JavaScript数据结构与算法 - 散列表
1. 概念
散列表:
- 散列表是字典的一种实现,所以可以用作关联数组。
- 散列表可以用来保存键和对表中记录的引用。如在关系型数据库中创建一个新的表时,同时创建一个索引可以更快查询到记录的key
- 可以使用散列表来表示对象。如JavaScript语言内部就是使用散列表来表示每个对象。
散列算法:
- 尽可能快地在数据结构中找到一个值。
- 不需要迭代整个数据结构来找到值。如果使用散列函数,就知道值的具体位置,因此能够快速检索到该值。
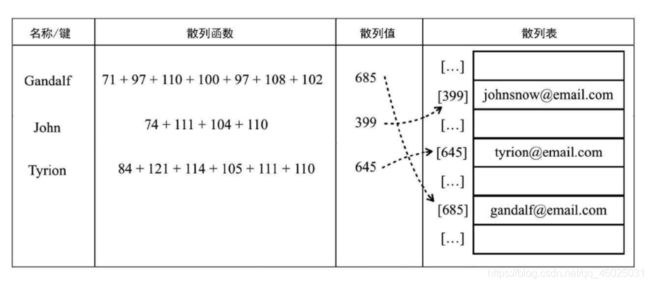
散列函数:
- 散列函数的作用是给定一个键值,然后返回值在表中的地址。
- 散列函数——lose lose散列函数,方法是简单地将每个键值中的每个字母的ASCII值相加,相加的结果就是散列值
2. 创建散列表
使用一个关联数组(对象)来表示数据结构,类似于在Dictionary类中的做法。
搭建骨架:
class hashTable {
constructor(toStrFn = defaultToString) {
this.toStrFn = toStrFn;
this.table = {
};
}
}
常用方法:
- put(key, value):向散列表增加一个新的项(也能更新散列表)
- remove(key):根据键值从散列表中移除值
- get(key):返回根据键值检索到的特定的值
2.1 创建散列函数
loseloseHashCode(key) {
// 先检验key是否是一个数
if (typeof key === 'number') {
return key;
}
// 将key转换为一个字符串
const tableKey = this.toStrFn(key);
// 存储总和
let hash = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < tableKey.length; i++) {
hash += tableKey.charCodeAt(i);
}
// hash和一个任意数做除法的余数,可以规避操作数超过数值变量最大表示范围的风险
return hash % 37;
}
hashCode(key) {
return this.loseloseHashCode(key);
}
2.2 向散列表添加一个新的项
put(key, value) {
// 检验是否合法
if (key != null && value != null) {
const position = this.hashCode(key);
// 信息备份,将原始的key保存下来
this.table[position] = new ValuePair(key, value);
return true;
}
return false;
}
2.3 从散列表中获取一个值
get(key) {
const valuePair = this.table[this.hashCode(key)];
return valuePair == null ? undefined : valuePair.value;
}
2.4 从散列表中移除一个元素
remove(key) {
// 获取hash来知道值所在的位置
const hash = this.hashCode(key);
const valuePair = this.table[hash];
if (valuePair != null) {
delete this.table[hash];
return true;
}
return false;
}
3. 使用hashTable类
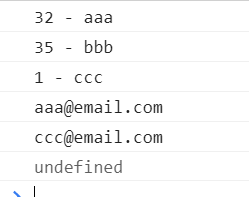
const hash = new hashTable();
hash.put('aaa', '[email protected]');
hash.put('bbb', '[email protected]');
hash.put('ccc', '[email protected]');
console.log(hash.hashCode('aaa') + ' - aaa');
console.log(hash.hashCode('bbb') + ' - bbb');
console.log(hash.hashCode('ccc') + ' - ccc');
console.log(hash.get('aaa'));
console.log(hash.get('ccc'));
hash.remove('bbb');
console.log(hash.get('bbb'));
4. 散列集合
散列集合由一个集合构成,但是插入、移除或获取元素时使用hashCode函数,且只存储不重复的唯一值。
5. 处理散列表中的冲突
问题:一些键会有相同的散列值。不同的值在散列表中对应相同位置的时候,称为冲突。
如输入以下代码:
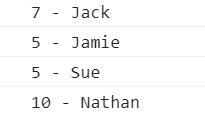
