Github地址 https://github.com/zhangxiaomeng1/XMLineChartView
由于CoreGraphics框架有太多的API,对于初次接触或者对该框架不是十分了解的人,在绘图时,对API的选择会感到有些迷茫,甚至会觉得iOS的图形绘制有些繁琐。因此,本文主要介绍一下iOS的绘图方法和分析一下CoreGraphics框架的绘图原理。
一、绘图系统简介
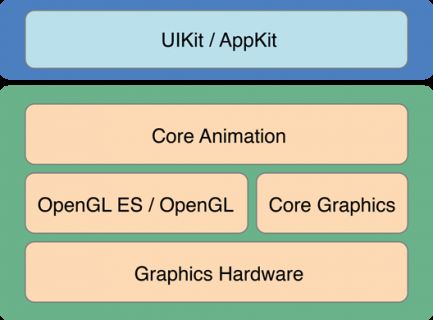
iOS的绘图框架有多种,我们平常最常用的就是UIKit,其底层是依赖CoreGraphics实现的,而且绝大多数的图形界面也都是由UIKit完成,并且UIImage、NSString、UIBezierPath、UIColor等都知道如何绘制自己,也提供了一些方法来满足我们常用的绘图需求。除了UIKit,还有CoreGraphics、Core Animation,Core Image,OpenGL ES等多种框架,来满足不同的绘图要求。各个框架的大概介绍如下:
UIKit:最常用的视图框架,封装度最高,都是OC对象
CoreGraphics:主要绘图系统,常用于绘制自定义视图,纯C的API,使用Quartz2D做引擎
CoreAnimation:提供强大的2D和3D动画效果
CoreImage:给图片提供各种滤镜处理,比如高斯模糊、锐化等
OpenGL-ES:主要用于游戏绘制,但它是一套编程规范,具体由设备制造商实现
绘图系统
二、绘图方式
实际的绘图包括两部分:视图绘制和视图布局,它们实现的功能是不同的,在理解这两个概念之前,需要了解一下什么是绘图周期,因为都是在绘图周期中进行绘制的。
绘图周期:
iOS在运行循环中会整合所有的绘图请求,并一次将它们绘制出来
不能在子线程中绘制,也不能进行复杂的操作,否则会造成主线程卡顿
1.视图绘制
调用UIView的drawRect:方法进行绘制。如果调用一个视图的setNeedsDisplay方法,那么该视图就被标记为重新绘制,并且会在下一次绘制周期中重新绘制,自动调用drawRect:方法。
2.视图布局
调用UIView的layoutSubviews方法。如果调用一个视图的setNeedsLayout方法,那么该视图就被标记为需要重新布局,UIKit会自动调用layoutSubviews方法及其子视图的layoutSubviews方法。
在绘图时,我们应该尽量多使用布局,少使用绘制,是因为布局使用的是GPU,而绘制使用的是CPU。GPU对于图形处理有优势,而CPU要处理的事情较多,且不擅长处理图形,所以尽量使用GPU来处理图形。
三、绘图状态切换
iOS的绘图有多种对应的状态切换,比如:pop/push、save/restore、context/imageContext和CGPathRef/UIBezierPath等,下面分别进行介绍:
1.pop / push
设置绘图的上下文环境(context)
push:UIGraphicsPushContext(context)把context压入栈中,并把context设置为当前绘图上下文
pop:UIGraphicsPopContext将栈顶的上下文弹出,恢复先前的上下文,但是绘图状态不变
下面绘制的视图是黑色
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect {
[[UIColor redColor] setFill];
UIGraphicsPushContext(UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext());
[[UIColor blackColor] setFill];
UIGraphicsPopContext();
UIRectFill(CGRectMake(90, 340, 100, 100)); // black color
}
2.save / restore
设置绘图的状态(state)
save:CGContextSaveGState 压栈当前的绘图状态,仅仅是绘图状态,不是绘图上下文
restore:恢复刚才保存的绘图状态
下面绘制的视图是红色
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect {
[[UIColor redColor] setFill];
CGContextSaveGState(UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext());
[[UIColor blackColor] setFill];
CGContextRestoreGState(UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext());
UIRectFill(CGRectMake(90, 200, 100, 100)); // red color
}
3.context / imageContext
iOS的绘图必须在一个上下文中绘制,所以在绘图之前要获取一个上下文。如果是绘制图片,就需要获取一个图片的上下文;如果是绘制其它视图,就需要一个非图片上下文。对于上下文的理解,可以认为就是一张画布,然后在上面进行绘图操作。
context:图形上下文,可以通过UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext:获取当前视图的上下文
imageContext:图片上下文,可以通过UIGraphicsBeginImageContextWithOptions:获取一个图片上下文,然后绘制完成后,调用UIGraphicsGetImageFromCurrentImageContext获取绘制的图片,最后要记得关闭图片上下文UIGraphicsEndImageContext。
4.CGPathRef / UIBezierPath
图形的绘制需要绘制一个路径,然后再把路径渲染出来,而CGPathRef就是CoreGraphics框架中的路径绘制类,UIBezierPath是封装CGPathRef的面向OC的类,使用更加方便,但是一些高级特性还是不及CGPathRef。
UIView和CALayer的区别
对于继承
UIView —> UIResponder —> NSObject
