可能是由于yolact官方更新过其项目代码,所以网上其他人的yolact训练使用的config文件和我的稍微有区别。但总体还是差不多的。
1:提前准备好自己的数据集
使用labelme来制作分割数据集,但是得到的是一个个单独的json文件。需要将其转换成coco。
labelme2coco.py如下所示(代码来源:github链接):
import os
import json
import numpy as np
import glob
import shutil
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
np.random.seed(41)
#0为背景,此处根据你数据集的类别来修改key
classname_to_id = {"1": 1}
class Lableme2CoCo:
def __init__(self):
self.images = []
self.annotations = []
self.categories = []
self.img_id = 0
self.ann_id = 0
def save_coco_json(self, instance, save_path):
json.dump(instance, open(save_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8'), ensure_ascii=False, indent=1) # indent=2 更加美观显示
# 由json文件构建COCO
def to_coco(self, json_path_list):
self._init_categories()
for json_path in json_path_list:
obj = self.read_jsonfile(json_path)
self.images.append(self._image(obj, json_path))
shapes = obj['shapes']
for shape in shapes:
annotation = self._annotation(shape)
self.annotations.append(annotation)
self.ann_id += 1
self.img_id += 1
instance = {}
instance['info'] = 'spytensor created'
instance['license'] = ['license']
instance['images'] = self.images
instance['annotations'] = self.annotations
instance['categories'] = self.categories
return instance
# 构建类别
def _init_categories(self):
for k, v in classname_to_id.items():
category = {}
category['id'] = v
category['name'] = k
self.categories.append(category)
# 构建COCO的image字段
def _image(self, obj, path):
image = {}
from labelme import utils
img_x = utils.img_b64_to_arr(obj['imageData'])
h, w = img_x.shape[:-1]
image['height'] = h
image['width'] = w
image['id'] = self.img_id
image['file_name'] = os.path.basename(path).replace(".json", ".jpg")
return image
# 构建COCO的annotation字段
def _annotation(self, shape):
label = shape['label']
points = shape['points']
annotation = {}
annotation['id'] = self.ann_id
annotation['image_id'] = self.img_id
annotation['category_id'] = int(classname_to_id[label])
annotation['segmentation'] = [np.asarray(points).flatten().tolist()]
annotation['bbox'] = self._get_box(points)
annotation['iscrowd'] = 0
annotation['area'] = 1.0
return annotation
# 读取json文件,返回一个json对象
def read_jsonfile(self, path):
with open(path, "r", encoding='utf-8') as f:
return json.load(f)
# COCO的格式: [x1,y1,w,h] 对应COCO的bbox格式
def _get_box(self, points):
min_x = min_y = np.inf
max_x = max_y = 0
for x, y in points:
min_x = min(min_x, x)
min_y = min(min_y, y)
max_x = max(max_x, x)
max_y = max(max_y, y)
return [min_x, min_y, max_x - min_x, max_y - min_y]