hash.put('Jack', '[email protected]');
hash.put('Jamie', '[email protected]');
hash.put('Sue', '[email protected]');
hash.put('Nathan', '[email protected]');
console.log(hash.hashCode('Jack') + ' - Jack');
console.log(hash.hashCode('Jamie') + ' - Jamie');
console.log(hash.hashCode('Sue') + ' - Sue');
console.log(hash.hashCode('Nathan') + ' - Nathan');
使用toString方法获得结果:
toString() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return '';
}
const keys = Object.keys(this.table);
let objString = `{
${
key[0]} => ${
this.table[keys[0]].toString()}}`;
for (let i = 1; i < keys.length; i++) {
objString = `${
objString}, {
${
keys[i]} => {
${
this.table[keys[i]].toString()}
}}`
}
return objString;
}
结果显示Sue是在hashTable实例中占据位置5的元素。Jamie会先占据这个位置,然后Sue占据这个位置。
处理方法:
- 分离链接
- 线性探查
- 双散列法
5.1 分离链接
分离链接法包括为散列表的每一个位置创建一个链表并将元素存储在里面。它是解决冲突的最简单的方法,但是在HashTable实例之外还需要额外的存储空间。
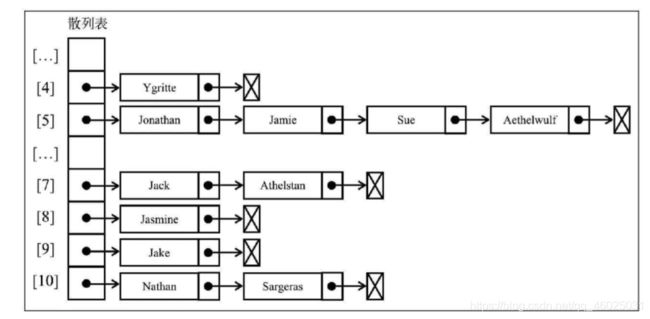
假设存在以下结果:
使用分离链接并用图表示的话,输出结果为:
- 在位置5上,将会有包含四个元素的LinkedList实例
- 在位置7和10上,将会有包含两个元素的LinkedList实例
- 在位置4、8和9上,将会有包含单个元素的LinkedList实例
需要重写三个方法:put、get和remove:
先声明类:
class HashTableSeparateChaining {
constructor(toStrFn = defaultTOString) {
this.toStrFn = toStrFn;
this.table = {
};
}
}
- put方法
put(key, value) {
if (key != null && value != null) {
const position = this.hashCode(key);
// 验证要加入的元素的位置是否已经被占据
if (this.table[position] == null) {
this.table[position] = new LinkedList();
}
this.table[position].push(new ValuePair(key, value));
return true;
}
return false;
}
- get方法
get(key) {
const position = this.hashCode(key);
// 在position位置检索linkedLink
const linkedList = this.table[position];
// 检验是否存在linkedList
if (linkedList != null && !linkedList.isEmpty()) {
let current = linkedList.getHead();
while (current != null) {
if (current.element.key === key) {
return current.element.value;
}
current = current.next;
}
}
return undefined;
}
- remove方法
remove(key) {
const position = this.hashCode(key);
const linkedList = this.table[position];
if (linkedList != null && !linkedList.isEmpty()) {
let current = linkedList.getHead();
while (current != null) {
if (current.element.key === key) {
// 使用remove方法将其从链表中移除
linkedList.remove(current.element);
if (linkedList.isEmpty()) {