CALayer —> NSObject对于响应用户事件
UIView继承自UIResponder,UIResponder是用来响应事件的,所以UIView可以响应事件
CALayer直接继承于NSObject,所以CALayer不能响应事件对于所属框架
UIView是在/System/Library/Frameworks/UIKit.framework中定义,UIKit主要是用来构建用户界面,并且是可以响应事件的
CALayer是在/System/Library/Frameworks/QuartzCore.framework定义,2D图像绘制都是通过QuartzCore.framework实现的对于基本属性
UIView:position、size、transform
CALayer:position、size、transform、animations总结
UIView相比CALayer最大区别是UIView可以响应用户事件,而CALayer不可以。UIView侧重于对显示内容的管理,CALayer侧重于对内容的绘制。对于UIView所管理的内容,显示任何图形都会受到CALayer的影响。UIView依赖于CALayer提供的内容,CALayer依赖于UIView提供的容器来显示绘制的内容。UIView与CALayer都有树状层级结构,CALayer内部有SubLayers,UIView内部也有SubViews。
UIView的显示原理
因为UIView依赖于CALayer提供的内容,而CALayer又依赖于UIView提供的容器来显示绘制的内容,所以UIView的显示可以说是CALayer要显示绘制的图形。当要显示时,CALayer会准备好一个CGContextRef(图形上下文),然后调用它的delegate(这里就是UIView)的drawLayer:inContext:方法,并且传入已经准备好的CGContextRef对象,在drawLayer:inContext:方法中UIView又会调用自己的drawRect:方法。
我们可以把UIView的显示比作“在电脑上使用播放器播放U盘上得电影”,播放器相当于UIView,视频解码器相当于CALayer,U盘相当于CGContextRef,电影相当于绘制的图形信息。不同的图形上下文可以想象成不同接口的U盘。
注意:当我们需要绘图到根层上时,一般在drawRect:方法中绘制,不建议在drawLayer:inContext:方法中绘图
四、具体绘图方法
由于iOS常用的绘图框架有UIKit和CoreGraphics两个,所以绘图的方法也有多种,下面介绍一下iOS的几种常用的绘图方法。
方法一:最原始的绘图方式
获取当前控件的图形上下文
描述绘画内容
a. 创建图形路径
b. 创建图形起始点
c. 添加图形的终点
把绘画内容添加到图形上下文
设置图形上下文的状态(线宽、颜色等)
渲染图形上下文
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect {
// 1. 获取当前控件的图形上下文
// CG:表示这个类在CoreGraphics框架里 Ref:引用
CGContextRef context = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
// 2. 描述绘画内容
// a. 创建图形路径
CGMutablePathRef path = CGPathCreateMutable();
// b. 创建图形起始点
CGPathMoveToPoint(path, NULL, 50, 50);
// c. 添加图形的终点
CGPathAddLineToPoint(path, NULL, 200, 50);
// 3. 把绘画内容添加到图形上下文
CGContextAddPath(context, path);
// 4. 设置图形上下文的状态(线宽、颜色等)
CGContextSetLineWidth(context, 5);
CGContextSetRGBStrokeColor(context, 0, 1, 0, 1);
// 5. 渲染图形上下文
CGContextStrokePath(context);
}
方法二:使用上下文直接绘图
注意:不用创建路径,也不需要把绘图内容添加到图形上下文,因为图形上下文封装了这些步骤。
获取当前控件的图形上下文
描述绘画内容
a. 创建图形起始点
b. 添加图形的终点
设置图形上下文的状态(线宽、颜色等)
渲染图形上下文
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect {
// 1. 获取当前控件的图形上下文
CGContextRef context = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
// 2. 描述绘画内容
// a. 创建图形起始点
CGContextMoveToPoint(context, 20, 50);
// b. 添加图形的终点
CGContextAddLineToPoint(context, 200, 150);
CGContextAddLineToPoint(context, 200, 55);
// 3. 设置图形上下文的状态(线宽、颜色等)
CGContextSetLineWidth(context, 5);
CGContextSetCMYKStrokeColor(context, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1);
// 4. 渲染图形上下文
CGContextStrokePath(context);
}
方法三:贝瑟尔路径(UIBezierPath)绘图
提示:
UIKit已经封装了一些绘图的功能:UIBezierPath,里面封装了很多东西,可以帮我画一些基本的线段,矩形,圆等等,一般开发中用贝塞尔路径绘图。
CGPath转换:UIKit框架转CoreGraphics直接 .CGPath 就能转换
优点: 用UIBezierPath 画多根不连接的线,可以管理各个线的状态
缺点: UIBezierPath 不能画曲线
注意:
使用贝瑟尔路径绘图只能在drawRect里进行,因为底层要用到上下文,图形上下文只能在drawRect里获取,不能在其他方法里面绘图,比如:不能在awakeFromNib里绘图!
