cuda编程与gpu并行计算(六):图稀疏矩阵转为CSR结构并传入gpu
虽然sepgraph有这部分代码,还是自己先试着实现一下,这样读起来也方便
行压缩格式Compressed Sparse Row (CSR)
CSR需要三种数据来表达:数值、列号、行转移。CSR不是三元组,而是整体的编码方式。
CSR
编码:
行优先遍历矩阵Matrix
values数组中保存矩阵中非零元素。
column indices数组保存values数组中对应位置非零元素的列索引。
row offsets数组的下标表示每一行第一个非零元素的行索引,元素值为values数组的下标,最后一个元素值为非零元素的个数。
解码:
遍历values数组,对其中的元素值x(下标记为index_X)去column indices数组中对应位置取出x在原矩阵中的列索引(记为col_index),然后在row offsets数组查找index_X,如果index_X在row offsets中,其在row offsets中的下标即为x在原矩阵中的行索引(记为row_index),如果index_X不在row offsets中,则使用上一个row_index值(因为编码时是逐行编码,且row offsets仅保存每行的第一个非零元素,所以当前x与上一x在同一行)。
此为前言,清楚逻辑,代码就好办了
#include运行的结果如下
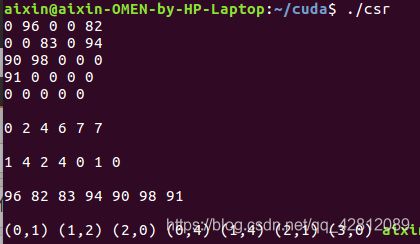 先输出一个随机生成的带权重有向稀疏图,在cpu中将其压缩为csr格式并输出,再传递到gpu上,并输出每一条边的起点和终点。
先输出一个随机生成的带权重有向稀疏图,在cpu中将其压缩为csr格式并输出,再传递到gpu上,并输出每一条边的起点和终点。