贝叶斯网络K2算法及其增量算法的实现(基于matlab FullBNT -1.0.7 )
众所周知,K2算法是贝叶斯网络结构学习的经典算法,其本质是一种结合了爬山算法和贝叶斯评分算法的综合算法。本文就将基于贝叶斯工具箱,详细阐述其算法的原理,以及结合了论文Yasin A, Leray P. iMMPC: a local search approach for incremental Bayesian network structure learning[C]// International Symposium on Intelligent Data Analysis. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2011:401-412.
中的增量的思想,对K2算法的一种改进。实现在大量数据下显著提高算法的效率。
其实该思想是很简单的:我们可以先利用K2算法学习出一个基本的结构,在学习的过程中,可以保存下来我学习的路径,即算法每一次的决策,那么我改进的地方在哪里呢,就是我不仅保存了最优的路径,而且我保存住几条次优的路径(算法中加上最优一共是4个路径),我将次优的路径作为我下一次搜索的空间,注意:这里有一个假设,同时也是这个算法的缺陷,假定此次决策不是最优的,那么也会是在评分较高的几个选择里面,所以算法剔除掉了低分的模型,缩小了搜索空间,提升了算法的效率。
如下图,左边是算法第一次的执行过程,此时每一步保存了4个候选步骤,在新的数据到来之后,将采用增量算法,即右边的算法,每一次搜索的空间大大减小(只有4个选择,你说快不快)。
废话不多说,贴代码:
function dag = learn_struct_K2(data, ns, order, varargin)
% LEARN_STRUCT_K2 Greedily learn the best structure compatible with a fixed node ordering
% best_dag = learn_struct_K2(data, node_sizes, order, ...)
%
% data(i,m) = value of node i in case m (can be a cell array).
% node_sizes(i) is the size of node i.
% order(i) is the i'th node in the topological ordering.
%
% The following optional arguments can be specified in the form of name/value pairs:
% [default value in brackets]
%
% max_fan_in - this the largest number of parents we allow per node [N]
% scoring_fn - 'bayesian' or 'bic' [ 'bayesian' ]
% Currently, only networks with all tabular nodes support Bayesian scoring.
% type - type{i} is the type of CPD to use for node i, where the type is a string
% of the form 'tabular', 'noisy_or', 'gaussian', etc. [ all cells contain 'tabular' ]
% params - params{i} contains optional arguments passed to the CPD constructor for node i,
% or [] if none. [ all cells contain {'prior', 1}, meaning use uniform Dirichlet priors ]
% discrete - the list of discrete nodes [ 1:N ]
% clamped - clamped(i,m) = 1 if node i is clamped in case m [ zeros(N, ncases) ]
% verbose - 'yes' means display output while running [ 'no' ]
%
% e.g., dag = learn_struct_K2(data, ns, order, 'scoring_fn', 'bic', 'params', [])
%
% To be backwards compatible with BNT2, you can also specify arguments as follows
% dag = learn_struct_K2(data, node_sizes, order, max_fan_in)
%
% This algorithm is described in
% - Cooper and Herskovits, "A Bayesian method for the induction of probabilistic
% networks from data", Machine Learning Journal 9:308--347, 1992
[n ncases] = size(data);
% set default params
type = cell(1,n);
params = cell(1,n);
for i=1:n
type{i} = 'tabular';
%params{i} = { 'prior', 1 };
params{i} = { 'prior_type', 'dirichlet', 'dirichlet_weight', 1 };
end
scoring_fn = 'bayesian';
discrete = 1:n;
clamped = zeros(n, ncases);
max_fan_in = n;
verbose = 0;
args = varargin;
nargs = length(args);
if length(args) > 0
if isstr(args{1})
for i=1:2:nargs
switch args{i},
case 'verbose', verbose = strcmp(args{i+1}, 'yes');
case 'max_fan_in', max_fan_in = args{i+1};
case 'scoring_fn', scoring_fn = args{i+1};
case 'type', type = args{i+1};
case 'discrete', discrete = args{i+1};
