主要内容:
a. 实时监控网站访问情况 stub_status
b. 网站日志记录功能配置
c. 利用location对uri进行匹配 ******
d. 实现网站页面跳转功能
1) 实现域名进行跳转
2) 实现uri信息跳转
nginx索引信息指令也属于相应不同的模块。模块里的指令会显示语法怎么用,能配置在哪个区域中。
网站服务状态监控功能
第一个历程: 编写配置文件
location = /basic_status {
stub_status; --- 开启状态监控功能
}
配置完之后访问
http://www.oldboy.com/basic_status,浏览器显示
Active connections: 1
server accepts handled requests
3 3 5
Reading: 0 Writing: 1 Waiting: 0
监控显示参数的意义
· Active connections 激活连接 *******
The current number of active client connections including Waiting connections.
#客户端目前连接数量/包含等待连接
# 客户端 ---- 服务端 max 2个 异步网络通讯模型机制就是客户端访问服务端超过最大连接数的时候,其余的连接会放入队列中进行等待。
· accepts 接受
The total number of accepted client connections.
接受客户端连接总的连接数量
· handled 处理
The total number of handled connections.
处理客户端连接总的处理连接数量
Generally, the parameter value is the same as accepts unless some resource limits have been reached
(for example, the worker_connections limit).
#特殊情况,到达服务器连接限制,也会造成处理数值和接收数值不一致
#当处理的请求数达到的了上线的时候其他连接的就在队列中等待这时候会造成处理数值和接受数值不想等。
· requests (长连接)
The total number of client requests.
总的客户端请求数量 发送了多个HTTP请求报文
vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
keepalive_timeout 0; --- 表示短连接,一次请求,一次断开。
PS: requests数量 == 处理连接数量
· Reading
The current number of connections where nginx is reading the request header.
目前读取用户请求头数量, 负载压力不大时, 数值几乎0或者1
· Writing
The current number of connections where nginx is writing the response back to the client.
目前响应信息发送数量,如果过高的时候也会表示网站的负载过大。
· Waiting *****
The current number of idle client connections waiting for a request.
客户端连接请求信息等待处理的数量,数值过大的时候也会表示服务器负载过大。(队列排队)
curl www.oldboy.com/basic_status -s|awk 'NR==1{print $3}'
#以后可以用zabbix跟网站的一些数值做比对,超过阈值则进行报警。
#-s 表示静默 只匹配过滤的内容。
网站服务日志配置
错误日志: error.log
tail -f /var/log/nginx/error.log 追踪nginx错误日志
在nginx主配置文件中
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log warn;
日志保存路径 日志错误级别
- 错误级别
debug 日志调试级别 配置此种级别,显示的信息会更多。最低的级别,如果将错误级别的调高,则低一级的信息级别则不会显示。
info 日志信息级别
notice 日志通知级别
warn 日志警告级别 错误 *****
error 日志错误级别 服务无法正常运行或者服务可运行页面则无法显示。 *****
crit 日志严重级别
alert 日志报警级别 服务程序异常
emerg 日志灾难级别 很难看到这种级别
重点关注 warn error 一般配置 warn
访问日志: access.log
1) 配置信息
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';#定义一种格式,下面调用这种格式
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
- 格式信息:
10.0.0.1 - - [01/Aug/2019:15:54:12 +0800] "GET /basic_status HTTP/1.1" 200 97 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; rv:68.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/68.0" "-"
"-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/537.36" "-"
$remote_addr//nginx内置变量 192.168.20.17 记录客户端源IP地址
$remote_user - 记录认证用户信息
[$time_local] [01/Aug/2019:10:12:15 +0800] 记录访问网站时间信息
$request "GET / HTTP/1.1" 记录请求行信息
$status 403 记录响应状态码信息
$body_bytes_sent 555 网站记录响应数据信息流量多少,如oldboy.jpg 15字节
awk '{i=i+$9}END{print i*8/1024/1024}' /var/log/nginx/access.log
记录了网站一共消耗了多少流量
$http_referer 显示盗取资源网站信息
$http_user_agent Chrome/75.0.3770.100 记录用户浏览器客户端信息
$http_x_forwarded_for 暂时没涉及
补充盗链的代码
[root@web02 bbs]# cat /html/bbs/index.html
老女孩教育
老女孩的博客!