创建贝瑟尔路径
描述绘画内容
a. 创建图形起始点(moveToPoint)
b. 添加图形的终点(addLineToPoint)
设置路径状态
绘制路径
// 创建基本路径
+ (instancetype)bezierPath;
// 创建矩形路径
+ (instancetype)bezierPathWithRect:(CGRect)rect;
// 创建椭圆路径
+ (instancetype)bezierPathWithOvalInRect:(CGRect)rect;
// 创建圆角矩形
+ (instancetype)bezierPathWithRoundedRect:(CGRect)rect cornerRadius:(CGFloat)cornerRadius; // rounds all corners with the same horizontal and vertical radius
// 创建指定位置圆角的矩形路径
+ (instancetype)bezierPathWithRoundedRect:(CGRect)rect byRoundingCorners:(UIRectCorner)corners cornerRadii:(CGSize)cornerRadii;
// 创建弧线路径
+ (instancetype)bezierPathWithArcCenter:(CGPoint)center radius:(CGFloat)radius startAngle:(CGFloat)startAngle endAngle:(CGFloat)endAngle clockwise:(BOOL)clockwise;
// 通过CGPath创建
+ (instancetype)bezierPathWithCGPath:(CGPathRef)CGPath;
相关属性和方法
// 与之对应的CGPath
@property(nonatomic) CGPathRef CGPath;
- (CGPathRef)CGPath NS_RETURNS_INNER_POINTER CF_RETURNS_NOT_RETAINED;
// 是否为空
@property(readonly,getter=isEmpty) BOOL empty;
// 整个路径相对于原点的位置及宽高
@property(nonatomic,readonly) CGRect bounds;
// 当前画笔位置
@property(nonatomic,readonly) CGPoint currentPoint;
// 线宽
@property(nonatomic) CGFloat lineWidth;
// 终点类型 (路径的终点形状,该属性适用于开放路径的起点和终点, 默认为kCGLineCapButt(方形结束, 结束位置正好为精确位置), 其他可选项为kCGLineCapRound(圆形结束, 结束位置超过精确位置半个线宽)和kCGLineCapSquare(方形结束, 结束位置超过精确位置半个线宽))
@property(nonatomic) CGLineCap lineCapStyle;
typedef CF_ENUM(int32_t, CGLineCap) {
kCGLineCapButt,
kCGLineCapRound,
kCGLineCapSquare
};
// 交叉点的类型(路径的连接点形状,默认为kCGLineJoinMiter(全部连接), 其他可选项为kCGLineJoinRound(圆形连接)和kCGLineJoinBevel(斜角连接))
@property(nonatomic) CGLineJoin lineJoinStyle;
typedef CF_ENUM(int32_t, CGLineJoin) {
kCGLineJoinMiter,
kCGLineJoinRound,
kCGLineJoinBevel
};
// 两条线交汇处内角和外角之间的最大距离,需要交叉点类型为kCGLineJoinMiter是生效,最大限制为10
@property(nonatomic) CGFloat miterLimit;
// 个人理解为绘线的精细程度,默认为0.6,数值越大,需要处理的时间越长
@property(nonatomic) CGFloat flatness;
// 决定使用even-odd或者non-zero规则
@property(nonatomic) BOOL usesEvenOddFillRule;
//反方向绘制path
- (UIBezierPath *)bezierPathByReversingPath;
// 设置画笔起始点
- (void)moveToPoint:(CGPoint)point;
// 从当前点到指定点绘制直线
- (void)addLineToPoint:(CGPoint)point;
// 添加弧线
- (void)addArcWithCenter:(CGPoint)center radius:(CGFloat)radius startAngle:(CGFloat)startAngle endAngle:(CGFloat)endAngle clockwise:(BOOL)clockwise NS_AVAILABLE_IOS(4_0);
// center弧线圆心坐标 radius弧线半径 startAngle弧线起始角度 endAngle弧线结束角度 clockwise是否顺时针绘制
//添加贝塞尔曲线
- (void)addQuadCurveToPoint:(CGPoint)endPoint controlPoint:(CGPoint)controlPoint;
// endPoint终点 controlPoint控制点
- (void)addCurveToPoint:(CGPoint)endPoint controlPoint1:(CGPoint)controlPoint1 controlPoint2:(CGPoint)controlPoint2;
// endPoint终点 controlPoint1、controlPoint2控制点
// 移除所有的点,删除所有的subPath
- (void)removeAllPoints;
//填充
- (void)fill;
// 路径绘制
- (void)stroke;
//使用一条直线闭合路径的起点和终点, 该方法同时也会更新当前点到新直线的终点(即路径的起点)
//- (void)closePath
参考链接
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect {
// 1. 创建贝瑟尔路径
UIBezierPath *path = [UIBezierPath bezierPath];
// 2. 设置起点
[path moveToPoint:CGPointMake(20, 20)];
// 3. 设置终点
[path addLineToPoint:CGPointMake(80, 150)];
// 4. 设置路径状态
// 设置颜色
[[UIColor redColor] set];
// 设置线宽
[path setLineWidth:5];
// 4. 绘制路径
[path stroke];
// 1. 创建贝瑟尔路径
UIBezierPath *path1 = [UIBezierPath bezierPath];
// 2. 设置起点
[path1 moveToPoint:CGPointMake(50, 20)];
// 3. 设置拐点
[path1 addLineToPoint:CGPointMake(200, 100)];
// 3. 设置终点
[path1 addLineToPoint:CGPointMake(50, 230)];
// 4. 设置路径状态
// 设置颜色
[[UIColor blueColor] set];
// 设置线宽
[path1 setLineWidth:15];
// 设置连接样式
[path1 setLineJoinStyle:kCGLineJoinRound];
// 设置顶角样式
[path1 setLineCapStyle:kCGLineCapRound];
// 4. 绘制路径
[path1 stroke];
// 画一段圆弧
UIBezierPath *bezierPath = [[UIBezierPath alloc] init];
[[UIColor redColor] setStroke];
bezierPath.lineWidth = 11;
bezierPath.lineCapStyle = kCGLineCapButt;
bezierPath.lineJoinStyle = kCGLineJoinRound;
[bezierPath moveToPoint:CGPointMake(150, 100)];
