秋招算法充分理解回溯(leetcode中级难度)
回溯
回溯法是一种探索所有潜在可能性找到解决方案的算法。如果当前方案不是正确的解决方案,或者不是最后一个正确的解决方案,则回溯法通过修改上一步的值继续寻找解决方案。
17. 电话号码的字母组合
给定一个仅包含数字 2-9 的字符串,返回所有它能表示的字母组合。
给出数字到字母的映射如下(与电话按键相同)。注意 1 不对应任何字母。
![]()
示例:
输入:"23"
输出:["ad", "ae", "af", "bd", "be", "bf", "cd", "ce", "cf"].
解法一 (DFS+剪枝)
先创建字典,然后遍历DFS,字符下标位移,循环字典字符串,剪枝回溯循环
class Solution {
public List<String> letterCombinations(String digits) {
List<String> combinations = new ArrayList<String>();
if (digits.length() == 0) {
return combinations;
}
Map<Character, String> phoneMap = new HashMap<Character, String>() {
{
put('2', "abc");
put('3', "def");
put('4', "ghi");
put('5', "jkl");
put('6', "mno");
put('7', "pqrs");
put('8', "tuv");
put('9', "wxyz");
}};
backtrack(combinations, phoneMap, digits, 0, new StringBuffer());
return combinations;
}
public void backtrack(List<String> combinations, Map<Character, String> phoneMap, String digits, int index, StringBuffer combination) {
if (index == digits.length()) {
combinations.add(combination.toString());
} else {
char digit = digits.charAt(index);
String letters = phoneMap.get(digit);
int lettersCount = letters.length();
for (int i = 0; i < lettersCount; i++) {
combination.append(letters.charAt(i));
backtrack(combinations, phoneMap, digits, index + 1, combination);
combination.deleteCharAt(index);
}
}
}
}
解法二 (队列辅助器)
class Solution {
public List<String> letterCombinations(String digits) {
if(digits==null || digits.length()==0) {
return new ArrayList<String>();
}
//一个映射表,第二个位置是"abc“,第三个位置是"def"。。。
//这里也可以用map,用数组可以更节省点内存
String[] letter_map = {
" ","*","abc","def","ghi","jkl","mno","pqrs","tuv","wxyz"
};
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
//先往队列中加入一个空字符
res.add("");
for(int i=0;i<digits.length();i++) {
//由当前遍历到的字符,取字典表中查找对应的字符串
String letters = letter_map[digits.charAt(i)-'0'];
int size = res.size();
//计算出队列长度后,将队列中的每个元素挨个拿出来
for(int j=0;j<size;j++) {
//每次都从队列中拿出第一个元素
String tmp = res.remove(0);
//然后跟"def"这样的字符串拼接,并再次放到队列中
for(int k=0;k<letters.length();k++) {
res.add(tmp+letters.charAt(k));
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
332. 重新安排行程
难度中等174收藏分享切换为英文关注反馈
给定一个机票的字符串二维数组 [from, to],子数组中的两个成员分别表示飞机出发和降落的机场地点,对该行程进行重新规划排序。所有这些机票都属于一个从 JFK(肯尼迪国际机场)出发的先生,所以该行程必须从 JFK 开始。
说明:
- 如果存在多种有效的行程,你可以按字符自然排序返回最小的行程组合。例如,行程 [“JFK”, “LGA”] 与 [“JFK”, “LGB”] 相比就更小,排序更靠前
- 所有的机场都用三个大写字母表示(机场代码)。
- 假定所有机票至少存在一种合理的行程。
示例 1:
输入: [["MUC", "LHR"], ["JFK", "MUC"], ["SFO", "SJC"], ["LHR", "SFO"]]
输出: ["JFK", "MUC", "LHR", "SFO", "SJC"]
示例 2:
输入: [["JFK","SFO"],["JFK","ATL"],["SFO","ATL"],["ATL","JFK"],["ATL","SFO"]]
输出: ["JFK","ATL","JFK","SFO","ATL","SFO"]