我的博客是
博客地址
 #盗链的信息直接消耗其他网站的流量。
#盗链的信息直接消耗其他网站的流量。
此时显示的favicion和响应码是浏览器发起的,主要用作网页头部的图标,如果站点没有,则响应的状态为404,后续则不再请求。
网站服务location配置
作用说明: 匹配不同的uri, 作出不同处理动作
匹配方式:
~ 区分大小写匹配信息 03
~* 不区分大小写匹配信息 03
= 精准匹配 匹配优先级最高
^~ 优先匹配信息 02
/目录/ 直接匹配指定uri 04
oldboy.jpg
/ 默认匹配 05
实践操作:
bbs.conf
location ~ /oldboy/ {
return 200;
}
location ~* \.jpg$ {
return 301;
}
location = / {
return 302;
PS:匹配目录时时正常现象,匹配文件时会有问题。
}
PS:
在指定目录信息时, 可以精准匹配
在指定文件信息时, 不可以精准匹配
location / {
return 401;
}
location ^~ /image/ {
return 403;
}
location /old/ {
return 501;
}
实际应用:
可以灵活管理网站资源路径信息
案例:当一个网站去加载了一个图片,如果站点下的目录图片更改路径的情况下,站点下的html文本会调取图片信息,根据配置文件会找location默认匹配的的站点去找,此时可以在配置文件加上一个location的匹配信息,则开发人员不用更改代码网站上的图片会继续加载出来。
location ~* \.jpg$ { #匹配jpg结尾的会去此站点中加载图片。
root /html/www;
}
网站页面跳转
- a 实现uri信息跳转
- b 实现url信息跳转
- c 实现HTTPS跳转
- d 实现伪静态配置
- 实现跳转方式:
rewrite:Syntax: rewrite regex replacement [flag];
regex: 要替换的信息/正则方式匹配
replacement 替换成什么信息
flag: 设置标记
标记的信息
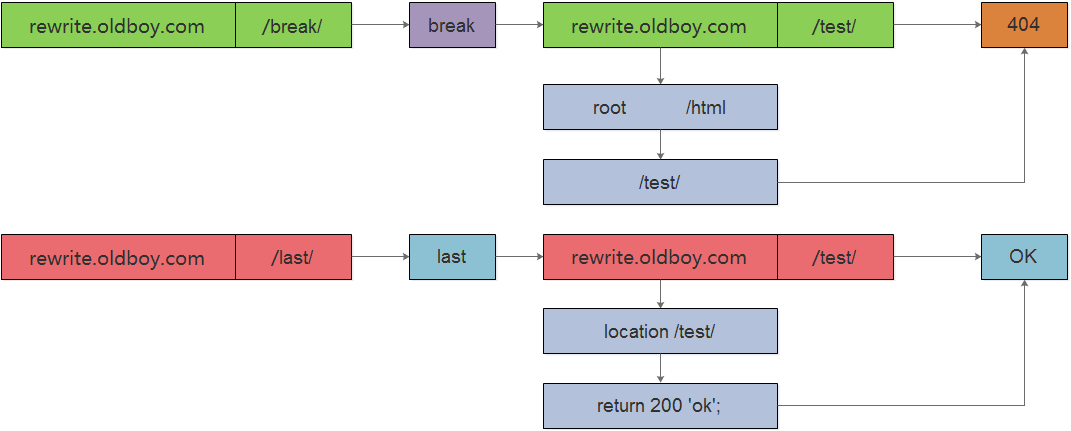
- · last == continue -- shell
stops processing the current set of ngx_http_rewrite_module directives and starts a search for a new location matching the changed URI;
实现跳转之后, 会重新发起访问,匹配其他location, 执行相应动作 - · break == exit
stops processing the current set of ngx_http_rewrite_module directives as with the break directive;
实现跳转之后, 不会重新发起访问, 直接到指定站点目录进行访问
PS: 以上两种跳转方式, 实现地址跳转后, 不会修改uri信息
break会去全局的站点目录去寻找,如果没有则返回404
last 会去匹配其他的location
PS: 以上两种跳转方式, 实现地址跳转后, 不会修改uri信息
- · redirect 302 应用比较广 ******
returns a temporary redirect with the 302 code; used if a replacement string does not start with “http://”, “https://”, or “$scheme”;
进行临时跳转
rewrite.oldboy.com/break/ --> rewrite.oldboy.com/test01/
rewrite.oldboy.com/break/ -服务端- rewrite.oldboy.com/test01/ --- web服务器 - · permanent 301
returns a permanent redirect with the 301 code.
