(一)IO流——字节流,FileInputStream、FileOutputStream、Properties集合
IO:实际就是Java源程序与操作系统上的文件进行的操作
根据数据的流向分为:输入流和输出流。
输入流 :把数据从其他设备上读取到内存中的流。
输出流 :把数据从内存 中写出到其他设备上的流。
根据数据的类型分为:字节流和字符流。
字节流 (Stream):以字节为单位,读写数据的流。能对任意文件进行操作
字符流 (Writer、Reader):以字符为单位,读写数据的流。只能对文本文件进行操作
字节流常用类
| 字节输入流(InputStream) | 字节输出流(OutputStream) |
| FileInputStream | FileOutputStream |
| BufferedInputStream | BufferedOutputStream |
| ObjectInputStream | ObjectOutputStream |
| PrintStream |
字符流常用类
| 字符输入流(Reader) | 字符输出流(Writer) |
| FileReader | FileWriter |
| BufferedReader | BufferedWriter |
| InputStreamReader | OutputStreamWriter |
| PrintWriter |
FileInputStream类:
FileInputStream构造方法:
public FileInputStream(File file) 创建字节输入流以写入由指定的 File对象表示的文件
File f = new File("\\b.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(f);public FileInputStream(String pathname) 创建字节输出流以写入由指定的 String路径表示的文件
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("\\b.txt");创建InputStream的对象File文件或String路径必须是实际存在的文件路径,不然会报FileNotFoundException异常
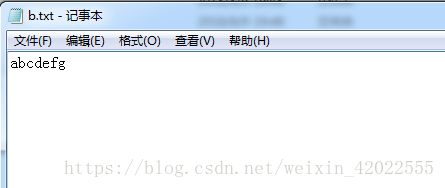
以下方法File均使用根目录下的b.txt文件,内容如图
public void close() 关闭此输入流并释放与此流相关联的任何系统资源
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(new File("\\b.txt"));
fis.close();完成流的操作之后都要关闭流,无论是什么流
public int read() 从输入流读取数据的下一个字节
File f = new File("\\b.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(f);
int i = fis.read();
System.out.println(i); //输出:97
System.out.println((char) i); //输出:a调用一次read()方法,就等于光标下移会返回下一个字节的整数
若读到文件内容末尾时会返回-1
public int read(byte[] b) 从输入流中读取一些字节数,并将它们存储到字节数组 b中
File f = new File("\\b.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(f);
byte[] b = new byte[5];
int i = fis.read(b);
System.out.println(i); //输出:5
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(b)); //输出:[97, 98, 99, 100, 101]使用字节数组来存放读取数组时,会将读取到的字节全部存入数组中,然后返回int型,代表存储了多少个元素
数组保存,和直接读取文件一样,读取完所有内容则会返回整数-1
根据以上的方法想要获取整个文件的字节可以利用字节读到末尾会返回-1的特性作结束标记
使用read()方法获取文件所有字节:
File f = new File("\\b.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(f);
int i = 0;
while ((i = fis.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println((char) i); //输出:a b c d e f g
}使用read(byte[] b )方法获取文件所有字节:
File f = new File("\\b.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(f);
int i = 0;
byte [] b = new byte[1024]; //作IO流存放字节的数组常用1024的整数倍大小数组
while ((i = fis.read(b)) != -1) {
System.out.print(new String(b,0,i)); //输出:abcdefg
}
FileOutputStream类:
FileOutputStream构造方法:
public FileOutputStream(File file) 由指定的File创建字节输出流对象
File f = new File("\\b.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(f);每次调用该输出流对象,若已存在该文件就会清空文件内容
若不存在该文件就会自动创建一个
public FileOutputStream(String name) 由指定的路径字符串创建字节输出流对象
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("\\b.txt");public FileOutputStream(File file, boolean append) 由指定的File创建可续写的字节输出流对象
File f = new File(\\b.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(f,true);创建FileOutputStream对象时加了true的参数,则不会清空源文件
输出的文件字节都会在原有基础上新增
public FileOutputStream(String name, boolean append) 由指定的路径字符串创建可续写的字节输出流对象
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("\\b.txt",true);
常用方法:
public void write(int b) 输出一个字节到文件中
File f = new File("c.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(f);
fos.write(98); //写入了一个98字节,对应ASCII码是一个 bpublic void write(byte[] b) 将字节数组的元素输出到文件中
File f = new File("c.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(f);
byte [] b = {85,56,98,68};
fos.write(b);将字节数组中的所有字节都对应ASCII码表,输出到c.txt文件中
public void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) 将字节数组的从off开始len个元素输出到文件中
File f = new File("c.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(f);
byte [] b = {85,56,98,68};
fos.write(b,0,3);将字节数组中从索引0开始的3个元素,也就是85,56,98 输出到c.txt文件中
若想用字节流输出一个字符串到文件中,可以使用String.getByte[]获取数组再用write()方法输出文件
文件复制:
利用InputStream和OutputStream的方法,可以实现复制文件到另一个地方
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("c.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("b.txt");
int i = 0;
while ((i = fis.read()) != -1) {
fos.write(i);
}
fos.close();
fis.close();先利用read()方法读文件度到末尾会返回-1位终止循环标志
然后每读c.txt文件一个字节,就会在b.txt上输出一个字节
由此循环就可以完成文件的复制
Stream字节流不止能复制txt文件还能复制视频图片等
Properties类:
项目中多数配置文件均使用Properties类作为,配置信息保存
其实Properties类就是一个Map
可Properties类可以直接将集合中的数据保存到文件中,还可以将文件保存的信息直接读取使用
Properties类文件后缀是: xxx.properties
每个键值对占一行,若想在文本中加入注释需以#开头写注释
Properties集合常用方法:
public Object setProperty(String key, String value) 添加键值对
Properties prop = new Properties(); //直接new一个Properties()创建对象
prop.setProperty("name", "jack");
prop.setProperty("sex", "man");若添加的键值对已存在,则使用新值替换旧值,并返回旧值
若添加的键值对不存在,则直接添加新的键和新的值,并返回null
public String getProperty(String key) 使用此属性列表中指定的键搜索属性值
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.setProperty("name", "jack");
prop.setProperty("sex", "man");
System.out.println(prop.getProperty("sex")); //输出:manpublic Set
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.setProperty("name", "jack");
prop.setProperty("sex", "man");
Set s = prop.stringPropertyNames();
System.out.println(s); //输出:[sex, name] 相当于HashMap的keySet()方法,可用作遍历
Properties处理文件方法:
public void load (InputStream inStream) 将流相关联文件中的数据加载到集合中
Properties prop = new Properties();
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("a.properties");
prop.load(fis);
System.out.println(prop);
fis.close();这样就将a.properites文件中的键值对都保存到prop集合中
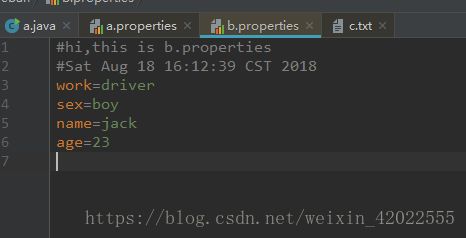
public void store (OutputStream out, String comments) 将集合中的数据保存到流相关联的目标文件中
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.setProperty("name", "jack");
prop.setProperty("sex", "boy");
prop.setProperty("age", "23");
prop.setProperty("work", "driver");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("b.properties");
prop.store(fos, "hi,this is b.properties");
fos.close();comments是创建该文件时,第一行的注释语句,不想写可以传null
输出结果文件如图: