Pytorch学习笔记(一)自用
涉及资源
1.官网DEEP LEARNING WITH PYTORCH: A 60 MINUTE BLITZ
2.莫烦python 个人网站 、 b站视频、参考代码
3.函数搜索:https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/index.html
系列学习笔记:
Pytorch学习笔记(一)
Pytorch学习笔记(二)
Pytorch学习笔记(三)
本周学习内容:
Numpy torch对比
激励函数
pytorch实现Regression
pytorch实现Classification
pytorch快速搭建法实现Classification
pytorch实现网络的保存与提取
pytorch实现batch_train
pytorch实现optimizer性能比对
pytorch实现CNN,识别MNIST数据集
环境配置:
python=3.7; torch=1.6.0; torchvision=0.7.0
1、Regression
import torch
from torch.autograd import Variable
import torch.nn.functional as F # 拿到一些激励函数
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
## data
x = torch.unsqueeze(torch.linspace(-1, 1, 100), dim=1) # unsqueeze多加一维,因为Variable输入为二维
y = x.pow(2) + 0.2 * torch.rand(x.size())
# x, y = Variable(x), Variable(y) # 放在Varible的篮子里
# plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy())
# plt.show()
## NET
class Net(torch.nn.Module): # 继承torch的模块
def __init__(self, n_feature, n_hidden, n_output):# 定义层
super(Net, self).__init__()# 调用父类的初始化
self.hidden = torch.nn.Linear(n_feature, n_hidden)
self.predict = torch.nn.Linear(n_hidden, n_output)
def forward(self, x):# 前向传递,搭建神经网络,x = inputData
x = F. relu(self.hidden(x))
x = self.predict(x) # 回归预测的时候一般不用激励函数,加了relu无法预测负值
return x
## 训练 + 可视化过程
net = Net(1, 15, 1)
print(net)
plt.ion() # 实时打印
plt.show()
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.5) # 网络优化.lr一般小于1
# loss_func = F.mse_loss()# 均方差
for t in range(100):# 训练100步
prediction = net(x)# output
loss = F.mse_loss(prediction, y)
# 优化
optimizer.zero_grad() # clear gradients for this training
loss.backward() # backpropagation, compute gradients
optimizer.step() # apply gradients
if t % 5 == 0:# 学习五步打印一次
plt.cla()# 清空
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy())# 散点图
plt.plot(x.data.numpy(), prediction.data.numpy(), 'r-', lw=5)
plt.text(0.5, 0, 'loss = %.4f' % loss.data.numpy(), fontdict={
'size': 20, 'color': 'red'})
plt.pause(0.1)
plt.ioff()
plt.show()
print(net)
Net(
(hidden): Linear(in_features=1, out_features=15, bias=True)
(predict): Linear(in_features=15, out_features=1, bias=True)
)
import torch
from torch.autograd import Variable
import torch.nn.functional as F # 拿到一些激励函数
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
## make fake data
n_data = torch.ones(100, 2)
x0 = torch.normal(2*n_data, 1) # class0 x data (tensor), shape=(100, 2)
y0 = torch.zeros(100) # class0 y data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
x1 = torch.normal(-2*n_data, 1) # class1 x data (tensor), shape=(100, 2)
y1 = torch.ones(100) # class1 y data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
# 数据和标签转换为 torch 中默认的形式
x = torch.cat((x0, x1), 0).type(torch.FloatTensor) # shape (200, 2) FloatTensor = 32-bit floating; cat合并
y = torch.cat((y0, y1), ).type(torch.LongTensor) # shape (200,) LongTensor = 64-bit integer
# 现在autograd 直接支持tensors了
# x, y = Variable(x), Variable(y) # 放在Varible的篮子里
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy()[:, 0], x.data.numpy()[:, 1], c=y.data.numpy(), s=50, lw=0, cmap='RdYlGn')
plt.show()
## method 1
class Net(torch.nn.Module): # 继承torch的模块
def __init__(self, n_feature, n_hidden, n_output):# 定义层
super(Net, self).__init__()# 调用父类的初始化
self.hidden = torch.nn.Linear(n_feature, n_hidden)
self.predict = torch.nn.Linear(n_hidden, n_output)
def forward(self, x):# 前向传递,搭建神经网络,x = inputData
x = F. relu(self.hidden(x))
x = self.predict(x) # 回归预测的时候一般不用激励函数,加了relu无法预测负值
return x
## 训练 + 可视化过程
net1 = Net(2, 10, 2)
## method 2
net2 = torch.nn.Sequential(# 一层一层
torch.nn.Linear(2, 10),
torch.nn.ReLU(),# 区别
torch.nn.Linear(10, 2),
)
print(net1)
print(net2)
plt.ion() # 实时打印
plt.show()
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net2.parameters(), lr=0.01) # 网络优化.lr一般小于1
for t in range(100):# 训练100步
out = net2(x)
loss = F.cross_entropy(out, y) # 交叉熵,用于多分类问题