解释: 另一种有效的行程是 ["JFK","SFO","ATL","JFK","ATL","SFO"]。但是它自然排序更大更靠后。
class Solution {
Map<String, PriorityQueue<String>> map = new HashMap<String, PriorityQueue<String>>();
List<String> itinerary = new LinkedList<String>();
public List<String> findItinerary(List<List<String>> tickets) {
//其实就是创建了一个key-value得字典
for (List<String> ticket : tickets) {
String src = ticket.get(0), dst = ticket.get(1);
if (!map.containsKey(src)) {
map.put(src, new PriorityQueue<String>());
}
map.get(src).offer(dst);
}
dfs("JFK");
Collections.reverse(itinerary);
return itinerary;
}
//拿第一个字母进来找下一个key,直到找不到,再回溯添加路径
public void dfs(String curr) {
while (map.containsKey(curr) && map.get(curr).size() > 0) {
String tmp = map.get(curr).poll();
dfs(tmp);
}
itinerary.add(curr);
}
}
46. 全排列
给定一个 没有重复 数字的序列,返回其所有可能的全排列。
示例:
输入: [1,2,3]
输出:
[
[1,2,3],
[1,3,2],
[2,1,3],
[2,3,1],
[3,1,2],
[3,2,1]
]
典型得回溯解法: 第一步先确定好起点,然后开始决策,往下走,而且要走完剪枝,这样能回溯
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
/* 主函数,输入一组不重复的数字,返回它们的全排列 */
// 记录「路径」
LinkedList<Integer> track = new LinkedList<>();
backtrack(nums, track);
return res;
}
// 路径:记录在 track 中
// 选择列表:nums 中不存在于 track 的那些元素
// 结束条件:nums 中的元素全都在 track 中出现
void backtrack(int[] nums, LinkedList<Integer> track) {
// 触发结束条件
if (track.size() == nums.length) {
res.add(new LinkedList(track));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 排除不合法的选择
if (track.contains(nums[i]))
continue;
// 做选择
track.add(nums[i]);
// 进入下一层决策树
backtrack(nums, track);
// 取消选择
track.removeLast();
}
}
}
面试题 08.07. 无重复字符串的排列组合
难度中等22收藏分享切换为英文关注反馈
无重复字符串的排列组合。编写一种方法,计算某字符串的所有排列组合,字符串每个字符均不相同。
示例1:
输入:S = "qwe"
输出:["qwe", "qew", "wqe", "weq", "ewq", "eqw"]
示例2:
输入:S = "ab"
输出:["ab", "ba"]
套路跟上面一模一样,这次我用得String来保存路径
class Solution {
List<String> result=new ArrayList<>();
String str="";
public String[] permutation(String S) {
dfs(S,str);
String [] a=new String[result.size()]; //创建string类型数组
result.toArray(a);//将list集合转成string数组
return a;
}
public void dfs(String S,String str){
if(str.length()==S.length()){
result.add(str);
}
for(int i=0;i<S.length();i++){
if(str.indexOf(S.charAt(i))!=-1){
continue;
}
str+=S.charAt(i);
dfs(S,str);
str=str.substring(0,str.length()-1);
}
}
}
面试题 08.08. 有重复字符串的排列组合
有重复字符串的排列组合。编写一种方法,计算某字符串的所有排列组合。
示例1:
输入:S = "qqe"
输出:["eqq","qeq","qqe"]
示例2:
输入:S = "ab"
输出:["ab", "ba"]
思路: 这种带有重复得字母得话,需要一个标记或者set去重,set的话比较简单,按照正常dfs然后存入路径然后再转String数组,这里我还用一个标记位数组,来标记我们已经选择过得字母,这样就不会出现aa,bb自己本身得
class Solution {
public String[] permutation(String S) {
Set<String> res = new HashSet<>();
combination(res,S,new StringBuilder(),new boolean[S.length()]);
return res.toArray(new String[res.size()]);
}
