前言
Room是Architecture Components(后面简称为架构组件)中的一员,官方给他的介绍是:Room库在SQLite上提供了一个抽象层,允许更健壮的数据库访问,同时利用SQLite的全部功能。文档链接:Room Persistence Library 。
下面开始正文。
导入
文档链接:Room
- 首先需要在根目录的
build.gradle中加上google的maven仓库依赖。
repositories {
google() //add Google Maven repository
jcenter()
}
- 在
app的build.gradle中加上需要的依赖
def room_version = "2.2.0" //room版本号
implementation "androidx.room:room-runtime:$room_version"
annotationProcessor "androidx.room:room-compiler:$room_version" // For Kotlin use kapt instead of annotationProcessor
//一般上面两句就可以了,下面是可选项
// optional - Kotlin Extensions and Coroutines support for Room
implementation "androidx.room:room-ktx:$room_version"
// optional - RxJava support for Room
implementation "androidx.room:room-rxjava2:$room_version"
// optional - Guava support for Room, including Optional and ListenableFuture
implementation "androidx.room:room-guava:$room_version"
// Test helpers
testImplementation "androidx.room:room-testing:$room_version"
使用
文档链接,下面通过一个student表为例来展示如何使用:
- 创建实体类
@Entity(tableName = "tb_student") //指定表名为tb_student
public class Student {
@PrimaryKey //标记为主键
private long id; //id
@NonNull //不能为null
@ColumnInfo(name = "first_name") //指定列名为first_name
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private String major; //专业
public Student() {
}
//省去get、set方法
}
说明:
- 首先实体类需要有一个构造函数,其次存储在数据库中的每个字段要么是公共的,要么有一个
getter方法。 -
@Entity:每个@Entity表示表中的一个实体。如果希望表名与类名不同,可通过tableName指定表名。 -
@PrimaryKey:标记主键 -
@NonNull:表示参数、字段或方法返回值永远不能为空。 -
@ColumnInfo:指定列名,如果希望列的名称与成员变量的名称不同,可以使用name指定表中的列的名称。
- 创建Dao对象
@Dao
public interface StudentDao {
@Insert(onConflict = OnConflictStrategy.IGNORE)
void insert(Student student);
@Query("DELETE FROM tb_student")
void deleteAll();
@Query("SELECT * FROM tb_student ORDER BY id ASC")
List getAlphabetizedStudents();
}
说明:
- 在DAO(数据访问对象)中,指定SQL查询并将其与方法调用关联。
DAO必须是接口或抽象类。 -
@Dao:标识为Room的DAO类。 -
@Insert:插入一个对象,这里可以不写任何SQL语句,另外还有@Delete和@Update注释,用于删除和更新行。 -
onConflict = OnConflictStrategy.IGNORE:如果冲突字词与列表中已有的字词完全相同,则冲突策略将忽略该字词。另外它还有另外两个可选项:OnConflictStrategy.ABORT(默认)和OnConflictStrategy.REPLACE(替换)。 -
@Query:使用@Query结合SQL语句可以用于读取和复杂的查询。
- 创建Room Database
@Database(entities = {Student.class}, version = 1)
public abstract class StudentRoomDatabase extends RoomDatabase {
//定义与数据库一起使用的DAO。为每个@Dao提供一个抽象的“ getter”方法。
public abstract StudentDao studentDao();
//设置为单例,防止同时打开多个数据库实例
private static volatile StudentRoomDatabase INSTANCE;
public static StudentRoomDatabase getDatabase(final Context context) {
if (INSTANCE == null) {
synchronized (StudentRoomDatabase.class) {
if (INSTANCE == null) {