[bezierPath addArcWithCenter:CGPointMake(100, 100) radius:50 startAngle:0 endAngle:M_PI_2 clockwise:YES];
[bezierPath stroke];
UIBezierPath *bezierPath1 = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithArcCenter:CGPointMake(300, 100) radius:50 startAngle:0 endAngle:M_PI_2 clockwise:NO];
[[UIColor orangeColor] setStroke];
[bezierPath1 stroke];
// 画圆
UIBezierPath *bezierPath2 = [[UIBezierPath alloc] init];
[[UIColor redColor] setStroke];
[bezierPath2 moveToPoint:CGPointMake(150, 250)];
[bezierPath2 addArcWithCenter:CGPointMake(100, 250) radius:50 startAngle:0 endAngle:M_PI * 2 clockwise:YES];
[bezierPath2 stroke];
UIBezierPath *bezierPath3 = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithArcCenter:CGPointMake(300, 250) radius:50 startAngle:0 endAngle:M_PI * 2 clockwise:NO];
[[UIColor orangeColor] setFill];
[bezierPath3 fill];
// 通过矩形来画出其内切圆或内切椭圆
UIBezierPath *bezierPath4 = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithOvalInRect:CGRectMake(50, 350, 100, 100)];
[[UIColor orangeColor] setStroke];
[bezierPath4 stroke];
UIBezierPath *bezierPath5 = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithOvalInRect:CGRectMake(250, 350, 100, 50)];
[[UIColor orangeColor] setStroke];
[bezierPath5 stroke];
// 画矩形
UIBezierPath *bezierPath = [[UIBezierPath alloc] init];
[[UIColor redColor] setStroke];
bezierPath.lineWidth = 11;
bezierPath.lineCapStyle = kCGLineCapButt;
bezierPath.lineJoinStyle = kCGLineJoinRound;
[bezierPath moveToPoint:CGPointMake(100, 100)];
[bezierPath addLineToPoint:CGPointMake(200, 100)];
[bezierPath addLineToPoint:CGPointMake(200, 200)];
[bezierPath addLineToPoint:CGPointMake(100, 200)];
[bezierPath closePath];// 或者[bezierPath addLineToPoint:CGPointMake(100, 100)];
[bezierPath stroke];
UIBezierPath *bezierPath1 = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithRect:CGRectMake(250, 100, 100, 100)];
[[UIColor orangeColor] setStroke];
[bezierPath1 stroke];
// 画圆角矩形
UIBezierPath *bezierPath2 = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithRoundedRect:CGRectMake(100, 250, 100, 100) cornerRadius:10];
[[UIColor orangeColor] setStroke];
[bezierPath2 stroke];
// 画指定圆角的矩形
UIBezierPath *bezierPath3 = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithRoundedRect:CGRectMake(100, 400, 100, 100) byRoundingCorners:(UIRectCornerTopLeft | UIRectCornerBottomRight) cornerRadii:CGSizeMake(40, 0)];
[[UIColor orangeColor] setStroke];
[bezierPath3 stroke];
// 画矩形
UIBezierPath *bezierPath = [[UIBezierPath alloc] init];
[[UIColor redColor] setStroke];
bezierPath.lineWidth = 11;
bezierPath.lineCapStyle = kCGLineCapButt;
bezierPath.lineJoinStyle = kCGLineJoinRound;
[bezierPath moveToPoint:CGPointMake(100, 100)];
[bezierPath addLineToPoint:CGPointMake(200, 100)];
[bezierPath addLineToPoint:CGPointMake(200, 200)];
[bezierPath addLineToPoint:CGPointMake(100, 200)];
[bezierPath closePath];// 或者[bezierPath addLineToPoint:CGPointMake(100, 100)];
[bezierPath stroke];
UIBezierPath *bezierPath1 = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithRect:CGRectMake(250, 100, 100, 100)];
[[UIColor orangeColor] setStroke];
[bezierPath1 stroke];
// 画圆角矩形
UIBezierPath *bezierPath2 = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithRoundedRect:CGRectMake(100, 250, 100, 100) cornerRadius:10];
[[UIColor orangeColor] setStroke];
[bezierPath2 stroke];
// 画指定圆角的矩形
UIBezierPath *bezierPath3 = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithRoundedRect:CGRectMake(100, 400, 100, 100) byRoundingCorners:(UIRectCornerTopLeft | UIRectCornerBottomRight) cornerRadii:CGSizeMake(40, 0)];
[[UIColor orangeColor] setStroke];
[bezierPath3 stroke];
// 画一条二次贝塞尔曲线
UIBezierPath *bezierPath = [[UIBezierPath alloc] init];
[[UIColor redColor] setStroke];
bezierPath.lineWidth = 11;
[bezierPath moveToPoint:CGPointMake(100, 100)];
[bezierPath addQuadCurveToPoint:CGPointMake(300, 100) controlPoint:CGPointMake(200, 200)];