private void combination(Set<String> res, String s, StringBuilder sb, boolean[] marked){
if(sb.length() == s.length()){
res.add(sb.toString());
return;
}
for(int i = 0;i<s.length();i++){
if(!marked[i]){
marked[i] = true; //在未剪枝前也就是选择路径得时候不能选已经选过的下标
sb.append(s.charAt(i));
combination(res,s,sb,marked);
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length()-1);
marked[i] = false; //回溯完一个节点,解封下标
}
}
}
}
79. 单词搜索
给定一个二维网格和一个单词,找出该单词是否存在于网格中。
单词必须按照字母顺序,通过相邻的单元格内的字母构成,其中“相邻”单元格是那些水平相邻或垂直相邻的单元格。同一个单元格内的字母不允许被重复使用。
示例:
board =
[
['A','B','C','E'],java
['S','F','C','S'],
['A','D','E','E']
]
给定 word = "ABCCED", 返回 true
给定 word = "SEE", 返回 true
给定 word = "ABCB", 返回 false
public class Solution {
private boolean[][] marked;
// x-1,y
// x,y-1 x,y x,y+1
// x+1,y
private int[][] direction = {
{
-1, 0}, {
0, -1}, {
0, 1}, {
1, 0}}; //上左右下
// 盘面上有多少行
private int m;
// 盘面上有多少列
private int n;
private String word;
private char[][] board;
public boolean exist(char[][] board, String word) {
m = board.length;
if (m == 0) {
return false;
}
n = board[0].length;
marked = new boolean[m][n];
this.word = word;
this.board = board;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (dfs(i, j, 0)) {
//找到第一个满足的字母 后续交给dfs如果true就返回true,否则就不行
return true; //返回
}
}
}
return false;
}
private boolean dfs(int i, int j, int start) {
if (start == word.length() - 1) {
//如果下标在单词的最后一个了,看看是否相等,相等就返回true
return board[i][j] == word.charAt(start);
}
if (board[i][j] == word.charAt(start)) {
//下标不是最后一个
marked[i][j] = true; //先标记已经走过
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
//往四个方向DFS
int newX = i + direction[k][0]; //{
{-1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}}
int newY = j + direction[k][1];
if (inArea(newX, newY) && !marked[newX][newY]) {
//如果这个个方向没越界,且没走过,就下标加一往下dfs,如果四周都没有满足的那要还原这个标志位,因为如果首字母在别处遍历过来还要判断这个走过没有
if (dfs(newX, newY, start + 1)) {
return true;
}
}
}
marked[i][j] = false;
}
return false;
}
private boolean inArea(int x, int y) {
return x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n;
}
}
39. 组合总和
给定一个无重复元素的数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的数字可以无限制重复被选取。
说明:
- 所有数字(包括
target)都是正整数。 - 解集不能包含重复的组合。
示例 1:
输入:candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7,
所求解集为:
[
[7],
[2,2,3]
]
示例 2:
输入:candidates = [2,3,5], target = 8,
所求解集为:
[
[2,2,2,2],
[2,3,3],
[3,5]
]
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.List;
public class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
int len = candidates.length;
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (len == 0) {
return res;
}
Deque<Integer> path = new ArrayDeque<>();
dfs(candidates, 0, len, target, path, res);
