大家使用jstack的时候偶尔会遇到这样的异常Unable to open socket file……
下面我们依据openjdk11的code进行分析。
从错误入手
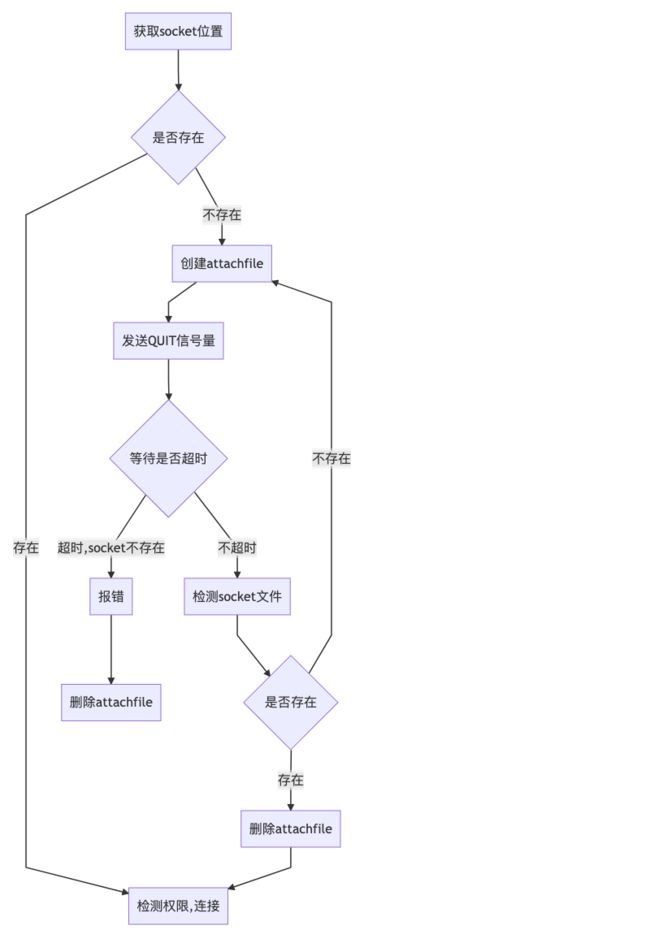
Unable to open socket file这个错误是jstack本身报的,算是一个客户端行为。什么情况下会出这个错误呢。我们直接用错误关键字进行搜索。
File socket_file = findSocketFile(pid, ns_pid);
socket_path = socket_file.getPath();
if (!socket_file.exists()) {
File f = createAttachFile(pid, ns_pid);
try {
sendQuitTo(pid);
// give the target VM time to start the attach mechanism
final int delay_step = 100;
final long timeout = attachTimeout();
long time_spend = 0;
long delay = 0;
do {
// Increase timeout on each attempt to reduce polling
delay += delay_step;
try {
Thread.sleep(delay);
} catch (InterruptedException x) { }
time_spend += delay;
if (time_spend > timeout/2 && !socket_file.exists()) {
// Send QUIT again to give target VM the last chance to react
sendQuitTo(pid);
}
} while (time_spend <= timeout && !socket_file.exists());
if (!socket_file.exists()) {
throw new AttachNotSupportedException(
String.format("Unable to open socket file %s: " +
"target process %d doesn't respond within %dms " +
"or HotSpot VM not loaded", socket_path, pid,
time_spend));
}
} finally {
f.delete();
}
}
方法内容相对比较简单,流程如下:
private File findSocketFile(int pid, int ns_pid) {
// A process may not exist in the same mount namespace as the caller.
// Instead, attach relative to the target root filesystem as exposed by
// procfs regardless of namespaces.
String root = "/proc/" + pid + "/root/" + tmpdir;
return new File(root, ".java_pid" + ns_pid);
}
socket的地址其实就是/tmp/.java_pid${ns_pid}
前面的/proc/pid/root/tmp指向的就是/tmp目录。
通过上面的流程,我们大概可以猜到流程中的quit的信号量,就是jvm做出对应操作的地方。
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_sun_tools_attach_VirtualMachineImpl_sendQuitTo
(JNIEnv *env, jclass cls, jint pid)
{
if (kill((pid_t)pid, SIGQUIT)) {
JNU_ThrowIOExceptionWithLastError(env, "kill");
}
}
发送的信号量就是SIGQUIT。
从信号量入手
#define SIGBREAK SIGQUIT
jvm里有一段宏,就是把SIGQUIT都可以用SIGBREAK代替。
switch (sig) {
case SIGBREAK: {
if (!DisableAttachMechanism && AttachListener::is_init_trigger()) {
continue;
}
VM_PrintThreads op;
...
当收到的信号量是SIGQUIT的时候,先看看DisableAttachMechanism。如果设置了-XX:+DisableAttachMechanism,那这里就直接跳过处理了。初始化socket的流程在后面的AttachListener::is_init_trigger里。
当加了-XX:+DisableAttachMechanism后,jstack关注的socket文件就无法创建了,会一定报错。
bool AttachListener::is_init_trigger() {
if (init_at_startup() || is_initialized()) {
return false; // initialized at startup or already initialized
}
...
if (ret == -1) {
log_trace(attach)("Failed to find attach file: %s, trying alternate", fn);
snprintf(fn, sizeof(fn), "%s/.attach_pid%d",
os::get_temp_directory(), os::current_process_id());
RESTARTABLE(::stat64(fn, &st), ret);
if (ret == -1) {
log_debug(attach)("Failed to find attach file: %s", fn);
}
}
if (ret == 0) {
// simple check to avoid starting the attach mechanism when
// a bogus non-root user creates the file
if (os::Posix::matches_effective_uid_or_root(st.st_uid)) {
init();
log_trace(attach)("Attach triggered by %s", fn);
return true;
} else {
log_debug(attach)("File %s has wrong user id %d (vs %d). Attach is not triggered", fn, st.st_uid, geteuid());
}
}
...
}
is_init_trigger会先检测attach file是否存在,只有存在的情况下,才会有后面的初始化操作。
init方法中开始启动Attach Listener线程。并且最终调用到AttachListener::pd_init()方法中,然后调用到 LinuxAttachListener::init() 去初始化socket。最终通过AttachListener::set_initialized();设置初始化成功标志。这里很重要,回头再去看is_init_trigger方法的最开始就是检测标志,如果被设置为成功就不再执行了。也就是说信号量的操作只能初始化一次,后面就再也不会初始化了。
nt LinuxAttachListener::init() {
char path[UNIX_PATH_MAX]; // socket file
char initial_path[UNIX_PATH_MAX]; // socket file during setup
int listener; // listener socket (file descriptor)
// register function to cleanup
::atexit(listener_cleanup);
int n = snprintf(path, UNIX_PATH_MAX, "%s/.java_pid%d",
os::get_temp_directory(), os::current_process_id());
if (n < (int)UNIX_PATH_MAX) {
n = snprintf(initial_path, UNIX_PATH_MAX, "%s.tmp", path);
}
if (n >= (int)UNIX_PATH_MAX) {
return -1;
}
// create the listener socket
listener = ::socket(PF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (listener == -1) {
return -1;
}
...
这里就是socket文件的创建过程。
小结
看完上面的流程,我们大概可以梳理以下几种情况,我们是会遇到异常的。
- 开启了-XX:+DisableAttachMechanism。
- 初始化完以后,删除了/tmp下的socket文件。
- 程序的各种问题(资源,夯死等)导致无法触发jvm代码运行。