//创建一个对象StudentRoomDatabase并将其命名"student_database"
INSTANCE = Room.databaseBuilder(context.getApplicationContext(),
StudentRoomDatabase.class, "student_database")
.allowMainThreadQueries() //允许在主线程进行查询操作
.build();
}
}
}
return INSTANCE;
}
}
说明:
-
Room类必须是抽象类,并且必须继承RoomDatabase。 -
@Database:注释为Room数据库,entities用于声明该数据库中的实体,version设置版本号。 -
allowMainThreadQueries(): 默认情况下,所有的查询操作都不能在主线程中进行,这里为了方便使用此方法开启主线程查询。
下面再来简单介绍一个Room Database,以下是官方文档对其的介绍的翻译:
Room是SQLite数据库之上的数据库层。Room负责处理您过去使用SQLiteOpenHelper处理的普通任务。
-
Room使用DAO向其数据库发出查询。 - 默认情况下,为避免
UI性能下降,Room不允许您在主线程上发出数据库查询。LiveData通过在需要时自动在后台线程上异步运行查询来应用此规则。 -
Room提供了SQLite语句的编译时检查。 - 您的
Room类必须是抽象类,并且必须扩展RoomDatabase。 - 通常,整个应用程序只需要一个
Room数据库实例。
- 创建Repository
public class StudentRepository {
private StudentDao mStudentDao;
private List mAllStudents;
public StudentRepository(Application application) {
StudentRoomDatabase db = StudentRoomDatabase.getDatabase(application);
mStudentDao = db.studentDao();
//Room在单独的线程上执行所有查询
mAllStudents = mStudentDao.getAlphabetizedStudents();
}
public List getAllStudents() {
return mAllStudents;
}
public void insert(Student student) {
//必须在非UI线程上调用dao的insert方法,否则应用程序将崩溃。
//所以这里采用了AsyncTask来进行异步的插入操作
new insertAsyncTask(mStudentDao).execute(student);
}
private static class insertAsyncTask extends AsyncTask {
private StudentDao mAsyncTaskDao;
insertAsyncTask(StudentDao dao) {
this.mAsyncTaskDao = dao;
}
@Override
protected Void doInBackground(Student... students) {
mAsyncTaskDao.insert(students[0]);
return null;
}
}
}
老规矩,下面是官方文档对repository的介绍:
Repository是一个类,它抽象了对多个数据源的访问。该存储库不是Architecture Components的一部分,但是,对于代码分离和体系结构来说,这是一个建议的最佳实践。一个Repository类处理数据操作。它为应用程序的其余部分提供了干净的API,以获取应用程序数据。
Repository管理查询线程,并允许您使用多个后端。在最常见的示例中,存储库实现了用于确定是从网络中获取数据还是使用本地数据库中缓存的结果的逻辑。
- 使用Repository操作数据库
到了这里,其实整个流程就走完了,需要操作数据库的地方直接创建上面的Repository对象并执行相应方法即可,所以下面就仅贴出MainActivity中的代码(完整代码地址在本文最后):
//MainActivity.java
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
StudentRepository mStudentRepository = new StudentRepository(getApplication());
//数据库操作
List students = mStudentRepository.getAllStudents();
RecyclerView recyclerView = findViewById(R.id.recycler_view);
recyclerView.setLayoutManager(new LinearLayoutManager(this));
//传入数据源并显示
recyclerView.setAdapter(new StudentAdapter(this,students));
}
}
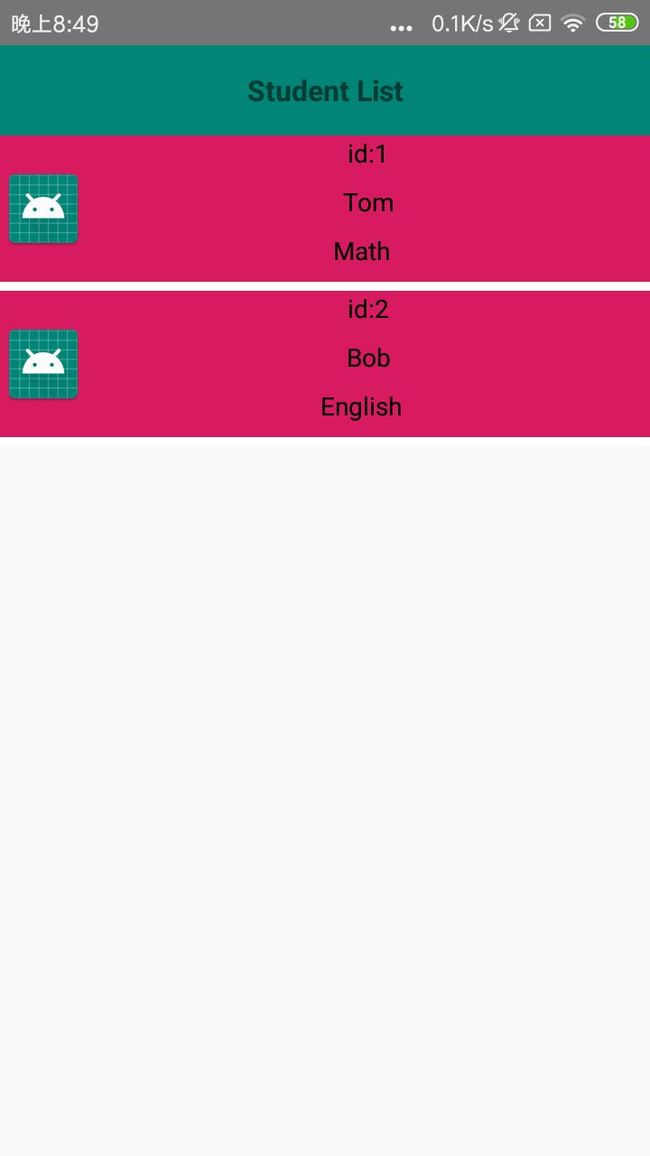
效果图:
初始化数据库
除了通过Repository可以向数据库添加数据意外,我们还可以在启动应用程序时向数据库中添加一些数据:
- 创建一个
RoomDatabase.Callback:
private static RoomDatabase.Callback sRoomDatabaseCallback = new RoomDatabase.Callback() {
@Override
public void onOpen(@NonNull SupportSQLiteDatabase db) {
