集成学习:AdaBoost
集成学习
集成学习通过构建并合并多个学习器来完成学习任务,有时也被称为多分类器系统。
如果在集成学习中我们使用的学习器只包括同种类型的个体学习器,如“决策树集成”中全是决策树,这种集成叫同质集成,这里面的个体学习器称之为“基学习器”,相应的学习算法称之为“基学习算法”,反之称为“异质集成”,个体学习器称为“组件学习器”。
集成学习的结果通过投票法产生,即“少数服从多数”。
对个体学习器的要求:
- 准确性:个体学习器应该有一定的准确性。
- 多样性:个体学习器间应该具有差异性。
集成学习大致可以分为两类:
- 个体学习器间存在强依赖关系,必须串行生成序列化的方法,如Boosting。
- 个体学习器间不存在强依赖关系,可同时生成的并行化方法,如Bagging,和随机森林。
AdaBoost
Boosting是一族可以将弱学习器提升为强学习器的算法,AdaBoost(adaptive boosting自适应增强)是Boost一族的典型代表。
AdaBoost算法流程
训练集 T = { ( x 1 , y 1 ) , ( x 2 , y 2 ) … ( x N , y N ) } T=\{(x_1,y_1), (x_2,y_2)…(x_N,y_N)\} T={ (x1,y1),(x2,y2)…(xN,yN)},其中 x i ∈ R n x_i \in R^n xi∈Rn, y i ∈ { − 1 , 1 } y_i \in \{-1,1\} yi∈{ −1,1},使用 M M M个弱学习器。
-
步骤一:
初始化训练数据的权值分布,一开始每一个样本赋予相同的权值 1 N \frac{1}{N} N1
D 1 = ( w 11 , w 1 , 2 , . . . , w 1 N ) , w 1 i = 1 N , i = 1 , 2 , . . . , N D_1=(w_{11},w_{1,2},...,w_{1N}),w_{1i}=\frac{1}{N},i=1,2,...,N D1=(w11,w1,2,...,w1N),w1i=N1,i=1,2,...,N -
步骤二:
进行多轮的迭代学习,使用具有权值分布的 D m D_m Dm的训练数据集来学习,得到基本分类器。分对的样本的权值会降低,分错的样本的权值会增加,目的是使分错的训练样本得到更多的关注。每个学习器都会有一个权值 a m a_m am, a m a_m am的值是基于每个弱分类器的错误率 ϵ m \epsilon_m ϵm进行计算的。
ϵ = 未 正 确 分 类 的 样 本 数 目 所 有 样 本 数 目 \epsilon=\frac{未正确分类的样本数目}{所有样本数目} ϵ=所有样本数目未正确分类的样本数目
ϵ m = P ( G m ( x i ) ≠ y i ) = Σ i = 1 N w m i I ( G m ( x i ) ≠ y i ) \epsilon_m=P(G_m(x_i) \ne y_i) =\Sigma_{i=1}^Nw_{mi}I(G_m(x_i) \ne y_i) ϵm=P(Gm(xi)=yi)=Σi=1NwmiI(Gm(xi)=yi)
学习器的权值为
α m = 1 2 l n ( 1 − ϵ ϵ ) \alpha_m = \frac{1}{2}ln(\frac{1-\epsilon}{\epsilon}) αm=21ln(ϵ1−ϵ)
从这个公式可以看出当 ϵ \epsilon ϵ小于0.5时 α > = 0 \alpha>=0 α>=0,意味着学习器的误差率越小的基学习器在最终的分类器中作用越大。
然后我们还需要做的就是更新样本的权值
D m + 1 = ( w m + 1 , 1 , w m + 1 , 2 , . . . , w m + 1 , N ) D_{m+1}=(w_{m+1,1},w_{m+1,2},...,w_{m+1,N}) Dm+1=(wm+1,1,wm+1,2,...,wm+1,N)
w m + 1 , i = w m i Z m e x p ( − α m y i G m ( x i ) ) , i = 1 , 2 , . . . , N w_{m+1,i}=\frac{w_{mi}}{Z_m}exp(-\alpha_m y_iG_m(x_i)),i=1,2,...,N wm+1,i=Zmwmiexp(−αmyiGm(xi)),i=1,2,...,N
这样可以使得被基本分类器Gm(x)误分类样本的权值增大,而被正确分类样本的权值减小。
其中 Z m Z_m Zm是规范化因子,可以使得 D m + 1 D_{m+1} Dm+1成为一个概率分布
Z m = Σ i = 1 N w m i e x p ( − α m y i G m ( x i ) ) Z_m= \Sigma_{i=1}^Nw_{mi}exp(-\alpha_m y_i G_m(x_i)) Zm=Σi=1Nwmiexp(−αmyiGm(xi))
具体的证明过程参见周志华《机器学习》P172~P176。 -
步骤三:
组合各弱学习器:
f ( x ) = Σ m = 1 M α m G m ( x ) f(x)=\Sigma_{m=1}^{M}\alpha_mG_m(x) f(x)=Σm=1MαmGm(x)
得到最终的分类器为
G ( x ) = s i g n ( f ( x ) ) = s i g n ( Σ m = 1 M α m G m ( x ) ) G(x)=sign(f(x))=sign(\Sigma_{m=1}^{M}\alpha_mG_m(x)) G(x)=sign(f(x))=sign(Σm=1MαmGm(x))
s i g n ( x ) sign(x) sign(x)在 x < 0 , x = 0 , x > 0 x<0,x=0,x>0 x<0,x=0,x>0时取值为-1,0,1
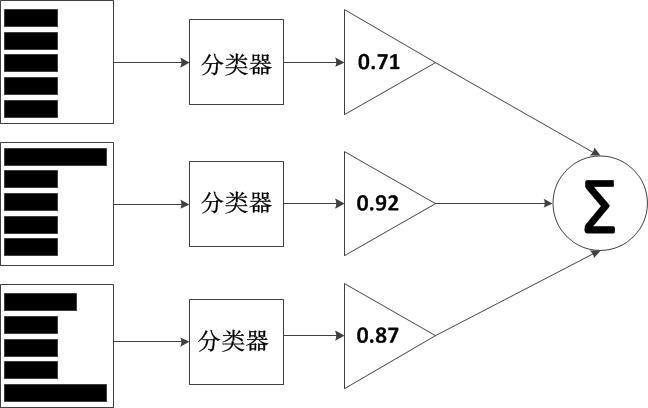
参考这个图片可以更加形象的理解AdaBoost的流程。
伪代码表示:

Python 实现
AdaBoost.py
#-*- coding=utf8 -*-
from numpy import *
def loadData():
dataMat = matrix([[1.,2.1],
[2.,1.1],
[1.3,1.1],
[1.,1.],
[2.,1.]])
