next == null) { // 如果next为空,则代表x节点为尾节点,则将last指向prev即可
last = prev;
} else { // 否则,x节点不为尾节点
next.prev = prev; // 将next节点的prev属性指向x节点的prev属性
x.next = null; // 将x的next属性清空
}
x.item = null; // 将x的值清空,以便垃圾收集器回收x对象
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
} - 定义element为x节点的值,next为x节点的下一个节点,prev为x节点的上一个节点
- 如果prev为空,则代表x节点为头结点,则将first指向next即可;否则,x节点不为头结点,将prev节点的next属性指向x节点的next属性,并将x的prev属性清空
- 如果next为空,则代表x节点为尾节点,则将last指向prev即可;否则,x节点不为尾节点,将next节点的prev属性指向x节点的prev属性,并将x的next属性清空
- 将x的item属性清空,以便垃圾收集器回收x对象
过程如图所示
ArrayList和LinkedList比较
ArrayList详解可以看我的另一篇文章:Java集合:ArrayList详解
- ArrayList底层基于动态数组实现,LinkedList底层基于链表实现
- 对于随机访问(get/set方法),ArrayList通过index直接定位到数组对应位置的节点,而LinkedList需要从头结点或尾节点开始遍历,直到寻找到目标节点,因此在效率上ArrayList优于LinkedList
- 对于插入和删除(add/remove方法),ArrayList需要移动目标节点后面的节点(使用System.arraycopy方法移动节点),而LinkedList只需修改目标节点前后节点的next或prev属性即可,因此在效率上LinkedList优于ArrayList。
参考
LinkedList源码(JDK 1.8)
—————END—————
![]()