return res;
}
/**
* @param candidates 候选数组
* @param begin 搜索起点
* @param len 冗余变量,是 candidates 里的属性,可以不传
* @param target 每减去一个元素,目标值变小
* @param path 从根结点到叶子结点的路径,是一个栈
* @param res 结果集列表
*/
private void dfs(int[] candidates, int begin, int len, int target, Deque<Integer> path, List<List<Integer>> res) {
// target 为负数和 0 的时候不再产生新的孩子结点
if (target < 0) {
return;
}
if (target == 0) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
// 重点理解这里从 begin 开始搜索的语意
for (int i = begin; i < len; i++) {
path.addLast(candidates[i]);
// 注意:由于每一个元素可以重复使用,下一轮搜索的起点依然是 i,这里非常容易弄错
dfs(candidates, i, len, target - candidates[i], path, res);
// 状态重置
path.removeLast();
}
}
}
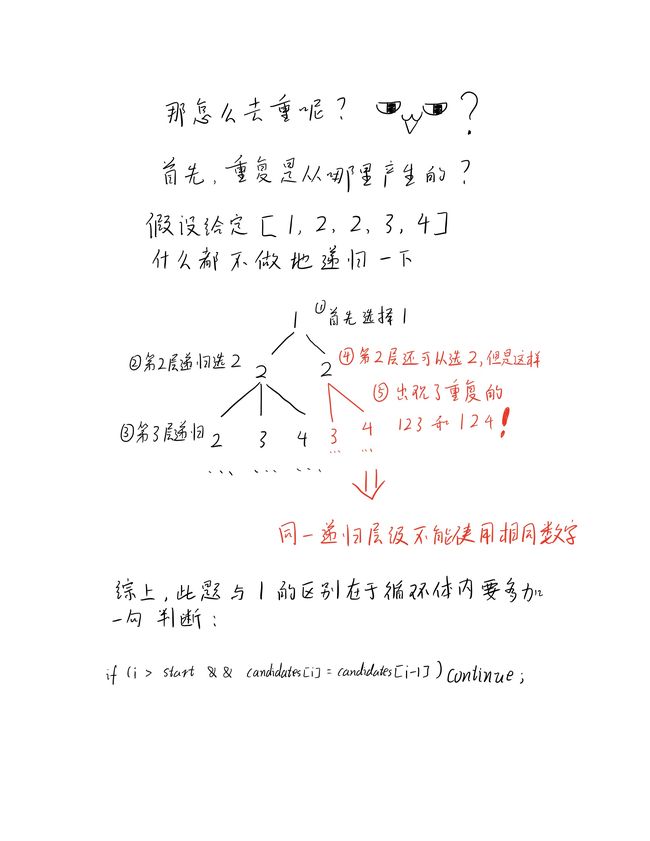
40. 组合总和 II
难度中等344收藏分享切换为英文关注反馈
给定一个数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次。
说明:
- 所有数字(包括目标数)都是正整数。
- 解集不能包含重复的组合。
示例 1:
输入: candidates = [10,1,2,7,6,1,5], target = 8,
所求解集为:
[
[1, 7],
[1, 2, 5],
[2, 6],
[1, 1, 6]
]
示例 2:
输入: candidates = [2,5,2,1,2], target = 5,
所求解集为:
[
[1,2,2],
[5]
]
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new LinkedList<>();
Arrays.sort(candidates);//先排序 1,2,2,2,5
backtrack(list, new ArrayList<>(), candidates, target, 0);
return list;
}
private void backtrack(List<List<Integer>> list, List<Integer> cur, int[] candidates, int target, int start) {
if (target == 0) {
list.add(new ArrayList<>(cur));
return;
}
for (int i = start; i < candidates.length; i++) {
if (target < candidates[i])
break;
if (i > start && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]) //循环横向发现重复,跳过
continue; //去掉重复的
cur.add(candidates[i]);
backtrack(list, cur, candidates, target - candidates[i], i + 1);
cur.remove(cur.size() - 1);
}
}
}
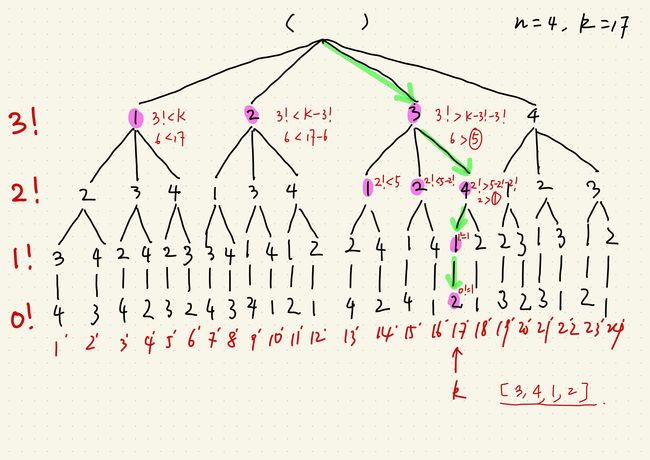
60. 第k个排列
给出集合 [1,2,3,…,*n*],其所有元素共有 n! 种排列。
按大小顺序列出所有排列情况,并一一标记,当 n = 3 时, 所有排列如下:
"123""132""213""231""312""321"
给定 n 和 k,返回第 k 个排列。
说明:
- 给定 n 的范围是 [1, 9]。
- 给定 k 的范围是[1, n!]。
示例 1:
输入: n = 3, k = 3
输出: "213"
示例 2:
输入: n = 4, k = 9
输出: "2314"
标准的去重DFS+剪枝
class Solution {
public String getPermutation(int n, int k) {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
StringBuilder solution = new StringBuilder();
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
backtrack(res,solution,n,k,visited);
return res.get(k-1);
}
void backtrack(List<String> res, StringBuilder solution,int n,int k,boolean[] visited){
if( res.size() == k) return;
if( solution.length() == n){
res.add(solution.toString());
return;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(visited[i-1]) continue;
visited[i-1] = true;
solution.append(i);
backtrack(res,solution,n,k,visited);
visited[i-1]=false;