super.onOpen(db);
//同理,插入操作不能在主线程中进行,所以这里使用了AsyncTask
new PopulateDbAsync(INSTANCE).execute();
}
};
private static class PopulateDbAsync extends AsyncTask {
private final StudentDao mDao;
PopulateDbAsync(StudentRoomDatabase db) {
this.mDao = db.studentDao();
}
@Override
protected Void doInBackground(Void... voids) {
mDao.deleteAll();
Student student = new Student(1, "Tom", "Math");
mDao.insert(student);
student = new Student(2, "Bob", "English");
mDao.insert(student);
return null;
}
}
- 创建RoomDatabase是加入这个callback:
INSTANCE = Room.databaseBuilder(context.getApplicationContext(),
StudentRoomDatabase.class, "student_database")
.allowMainThreadQueries() //允许在主线程进行查询操作
.addCallback(sRoomDatabaseCallback) //启动应用程序时删除所有内容并重新填充数据库
.build();
加入后,完整的StudentRoomDatabase.java如下:
@Database(entities = {Student.class}, version = 1)
public abstract class StudentRoomDatabase extends RoomDatabase {
//定义与数据库一起使用的DAO。为每个@Dao提供一个抽象的“ getter”方法。
public abstract StudentDao studentDao();
//设置为单例,防止同时打开多个数据库实例
private static volatile StudentRoomDatabase INSTANCE;
public static StudentRoomDatabase getDatabase(final Context context) {
if (INSTANCE == null) {
synchronized (StudentRoomDatabase.class) {
if (INSTANCE == null) {
//创建一个对象StudentRoomDatabase并将其命名"student_database"
INSTANCE = Room.databaseBuilder(context.getApplicationContext(),
StudentRoomDatabase.class, "student_database")
.allowMainThreadQueries() //允许在主线程进行查询操作
.addCallback(sRoomDatabaseCallback) //启动应用程序时删除所有内容并重新填充数据库
.build();
}
}
}
return INSTANCE;
}
private static RoomDatabase.Callback sRoomDatabaseCallback = new RoomDatabase.Callback() {
@Override
public void onOpen(@NonNull SupportSQLiteDatabase db) {
super.onOpen(db);
//同理,插入操作不能在主线程中进行,所以这里使用了AsyncTask
new PopulateDbAsync(INSTANCE).execute();
}
};
private static class PopulateDbAsync extends AsyncTask {
private final StudentDao mDao;
PopulateDbAsync(StudentRoomDatabase db) {
this.mDao = db.studentDao();
}
@Override
protected Void doInBackground(Void... voids) {
mDao.deleteAll();
Student student = new Student(1, "Tom", "Math");
mDao.insert(student);
student = new Student(2, "Bob", "English");
mDao.insert(student);
return null;
}
}
}
数据库版本更新
原文链接,文中给出了4种方案,但是在日常开发中,我们自然是要在保留原有数据的同时升级数据库版本了,假设我现在需要给student表添加一列from_where用于表示生源地,下面开始操作:
1.首先肯定先需要修改我们的Student实体类,给它添加一个字段:
@Entity(tableName = "tb_student") //指定表名为tb_student
public class Student {
...
@ColumnInfo(name = "from_where")
private String fromWhere;
public String getFromWhere() {
return fromWhere;
}
public void setFromWhere(String fromWhere) {
this.fromWhere = fromWhere;
}
...