[bezierPath stroke];
// 画一条三次贝塞尔曲线
UIBezierPath *bezierPath1 = [[UIBezierPath alloc] init];
[[UIColor redColor] setStroke];
bezierPath1.lineWidth = 11;
[bezierPath1 moveToPoint:CGPointMake(100, 300)];
[bezierPath1 addCurveToPoint:CGPointMake(300, 300) controlPoint1:CGPointMake(150, 350) controlPoint2:CGPointMake(250, 250)];
[bezierPath1 stroke];
画一条虚线
UIBezierPath *bezierPath = [[UIBezierPath alloc] init];
[[UIColor redColor] setStroke];
CGFloat pattern[] = {10, 10};
[bezierPath setLineDash:pattern count:2 phase:0];
[bezierPath moveToPoint:CGPointMake(100, 100)];
[bezierPath addLineToPoint:CGPointMake(300, 100)];
[bezierPath stroke];
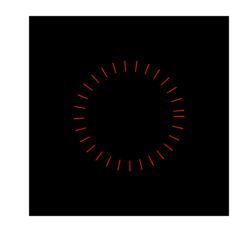
//虚线组成的圆,下面有图片
UIBezierPath *bezierPath3 = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithArcCenter:CGPointMake(100, 100) radius:50 startAngle:0 endAngle:M_PI * 2 clockwise:YES];
[[UIColor redColor] setStroke];
bezierPath3.lineWidth = 11;
CGFloat pattern3[] = {1, 10};
[bezierPath3 setLineDash:pattern3 count:2 phase:0];
[bezierPath3 stroke];
贝塞尔曲线的仿射变换
UIBezierPath *bezierPath = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithRect:CGRectMake(250, 100, 100, 100)];
[[UIColor orangeColor] setStroke];
bezierPath.lineWidth = 11;
bezierPath.lineCapStyle = kCGLineCapButt;
bezierPath.lineJoinStyle = kCGLineJoinRound;
[bezierPath applyTransform:CGAffineTransformMakeRotation(M_PI_4)];
[bezierPath stroke];
7、剪裁路径覆盖的区域
// 把图片切成任意你想要的形状显示
UIBezierPath *bezierPath = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithRoundedRect:CGRectMake(100, 100, 100, 100) byRoundingCorners:(UIRectCornerTopLeft | UIRectCornerBottomRight) cornerRadii:CGSizeMake(40, 0)];
[[UIColor orangeColor] setStroke];
[bezierPath stroke];
[bezierPath addClip];// 剪裁路径覆盖的区域
UIImage *image = [UIImage imageNamed:@"1.png"];
[image drawAtPoint:CGPointMake(100, 100)];
8、利用- (void)addLineToPoint:(CGPoint)point;画数学函数曲线
#import "CustomView.h"
#define kScreenWidth [UIScreen mainScreen].bounds.size.width
#define kScreenHeight [UIScreen mainScreen].bounds.size.height
@interface CustomView ()
@property (assign, nonatomic) float waveAmplitude;// 振幅
@property (assign, nonatomic) float waveSpeed;// 波纹流动的速度
@property (assign, nonatomic) float waveOffset;// 初相
@end
@implementation CustomView
- (instancetype)initWithFrame:(CGRect)frame {
if (self = [super initWithFrame:frame]) {
// 初始值
self.waveAmplitude = 20;
self.waveSpeed = 2.0;
self.waveOffset = 0.0;
CADisplayLink *displayLink = [CADisplayLink displayLinkWithTarget:self selector:@selector(wave)];
[displayLink addToRunLoop:[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] forMode:(NSRunLoopCommonModes)];
}
return self;
}
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect {
self.waveOffset += self.waveSpeed;
UIBezierPath *bezierPath = [[UIBezierPath alloc] init];
[[UIColor redColor] setStroke];
bezierPath.lineWidth = 1;
// 起始点
[bezierPath moveToPoint:CGPointMake(0, self.waveAmplitude)];
// 连接各点
for (CGFloat x = 0.0; x < kScreenWidth; x ++) {
CGFloat y = 100 + self.waveAmplitude * sinf(3 * M_PI * x / kScreenWidth + self.waveOffset * M_PI / kScreenWidth);
[bezierPath addLineToPoint:CGPointMake(x, y)];
}
// 渲染
[bezierPath stroke];
}
- (void)wave {
[self setNeedsDisplay];
}
}
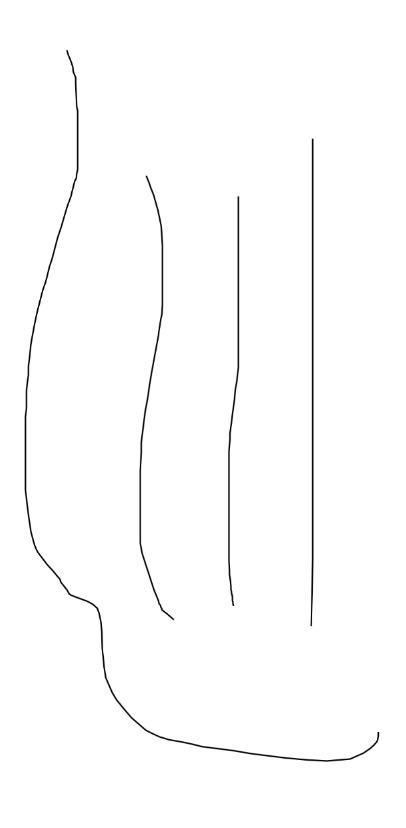
9、利用- (void)addLineToPoint:(CGPoint)point;画任意想要的曲线
#import "CustomView.h"
#define kScreenWidth [UIScreen mainScreen].bounds.size.width
#define kScreenHeight [UIScreen mainScreen].bounds.size.height
@interface CustomView ()
@property (strong, nonatomic) UIBezierPath *bezierPath;
@end
@implementation CustomView
- (instancetype)initWithFrame:(CGRect)frame {
if (self = [super initWithFrame:frame]) {
self.bezierPath = [[UIBezierPath alloc] init];
self.bezierPath.lineWidth = 1;// 笔的粗细
UIPanGestureRecognizer *panGesture = [[UIPanGestureRecognizer alloc] initWithTarget:self action:@selector(pan:)];