case 'clamped', clamped = args{i+1};
case 'params', if isempty(args{i+1}), params = cell(1,n); else params = args{i+1}; end
end
end
else
max_fan_in = args{1};
end
end
dag = zeros(n,n);
for i=1:n
ps = [];
j = order(i);
u = find(clamped(j,:)==0);
score = score_family(j, ps, type{j}, scoring_fn, ns, discrete, data(:,u), params{j});
if verbose, fprintf('\nnode %d, empty score %6.4f\n', j, score); end
done = 0;
while ~done & (length(ps) <= max_fan_in)
pps = mysetdiff(order(1:i-1), ps); % potential parents
nps = length(pps);
pscore = zeros(1, nps);
for pi=1:nps
p = pps(pi);
pscore(pi) = score_family(j, [ps p], type{j}, scoring_fn, ns, discrete, data(:,u), params{j});
if verbose, fprintf('considering adding %d to %d, score %6.4f\n', p, j, pscore(pi)); end
end
[best_pscore, best_p] = max(pscore);
best_p = pps(best_p);
if best_pscore > score
score = best_pscore;
ps = [ps best_p];
if verbose, fprintf('* adding %d to %d, score %6.4f\n', best_p, j, best_pscore); end
else
done = 1;
end
end
if ~isempty(ps) % need this check for matlab 5.2
dag(ps, j) = 1;
end
end
不要紧张,这个是贝叶斯网络工具箱里面的程序D:\matlab2016aAZ\toolbox\FullBNT-1.0.7\bnt\BNT\learning\learn_struct_K2.m
当然,这个算法还是很容易理解的,我会在下面改进的程序稍加注释:
function [dag,candidate] = candidate_K2(data, ns, order, varargin)
%首先传入需要的参数,如训练数据,节点状态数,节点顺序,以及其余参数,并确定需要返回的值,我增加了一个candidate
% LEARN_STRUCT_K2 Greedily learn the best structure compatible with a fixed node ordering
% best_dag = learn_struct_K2(data, node_sizes, order, ...)
%
% data(i,m) = value of node i in case m (can be a cell array).
% node_sizes(i) is the size of node i.
% order(i) is the i'th node in the topological ordering.
%
% The following optional arguments can be specified in the form of name/value pairs:
% [default value in brackets]
%
% max_fan_in - this the largest number of parents we allow per node [N]
% scoring_fn - 'bayesian' or 'bic' [ 'bayesian' ]
% Currently, only networks with all tabular nodes support Bayesian scoring.
% type - type{i} is the type of CPD to use for node i, where the type is a string
% of the form 'tabular', 'noisy_or', 'gaussian', etc. [ all cells contain 'tabular' ]
% params - params{i} contains optional arguments passed to the CPD constructor for node i,
% or [] if none. [ all cells contain {'prior', 1}, meaning use uniform Dirichlet priors ]
% discrete - the list of discrete nodes [ 1:N ]
% clamped - clamped(i,m) = 1 if node i is clamped in case m [ zeros(N, ncases) ]
% verbose - 'yes' means display output while running [ 'no' ]
%
% e.g., dag = learn_struct_K2(data, ns, order, 'scoring_fn', 'bic', 'params', [])
%
% To be backwards compatible with BNT2, you can also specify arguments as follows
% dag = learn_struct_K2(data, node_sizes, order, max_fan_in)
%
% This algorithm is described in
% - Cooper and Herskovits, "A Bayesian method for the induction of probabilistic
% networks from data", Machine Learning Journal 9:308--347, 1992
[n ncases] = size(data);%n是节点数,ncases是一共多少条数据
count = 0;%这是我定义的一个计数变量,每决策一次,count加1.