}
- 其次需要修改
RoomDatabase,先将数据库版本升级,改为2
@Database(entities = {Student.class}, version = 2)
public abstract class StudentRoomDatabase extends RoomDatabase {
....
}
- 创建一个
Migration迁移
//1,2 表示从1升级到2
static final Migration MIGRATION_1_2 = new Migration(1, 2) {
@Override
public void migrate(@NonNull SupportSQLiteDatabase database) {
database.execSQL("ALTER TABLE tb_student ADD COLUMN from_where TEXT DEFAULT '未填写'");
}
};
- 将创建的
RoomDatabase时将迁移添加进去:
INSTANCE = Room.databaseBuilder(context.getApplicationContext(),
StudentRoomDatabase.class, "student_database")
.addMigrations(MIGRATION_1_2) //数据库升级迁移
...
.build();
我们来看一下addMigrations方法的声明:
public Builder addMigrations(@NonNull Migration... migrations)
所以如果以后再需要将据库版本升级到3的话只需要再创建一个Migration MIGRATION_2_3然后add进去就可以了。
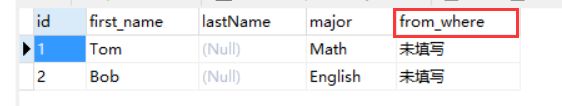
最后,导出数据库文件并用相关软件打开:
可以看到,生源地字段已成功加入到数据库当中。
完整代码已上传至github:地址链接。
补充
简介
Room是Google为了简化旧式的SQLite操作专门提供的。
- 拥有
SQLite的所有操作功能。 - 使用简单(类似于
Retrofit库),通过注解的方式实现相关功能。 -
LiveData,LifeCycle,Paging天然融合,支持。
RoomDatabase 的一些方法补充
/**
* exportSchema 生成json文件 默认为true。文件路径可在build.gradle中配置
**/
@Database(entities = {Cache.class}, version = 1, exportSchema = true)
public abstract class CacheDatabase extends RoomDatabase {
private static final CacheDatabase database;
static {
/*
创建一个内存数据库
这种数据库的数据只存在于内存中,也就是进程被杀之后,数据随时丢失
Room.inMemoryDatabaseBuilder()
Room.databaseBuilder //创建一个普通的数据库
*/
database = Room.databaseBuilder(AppUtils.getApplicationByReflect(), CacheDatabase.class, "ppjoke_cache")
.allowMainThreadQueries() //是否允许在主线程进行查询
//.addCallback() //数据库创建和打开后的回调
//.setQueryExecutor() //设置查询的线程池
//.openHelperFactory()
//.setJournalMode() //room的日志模式
//.fallbackToDestructiveMigration() //数据库升级一场之后的回滚
//.fallbackToDestructiveMigrationFrom() //数据库升级异常后根据指定版本进行回滚
//.addMigrations(CacheDatabase.sMigration)
.build();
}
static Migration sMigration = new Migration(1, 3) {
@Override
public void migrate(@NonNull SupportSQLiteDatabase database) {
database.execSQL("alter table teacher rename to student");
database.execSQL("alter table teacher add columu teacher_age INTEGER NOT NULL default 0");
}
};
}
- 生成的json文件路径可在
build.gradle中进行配置android { ... defaultConfig { ... testInstrumentationRunner "androidx.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner" consumerProguardFiles 'consumer-rules.pro' javaCompileOptions { annotationProcessorOptions { //配置数据库生成的json文件路径 arguments = ["room.schemaLocation":"$projectDir/schemas".toString()] } } } ... }
@Entity相关
@Entity(tableName = "cache" //表名
// , indices = {@Index(value = "key", unique = false)}//本表索引,用于大量数据的查询优化,unique有时候需要保证数据表的某个或者某些字段只有唯一的记录,可以通过设置@Index注解的unique属性实现。以下实例代码实现了避免有两条记录包含一样的key值。
// , inheritSuperIndices = false//如果 该值为true,那么父类中标记的indices{}索引也会算作该表的索引
// , primaryKeys = {"key"}//主键,一些策略逻辑会用到,比如插入一条数据时如果已存在,则更新否则算新的插入,那么怎么判断 ,数据库中是否已存在该条数据呢?就判断提供的主键,在表中是否已存在
// , foreignKeys = {
//外键,一般用于多表数据查询.可以配置多个外键
