CityEngine2016-学习笔记(1)Writing Rules
CityEngine2016-学习笔记(1)writing rules
这是学习CGA规则的笔记,版本是cityengine 2016.0,参考help文件。
CityEngine Help Manual > Rule-based Modeling > Writing Rules
1 Standard Rule 标准规则
形式上:
PredecessorShape --> Successor
示例:
Lot -->
s('0.8, '1, '0.8) center(xz) extrude(20) Envelope
Envelope -->
split(y) { ~4: Floor.} *
注意:在Floor后面加“.”,可以避免编辑器的错误提醒“undefined”
1.1 物体坐标
1.2 s operation
s(float xSize, float ySize, float zSize)
参数:xSize (float), ySize (float), zSize (float)
Sizes of the new scope dimensions.
s命令设置向量“scope.s”,相对操作符“’”设置相对的比例,举例:
s('sx, 0, 0) 等价于 s(sx * scope.sx, 0, 0)
举栗:
s('0.5,'1,'1.5) 等价于 s(0.5scope.sx,scope.sy,1.5scope.sz)
1.3 center()
center(axesSelector)
参数:axesSelector (keyword)
Axes to include in center calculation (x|y|z|xy|xz|yz|xyz).
轴选项,可以使xyz的任意平面、轴,或者xyz三维空间
The center operation moves the scope of the current shape tothe center of the previous shape’s scope.‘Previous shape’ means the previous shape on the shape stack.
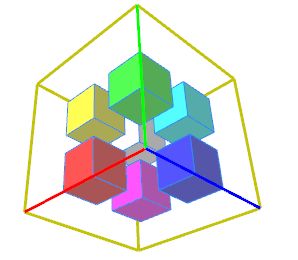

在代码示例中,center是解释s操作的,cityengine坐标轴如上图所示,与cad中不一致,纵向是y轴。
1.4 extrude()
extrude(distance)
extrude(extrusionType, distance)
1.5 split()
XYZ Split (Cartesian Space)
split(splitAxis) { size1 : operations1 | size2 : operations2 | … | sizen-1 : operationsn-1 }
split(splitAxis) { size1 : operations1 | size2 : operations2 | … | sizen-1 : operationsn-1 }*
split(splitAxis, adjustSelector) { size1 : operations1 | … | sizen-1 : operationsn-1 }
split(splitAxis, adjustSelector) { size1 : operations1 | … | sizen-1 : operationsn-1 }*
UV Split (Texture Space)
split(splitDirection, surfaceParameterization, uvSet) { size1 : operations1 | … | sizen-1 : operationsn-1 }*
按给定轴向切割模型。
注意:关于 * ——Repeat switch: the repeat switch triggers the repetition of the defined split into the current shape’s scope, as many times as possible. The number of repetitions and floating dimensions are adapted to the best solution (best number of repetitions and least stretching).
2 Parameterized Rule 参数化规则
注意:不需要明确的参数数据类型。cga语法中有三种简单类型:float, boolean, string,分别是浮点数、布尔数、字符串。所有数字都是浮点数,整数也是。
举栗1:
Lot -->
s('0.8, '1, '0.8)
center(xz)
Footprint(20)
Footprint(height) -->
extrude(height * 0.8)
Envelope.
Lot -->
s(0.5*scope.sx, '1, '1)
center(xz)
Footprint(20, geometry.area)
Footprint(height, area) -->
t(0,0,0)
extrude(height)
Envelope(area)
Envelope(area) -->
split(y) {~4 : Floor.} *
Lot -->
Footprint("just an example")
Footprint(height,area) -->
t(0,0,1)
extrude(height)
Envelope(area)
Footprint(text) -->
print(text)
Finally, rule overloading is shown in example 3. There are two Footprint rules, one with two float parameters and one with one string parameter. The compiler automatically makes sure that only the matching one is used during shape creation (i.e. during execution of the Lot rule above, a Footprint shape with a string parameter is created).
Note: If no matching rule exists a new leaf is generated.
3 Conditional Rule 条件判断规则
PredecessorShape -->
case condition1: Successor1
case condition2: Successor2
…
else: SuccessorN
举栗1:
Footprint(type) -->
case type == "residential" :
extrude(10) Envelope
case geometry.area / 2 < 200 :
extrude(20) Envelope
else:
NIL
举栗2:
Footprint(type) -->
case type == "residential" || type == "park" :
case geometry.area/2 < 200 && geometry.area > 10 : extrude(10) Envelope
else: extrude(15) Envelope
case type == "industrial" : extrude(100) Factory
else : NIL
栗子2是嵌套的条件判断和布尔运算。
4 stochastic rule 随机规则
与条件规则类似,cga语法允许随机规则,比如创建随机变量。
PredecessorShape -->
percentage%: Successor1
percentage%: Successor2
...