delete this.table[position];
}
return true;
}
current = current.next;
}
}
return false;
}
5.2 线性排查
线性排查处理冲突的方法是将元素直接存储到表中,而不是在单独的数据结构中。
当想向表中某个位置添加一个新元素的时候,如果索引为position的位置已经被占据了,就尝试position+1的位置。如果position+1的位置也被占据了,就尝试position+2的位置,以此类推,直到在散列表中找到一个空闲的位置。
- 软删除:使用一个特殊的值(标记)来表示键值对被删除了(惰性删除或软删除),不是真的删除它。经过一段时间,散列表被操作过后,会得到一个标记了若干删除位置的散列表。这会逐渐降低散列表的效率,因为搜索键值会随时间变得更慢。

- 第二种方法需要检验是否有必要将一个或多个元素移动到之前的位置。当搜索一个键的时候,这种方法可以避免找到一个空位置。如果移动元素是必要的,我们就需要在散列表中挪动键值对。(以下代码实现这种方法)

- put方法
put(key, value) {
if (key != null && value != null) {
const position = this.hashCode(key);
// 验证这个位置是否有元素存在
if (this.table[position] == null) {
// 没有元素存在,添加新元素
this.table[position] = new ValuePair(key, value);
}
// 如果该位置被占据了,就找下一个没有被占据的位置
else {
let index = position + 1;
while (this.table[index] != null) {
index++;
}
this.table[index] = new ValuePair(key, value);
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
实现效果:
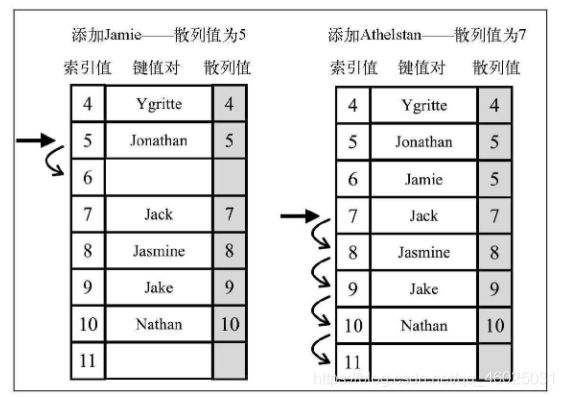
- 插入Ygritte。它的散列值是4,由于散列表刚刚被创建,位置4还是空的,可以在这里插入数据
- 在位置5插入Jonathan。它也是空的,所以可以插入这个姓名
- 在位置5插入Jamie,因为它的散列值也是5。位置5已经被Jonathan占据了,所以需要检查索引值为position+1的位置(5+1),位置6是空的,所以可以在位置6插入Jamie
- 在位置7插入Jack。它是空的,所以可以插入这个姓名,不会有冲突
- 在位置8插入Jasmine。它是空的,所以可以插入这个姓名,不会有冲突
- 在位置9插入Jake。它是空的,所以可以插入这个姓名,不会有冲突
- 在位置10插入Nathan。它是空的,所以可以插入这个姓名,不会有冲突
- 在位置7插入Athelstan。位置7已经被Jack占据了,所以需要检查索引值为position+1的位置(7+1)。位置8也被占据了,所以迭代到下一个空位置,也就是位置11,并插入Athelstan
- 在位置5插入Sue,位置5到11都被占据了,所以在位置12插入Sue
- 在位置5插入Aethelwulf,位置5到12都被占据了,所以在位置13插入Aethelwulf
- 在位置10插入Sargeras,位置10到13都被占据了,所以在位置14插入Sargeras。
- get方法
get(key) {
const position = this.hashCode(key);
// 先确定键存在
if (this.table[position] != null) {
// 检查要找的值是否在原始位置上
if (this.table[position].key === key) {
return this.table[position].value;
}
// 在下一个位置继续查找
let index = position + 1;
// 位置递增的顺序查找散列表上的元素直到找到想要的元素或找到一个空位置
while (this.table[index] != null && this.table[index].key != key) {
index++;
}
// 验证元素的键是不是要找的键
if (this.table[index] != null && this.table[index].key === key) {
return this.table[position].value;
}
}
// 键不存在
return undefined;
}
- remove方法
remove方法和get方法基本相同。
remove(key) {
const position = this.hashCode(key);
if (this.table[position] != null) {
if (this.table[position].key === key) {
delete this.table[position];