panGesture.maximumNumberOfTouches = 1;// 一个指头画
[self addGestureRecognizer:panGesture];
}
return self;
}
- (void)pan:(UIPanGestureRecognizer *)panGesture {
// 获取平移到的点
CGPoint currentPoint = [panGesture locationInView:self];
if (panGesture.state == UIGestureRecognizerStateBegan) {
// 设置起始点
[self.bezierPath moveToPoint:currentPoint];
}else if (panGesture.state == UIGestureRecognizerStateChanged) {
// 连接平移点
[self.bezierPath addLineToPoint:currentPoint];
}
// 触发-drawRect:方法
[self setNeedsDisplay];
}
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect {
// 笔的颜色
[[UIColor redColor] setStroke];
// 渲染出曲线
[self.bezierPath stroke];
}
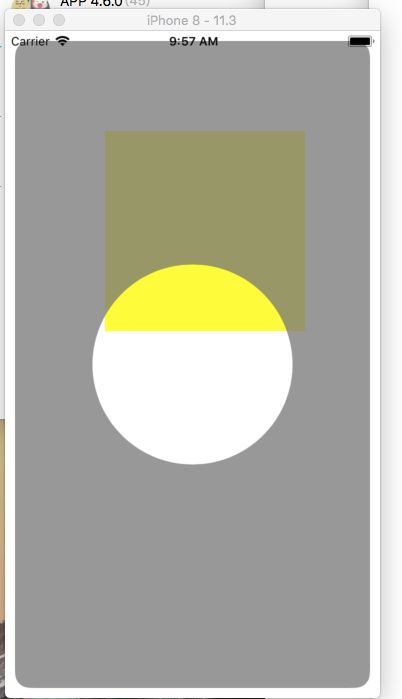
// iOS 中间镂空效果的View
UIView *maskView = [[UIView alloc] initWithFrame:self.view.bounds];
maskView.backgroundColor = [UIColor grayColor];
maskView.alpha = 0.8;
[self.view addSubview:maskView];
//贝塞尔曲线 画一个带有圆角的矩形
UIBezierPath *bpath = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithRoundedRect:CGRectMake(10, 10, self.view.frame.size.width - 20, self.view.frame.size.height - 20) cornerRadius:15];
//贝塞尔曲线 画一个圆形
[bpath appendPath:[UIBezierPath bezierPathWithArcCenter:maskView.center radius:100 startAngle:0 endAngle:2*M_PI clockwise:NO]];
//创建一个CAShapeLayer 图层
CAShapeLayer *shapeLayer = [CAShapeLayer layer];
shapeLayer.path = bpath.CGPath;
//添加图层蒙板
maskView.layer.mask = shapeLayer;
七. 绘制曲线
方法一:最原始绘图方法
- 获取当前控件的图形上下文
- 描述绘画图形内容
a. 获取图形路径
b. 添加起始点
c. 添加控制点和终点 - 把绘制图形内容添加到图形上下文
- 设置图形上下文状态
- 渲染图形上下文
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect {
// 1\. 获取当前控件的图形上下文
CGContextRef context = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
// 2\. 描述绘画图形内容
// a. 获取图形路径
CGMutablePathRef path = CGPathCreateMutable();
// b. 添加起始点
CGPathMoveToPoint(path, NULL, 0, 0);
// C. 添加控制点和终点,控制点(150,150)、终点(0,250)
CGPathAddQuadCurveToPoint(path, NULL, 250, 150, 0, 250);
// 3\. 把绘制图形内容添加到图形上下文
CGContextAddPath(context, path);
// 4\. 设置图形上下文状态
// 设置颜色
[[UIColor redColor] set];
// 设置线宽
CGContextSetLineWidth(context, 10);
// 5\. 渲染图形上下文
CGContextStrokePath(context);
}
方法二:使用上下文直接绘图
获取当前控件的图形上下文
描述绘画图形内容
a. 创建图形起始点
b. 添加控制点和终点
设置图形上下文状态
渲染图形上下文
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect {
// 1. 获取当前控件的图形上下文
CGContextRef context = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
// 2. 描述绘画图形内容
// a. 创建图形起始点
CGContextMoveToPoint(context, 0, 0);
// b. 添加控制点和终点,控制点(300,200),终点(0,250)
CGContextAddQuadCurveToPoint(context, 300, 200, 0, 250);
// 3. 设置图形上下文状态
// 设置颜色
[[UIColor redColor] set];
// 设置线宽
CGContextSetLineWidth(context, 10);
// 4. 渲染图形上下文
CGContextStrokePath(context);
}
三.CoreGraphics绘图
由于像素是依赖于目标的,所以2D绘图并不能操作单独的像素,我们可以从上下文(Context)读取它。所以我们在绘制之前需要通过
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext()
获取当前推入堆栈的图形,相当于你所要绘制图形的图纸,然后绘图就好比在画布上拿着画笔机械的进行画画,通过制定不同的参数来进行不同的绘制。
画完之后我们需要通过
CGContextSetFillColorWithColor(CGContextRef c, CGColorRef color)
CGContextFillPath(CGContextRef c)
来填充颜色并完成最后的绘制。下面我们来完成和UIBezierPath一样的绘制。
1.绘制矩形
绘制矩形需要先定义矩形的rect,然后使用
CGContextAddRect(CGContextRef c, CGRect rect)
进行绘制即可。如下:
- (void)drawRectangle {
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
CGRect rectangle = CGRectMake(10, 10, 60, 60);
CGContextAddRect(ctx, rectangle);
CGContextSetFillColorWithColor(ctx, [UIColor lightGrayColor].CGColor);
CGContextFillPath(ctx);
}
如下:
2.圆和椭圆
我们使用下面这个方法来绘制弧线:
CGContextAddArc(CGContextRef c, CGFloat x, CGFloat y, CGFloat radius, CGFloat startAngle, CGFloat endAngle, int clockwise)
其中的参数说明如下:
c 当前图形
x 圆弧的中心点坐标x
y 曲线控制点的y坐标
radius 指定点的x坐标值
startAngle 弧的起点与正X轴的夹角,
endAngle 弧的终点与正X轴的夹角
clockwise 指定1创建一个顺时针的圆弧,或是指定0创建一个逆时针圆弧
所以我们可以通过下面创建圆形:
- (void)drawCircleAtX:(float)x Y:(float)y {
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
CGContextAddArc(ctx, x, y, 150, 0, 2 * M_PI, 1);
CGContextSetFillColorWithColor(ctx, [UIColor blackColor].CGColor);
