HashMap
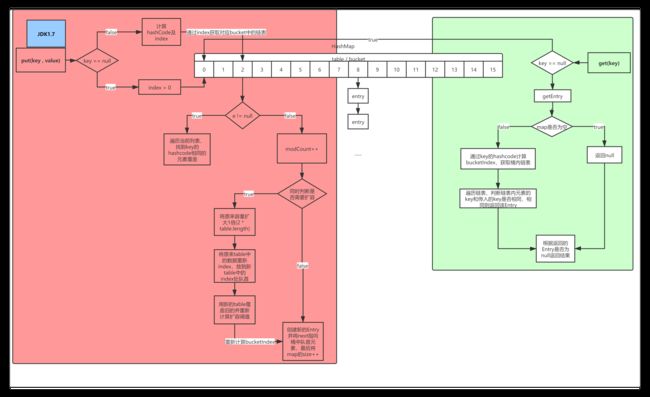
hashMap1.7的数据结构
1.7的结构如下图,底层是一个大的Entry数组,每个数组元素为一个链表。图中同时可以看出put和get的流程。下面对put和get的部分代码用图示方式展示,同时可以参考源码自己分析。
put方法源码
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
// 初始化桶
inflateTable(threshold);
}
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key);
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (Entry e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
// 此处扩容
resize(2 * table.length);
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
// 创建键值对并加入map中
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
}
get方法源码
public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
Entry entry = getEntry(key);
return null == entry ? null : entry.getValue();
}
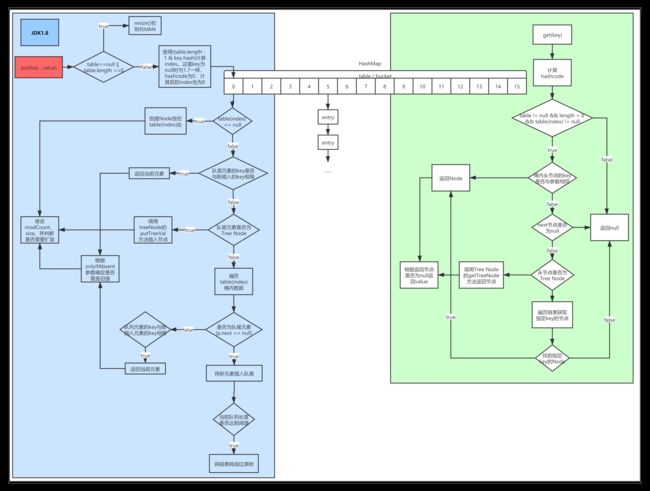
hashMap1.8的数据结构
1.8的数据结构如下图,同时跟1.7一样,put个get操作的大体流程也绘制在图中了。朋友们可以对照着源码和图自行消化一下。
老规矩,源码说话。
put方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
// 先计算hashcode,key为0时直接返回0
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node[] tab; Node p; int n, i;
// 创建Map时并未初始化table,第一次put时先进行初始化操作
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
// 初始化也是通过resize来实现的
n = (tab = resize()).length;
// 根据hashcode和table长度计算index,确定对应index下是否已经有值。
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null只
// 为空时直接创建Node并插入
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
// 否则先判断key是否与表头元素相同,相同则直接返回node节点
Node e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
// 不同时判断是否为树节点,若为树节点则通过红黑树插入元素
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
// 不是树节点说明还是链表,遍历链表
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
// 判断是否为链尾,链尾的话直接插入
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
// 插入元素后判断元素个数是否超过阈值,超过则将链表转成红黑树
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
// 不是链尾就继续判断是否和key相同,相同则将node返回
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
// 如果改key已经存在,则根据onlyIfAbsent参数或旧值是否为空判断是否要覆盖元素
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
// 修改modCount
++modCount;
// 修改map的size并判断是否需要扩容
if (++size > threshold)
// 扩容
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
get方法
public V get(Object key) {
Node e;
// 同样还是先计算hashcode,然后通过getNode返回的节点获取value
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
final Node getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node[] tab; Node first, e; int n; K k;
// 当map不为空且根据hash与table.length计算得到的index处元素不为空时
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
// 这里判断头元素是否与给定key相同,相同就返回该node
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
// 如果不是尾节点
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
// 为红黑树时调用红黑树的方法获取元素
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
// 否则遍历链表获取指定key的元素
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}
HashMap 1.7和1.8的区别
主要有如下几点区别:
1.7与1.8在数据结构上来说底层都是一个大数组来存储,唯一的区别是数组的每个元素类型不同,1.7下是一个链表。1.8为了优化链表的检索速度将数组其结构改成了链表+红黑树。默认情况下在链表长度大于等于8时会将链表转成红黑树,在长度小于等于6时会退回链表。
在put时1.7采用的是头插法,而1.8采用的是尾插法。感兴趣的朋友可以继续深入看看为什么会有这种修改。
1.7的扩容发生在addEntry之前,而1.8的扩容发生在put结束之后。
如果还有其他的区别还请大家和我联系,我会补充上去。
ConcurrentHashMap
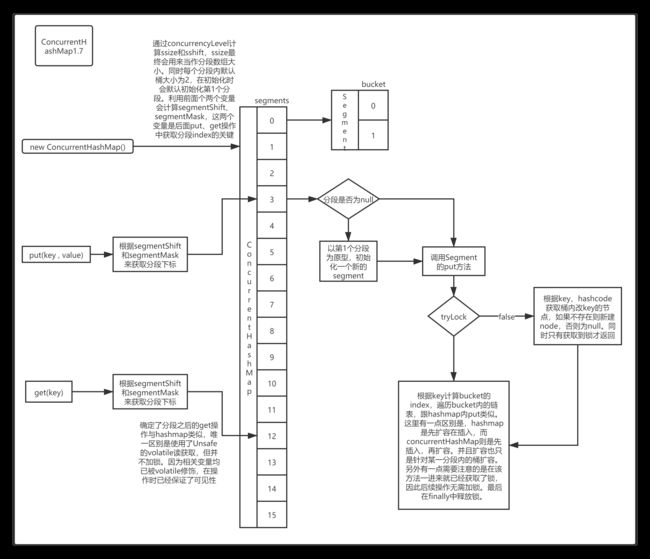
ConcurrentHashMap1.7的数据结构
1.7中ConcurrentHashMap采用了分段锁+Entry数组的结构,每个Segment其实是ReentrantLock的子类。因此天然拥有加锁的功能,其数据结构如下图。
1.7中的put和get流程如上图所示。其实并不复杂,由于表示数据的几个关键变量都被volatile修饰。因此大部分操作不需要加锁,仅在put时对所操作的分段加锁。get操作不加锁,size方法视具体情况而定,下面单独分析。
ConcurrentHashMap1.7的几处关键代码
初始化ConcurrentHashMap时确定分段大小即其他分段参数。
public ConcurrentHashMap(){
// ...省略其他代码
int sshift = 0;
// 分段大小
int ssize = 1;
// 默认concurrencyLevel是16,这里ssize每次 * 2,即循环可以执行4次,此时sshift=4,ssize = 16
while (ssize < concurrencyLevel) {
++sshift;
ssize <<= 1;
}
// 从上方计算结果可以得到,segmentShift = 28
this.segmentShift = 32 - sshift;
// segmentMark = 15
this.segmentMask = ssize - 1;
// ...省略其他代码
// create segments and segments[0]
Segment s0 =
new Segment(loadFactor, (int)(cap * loadFactor),
(HashEntry[])new HashEntry[cap]);
Segment[] ss = (Segment[])new Segment[ssize];
UNSAFE.putOrderedObject(ss, SBASE, s0); // ordered write of segments[0]
this.segments = ss;
}
segments数组的大小仅在上述初始化创建代码中确定,一旦map创建成功后分段个数不会改变,每次扩容也只针对某个分段内的桶进行扩容。
put方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
Segment s;
if (value == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = hash(key);
// 通过segmentShift和segmentMask计算key所在的分段位置
int j = (hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask;
// 如果分段尚未初始化(==null),则初始化该分段(即使用第一分段为原型创建新对象)
if ((s = (Segment)UNSAFE.getObject // nonvolatile; recheck
(segments, (j << SSHIFT) + SBASE)) == null) // in ensureSegment
s = ensureSegment(j);
// 委托给分段的put方法
return s.put(key, hash, value, false);
}
private Segment ensureSegment(int k) {
final Segment[] ss = this.segments;
long u = (k << SSHIFT) + SBASE; // raw offset
Segment seg;
if ((seg = (Segment)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u)) == null) {
// 使用第一个分段作为原型
Segment proto = ss[0]; // use segment 0 as prototype
int cap = proto.table.length;
float lf = proto.loadFactor;
int threshold = (int)(cap * lf);
HashEntry[] tab = (HashEntry[])new HashEntry[cap];
if ((seg = (Segment)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u))
== null) { // recheck
Segment s = new Segment(lf, threshold, tab);
while ((seg = (Segment)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u))
== null) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(ss, u, null, seg = s))
break;
}
}
}
return seg;
}
final V put(K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
// 尝试获取锁,这里肯定能拿到锁,否则会挂起,直到拿到锁为止
HashEntry node = tryLock() ? null :
scanAndLockForPut(key, hash, value);
V oldValue;
try {
HashEntry[] tab = table;
// scanAndLockForPut方法中获取node节点时bucket的index计算方法与此处计算方法不同,下面对node进行操作时有什么影响?
int index = (tab.length - 1) & hash;
HashEntry first = entryAt(tab, index);
for (HashEntry e = first;;) {
if (e != null) {
K k;
if ((k = e.key) == key ||
(e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) {
oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent) {
e.value = value;
++modCount;
}
break;
}
e = e.next;
}
else {
// node不为null说明获取锁的时候创建了node对象,直接将node插入表头即可
if (node != null)
node.setNext(first);
else
node = new HashEntry(hash, key, value, first);
int c = count + 1;
// 判断是否需要扩容
if (c > threshold && tab.length < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
rehash(node);
else
setEntryAt(tab, index, node);
++modCount;
count = c;
oldValue = null;
break;
}
}
} finally {
// 释放锁
unlock();
}
return oldValue;
}
get方法
public V get(Object key) {
Segment s; // manually integrate access methods to reduce overhead
HashEntry[] tab;
int h = hash(key);
long u = (((h >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask) << SSHIFT) + SBASE;
if ((s = (Segment)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(segments, u)) != null &&
(tab = s.table) != null) {
for (HashEntry e = (HashEntry) UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile
(tab, ((long)(((tab.length - 1) & h)) << TSHIFT) + TBASE);
e != null; e = e.next) {
K k;
if ((k = e.key) == key || (e.hash == h && key.equals(k)))
return e.value;
}
}
return null;
}
size方法
public int size() {
// Try a few times to get accurate count. On failure due to
// continuous async changes in table, resort to locking.
final Segment[] segments = this.segments;
int size;
boolean overflow; // true if size overflows 32 bits
long sum; // sum of modCounts
long last = 0L; // previous sum
int retries = -1; // first iteration isn't retry
try {
for (;;) {
// RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK默认为2,说明先尝试3次,如果其中连续两次结果一样则直接返回。如果没有则对所有分段加锁,在计算。随后解锁
if (retries++ == RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK) {
for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j)
ensureSegment(j).lock(); // force creation
}
sum = 0L;
size = 0;
overflow = false;
for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j) {
Segment seg = segmentAt(segments, j);
if (seg != null) {
sum += seg.modCount;
int c = seg.count;
// 如果大小溢出的话标识位设为true
if (c < 0 || (size += c) < 0)
overflow = true;
}
}
// last用来记录上次循环的计算结果,sum为本次循环的计算结果。如果连续两次结果一致则退出循环
if (sum == last)
break;
last = sum;
}
} finally {
// 如果重试次数超过加锁所需的次数,则对所有分段解锁
if (retries > RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK) {
for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j)
segmentAt(segments, j).unlock();
}
}
// 如果溢出则返回Integer.MAX_VALUE,否则返回正确size
return overflow ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : size;
}
ConcurrentHashMap1.8的数据结构
未完待续
ConcurrentHashMap与hashtable的区别
未完待续