else: SuccessorN
注意:比例汇总不能大于100%
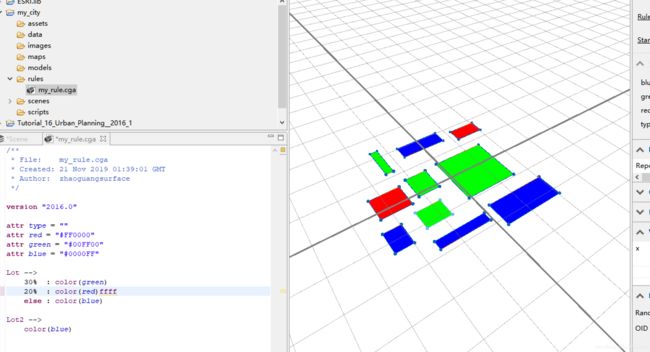
举栗1:
attr red = "#FF0000"
attr green = "#00FF00"
attr blue = "#0000FF"
Lot -->
30% : color(green)
20% : color(red)
else : color(blue)
这一段是按比例随机赋给红绿蓝三种颜色。
 举栗2:
举栗2:
嵌套的随机规则。
Lot -->
30% :
50% : Lot("residential")
else : NIL
20% : Lot("retail")
else : Lot("industrial")
注意:else是必须的,总比例加在一起不要超过100%
5 attribute 属性
属性在cga文件中是一系列全局变量。每一个属性在文件中都会初始化赋予一个数值。但是针对每个形状,都可以赋予一个独立的属性值,同时这个属性值也可以在检查页(inspector)中修改。
举栗:
attr height = 150
attr landuse = "residential"
Lot --> extrude(height) Envelope(landuse)
用attr定义了两个属性,height和landuse,用在Lot规则中。
属性也可以设置成条件式或者随机数。
attr landuse = 50% : "residential"
else: "industrial"
注意:在属性定义时使用条件或者随机形式的时候,在整个生成过程,属性值只计算一次。如果一个这样的属性被赋予了多个形状,那么这些属性将被一次性计算出来,并且会一直保持下去。
同样滴,也可以使用rand()函数:
attr height = rand(30, 50)
Lot -->
extrude(height) Envelope
Envelope -->
case height < 40 : SmallBuilding
else: LargeBuilding
被赋予height数值,起始规则为Lot的形状,height属性将为30-50的浮点数,并且会一直保持静态不变。
6 style 风格
理解不深刻,以后再补。
7 import 导入
Rules from an existing rule filecan be imported by a rule file through “import”. Importing a rule file makes all rules,attributes and functions of the importedrule file available under the given prefix.
关键字import用于导入已经存在的rule文件,导入rule文件使得被导入文件的规则、属性、函数在当前文件中可以使用。
举栗:在一个结构中合并两个立面
# -- facade1.cga
actualFloorHeight = scope.sy/rint(scope.sy/4)
actualTileWidth = scope.sx/rint(scope.sx/4)
Facade -->
setupUV(0, 8*actualTileWidth, 8*actualFloorHeight)
set(material.colormap, "f1.tif")
bakeUV(0)
# -- facade2.cga
actualFloorHeight = scope.sy/rint(scope.sy/6)
actualTileWidth = scope.sx/rint(scope.sx/4)
Facade -->
setupUV(0, 8*actualTileWidth, 8*actualFloorHeight)
set(material.colormap, "f2.tif")
bakeUV(0)
# -- structure.cga
// the attribute height will be overridden by the
// attribute height from "main.cga" if this rule
// file is included. Thus if this rule file is
// used standalone, the buildings will be of height
// 100, if this rule file is included by "main.cga",
// the buildings will be of height 200.
attr height = 100
Lot-->extrude(height) Mass
Mass-->comp(f){ side: Facade | top: Roof }# -- main.cga
// define an attribute "height", potentially
// overriding the same attribute in imported
// rule files.
attr height = 200
// import facades
import f1 : "facade1.cga"
import f2 : "facade2.cga"
// import structure
import st : "structure.cga"
Lot-->
// reference rule "Lot" in structure.cga
st.Lot
// define rule "Facade" for structure.cga
st.Facade-->
// reference rule "Facade" in facade1.cga
50% : f1.Facade
// reference rule "Facade" in facade2.cga
else : f2.Facade
8 function 函数
函数用于在规则中封装多次使用的计算估值。和规则不同,函数返回一个数值,但是不改变现有的形状。函数可以带参数,条件式或者使用随机数。
举栗:
getHeight(area) =
case area > 1000: 300
case area > 500:
20%: 200
50%: 150
else: 100
else: rand(20,50)
调用函数:
Lot -->
extrude(getHeight(geometry.area)) Envelope.
注意:与属性相反,在每次调用中都会对函数进行评估。 这意味着像height = rand(30,50)这样的函数仅出于专用目的才有意义,因为每次使用它都会返回一个不同的值。
静态函数:
可以使用const关键字使函数变成静态函数。 const函数的行为与attrs相同,唯一的区别是const函数在规则文件内部,不能在检查器中映射修改。
9 comments 注释
cga文件使用“//”或者“#”进行注释。
也可以使用块注释“/* … */”
/* block comments
can be used to write
multi-line comments
*/
or inline comments
Lot -->
Garden House /*Garage*/ Fence
...
comp(f){front : F | /* side : S | */ top : T}