# 优化
optimizer.zero_grad() # pytorch计算梯度不是覆盖,与上一次的求和,net.parameters手动清0
loss.backward() # Variable反向传递
optimizer.step() # 更新参数
if t % 2 == 0:
# plot and show learning process
plt.cla()
prediction = torch.max(out, 1)[1] # softmax变成prediction,概率
pred_y = prediction.data.numpy()
target_y = y.data.numpy()
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy()[:, 0], x.data.numpy()[:, 1], c=pred_y, s=100, lw=0, cmap='RdYlGn')
accuracy = float((pred_y == target_y).astype(int).sum()) / float(target_y.size)
plt.text(1.5, -4, 'Accuracy=%.2f' % accuracy, fontdict={
'size': 20, 'color': 'red'})
plt.pause(0.1)
plt.ioff()
plt.show()
print(net1)
Net(
(hidden): Linear(in_features=2, out_features=10, bias=True)
(predict): Linear(in_features=10, out_features=2, bias=True)
)
print(net2)
Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=2, out_features=10, bias=True)
(1): ReLU()
(2): Linear(in_features=10, out_features=2, bias=True)
)
3、save_reload
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch.nn.functional as F
# torch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible
# data
x = torch.unsqueeze(torch.linspace(-1, 1, 100), dim=1) # x data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
y = x.pow(2) + 0.2*torch.rand(x.size()) # noisy y data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
# Pytorch 0.4可以直接用tensors
# x, y = Variable(x, requires_grad=False), Variable(y, requires_grad=False)
def save():
# save net1
net1 = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Linear(1, 10),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Linear(10, 1)
)
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net1.parameters(), lr=0.5)
# loss_func = torch.nn.MSELoss()
for t in range(100):
prediction = net1(x)
loss = F.mse_loss(prediction, y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
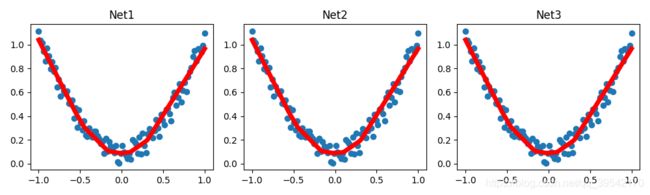
# plot result
plt.figure(1, figsize=(10, 3))
plt.subplot(131)
plt.title('Net1')
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy())
plt.plot(x.data.numpy(), prediction.data.numpy(), 'r-', lw=5)
# 2 ways to save the net
torch.save(net1, 'net.pkl') # save entire net,以pkl形式保存
torch.save(net1.state_dict(), 'net_params.pkl') # save only the parameters
def restore_net():
net2 = torch.load('net.pkl')
prediction = net2(x)
# plot result
plt.subplot(132)
plt.title('Net2')
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy())
plt.plot(x.data.numpy(), prediction.data.numpy(), 'r-', lw=5)
def restore_params():
net3 = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Linear(1, 10),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Linear(10, 1)
)
# copy net1's parameters into net3
net3.load_state_dict(torch.load('net_params.pkl'))
prediction = net3(x)
# plot result
plt.subplot(133)
plt.title('Net3')
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy())
plt.plot(x.data.numpy(), prediction.data.numpy(), 'r-', lw=5)
plt.show()
save()
restore_net()
restore_params()
import torch
import torch.utils.data as Data
# BATCH_SIZE = 5
BATCH_SIZE = 8
x = torch.linspace(1, 10, 10) # torch tensor
y = torch.linspace(10,1,10) # torch tensor
torch_dataset = Data.TensorDataset(x, y)
loader = Data.DataLoader(
dataset=torch_dataset,
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
shuffle=True,#打乱数据
num_workers=0,# 2线程
)
for epoch in range(3):
for step, (batch_x, batch_y) in enumerate(loader):
# training
print('Epoch: ',epoch,'| Step: ', step, '| batch x: ',batch_x.numpy(), '| batch y: ', batch_y.numpy())
数据个数为10,BATCH_SIZE = 8,EPOCH = 3时
Epoch: 0 | Step: 0 | batch x: [ 2. 1. 8. 9. 4. 5. 10. 3.] |batch y: [ 9. 10. 3. 2. 7. 6. 1. 8.]
Epoch: 0 | Step: 1 |batch x: [6. 7.] | batch y: [5. 4.]
Epoch: 1 | Step: 0 | batch x: [ 1. 10. 6. 9. 2. 5. 4. 8.] | batch y: [10. 1. 5. 2. 9. 6.7. 3.]
Epoch: 1 | Step: 1 | batch x: [3. 7.] | batch y: [8. 4.]
