题目2:隐式图的搜索问题(A*算法解决八数码)
数据结构课程实践系列
题目1:学生成绩档案管理系统(实验准备)
题目2:隐式图的搜索问题(A*算法解决八数码)
题目3:文本文件单词的检索与计数(实验准备)
文章目录
- 数据结构课程实践系列
-
- 题目1:学生成绩档案管理系统(实验准备)
- 题目2:隐式图的搜索问题(A*算法解决八数码)
- 题目3:文本文件单词的检索与计数(实验准备)
- 声明
-
- 题目要求
- 何为八数码?
- 状态如何表示
- 所需知识
- 导出所需知识
-
- 优先队列BFS算法缺陷
- A*搜索算法
- 总结:
- 实际操作
-
- 搜索过程描述
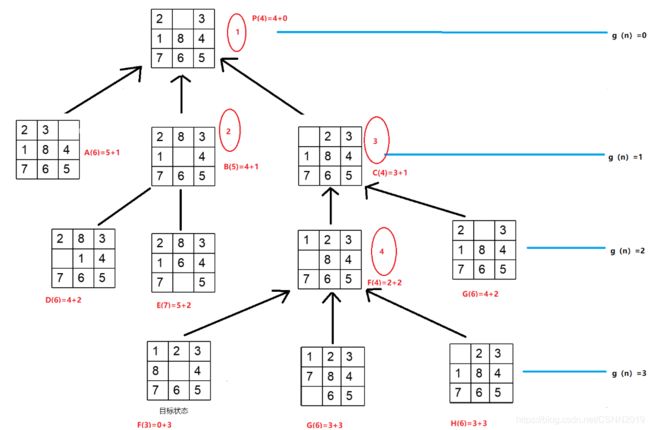
- 启发式策略工作工程:红圈数字表示扩展顺序
- 代码实现
-
- Map+BFS+A*
- Hash+BFS+A*
- GAMEOVER
声明
题目要求
总结:利用A*来解决八数码问题,状态很好找,每次移动空格就会形成一种新的状态,
何为八数码?
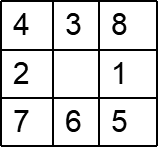
八数码游戏包括一个3X3的棋盘,棋盘上摆放着8个数字的棋子,留下一个空位。与空位相邻的棋子可以滑动到空位中。游戏的目的是要达到一个特定的目标状态。标注的形式化如下(举例):
| 2 | 3 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8 | 4 |
| 7 | 6 | 5 |
(初始状态)
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|
| 8 | 4 | |
| 7 | 6 | 5 |
(目标状态)
状态如何表示
- 每个状态都用3*3的数组表示,但是BFS中需要入队出队,比较麻烦而且空间占用较大
- 状态压缩,采用一个整数保存状态的数字序列,例如状态1表示为203184765,状态2表示为123804765
所需知识
优先队列BFS算法,因为A*算法就是带有估价函数的优先队列BFS。
导出所需知识
优先队列BFS算法缺陷
该算法维护了一个优先队列(二叉堆),不断从堆中取出“当前代价最小”的状态(堆顶)去进行扩展。但是它得到只是初态到该状态的最小代价(并没有去考虑从该状态出发到目标状态的情况)
举例说明:
如果给定一个“目标状态”,需要求出从初态到目标状态的最小代价,优先队列BFS显然不行。因为一个状态的当前代价最小,只能说明从起始状态到该状态的代价很小,而在未来的探索中,从该状态到目标状态可能会花费很大的代价;另外一些状态虽然当前代价略大,但是未来到目标状态的代价可能会很小,于是从起始状态到目标状态的总代价反而更优。
A*搜索算法
于是,我们为了解决上面的问题:可以对未来可能产生的代码进行预估。详细地讲,我们去设计一个**“估价函数”**,以任意状态为输入,计算出从该状态到目标状态所需代价的估计值。在搜索之中,仍然维护了一个堆,不断从堆中取出“当前代价+未来估价”最小的状态来进行扩展。
为了保证第一次从堆中取出目标状态时得到的就是最优解,我们设计的估价函数需要满足一个基本准则:
设当前状态state到目标状态所需代价的估计值为f(state);设在未来的探索中,实际求出的从当前状态state到目标状态的最小代价为g(state)
对于任意的state,应该有f(state)<=g(state)
也就是说,估价函数的估值不能大于未来实际代价,估价比实际代价更优。估价函数f(n)=g(n)+h(n)
总结:
这种带有估价函数的优先队列BFS就成为A* 算法。只要保证对于任意状态state,都有f(state)<=g(state),A* 算法就一定能在目标状态第一次从堆中被取出时得到最优解,并且在搜索过程中每个状态只需要扩展一次(之后再被取出就可以直接忽略 )。估价f(state)越准确,越接近g(state),A*算法的效率越高。如果估价始终为0,就等于普通的优先队列BFS。
实际操作
搜索过程描述
A算法又称为启发式搜索算法。对启发式搜索算法,又可根据搜索过程中选择扩展节点的范围,将其分为全局择优搜索算法和局部择优搜索算法。
在全局择优搜索中,每当需要扩展节点时,总是从 Open 表的所有节点中选择一个估价函数值最小的节点进行扩展。其搜索过程可能描述如下:
- 把初始节点 S0 放入 Open 表中, f(S0)=g(S0)+h(S0) ;
- 如果 Open 表为空,则问题无解,失败退出;
- 把 Open 表的第一个节点取出放入 Closed 表,并记该节点为 n ;
- 考察节点 n 是否为目标节点。若是,则找到了问题的解,成功退出;
- 若节点 n 不可扩展,则转到第 (2) 步;
- 扩展节点 n ,生成子节点 ni ( i =1,2, …… ) ,计算每一个子节点的估价值 f( ni ) ( i =1,2, …… ) ,并为每一个子节点设置指向父节点的指针,然后将这些子节点放入 Open 表中;
- 根据各节点的估价函数值,对 Open 表中的全部节点按从小到大的顺序重新进行排序;
- 转第 (2) 步。
这里采用的启发式策略为:f(n) = g(n) + h(n),其中g(n)为从初始节点到当前节点的步数(层数),h(n)为 当前节点 “不在位 ”的方块数(也就是说不在位的方块数越少,那么临目标状态越近)例如下图中的h(n)=5,有的讲解的是不包含空格,我这里是包含了的,经测试只要前后标准一致,包不包含空格都一样。
g(n)为已经消耗的实际代价,即已经走了的步数。
h(n)为预测路径,即还有几个数字待走。
启发式策略工作工程:红圈数字表示扩展顺序
代码实现
Map+BFS+A*
#includechangeId[9][4] = {
{
-1,-1,3,1},{
-1,0,4,2},{
-1,1,5,-1},
{
0,-1,6,4},{
1,3,7,5},{
2,4,8,-1},
{
3,-1,-1,7},{
4,6,-1,8},{
5,7,-1,-1} };
这个数组也就代表九个位置中四个方向的可置换的数组元素下标(-1表示该方向不能交换),注意:这里的四个方向的话,是逆时针,(上左下右)
Hash+BFS+A*
#include