this.verifyRemovesSideEffect(key, position);
return true;
}
let index = position + 1;
while (this.table[index] != null && this.table[index].key != key) {
index++;
}
if (this.table[index] != null && this.table[index].key === key) {
delete this.table[index];
this.verifyRemovesSideEffect(key, index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
由于不知道在散列表的不同位置上是否存在具有相同hash的元素,需要验证删除操作是否有副作用。如果有,就需要将冲突的元素移动至一个之前的位置,这样就不会产生空位置。
借助verifyRemovesSideEffect方法:
verifyRemovesSideEffect(key, removedPosition) {
// 获取被删除key的hash值
const hash = this.hashCode(key);
// 从下一个位置开始迭代散列表
let index = removedPosition + 1;
while (this.table[index] != null) {
// 直到找到一个空位置
// 当迭代随后的元素时,需要计算当前位置上元素的hash值
const posHash = this.hashCode(this.table[index].key);
// 如果当前元素的hash值小于或等于原始的hash值或者当前元素的hash值小于或等于removedPosition
if (posHash <= hash || posHash <= removedPosition) {
// 将当前元素移动至removedPosition的位置
this.table[removedPosition] = this.table[index];
delete this.table[index];
removedPosition = index;
}
index++;
}
}
代码执行过程:
- 在位置5找到并删除Jonathan。位置5现在空闲了。之后将验证一下是否有副作用
- 来到存储Jamie的位置6,现在的散列值为5,它的散列值5小于等于散列值5,所以要将Jamie复制到位置5并删除Jamie。位置6现在空闲了,验证下一个位置
- 来到位置7,这里保存了Jack,散列值为7。它的散列值7大于散列值5,并且散列值7大于removedPosition的值6,所以我们不需要移动它。下一个位置也被占据了,验证下一个位置
- 来到位置8,此处保存了Jasmine,散列值为8。散列值8大于Jasmine的散列值5,并且散列值8大于removedPosition的值6,因此不需要移动它。下一个位置也被占了,验证下一个位置
- 来到位置9,这里保存了Jake,它的散列值是9。散列值9大于散列值5,并且散列值9大于removedPosition的值6,所以不需要移动它。下一个位置也被占了,验证下一个位置
- 重复相同的过程,直到位置12
- 来到位置12,此处保存了Sue,它的散列值为5。散列值5小于等于散列值5,并且散列值5小于等于removedPosition的值6,将Sue复制到位置6,并删除位置12的Sue。位置12现在空闲了。下一个位置也被占据了,验证下一个位置
- 来到位置13,此处保存了Aethelwulf,它的散列值为5。散列值5小于等于散列值5,并且散列值5小于等removedPosition的值12,需要将Aethelwulf复制到位置12并删除位置13的值。位置13现在空闲了。下一个位置也被占据了,验证下一个位置
- 来到位置14,此处保存了Sargeras,散列值为10。散列值10大于Aethelwulf的散列值5,但是散列值10小于等于removedPosition的值13,因此要将Sargeras复制到位置13并删除位置14的值。位置14现在空闲了。下一个位置也是空闲的,那么本次执行完成了
6. 更好的散列函数
lose lose散列函数会产生太多冲突。而表现良好的散列函数需要:插入和检索元素的时间(性能),降低冲突的可能性。
djb2HashCode(key) {
const tableKey = this.toStrFn(key);
// 初始化一个hash变量并赋值为一个5381的质数
let hash = 5381;
for (let i = 0; i < tableKey.length; i++) {
// 将hash与33相乘,用作一个幻数(幻数在编程中指直接使用的常数)
hash = (hash * 33) + tableKey.charCodeAt(i);
}
// 使用相加的和与另一个随机质数相除的余数
return hash % 1013;
}
上例散列表大小为1000