candidate = [];%这是候选父节点的矩阵,也就是保存搜索路径的关键变量
% set default params
type = cell(1,n);%这个相当于是定义一个python中的字典一样的概念,matlab中的cell可以存储多种变量
params = cell(1,n);
for i=1:n
type{i} = 'tabular';
%params{i} = { 'prior', 1 };
params{i} = { 'prior_type', 'dirichlet', 'dirichlet_weight', 1 };
end
scoring_fn = 'bayesian';
discrete = 1:n;
clamped = zeros(n, ncases);%clamped变量可能是为了在评分时方便找到对应的数据集
max_fan_in = n;
verbose =0;%verbose=1-->每次循环时都要输出相应的结果
args = varargin;%把剩余变量给放到变量args中,下面再依次传入相应的变量。
nargs = length(args);
if length(args) > 0
if isstr(args{1})
for i=1:2:nargs
switch args{i},
case 'verbose', verbose = strcmp(args{i+1}, 'yes');
case 'max_fan_in', max_fan_in = args{i+1};
case 'scoring_fn', scoring_fn = args{i+1};
case 'type', type = args{i+1};
case 'discrete', discrete = args{i+1};
case 'clamped', clamped = args{i+1};
case 'params', if isempty(args{i+1}), params = cell(1,n); else params = args{i+1}; end
end
end
else
max_fan_in = args{1};
end
end
dag = zeros(n,n);
for i=1:n
ps = [];
j = order(i);%j是第i个变量,
u = find(clamped(j,:)==0);
score = score_family(j, ps, type{j}, scoring_fn, ns, discrete, data(:,u), params{j});%这里评分是对不加任何父节点的评分
if verbose, fprintf('\nnode %d, empty score %6.4f\n', j, score); end
done = 0;
while ~done & (length(ps) <= max_fan_in)
pps = mysetdiff(order(1:i-1), ps); % potential parents,在A不在B中的元素,把父节点去掉之后的,i之前的所有元素作为潜在父节点
nps = length(pps);
pscore = zeros(1, nps);
for pi=1:nps
p = pps(pi);%对潜在父节点依次进行评分(评分的过程中要添加原来的父节点一起评分。)
pscore(pi) = score_family(j, [ps p], type{j}, scoring_fn, ns, discrete, data(:,u), params{j});
if verbose, fprintf('considering adding %d to %d, score %6.4f\n', p, j, pscore(pi)); end
end
[best_pscore, best_p] = max(pscore);%best_p是一个位置
pscore(best_p)=min(pscore);%这里在用简单粗暴的方法找到第2,3,4,的评分及其对应的父节点
[se_pscore,se_p] = max(pscore);
se_action = pps(se_p);
pscore(se_p) = min(pscore);
[thi_pscore,thi_p] = max(pscore);
thi_action = pps(thi_p);
pscore(thi_p) = min(pscore);
[for_pscore,for_p] = max(pscore);
for_action= pps(for_p);
best_p = pps(best_p);
if best_pscore > score%判定最好得分是否大于无父节点的得分。
score = best_pscore;
ps = [ps best_p];
count = count +1;
candidate(count,1) = j;%这里在构造candidate矩阵,依次将best_p,se_action,thi_action,for_action放进去
candidate(count,2) = best_p;
candidate(count,3) = se_action;
candidate(count,4) = thi_action;
candidate(count,5) = for_action;
if verbose, fprintf('* adding %d to %d, score %6.4f\n2ed,3rd,4th分别是 %d %d %d \n', best_p, j, best_pscore,se_action,thi_action,for_action);