CGContextFillPath(ctx);
}
现在看起来:
绘制椭圆我们需要先给定一个容纳椭圆的矩形,然后使用
CGContextAddEllipseInRect(CGContextRef context, CGRect rect)
进行绘制,如下:
- (void)drawEllipseAtX:(float)x Y:(float)y {
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
CGRect rectangle = CGRectMake(x, y, 60, 30);
CGContextAddEllipseInRect(ctx, rectangle);
CGContextSetFillColorWithColor(ctx, [UIColor redColor].CGColor);
CGContextFillPath(ctx);
}
现在看起来:
3.多边形
绘制多边形需要通过CGContextMoveToPoint从一个开始点开始一个新的子路径,然后通过CGContextAddLineToPoint在当前点追加直线段,最后通过CGContextClosePath关闭路径即可。如下我们绘制一个三角形:
- (void)drawTriangle {
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
CGContextBeginPath(ctx);
CGContextMoveToPoint(ctx, 160, 40);
CGContextAddLineToPoint(ctx, 190, 80);
CGContextAddLineToPoint(ctx, 130, 80);
CGContextClosePath(ctx);
CGContextSetFillColorWithColor(ctx, [UIColor blackColor].CGColor);
CGContextFillPath(ctx);
}
现在看起来:
4.不规则形状
1).绘制一段弧度:[self drawCurve];
a).第一种:和贝塞尔曲线中的第一种一样,我们同样需要给定起始点
CGContextMoveToPoint(CGContextRef c, CGFloat x, CGFloat y)
给定控制点和终点:
CGContextAddQuadCurveToPoint(CGContextRef c, CGFloat cpx, CGFloat cpy, CGFloat x, CGFloat y)
其中:
cpx: 曲线控制点的x坐标
cpy: 曲线控制点的y坐标
- (void)drawQuadCurve {
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
CGContextBeginPath(ctx);
CGContextMoveToPoint(ctx, 50, 130);
CGContextAddQuadCurveToPoint(ctx, 0, 100, 25, 170);
CGContextSetLineWidth(ctx, 10);
CGContextSetStrokeColorWithColor(ctx, [UIColor brownColor].CGColor);
CGContextStrokePath(ctx);
}
我们画两个如上的曲线,现在看起来:
b).第二种:
第二种我们需要给两个控制点:
- (void)drawCurve2{
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
CGContextBeginPath(ctx);
CGContextMoveToPoint(ctx, 170, 170);
CGContextAddCurveToPoint(ctx, 160, 250, 230, 250, 160, 290);
CGContextSetLineWidth(ctx, 10);
CGContextSetStrokeColorWithColor(ctx, [UIColor brownColor].CGColor);
CGContextStrokePath(ctx);
}
现在看起来:
还不错。
5.加阴影效果
可以通过
CGContextSetShadowWithColor(CGContextRef context, CGSize offset, CGFloat blur, CGColorRef color)
设置阴影效果,4个参数分别是图形上下文,偏移量(CGSize),模糊值,和阴影颜色。我们在画圆圈的方法中加入它:
- (void)drawCircleAtX:(float)x Y:(float)y {
CGContextRef ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
CGContextAddArc(ctx, x, y, 150, 0, 2 * M_PI, 1);
CGContextSetShadowWithColor(ctx, CGSizeMake(10, 10), 20.0f, [[UIColor grayColor] CGColor]);
CGContextSetFillColorWithColor(ctx, [UIColor yellowColor].CGColor);
CGContextFillPath(ctx);
}
注意,它除了会在会在边缘绘制阴影效果,还会在有子控件的地方绘制,如下:
6.渐变色效果
1)放射式渐变:CGContextDrawRadialGradient
放射式渐变以某种颜色从一点开始,以另一种颜色在其它点结束。它看起来会是一个圆。
为了创建一个放射式渐变,你要调用CGGradientCreateWithColors函数。这个函数的返回值是一个新的类型为CGGradientRef的渐变。
CGGradientCreateWithColors包含以下3个参数:
Color Space:这是一个色彩范围的容器,类型是CGColorSpaceRef. 这个参数,我们可以传入CGColorSpaceCreateDeviceRGB函数的返回值,它将给我们一个RGB色彩空间。
颜色分量的数组:这个数组必须包含颜色的数组值。
位置数组:颜色数组中各个颜色的位置,此参数控制该渐变从一种颜色过渡到另一种颜色的速度有多快。
如下:
-(void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect
{
[super drawRect:rect];
// /先创造一个CGGradientRef,颜色是白,黑,location分别是0,1
CGColorSpaceRef colorSpace = CGColorSpaceCreateDeviceRGB();
NSArray* gradientColors = [NSArray arrayWithObjects:
(id)[UIColor whiteColor].CGColor,
(id)[UIColor blackColor].CGColor, nil];
CGFloat gradientLocations[] = {0, 1};
CGGradientRef gradient = CGGradientCreateWithColors(colorSpace,
(__bridge CFArrayRef)gradientColors,
gradientLocations);
CGPoint startCenter = CGPointMake(CGRectGetMidX(rect), CGRectGetMidY(rect));
CGFloat radius = MAX(CGRectGetHeight(rect), CGRectGetWidth(rect));
CGContextRef context = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
CGContextDrawRadialGradient(context, gradient,
startCenter, 0,
startCenter, radius,
0);
CGGradientRelease(gradient);
CGColorSpaceRelease(colorSpace);
}
进行上下文绘制,参数说明如下:
CGPoint startCenter:白色的起点(中心圆点)
CGFloat startRadius:起点的半径,这个值多大,中心就是多大一块纯色的白圈
CGPoint endCenter:白色的终点, 可以和起点一样,不一样的话就像探照灯一样从起点投影到这个终点
CGFloat endRadius:终点的半径,
如下:
