内事不决问张昭,外事不决问周瑜,“ 排序 ”不决问威少
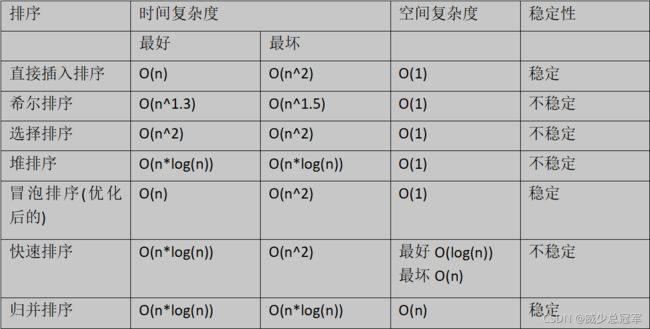
排序
- 排序的稳定性
- 一、直接插入排序
- 二、希尔排序
- 三、选择排序
- 四、冒泡排序
- 五、堆排序
- 六、快速排序
-
- Partition
-
- 挖坑法实现Partition
- Hoare法实现Partition
- 递归分治
-
- 时间空间复杂度
- 优化
-
- 三数取中
- 非递归分治
- 七、归并排序
-
- 归并排序(递归)
- 非递归的归并排序
- 时间复杂度与空间复杂度
-
- 计算运行时间的小妙招
- 买七送一(基数排序)
排序的稳定性
两个相等的数据,经过排序后,排序算法保证其相对位置不发生变化,则称这个排序算法就有稳定性

判断方法:如果再比较的过程中没有发生跳跃式的交换(即非相邻的交换),那么就是稳定的
一、直接插入排序
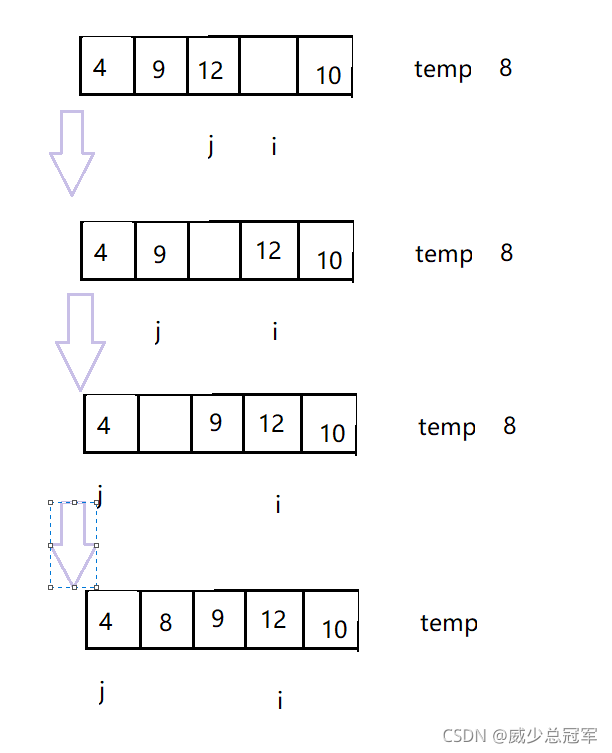
- 用 i 遍历数组,j = i - 1,将当前元素找到合适的位置插入,这个位置要满足 前面元素小于它
- 将当前元素存在 temp 中,j 下标的元素与temp 比较,如果array[ j ]>temp,说明temp插入的位置 j 下标前面,将 j 下标的元素后移一位,j - -
- 再进入循环判断
- 当 j < 0 的时候,退出循环,说明当前元素的位置是0下标
- 如果array[ j ] < temp , 将temp 放到 j+1 下标中,退出循环,说明当前元素已经找到了合适的位置
- 此时 temp 前的区间有序了
public static void insertSort(int[] array){
for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {
int temp = array[i];
int j = i-1;
for (; j >= 0; j--) {
if(array[j] > temp){
//此处>=就不稳定了
array[j+1] = array[j];
}else{
array[j+1] = temp;
break;
}
}
if(j < 0){
array[0] = temp;
}
}
}
如果一组数据量比较小,越趋近于有序,用直接插入排序越快
二、希尔排序
-
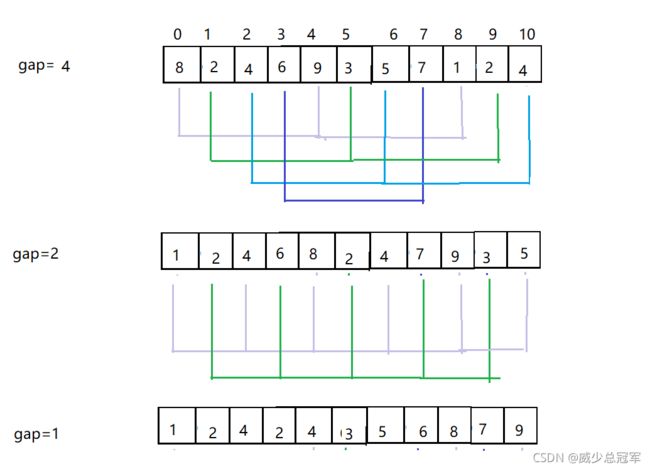
希尔排序是对直接插入排序的优化
-
先分组进行预排序,即对每组进行直接插入排序,每组的数据量小,排序快
-
不断减少组数,进行预排序,进一步提高整体数据的有序性
-
直到最后为一组,进行直接插入排序
-
每分一次组,就进行一次直接插入排序;数据量不同,分组的方式也不同,必须保证最后一次只有一组
-
gap越大,步子越大,移动的越快,越无序
public static void shell(int[] array, int gap){
for (int i = gap; i < array.length; i++) {
int temp = array[i];
int j = i-gap;
for (; j >=0 ; j -= gap) {
if(array[j] > temp){
array[j+gap] = array[j];
}else{
array[j+gap] = temp;
break;
}
}
if(j < 0){
array[gap+j] = temp;
}
}
}
public static void shellSort(int[] array){
int gap = array.length;
while(gap > 1){
gap = gap/3+1;
// gap = gap/2;
shell(array,gap);
}
}
三、选择排序
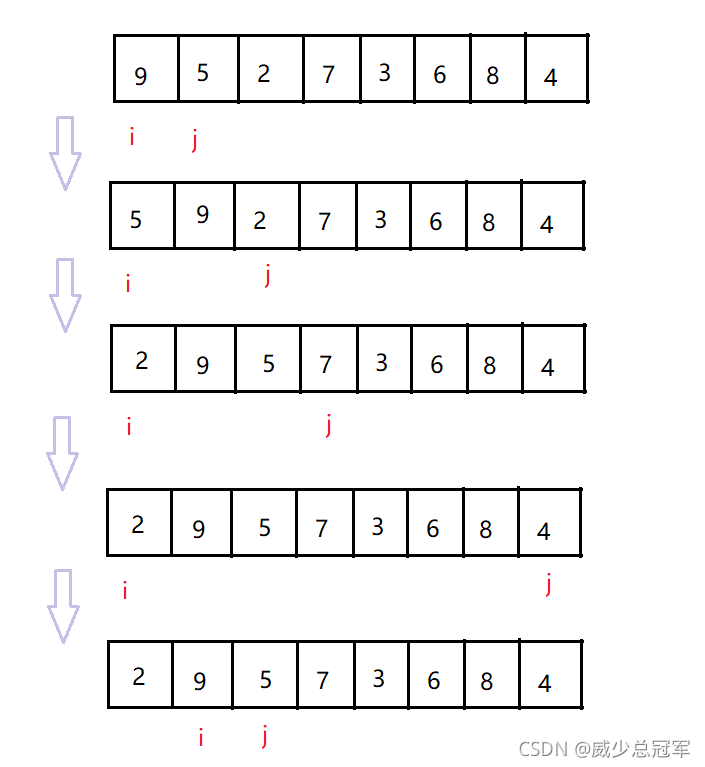
- 用 i 遍历一次整个数组
