【SpringBoot】教你写个QQ机器人(3)让你的机器人学会垃圾分类
教你写个QQ机器人(3)让你的机器人学会垃圾分类
事前废话
自从上海实行垃圾分类后,上海老百姓生活于水生火热之中,如今战火蔓延到了苏州,身为正义化身的我,决定让我的机器人学会垃圾分类。
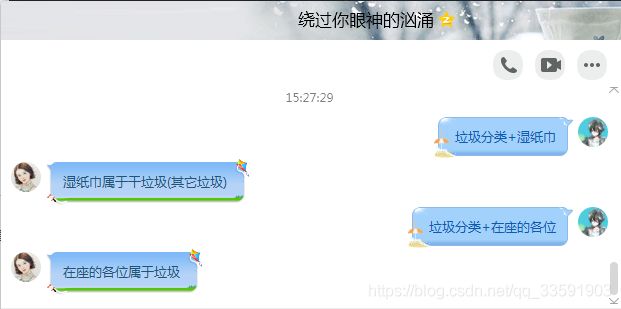
我们的需求:用户输入垃圾分类+垃圾后,机器人返回该垃圾的分类类型。
例如:用户输入垃圾分类+湿纸巾 机器人返回湿纸巾属于干垃圾(其它垃圾)
事中准备
垃圾分类查询api:垃圾分类查询
SpringBoot中网络请求工具RestTemplate
Jsoup,抓取网页中特定的值
Redis,为了加快查询效率
MySQL,将查询后的数据存入数据库
开干
在上一节【JAVA】教你写个QQ机器人(2)搭建项目框架中,handleReceiveMsg方法依据消息类型,调用了handlerPrivateMsg方法。其中该类的sendPrivateMsg方法用于发送私聊消息,发送的目标对象QQ与消息实体被封装在PrivateMsg中。
public class PrivateMsgServiceImpl implements PrivateMsgService {
@Autowired
RestTemplate restTemplate;
@Autowired
RubbishService rubbishService;
@Override
public Result sendPrivateMsg(PrivateMsg msg) {
Result result = restTemplate.postForObject(URL + SEND_PRIVATE_MSG, msg, Result.class);
return result;
}
public ReplyMsg handlePrivateMsg(ReceiveMsg receiveMsg) {
String raw_message = receiveMsg.getRaw_message();
if (raw_message.contains("垃圾分类+")) {
String type = rubbishService.handleRubbishType(raw_message);
ReplyMsg replyMsg = new ReplyMsg();
replyMsg.setReply(type);
return replyMsg;
}
return null;
}
}如果用户输入其他消息,即不包含“垃圾分类+”的消息,机器人默认不回应消息。
下面看rubbishServiceImpl中的handleRubbisType方法
public String handleRubbishType(String raw_message) {
StringBuilder returnMsg = new StringBuilder();
String name = raw_message.split("\\+")[1];
Rubbish rubbish = getRubbishByName(name);
if (null == rubbish) {
returnMsg.append("暂未查找到该垃圾的分类" + "\n");
} else {
returnMsg.append(name + "属于" + rubbish.getType());
}
return returnMsg.toString();
}name为截取到的垃圾的名称,调用getRubbishByName方法获得垃圾类型。该方法会先在Redis缓存中查找,没有再去数据中查找,没有再去请求api,有的话就存入数据库与Redis中,下次再查询相同的垃圾直接从缓存中返回。
@Override
public Rubbish getRubbishByName(String name) {
Rubbish rubbish = null;
//首先在redis中查找
rubbish = getRubbishFromRedis(name);
//System.out.println("查询redis");
if (rubbish == null) {
//再去数据库中查找
rubbish = getRubbishFromDB(name);
//System.out.println("查询数据库");
if (rubbish == null) {
rubbish = getRubbishFromAPI(name);
//System.out.println("查询api");
}
}
return rubbish;
}
public Rubbish getRubbishFromRedis(String name) {
Rubbish rubbish = (Rubbish) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(name);
return rubbish;
}
public Rubbish getRubbishFromDB(String name) {
QueryWrapper rubbishQW = new QueryWrapper<>();
rubbishQW.eq("name", name);
Rubbish rubbish = rubbishMapper.selectOne(rubbishQW);
saveRubbishFromDBIntoRedis(rubbish);
return rubbish;
}
public Rubbish getRubbishFromAPI(String name) {
String type = null;
try {
name = URLEncoder.encode(name, "UTF-8");
String body = restTemplate.getForEntity(URLConst.GET_RUBBISH_TYPE + name, String.class).getBody();
Document document = Jsoup.parse(body);
//定位到row
Element element = document.select("div[class=row]").get(2);
Elements select = element.select("div").select("h1").select("span");
String preType = select.text();
if (preType == null || !preType.contains("属于")) {
return null;
}
type = select.get(2).text();
name = URLDecoder.decode(name, "UTF-8");
} catch (Exception e) {
//e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
Rubbish rubbish = new Rubbish(name, type);
saveRubbishFromAPTIntoDB(rubbish);
saveRubbishFromDBIntoRedis(rubbish);
return rubbish;
}
public boolean saveRubbishFromAPTIntoDB(Rubbish rubbish) {
if (rubbish == null) {
return false;
}
int line = rubbishMapper.insert(rubbish);
return line > 0;
}
public boolean saveRubbishFromDBIntoRedis(Rubbish rubbish) {
if (rubbish == null) {
return false;
}
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(rubbish.getName(), rubbish);
return true;
} 好了到这里,垃圾分类的整个流程已经走完了,下面我先替你们尝试一下。
完事
唉这很舒服,下一节预告:让你的机器人学会看妹子!!!