CGContextRef context = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
CGContextDrawRadialGradient(context, gradient,
startCenter, 0,
startCenter, radius,
0);
CGGradientRelease(gradient);
CGColorSpaceRelease(colorSpace);
}
效果如下;
2)线性渐变:CGGradientCreateWithColorComponents
线性渐变以某种颜色从一点开始,以另一种颜色在其它点结束。
你先要调用上面讲到的drawdrawRadialGradientWithRect 函数去创建一个gradient渐变,创建好gradient后,我们将使用
CGContextDrawLinearGradient(CGContextRef context, CGGradientRef gradient, CGPoint startPoint, CGPoint endPoint, CGGradientDrawingOptions options)
在图形上下文中绘制,此过程需要五个参数, 比上面的辐射渐变多了最后一个参数:
Gradient drawing options :指定当你的起点或者终点不在图形上下文的边缘内时该如何处理。你可以使用你的开始或结束颜色来填充渐变以外的空间。此参数为以下值之一:
KCGGradientDrawsAfterEndLocation扩展整个渐变到渐变的终点之后的所有点, KCGGradientDrawsBeforeStartLocation扩展整个渐变到渐变的起点之前的所有点。
0不扩展该渐变。
代码如下:
- (void)drawingLinearGradientWithStartPoint:(CGPoint)startPoint endPoint:(CGPoint)endPoint
{
CGColorSpaceRef colorSpace = CGColorSpaceCreateDeviceRGB();
NSArray* gradientColors = [NSArray arrayWithObjects:
(id)[UIColor whiteColor].CGColor,
(id)[UIColor purpleColor].CGColor, nil];
CGFloat gradientLocations[] = {0, 1};
CGGradientRef gradient = CGGradientCreateWithColors(colorSpace,
(__bridge CFArrayRef)gradientColors,
gradientLocations);
CGContextRef context = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
CGContextSaveGState(context);
CGContextDrawLinearGradient(context, gradient, startPoint, endPoint,0);
CGContextRestoreGState(context);
CGGradientRelease(gradient);
CGColorSpaceRelease(colorSpace);
}
效果如下:
你也可以用一个自定义的形状来抱住你创建的渐变,如下所示:
CGColorSpaceRef colorSpace = CGColorSpaceCreateDeviceRGB();
NSArray* gradientColors = [NSArray arrayWithObjects:
(id)[UIColor whiteColor].CGColor,
(id)[UIColor purpleColor].CGColor, nil];
CGFloat gradientLocations[] = {0, 1};
CGGradientRef gradient = CGGradientCreateWithColors(colorSpace,
(__bridge CFArrayRef)gradientColors,
gradientLocations);
CGContextRef context = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
CGContextSaveGState(context);
CGContextMoveToPoint(context, 100, 100);
CGContextAddArc(context, 100, 100, 60, 1.04 , 2.09 , 0);
CGContextClosePath(context);
CGContextClip(context);
CGPoint endshine;
CGPoint startshine;
startshine = CGPointMake(100 + 60 * cosf( 1.57 ),100+ 60 * sinf( 1.57 ));
endshine = CGPointMake(100,100);
CGContextDrawLinearGradient(context,gradient , startshine, endshine, kCGGradientDrawsAfterEndLocation);
CGContextRestoreGState(context);
效果如下:
上面除了使用drawdrawRadialGradientWithRect函数外,还可以使用
CGGradientCreateWithColorComponents包含以下4个参数:
Color Space:和上面一样
颜色分量的数组:这个数组必须包含CGFloat类型的红、绿、蓝和alpha值。数组中元素的数量和接下来两个参数密切。从本质来讲,你必须让这个数组包含足够的值,用来指定第四个参数中位置的数量。所以如果你需要两个位置(起点和终点),那么你必须为数组提供两种颜色。
位置数组:颜色数组中各个颜色的位置,此参数控制该渐变从一种颜色过渡到另一种颜色的速度有多快。
位置的数量:这个参数指明了我们需要多少颜色和位置。
例如:
CGGradientRef gradient = CGGradientCreateWithColorComponents(colorSpace, (CGFloat[]){
0.8, 0.2, 0.2, 1.0,
0.2, 0.8, 0.2, 1.0,
0.2, 0.2, 0.8, 1.0
}, (CGFloat[]){
0.0, 0.5, 1.0
}, 3);
3.一些可能需要注意的地方
上面我们将了自定义绘图,相对与它来讲,UIView及其子类是高度优化的,所以在能用UIView解决的地方,尽量不要使用自定义绘图,最快的绘图方式就是根本不绘制(废话=_=),iOS在尽量避免调用drawRect:方法,使用一个合适的contentMode方法,系统在旋转或重新调整大小时就不需要调用drawRect:方法,导致drawRect:方法运行的最常见情况是调用了setNeedDisplay。
应用:
1.使用CAGradientLayer实现颜色渐变和特效
CAGradientLayer *colorLayer = [CAGradientLayer layer];
colorLayer.frame = (CGRect){CGPointZero,CGSizeMake(200, 200)};
colorLayer.position = self.view.center;
//颜色分配
colorLayer.colors = @[(__bridge id)[UIColor colorWithRed:0.0/255 green:222.0/255 blue:200.0/255 alpha:1.0].CGColor,(__bridge id)[UIColor colorWithRed:75.0/255 green:255.0/255 blue:210.0/255 alpha:1.0].CGColor,(__bridge id)[UIColor colorWithRed:190.0/255 green:253.0/255 blue:220.0/255 alpha:1.0].CGColor];
colorLayer.startPoint = CGPointMake(0.0, 0.0);//起始点
colorLayer.endPoint = CGPointMake(1.0, 1.0);//结束点
colorLayer.locations = @[@(0.25),@(0.5),@(0.75)];//颜色渐变位置分割线
[self.view.layer addSublayer:colorLayer];