//ForeignKey用来设置关联表数据更新时所进行的操作,比如可以在@ForeignKey注解中设置onDelete=CASCADE,这样当Cache表中某个对应记录被删除时,ForeignTable表的所有相关记录也会被删除掉。
//对于@Insert(OnConflict=REPLACE)注解,SQLite是进行REMOVE和REPLACE操作,而不是UPDATE操作,这个可能影响到foreign key的约束。
//value:关联查询的表的Java.class,这里给定ForeignTable.class
//parentColumns:与之关联表ForeignTable表中的列名
//childColumns:本表的列的名称,必须要和parentColumns个数一致。这两个可以理解为根据cache表中的那个字段去比对ForeignTable表中的那个字段,认为是有关联关系的数据。
//onDelete:关联表中某条记录被delete或update时,本表应该怎么做:
// NO_ACTION:什么也不做,
// RESTRICT:本表跟parentColumns有关系的数据会立刻删除或更新,但不允许一对多的关系,
// SET_NULL:本表所跟parentColumns有关系的数据被设置为null值,
// SET_DEFAULT:本表所有跟parentColumns有关系的数据被设置为默认值,也是null值
// CASCADE:本表所有跟parentColumns有关系的数据一同被删除或更新
//onUpdate:本表中某条记录被更新时,与之关联的表应该怎么做
//deferred:本表某条记录变更时,与之关联表的数据变更是否要立即执行,还是等待本表事务处理完再来处理关联表。默认是同时处理。
// @ForeignKey(value = ForeignTable.class,
// parentColumns = "foreign_key",
// childColumns = "key",
// onDelete = 1,
// onUpdate = 1,
// deferred = false)}
//本表中 那些字段 不需要 映射到表中
// , ignoredColumns = {"data"}
)
public class Cache implements Serializable {
//PrimaryKey 必须要有,且不为空,autoGenerate 主键的值是否由Room自动生成,默认false
@PrimaryKey(autoGenerate = false)
@NonNull
public String key;
//@ColumnInfo(name = "_data") //指定该字段在表中的列的名字
public byte[] data;
//@Embedded 对象嵌套,ForeignTable对象中所有字段 也都会被映射到cache表中,
//同时也支持ForeignTable 内部还有嵌套对象
//public ForeignTable foreignTable;
/**
* 关联查询 根绝id查出对应的user
* entity -> User对象所对应的表
* parentColumn -> 当前表的列名 即Cache表
* entityColumn -> User表中的列名
* projection -> 需要查询的字段
*/
//@Relation(entity = User.class,parentColumn = "id",entityColumn = "id",projection = {})
//public User user;
//标记日期转换类
//@TypeConverters(value = {DateConverter.class})
//public Date date;
}
//public class ForeignTable implements Serializable {
// @PrimaryKey
// @NonNull
// public String foreign_key;
//
// //@ColumnInfo(name = "_data")
// public byte[] foreign_data;
//}
@Dao相关
@Dao
public interface CacheDao {
@Insert(onConflict = OnConflictStrategy.REPLACE)
long save(Cache cache);
/**
* 注意,冒号后面必须紧跟参数名,中间不能有空格。大于小于号和冒号中间是有空格的。
* select *from cache where【表中列名】 =:【参数名】------>等于
* where 【表中列名】 < :【参数名】 小于
* where 【表中列名】 between :【参数名1】 and :【参数2】------->这个区间
* where 【表中列名】like :参数名----->模糊查询
* where 【表中列名】 in (:【参数名集合】)---->查询符合集合内指定字段值的记录
*
* @param key key
*/
//如果是一对多,这里可以写List
@Query("select * from cache where `key`=:key")
Cache getCache(String key);
//只能传递对象,删除时根据Cache中的主键来比对的
@Delete
int delete(Cache cache);
//只能传递对象,删除时根据Cache中的主键来比对的
@Update(onConflict = OnConflictStrategy.REPLACE)
int update(Cache cache);
}
@TypeConverter相关
- 日期转换
/** * 用于Room中Date与long的相互转换 ** 使用时一般标记在字段上 : *
@TypeConverters(value = {DateConverter.class})** 详见{@link androidx.room.TypeConverters} database,dao ,entity上都可以用此标记 **/ public class DateConverter { @TypeConverter public static Long date2Long(Date date) { return date.getTime(); } @TypeConverter public static Date long2Date(long date) { return new Date(date); } }