进行永久跳转
PS: 以上两种跳转方式, 实现地址跳转后, 会修改uri信息
跳转测试配置01: 掌握last跳转和break跳转之间区别:
四种tag代码说明
server {
listen 80;
server_name rewrite.oldboy.com;
root /html;
location ~ ^/break/ {
rewrite ^/break/ /test/ break;
}
location ~ ^/last/ {
rewrite ^/last/ /test/ last;
}
location /test/ {
default_type application/json;
return 200 'ok';
}
}
测试: uri信息跳转
例1: 用户访问/oldboy/oldboy.html实际上真实访问是/oldboy/oldboy01/oldboy.html
server {
listen 80;
server_name rewrite.oldboy.com;
location / {
root /html;
#rewrite /oldboy/oldboy.html /oldboy/oldboy01/oldboy.html redirect;
rewrite (.*) /oldboy/oldboy01/oldboy.html redirect;
}
}
return:
server {
listen 80;
server_name rewrite.oldboy.com;
location / {
root /html;
return 302 http://rewrite.oldboy.com/oldboy/oldboy01/oldboy.html;
}
}
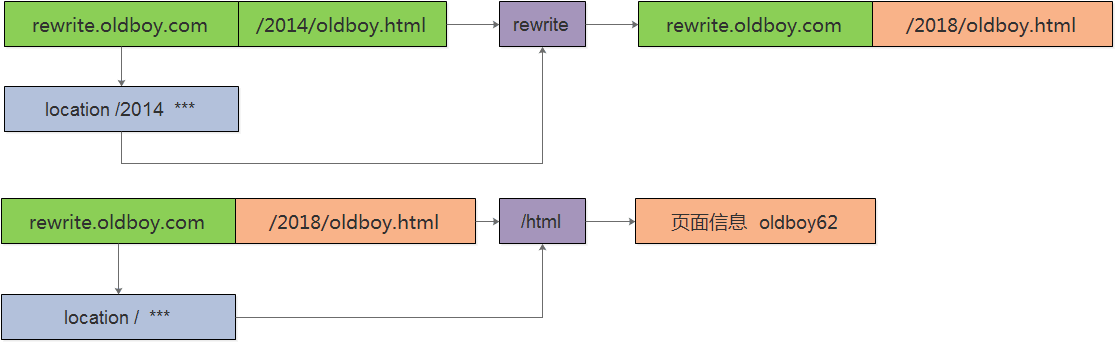
例2: 用户访问/2014/oldboy/oldgirl/oldboy.html实际上真实访问是/2018/oldboy/oldgirl/oldboy.html
第一个历程: 创建uri目录结构信息
mkdir 2014/oldboy/oldgirl/ -p --- 跳转前目录结构
echo oldboy62 >2014/oldboy/oldgirl/oldboy.html
mkdir 2018/oldboy/oldgirl/ -p --- 跳转后目录结构
echo oldboy62 >2018/oldboy/oldgirl/oldboy.html
/2014/oldboy/oldgirl/oldboy.html /2018/oldboy/oldgirl/oldboy.html
(.*)$ $1
第二个历程: 编写配置文件
server {
listen 80;
server_name rewrite.oldboy.com;
location / {
root /html;
}
location /2014/ {
rewrite ^/2014/(.*)$ /2018/$1 redirect;#.*代表所有$1代表后项引用前项
return 302 http://rewrite.oldboy.com/2018/oldboy/oldgirl/oldboy.html;
}
}
例题跳转的原理
1.第一种location为默认的时候,访问匹配默认的location然后进行跳转,有原来的rewrite.oldboy.com/2014 跳转到rewrite.oldboy.com/2014/oldboyhtml,跳转的时候继续匹配location,然后就形成死循环。
2.第二种匹配的location/2014 然后进行跳转,跳转后变为/2018/的目录,无法匹配2014的location然后匹配默认的location,然后从/html/www的站点去加载,找到oldboy.html文本。
例3:用户访问/test/oldboy.html目录下任何内容, 实际上真实访问是http://www.oldboy.com/oldboy.html
第一个历程: 创建站点目录环境
mkdir test ; echo oldboy62 >oldboy.html
方式一: 将oldboy.html 移动
mv test/oldboy.html ./
方式二: 不调整目录结构信息
location / {
root /html/test/;
}
第二个历程: 进行配置操作
server {
listen 80;
server_name rewrite.oldboy.com;
location / {
root /html;
}
location /test/ {
rewrite ^/test/(.*)$ http://rewrite.oldboy.com/$1 redirect;
}
}
例4:用户访问course-11-22-33.html实际上真实访问是/course/11/22/33/course_33.html
第一个历程: 准备站点目录环境
mkdir course/11/22/33/ -p
cd course/11/22/33/
echo oldboy62 >course_33.html
第二个历程:
[root@web01 33]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/rewrite.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name rewrite.oldboy.com;
location / {
root /html;
rewrite ^/course-(.*)-(.*)-(.*) /course/$1/$2/33/course_$3 last;
rewrite ^/course-(.*) /course/11/22/33/course_33.html last;
}
例5: 访问rewrite.oldboy.com --- www.jd.com 如何实现 url
解决方式一:
server {
listen 80;
server_name rewrite.oldboy.com;
rewrite ^/(.*) http://www.jd.com/$1 redirect;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.jd.com;
location / {
root /html;
index index.html;
}
}
解决方式二:
[root@web01 html]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/rewrite.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name rewrite.oldboy.com www.jd.com;
location / {
root /html;
index index.html;
if ($http_host ~* ^rewrite.oldboy.com$) {
rewrite ^/(.*) http://www.jd.com/$1 redirect;
}
}
}
---------------------------