end
else
done = 1;
end
end
if ~isempty(ps) % need this check for matlab 5.2
dag(ps, j) = 1;
end
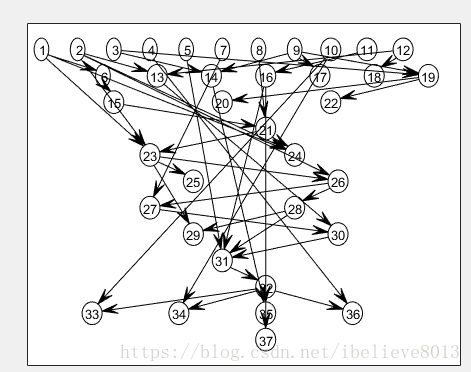
end对于这个K2算法,有一点不太清晰,就是在搜索的过程中,它是依次找每一个节点i的父节点,但是找候选父节点是取的1到i。你会问如果有22->5的边是不是就找不到?我的理解是它节点的顺序是和我们定义的顺序是有差别的,比如它的节点顺序是1-37,那么1-37是自上而下的,如下图,这样能保证在学习中始终是小指向大,只要没有大指向小,那是不会出现环结构的。
得到了候选列表,注意,我的候选列表行代表每一次决策,列1代表子节点,列2345分别是评分从高到低的4个父节点。如下表:
下面贴我的增量算法:
function dag = incremental_K2( data, ns, order, varargin )
[n ncases] = size(data);
candidate = [];
% set default params
type = cell(1,n);
params = cell(1,n);
for i=1:n
type{i} = 'tabular';
%params{i} = { 'prior', 1 };
params{i} = { 'prior_type', 'dirichlet', 'dirichlet_weight', 1 };
end
scoring_fn = 'bayesian';
discrete = 1:n;
clamped = zeros(n, ncases);
max_fan_in = n;
verbose =0;
args = varargin;
nargs = length(args);
if length(args) > 0
if isstr(args{1})
for i=1:2:nargs
switch args{i},
case 'verbose', verbose = strcmp(args{i+1}, 'yes');
case 'max_fan_in', max_fan_in = args{i+1};
case 'scoring_fn', scoring_fn = args{i+1};
case 'type', type = args{i+1};
case 'discrete', discrete = args{i+1};
case 'clamped', clamped = args{i+1};
case 'candidate' ,candidate = args{i+1};
case 'params', if isempty(args{i+1}), params = cell(1,n); else params = args{i+1};
end
end
end
else
max_fan_in = args{1};
end
end
p = [];
dag = zeros(n,n);
for i = 1:length(candidate)
child = candidate(i,1);
for j = 2:5
ppar = candidate(i,j);
u = find(clamped(child,:)==0);
score(j) = score_family(child,[ppar p], type{child}, scoring_fn, ns, discrete, data(:,u), params{j});
end
score(1) = -inf;
[max_score,best_p] = max([score]);
best_action = candidate(i,best_p);
dag(child,best_action) = 1;
if i< length(candidate) && child == candidate(i+1,1)
p = [p best_action];
else
p = [];
end
end
end
增量算法就很容易理解了,我在候选节点中去找评分最高的节点,作为我这一次的决策,这个效率不就很高了嘛。详细的注释就不加了,懒癌犯了。
测试代码如下:
%载入经典网络alarm,并且从中采样10000条。
bnet = mk_alarm_bnet;
figure;
draw_graph(bnet.dag)
seed = 0;
rand('state', seed);
randn('state', seed);
N = length(bnet.node_sizes);
ncases = 10000;
data = zeros(N, ncases);
for m=1:ncases
data(:,m) = cell2num(sample_bnet(bnet));
end然后进行测试:
dag1 = learn_struct_K2(data, ns, order, 'max_fan_in', max_fan_in);增量测试:
%假设5000条是原始数据,后5000条是增量数据
%这是原始步骤:
[dag2,candidate3] = candidate_K2(data(:,1:5000), ns, order, 'max_fan_in', max_fan_in);
%这是增量步骤:
dag3 = incremental_K2(data(:,5001:10000), ns, order, 'max_fan_in', max_fan_in,'candidate',candidate3);测试结果:
就问你屌不屌???是不是成功了?好了,吃饭去了。