分类
1)监督学习:
i)分类;
ii)回归
2)无监督学习:
i)聚类;
ii)密度估计;
iii)数据可视化。
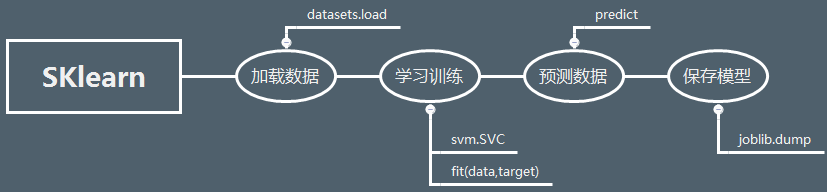
步骤
步骤简图
i)加载数据(datasets.load)
ii)学习训练(svm.SVC,.fit(data,target))
iii)预测数值(predict)
iv)保存模型(joblib.dump)
加载数据
通过如下指令获取数据,以手写数字数据集为例:
输入
$python
from sklearn import datasets
digits = datasets.load_digits()
输出
手写数字数据集保存到iris中。
Tip
i).data中存有数据信息
ii).target中存有监督学习所需的一个或多个响应参数,即标签
学习训练
输入
通过如下指令加载分类器,此处使用的是SVM分类器。
from sklearn import svm
clf = svm.SVC(gamma=0.001, C=100.)
输出
以gamma=0.001,C=100为参数加载了SVM分类器。
输入
训练模型,通过以下指令进行。
clf.fit(digits.data[:-1], digits.target[:-1])
输出
输出对应的分类器参数
SVC(C=100.0, cache_size=200, class_weight=None, coef0=0.0,
decision_function_shape='ovr', degree=3, gamma=0.001, kernel='rbf',
max_iter=-1, probability=False, random_state=None, shrinking=True,
tol=0.001, verbose=False)
预测数值
输入
输入期望预测的数据
clf.predict(digits.data[-1:])
输出
输出训练后模型预测的结果
array([8])
完整代码
输入
# encoding: utf-8
print(__doc__)
# 引用数据库
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets, svm, metrics
# 加载数据
digits = datasets.load_digits()
images_and_labels = list(zip(digits.images, digits.target))
# 显示训练数据
for index, (image, label) in enumerate(images_and_labels[:5]):
plt.subplot(2, 4, index + 1)
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(image, cmap=plt.cm.gray_r, interpolation='nearest')
plt.title('Training: %i' % label)
# 数据预处理
n_samples = len(digits.images)
data = digits.images.reshape((n_samples, -1))
# 学习训练
classifier = svm.SVC(gamma=0.001)
classifier.fit(data[:n_samples // 2], digits.target[:n_samples // 2])
# 预测数值
expected = digits.target[n_samples // 2:]
predicted = classifier.predict(data[n_samples // 2:])
# 分类器测试及混淆矩阵
print("Classification report for classifier %s:\n%s\n"
% (classifier, metrics.classification_report(expected, predicted)))
print("Confusion matrix:\n%s" % metrics.confusion_matrix(expected, predicted))
# 显示预测数值
images_and_predictions = list(zip(digits.images[n_samples // 2:], predicted))
for index, (image, prediction) in enumerate(images_and_predictions[:4]):
plt.subplot(2, 4, index + 5)
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(image, cmap=plt.cm.gray_r, interpolation='nearest')
plt.title('Prediction: %i' % prediction)
plt.show()
输出
Classification report for classifier SVC(C=1.0, cache_size=200, class_weight=None, coef0=0.0,
decision_function_shape='ovr', degree=3, gamma=0.001, kernel='rbf',
max_iter=-1, probability=False, random_state=None, shrinking=True,
tol=0.001, verbose=False):
precision recall f1-score support
0 1.00 0.99 0.99 88
1 0.99 0.97 0.98 91
2 0.99 0.99 0.99 86
3 0.98 0.87 0.92 91
4 0.99 0.96 0.97 92
5 0.95 0.97 0.96 91
6 0.99 0.99 0.99 91
7 0.96 0.99 0.97 89
8 0.94 1.00 0.97 88
9 0.93 0.98 0.95 92
micro avg 0.97 0.97 0.97 899
macro avg 0.97 0.97 0.97 899
weighted avg 0.97 0.97 0.97 899
Confusion matrix:
[[87 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0]
[ 0 88 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1]
[ 0 0 85 1 0 0 0 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 79 0 3 0 4 5 0]
[ 0 0 0 0 88 0 0 0 0 4]
[ 0 0 0 0 0 88 1 0 0 2]
[ 0 1 0 0 0 0 90 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 88 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 88 0]
[ 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 90]]
保存模型
i)方法1
输入
通过下列指令将clf参数赋予clf2
import pickle
s = pickle.dumps(clf)
clf2 = pickle.loads(s)
输出
clf2被赋予clf模型所应有的参数。
ii)方法2
输入
部分情况下可以通过joblib库进行,其可以将模型保存到具体文件中。
输入如下指令
from sklearn.externals import joblib
joblib.dump(clf, 'filename.pkl')
clf = joblib.load('filename.pkl')
输出
dump指令将clf模型保存到filename.pkl文件中,load指令让clf读入保存的模型参数
参考
[1]An introduction to machine learning with scikit-learn