- j = i+1, j 向后遍历,如果当前 j 下标的元素小于当前 i 下标的元素,交换这两个元素,j 继续向后遍历;第一次遍历完成后 i 下标的元素就是当前数组最小的元素
- 当 i 遍历完成这个数组,排序完毕
public void selectSort(int[] array){
for (int i = 0; i < array.length-1; i++) {
for (int j = i+1; j < array.length; j++) {
if(array[i] > array[j]){
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
}
}
}
四、冒泡排序
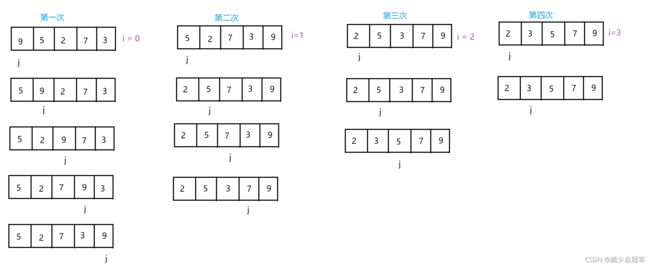
- i 表示排序的次数
- 通过 j 遍历数组,如果 j 下标的元素 > j + 1下标的元素,交换这两个元素,j 继续向后遍历,第一趟排序后最后一个元素就是最大的元素
- 再进行第二趟排序,注意 j 的结束下标的位置
public static void bullerSort(int[] array){
boolean flg = true;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length-1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < array.length-1-i; j++) {
if(array[j] > array[j+1]){
int temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j+1];
array[j+1] = temp;
flg = false;
}
}
if(flg){
break;
}
}
}
五、堆排序
- 先将数组变成一个大堆
- 堆顶元素与堆尾的元素互换
- 从堆顶元素向下调整,再次成为大堆,注意调整区间的范围(较上一次-1)
- 堆顶元素和倒数第二个元素互换
- 再次向下调整
- 照此循环,直至堆顶元素
//向下调整
//这里的end是结束区间的下标,注意不是长度len
public static void adjustDown(int[] array, int begin, int end){
int parent = begin;
int child = parent*2+1;
while(child <= end){
if(child+1 <= end && array[child+1] > array[child]){
child++;
}
if(array[parent] < array[child]){
int temp = array[parent];
array[parent] = array[child];
array[child] = temp;
}else{
break;
}
parent = child;
child = child*2+1;
}
}
//建立一个大堆
public static void creayHeap(int[] array){
int parent = (array.length-1-1)/2;
for (int i = parent; i >= 0; i--) {
adjustDown(array,i,array.length-1);
}
}
//堆排序
public static void heapSort(int[] array){
creayHeap(array);
int end = array.length-1;
while(end > 0){
int temp = array[0];
array[0] = array[end];
array[end] = temp;
end--;
adjustDown(array,0,end);
}
}
六、快速排序
- 从待排序区间里选一个数,作为基准值(pivot)
- Partition:遍历整个区间,将比基准值小的放到基准值的左边,将比基准值大的放到基准值的右边