if __name__ == '__main__':
labelme_path = "labelme/" # 此处根据你的数据集地址来修改
saved_coco_path = "./"
# 创建文件
if not os.path.exists("%scoco/annotations/"%saved_coco_path):
os.makedirs("%scoco/annotations/"%saved_coco_path)
if not os.path.exists("%scoco/images/train2017/"%saved_coco_path):
os.makedirs("%scoco/images/train2017"%saved_coco_path)
if not os.path.exists("%scoco/images/val2017/"%saved_coco_path):
os.makedirs("%scoco/images/val2017"%saved_coco_path)
# 获取images目录下所有的joson文件列表
json_list_path = glob.glob(labelme_path + "/*.json")
# 数据划分,这里没有区分val2017和tran2017目录,所有图片都放在images目录下
train_path, val_path = train_test_split(json_list_path, test_size=0.12)
print("train_n:", len(train_path), 'val_n:', len(val_path))
# 把训练集转化为COCO的json格式
l2c_train = Lableme2CoCo()
train_instance = l2c_train.to_coco(train_path)
l2c_train.save_coco_json(train_instance, '%scoco/annotations/instances_train2017.json'%saved_coco_path)
for file in train_path:
shutil.copy(file.replace("json","jpg"),"%scoco/images/train2017/"%saved_coco_path)
for file in val_path:
shutil.copy(file.replace("json","jpg"),"%scoco/images/val2017/"%saved_coco_path)
# 把验证集转化为COCO的json格式
l2c_val = Lableme2CoCo()
val_instance = l2c_val.to_coco(val_path)
l2c_val.save_coco_json(val_instance, '%scoco/annotations/instances_val2017.json'%saved_coco_path)
只需要修改两个地方即可,然后放到data文件夹下。
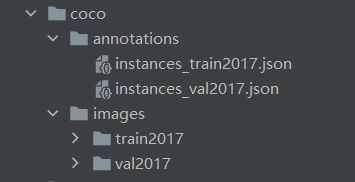
最后,得到的coco格式的数据集如下所示:
至此,数据准备已经结束。
2:下载github存储库
网址:YOLACT
之后解压,但是我解压的时候不知道为啥没有yolact.py这个文件。后来又建了一个py文件,复制了里面的代码。
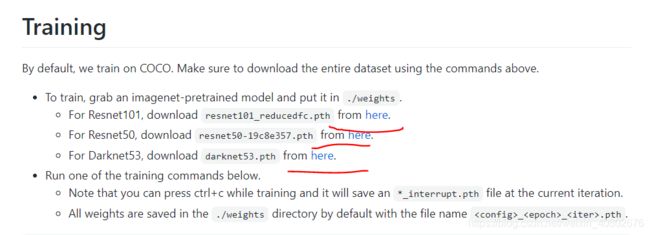
下载权重文件,把权重文件放到yolact-master下的weights文件夹里(没有就新建):
3:修改config.py
文件所在位置:
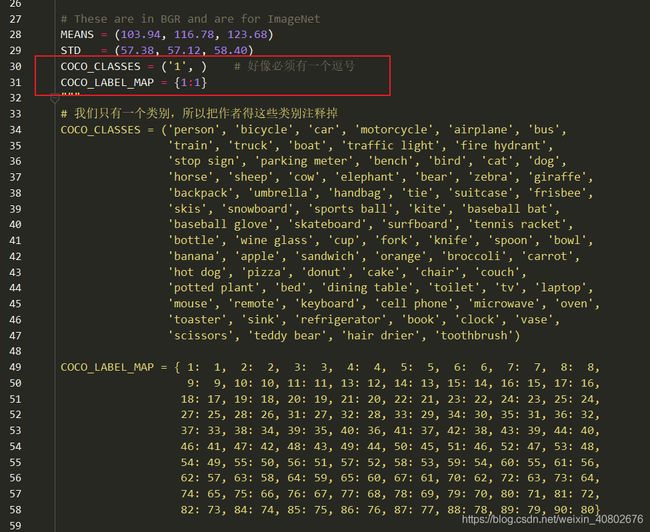
修改类别,把原本的coco的类别全部注释掉,修改成自己的(如红色框),注意COCO_CLASSES里有一个逗号。
修改数据集地址dataset_base:
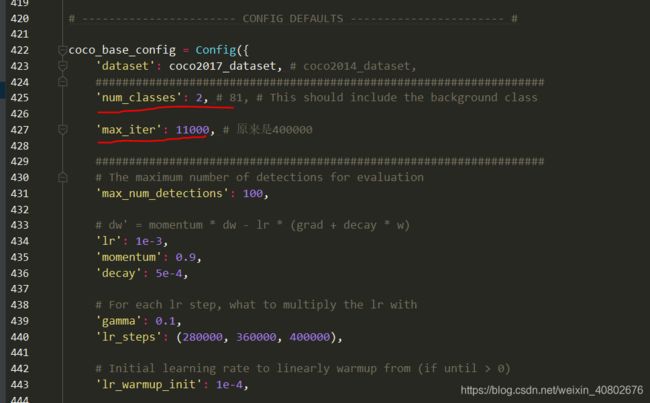
修改coco_base_config(下面第二个横线max_iter并不是控制训练轮数的,第二张图中的max_iter才是)
4:训练
cd到指定路径下,执行下面命令即可
python train.py --config=yolact_base_config
刚开始:
因为我是租的云服务器,在jupyter notebook里训练的。输出的训练信息比较乱。
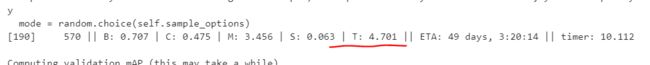
训练几分钟后:
主要看T后面的数字即可,好像他就是总的loss,如果它收敛了,按下Ctrl+C,即可中止训练,保存模型权重。
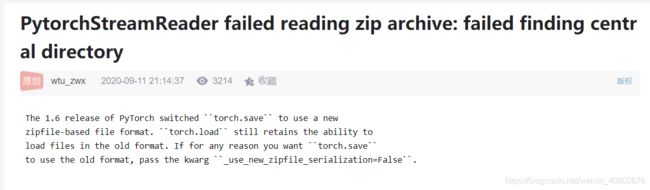
第一个问题:
PytorchStreamReader failed reading zip archive: failed finding central directory
第二个问题:
(但是不知道为啥,我训练时如果中断,保存的模型不能用来测试,会爆出下面的错误)
RuntimeError: unexpected EOF, expected *** more bytes. The file might be corruptrd
没办法解决,所以只能跑完,自动结束之后保存的模型拿来测试(自动保存的必中断保存的要大十几兆)
模型保存的格式:
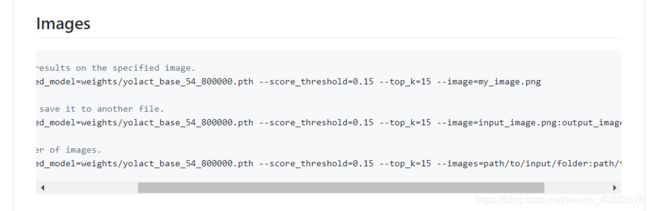
5:测试
使用官网的测试命令即可
以上就是python 使用Yolact训练自己的数据集的详细内容,更多关于python 训练数据集的资料请关注脚本之家其它相关文章!