Epoch: 2 | Step: 0 | batch x: [ 4. 7. 10. 8. 9. 6. 5. 2.] | batch y: [7. 4. 1. 3. 2. 5. 6. 9.]
Epoch: 2 | Step: 1 | batch x: [1. 3.] | batch y: [10. 8.]
数据个数为10,BATCH_SIZE = 5,EPOCH = 3时
Epoch: 0 | Step: 0 | batch x: [ 7. 10. 5. 1. 8.] | batch y: [4. 1. 6. 10. 3.]
Epoch: 0 | Step: 1 | batch x: [6. 3. 2. 9. 4.] | batch y: [5. 8. 9. 2. 7.]
Epoch: 1 | Step: 0 | batch x: [4. 7. 2. 5. 1.] | batch y: [ 7. 4. 9. 6. 10.]
Epoch: 1 | Step: 1 | batch x: [ 9. 10. 8. 3. 6.] | batch y: [2. 1. 3. 8. 5.]
Epoch: 2 | Step: 0 | batch x: [ 7. 4. 8. 10. 1.] | batch y: [ 4. 7. 3. 1. 10.]
Epoch: 2 | Step: 1 | batch x: [6. 5. 9. 3. 2.] | batch y: [5. 6. 2. 8. 9.]
5、optimizer
import torch
import torch.utils.data as Data
import torch.nn.functional as F
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# hyper para
LR = 0.01
BATCH_SIZE = 32
EPOCH = 12
# fake dataset
x = torch.unsqueeze(torch.linspace(-1, 1, 1000), dim=1)# unsqueeze多加一维
y = x.pow(2) + 0.1*torch.normal(torch.zeros(*x.size()))
# put dateset into torch dataset
torch_dataset = Data.TensorDataset(x, y)
loader = Data.DataLoader(
dataset=torch_dataset,
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
shuffle=True, # 打乱数据
num_workers=0, # 2线程
)
# default network
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.hidden = torch.nn.Linear(1, 20) # hidden layer
self.predict = torch.nn.Linear(20, 1) # output layer
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.hidden(x)) # activation function for hidden layer
x = self.predict(x) # linear output
return x
if __name__ == '__main__':
# different nets
net_SGD = Net()
net_Momentum = Net()
net_RMSprop = Net()
net_Adam = Net()
nets = [net_SGD, net_Momentum, net_RMSprop, net_Adam] #放在一个list当中
# different optimizers
opt_SGD = torch.optim.SGD(net_SGD.parameters(), lr=LR)
opt_Momentum = torch.optim.SGD(net_Momentum.parameters(), lr=LR, momentum=0.8)
opt_RMSprop = torch.optim.RMSprop(net_RMSprop.parameters(), lr=LR, alpha=0.9)
opt_Adam = torch.optim.Adam(net_Adam.parameters(), lr=LR, betas=(0.9, 0.99))
optimizers = [opt_SGD, opt_Momentum, opt_RMSprop, opt_Adam]
losse_his = [[],[],[],[]] # record loss
for epoch in range(EPOCH):
print(epoch)
for step,(batch_x, batch_y) in enumerate(loader):
for net, opt, l_his in zip(nets, optimizers, losse_his):
output = net(batch_x) # get output for every net
loss = F.mse_loss(output, batch_y) # compute loss for every net
l_his.append(loss.data.numpy()) # loss recoder
opt.zero_grad() # clear gradients for next train
loss.backward() # backpropagation, compute gradients
opt.step() # apply gradients
labels = ['SGD', 'Momentum', 'RMSprop', 'Adam']
for i, l_his, in enumerate(losse_his):
plt.plot(l_his, label=labels[i])
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.xlabel('Steps')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.ylim((0, 0.2))
plt.show()
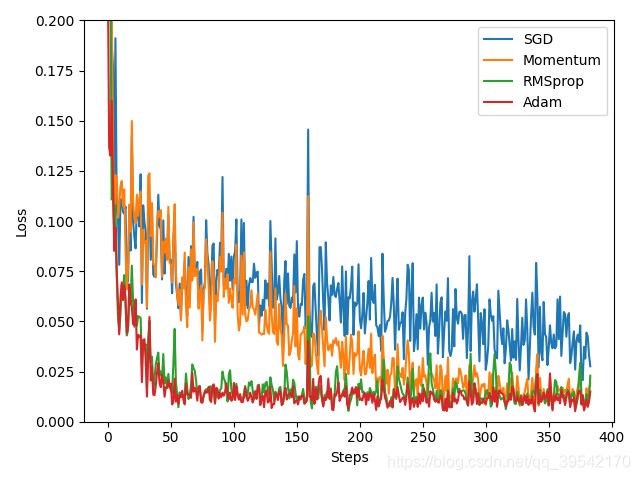
优化器理论可参考:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_40170902/article/details/80092628