- 分治思想,对左右两个小区间按照同样的方式处理,知道小区间的长度为1,代表已经有序;或小区间的长度为0,代表没有数据
Partition
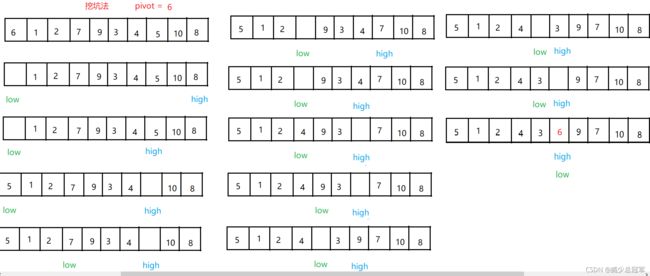
挖坑法实现Partition
- 取第一个元素作为基准(pivot)
- low下标从左边开始遍历,high下标从右边开始遍历,low和high就是“坑”
- 首先low下标作为“坑”,需要比 pivot 小的元素填坑,high–,找到比pivot 小的元素,赋值给low
- 然后high下标作为“坑”,需要比pivot 大的元素填坑,low++,找到比pivot 大的元素,赋值给high
- 当low和high相遇时,此下标指向的元素就是 pivot
- 一次Patition结束,此时low/high的左边是比pivot小的元素,low/high右边是比pivot大的元素
- 返回pivot的下标(low/high),作为下一次Patition的区间
public static int Partition(int[] array, int low, int high){
int pivot = array[low];
while(low < high){
//注意这两个循环的顺序,先low后high,第一个坑没法填,最后一个数白白丧失
//注意一定是>= / <= ,而不是> <,如果< , > 相等的也交换,死循环
while(low < high && array[high] >= pivot){
high--;
}
array[low] = array[high];
while(low < high && array[low] <= pivot){
low++;
}
array[high] = array[low];
}
array[low] = pivot;
return low;
}
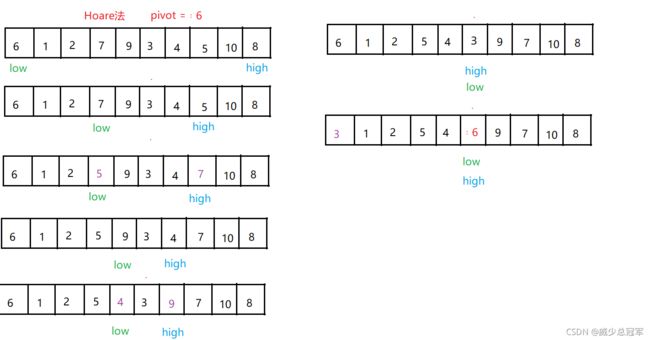
Hoare法实现Partition
- 第一个元素作为基准(pivot)
- high从右边开始遍历,left从左边开始遍历
- high找到比 pivot 小的元素,low找到比 pivot 大的元素,交换元素
- high与left相遇时,此下标指向的元素 小于pivot ,与 区间起点 的元素交换
- 返回pivot的下标(low/high),作为下一次Patition的区间
public static void Swap(int[] array, int i, int j){
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
public static int Hoare(int[] array, int low, int high){
int start = low;
int pivot = array[low];
while(low < high){
//注意顺序,先后再前,让high去找low,两者相遇的地方是比temp小的数
//同样的必须是>= <=,如果是>,< 会死循环的
while(low < high && array[high] >= pivot){
high--;
}
while(low < high && array[low] <= pivot){
low++;
}
Swap(array,low,high);
}
Swap(array,low,start);
return low;
}
递归分治
- 通过递归的方式对左右两个小区间再进行快速排序,直到区间长度为1时,递归结束
public static void quickSort(int[] array, int start, int end){
if(start >= end){
return;
}
int pivot = Partition(array,start,end);
quickSort(array,start,pivot-1);
quickSort(array,pivot+1,end);
