【数字图像处理】Hough变换C语言实现
文章目录
- (一)Hough圆检测
-
- 程序设计
- (1) 因为如果直接进行Hough圆的投票的话,我们需要一个3维的表保存行,列,角度信息。我们将这个投票过程分成两个步骤。
- (2) 首先完成对于固定半径的圆的投票。然后在对每一个半径的圆的投票进行比较。
- (3) 对一个半径范围内的所有圆进行一次(1)中的操作,然后,从中选取票数最高的圆,那么这个圆就是我们想要的圆了。
- (4) 具体程序请参考Litecv/Imgproc/li_canny.c
- (二) Hough直线检测
- (三)代码实现
- (四)效果展示
- (五)写在后面
(一)Hough圆检测
经过图像的预处理后,我们得到了只保留边缘信息的二值图像,统计可以发现在一个320x240的图像中最后有效的信息点只有5000个左右现在就是通过对这5000个点的统计与运算完成对圆与直线的检测。直线检测最容易受到环境干扰,如果直接对一幅图像进行直线检测,检测出最长的那根直线不一定,是你想要的直线。所以我们首先要进行的是Hough圆的检测。
Hough变换不仅适用于直线检测,还适用于任何形式的f(x,a)=0所表示的图形的检测,其中x 表示坐标向量,a表示系数向量。下边我们对Hough变换检测圆的原理做简要介绍。
对于一个半径为r,圆心为(a,b)的圆,我们将其表示为:
![]() 此时x=[x,y]T,a=[a,b,r]T,其参数空间为三维。
此时x=[x,y]T,a=[a,b,r]T,其参数空间为三维。
显然,图像空间上的一点(x,y),在参数空间中对应着一个圆锥,如下图所示。
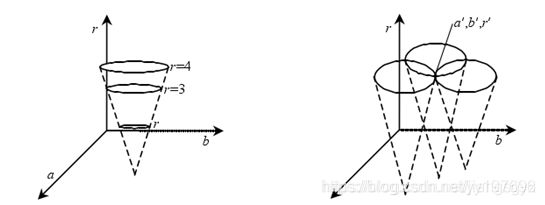
而图像空间的一个圆就对应着这一簇圆锥相交的一个点,这个特定点在参数空间的三维参数一定,就表示一定半径一定圆心坐标的图像空间的那个圆。
上述方法是经典的Hough圆检测方法的原理,它具有精度高,抗干扰能力强等优点,但由于该方法的参数空间为三维,要在三维空间上进行证据累计的话,需要的时间和空间都是庞大的,在实际应用中不适用。
程序设计
Hough变换的具体算法步骤如下:
• 适当的量化参数空间。
• 将参数空间的每一个单元看作一个累加器。
• 初始化累加器为0。
• 对图像空间的每一点,在其所满足参数方程对应的累加器上加1。
• 累加器存储的最大值即为对应的图形的参数。
程序实际思路:
(1) 因为如果直接进行Hough圆的投票的话,我们需要一个3维的表保存行,列,角度信息。我们将这个投票过程分成两个步骤。
(2) 首先完成对于固定半径的圆的投票。然后在对每一个半径的圆的投票进行比较。
1) 建立一张与原图大小一致的投票表,用来表示每个点作为圆心会有多少个点与之匹配:
int AccuArrLength=img->width * img->height;;
pAccumulateArr=(int*)malloc(AccuArrLength*sizeof(int));
2)在根据极坐标运算公式,对每一个点可能对应的圆心进行投票,通过遍历每一个点,然后对经过这个点所有的圆的圆心位置进行一次计票
int x = i - R * cos(theta);//得到理想圆心x坐标
int y = j - R * sin(theta);//得到理想圆心y坐标
if(x>0&&x<img->width&&y>0&&y<img->height&&x<range[1]&&x>range[0]&&y<range[3]&&y>range[2])
{
pAccumulateArr[y * img->width + x]++;
}
3) 找到对应票数最高的圆心位置
for(int i = 0; i < img->height; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < img->width; j++)
{
int value_ = pAccumulateArr[i * img->width + j];
if(value_>max_value)
{
//printf("(%d,%d,%d,%d)",max_value,value_,i,j);
max_value=value_;
circles->x=j;
circles->y=i;
circles->r=R;
}
}
然后我们就可以找到想要的圆了。
(3) 对一个半径范围内的所有圆进行一次(1)中的操作,然后,从中选取票数最高的圆,那么这个圆就是我们想要的圆了。
(4) 具体程序请参考Litecv/Imgproc/li_canny.c
(二) Hough直线检测
Hough变换的方法基本思想可以从检测图像中的直线这个简单问题中看到。直线由两点A=(X1,Y1)和B=(X2,Y2)定义,所下图1(a)示。通过点A的所有直线由y1=kx1+q表示,k和q是某些值。这意味着同一个方程可以解释为参数空间k,q的方程。因此通过点A的所须直线可以表示为方程q=-x1k+y1图1.(b)。类似地通过点B的直线可以表示q=-x2*k+y2。在参数空间k和q中,两条直线的唯一公共点是在原图像空间中表示连接点A和B的唯一存在的直线。
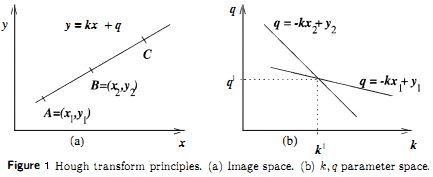
这意味着图像中的每条直线在参数空k,q中由单独一个点表示,直线的任何一部分都变换为同一个点。直线检测的主要思想是确定图中所在的直线像素,将通过这些像素的所在直线变换到参数空间的对应点,在参数空间检测点(a,b),此点是图像中出现的直线y=ax+b的Hough变换的结果。
我们可以注意到直线的参数方程y =kx+q只适合解释Hough变换原理,在检测垂直线条和参数的非线性离散化时会遇到困难。如果直线表示成s=xcosθ+ysinθ。Hough变换就没有这些局限性。直线还是被变换为单个点,因此可用该原理进行直线检测。如下图2所示:
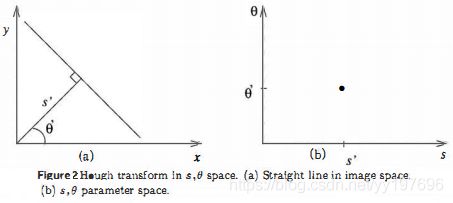
我们要注意到Hough变换的重要性质是对图像中直线的殘缺部分、噪声以及其它共存的非直线结构不敏感。因为从图像空间到累计空间的变换的鲁棒性引起的,直线殘缺的部分只会造成较低的局部极值。
(三)代码实现
#ifndef LI_CANNY_C
#define LI_CANNY_C
#include "cv.h"
#include "li_image_proc.h"
#include (四)效果展示
(五)写在后面
因为LiteCV项目才刚刚写了一个开头,代码中有错误的地方还望指出。我已经将项目同步到了github,我会实时更新这个代码仓库。
项目github地址:
LiteCV