classLabel = [1.0,1.0,-1.0,-1.0,1.0]
return dataMat,classLabel
#根据数据与阀值的比较进行分类
def stumpClassify(dataMatrix,dimen,threshVal,threshIneg):
retArray = ones((shape(dataMatrix)[0],1))
if threshIneg == 'lt':
retArray[dataMatrix[:,dimen]<= threshVal] = -1.0
else:
retArray[dataMatrix[:,dimen]> threshVal] = -1.0
return retArray
#创建最佳的单层决策树
def buildStump(dataArr,classLabels,D):
dataMatrix = mat(dataArr);
labelMat = mat(classLabels).T
m,n=shape(dataMatrix)
#initial
numSteps = 10.0
bestStump ={}
bestClasEst = mat(zeros((m,1)))
minerror = inf
#遍历属性
for i in range(n):
rangeMin = dataMatrix[:,i].min()
rangeMax = dataMatrix[:,i].max()
stepSize = (rangeMax -rangeMin)/numSteps
for j in range(-1,int(numSteps)+1):
for inequal in ['lt','gt']:
#设定阀值
threshVal = (rangeMin+float(j)*stepSize)
predictedVals = stumpClassify(dataMatrix,i,threshVal,inequal)
errArr = mat(ones((m,1)))
errArr[predictedVals==labelMat]=0
weightedError = D.T*errArr
if weightedError < minerror:
minerror = weightedError
bestClasEst = predictedVals.copy()
bestStump['dim'] = i
bestStump['thresh']=threshVal
bestStump['ineq'] = inequal
#返回单层决策树的节点,误差,以及预测值
return bestStump,minerror,bestClasEst
#基于单层决策树的AdaBoost训练过程
def AdaBoostTrainDS(dataArr,classLabels,numIt=40):
#弱分类器的列表
weakClassArr=[]
m = shape(dataArr)[0]
#step1:初始化训练数据的权值
D = ones((m,1))/m
aggClassEst = mat(zeros((m,1)))
#串行训练各个弱分类器
for i in range(numIt):
bestStump,error,classEst = buildStump(dataArr,classLabels,D)
print "D: ",D.T
#计算学习器的权值
alpha = float(0.5 * log((1.0 - error)/max(error, 1e-16)))
bestStump['alpha']=alpha
weakClassArr.append(bestStump)
print "classEst: ",classEst.T
#更新数据的权值
expon = multiply(-1*alpha*mat(classLabels).T,classEst)
D = multiply(D,exp(expon))
D = D/D.sum()
aggClassEst += alpha * classEst
print "aggClassEst: ",alpha*classEst
aggErrors = multiply(sign(aggClassEst)!=mat(classLabels).T,ones((m,1)))
errorRate = aggErrors.sum()/m
print "total error: ",errorRate,"\n"
if errorRate == 0.0:
break;
return weakClassArr
#AdaBoost分类器
def adaClassify(datToClass,classfierArr):
dataMatrix = mat(datToClass)
m = shape(dataMatrix)[0]
aggClassEst = mat(zeros((m,1)))
for i in range(len(classfierArr)):
classEst = stumpClassify(dataMatrix,classfierArr[i]['dim'],classfierArr[i]['thresh'],classfierArr[i]['ineq'])
aggClassEst +=classfierArr[i]['alpha']*classEst
print aggClassEst
return sign(aggClassEst)
test.py
import AdaBoost
from numpy import *
#import api
#test loadData
dataMat,classLabel = AdaBoost.loadData()
print dataMat
#test buildStump
D = mat(ones((5,1))/5)
print AdaBoost.buildStump(dataMat,classLabel,D)
#test AdaBoost
classifierArr=AdaBoost.AdaBoostTrainDS(dataMat,classLabel,9)
#test classifier
print AdaBoost.adaClassify([[0,0],[5,5]],classifierArr)