}
public static void quickSort(int[] array){
quickSort(array,0,array.length-1);
}
时间空间复杂度
稳定性:不稳定
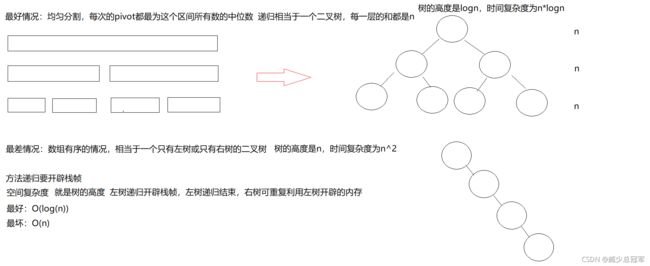
最坏情况时,可能会出现栈溢出的情况
所以可以通过基准值的选择进行优化
优化
- 基准值的选择
- 选择边上(low或者high)
- 随机选择,可以将随机下标的值与low下标的值互换
- 三数取中,要求 array[mid] <= array[low] <= array[high]
- 待排序区间小于一个阈值时,使用直接插入排序
三数取中
还是array[low] 作基准(pivot)
三数取中
array[mid] <= array[low] <= array[high]
可以确定其中最大/最小数的位置,在比较其余两个数
//元素交换
public static void Swap(int[] array, int i, int j){
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
//array[mid] <= array[low] <= array[high]
public static void ThreeMiddle(int[] array,int low, int high){
int mid = (low+high)/2;
if(array[low] < array[mid]){
Swap(array,low,mid);
}
if(array[high] < array[low]){
Swap(array,low,high);
}
if(array[low] < array[mid]){
Swap(array,low,mid);
}
//先确定mid的位置
if(array[mid] > array[start]){
swap(array,start,mid);
}
if(array[mid] > array[end]){
swap(array,mid,end);
}
//确定完成
if(array[start] > array[end]){
swap(array,start,end);
}
//先确定high的位置
if(array[mid] > array[high]){
Swap(array,mid,high);
}
if(array[low] > array[high]){
Swap(array,low,high);
}
//确定完成
if(array[mid] > array[low]){
Swap(array,mid,low);
}
}
非递归分治
- 调用Partition后,找到pivot
- 把当前pivot的左区间和右区间的边界下标放到栈中,当这个区间至少有两个元素的时候,才入栈;若只有一个元素,说明有序了,不再入栈
- 判断栈是否为空,如果不为空的话,弹出栈顶的两个元素,放的顺序决定第一个元素给low还是给high
- 再进行Partition
public static void quickSort2(int[] array){
if(array.length == 0){
return;
}
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(0);
stack.push(array.length-1);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
int high = stack.pop();
int low = stack.pop();
int pivot = Partition(array,low,high);
if(pivot > low+1) {
stack.push(low);
stack.push(pivot - 1);
}
if(pivot < high-1) {
stack.push(pivot + 1);