solution.deleteCharAt(solution.length() -1);
}
}
}
78. 子集
给定一组不含重复元素的整数数组 nums,返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
**说明:**解集不能包含重复的子集。
示例:
输入: nums = [1,2,3]
输出:
[
[3],
[1],
[2],
[1,2,3],
[1,3],
[2,3],
[1,2],
[]
]
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> output = new ArrayList();
int n, k;
//DFS方法
public void backtrack(int first, ArrayList<Integer> curr, int[] nums) {
// if the combination is done
if (curr.size() == k)
output.add(new ArrayList(curr));
for (int i = first; i < n; ++i) {
// add i into the current combination
curr.add(nums[i]);
// use next integers to complete the combination
backtrack(i + 1, curr, nums);
// backtrack
curr.remove(curr.size() - 1);
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
n = nums.length;
for (k = 0; k < n + 1; ++k) {
backtrack(0, new ArrayList<Integer>(), nums);
}
return output;
}
}
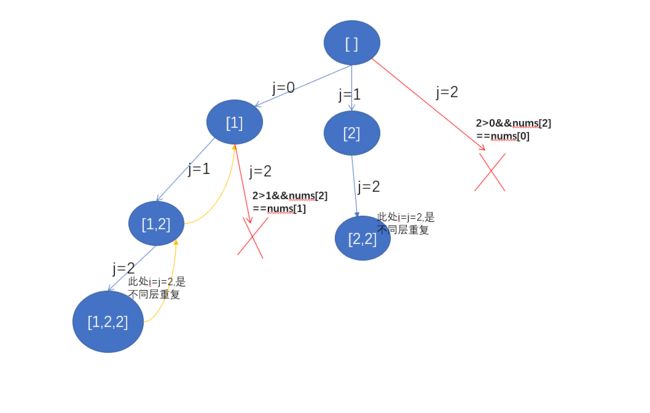
90. 子集 II
给定一个可能包含重复元素的整数数组 nums,返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
**说明:**解集不能包含重复的子集。
示例:
输入: [1,2,2]
输出:
[
[2],
[1],
[1,2,2],
[2,2],
[1,2],
[]
]
同层去重的关键就是 : 排序并且判断同层循环的元素有无重复
if(j>i&&nums[j]==nums[j-1]) continue;//同层重复,跳过
class Solution {
ArrayList<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> one_path=new ArrayList<>();//一个可能的子集
int n;
int [] nums;
public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int[] nums) {
this.nums=nums;
n=nums.length;
//先排序,这样相同的两个元素必相邻
Arrays.sort(nums);
backtarck(0);
res.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());//补上一个空集
return res;
}
private void backtarck(int i){
//将要填入下标为i的元素,也就是说该层从nums[i]处的元素开始for循环
if(i==n){
return;
}
//再dfs地加子节点
for(int j=i;j<n;j++){
//做的是子集,子集是组合,所以是从当前元素开始遍历
if(j>i&&nums[j]==nums[j-1]) continue;//同层重复,跳过
one_path.add(nums[j]);
res.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(one_path));
backtarck(j+1);
one_path.remove(one_path.size()-1);//撤销选择
}
}
}
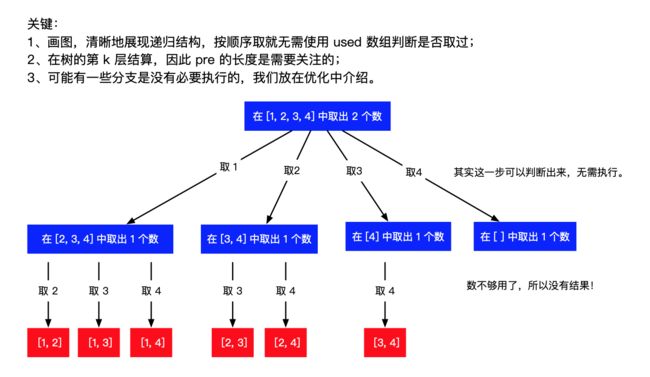
77. 组合
给定两个整数 n 和 k,返回 1 … n 中所有可能的 k 个数的组合。
示例:
输入: n = 4, k = 2
输出:
[
[2,4],
[3,4],
[2,3],
[1,2],
[1,3],
[1,4],
]
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
private List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
private void findCombinations(int n, int k, int begin, Stack<Integer> pre) {
if (pre.size() == k) {
// 够数了,就添加到结果集中
res.add(new ArrayList<>(pre));
return;
}
// 关键在于分析出 i 的上界
for (int i = begin; i <= n; i++) {
pre.add(i);
findCombinations(n, k, i + 1, pre);
pre.pop();
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {
// 特判
if (n <= 0 || k <= 0 || n < k) {
return res;
}
// 从 1 开始是题目的设定
findCombinations(n, k, 1, new Stack<>());
return res;
}
}