stack.push(high);
}
}
}
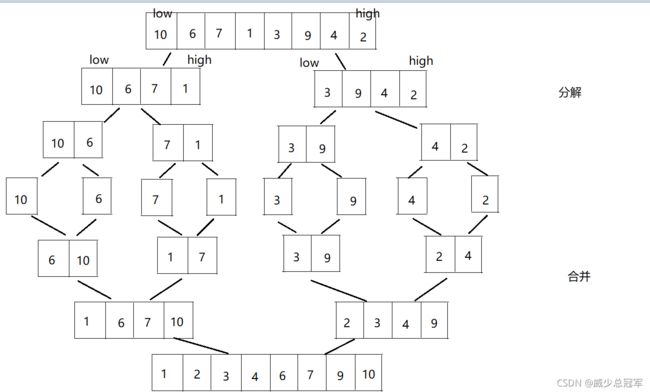
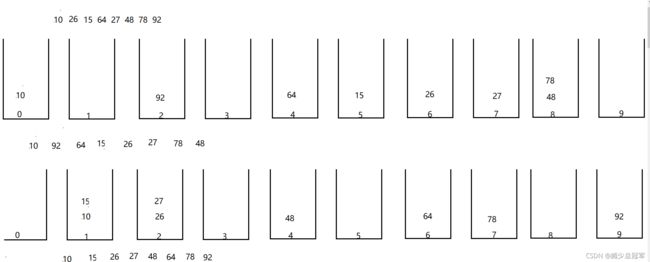
七、归并排序
先将已有的序列分解成较短的子序列,使每个子序列有序,再将已经有序的子序列合并,得到完全有序的序列,即分解与合并
归并排序(递归)
- 将数组通过递归分解,直到low=high时(即只有一个元素的时候),递归结束
- 将两个有序数组 合并成 一个有序数组
public static void merge(int[] array, int low, int mid, int high){
int[] temp = new int[high-low+1];
int k = 0;
int s1 = low;
int e1 = mid;
int s2 = mid+1;
int e2 = high;
while(s1 <= e1 && s2 <= e2){
while(s1 <= e1 && array[s1] <= array[s2]){
temp[k++] = array[s1++];
}
while(s2 <= e2 && array[s2] <= array[s1]){
temp[k++] = array[s2++];
}
}
while(s1 <= e1){
temp[k++] = array[s1++];
}
while(s2 <= e2){
temp[k++] = array[s2++];
}
for (int i = 0; i < temp.length; i++) {
array[i+low] = temp[i];
}
}
public static void mergeSort(int[] array, int low, int high){
if(low == high){
return;
}
int mid = (low+high)/2;
mergeSort(array,low,mid);
mergeSort(array,mid+1,high);
merge(array, low, mid, high);
}
public static void mergeSort(int[] array){
mergeSort(array,0,array.length-1);
}
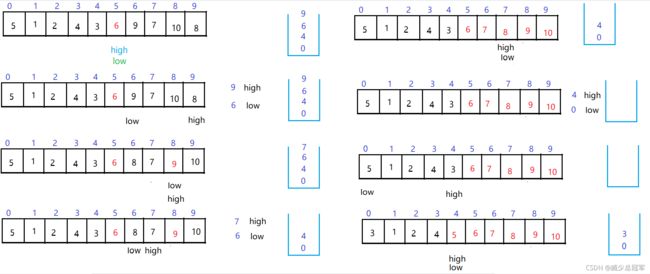
非递归的归并排序
- 通过gap控制需要合并的两个序列的长度,1–>2–>4–>8…
- 在gap的一次循环中,s1、e1、s2、e2遍历所有的序列,合并两个有序的序列
- 可能序列正好匹配 可能只剩下一段序列(没有与之合并的第二段序列);如果剩下无法合并的序列,不做改变
public static void merge(int[] array, int gap){
int[] temp = new int[array.length];
int k = 0;
int s1 = 0;
int e1 = s1+gap-1;
int s2 = e1+1;
int e2 = s2+gap-1 > array.length-1 ? array.length-1 : s2+gap-1;
//有两段
while(s2 < array.length) {
while (s1 <= e1 && s2 <= e2) {
while (s1 <= e1 && array[s1] <= array[s2]) {
temp[k++] = array[s1++];
}
while (s2 <= e2 && array[s2] <= array[s1]) {
temp[k++] = array[s2++];
}
}
while(s1 <= e1) {
temp[k++] = array[s1++];
}
while(s2 <= e2){
temp[k++] = array[s2++];
}
s1 = e2+1;
e1 = s1+gap-1;
s2 = e1+1;
e2 = s2+gap-1 > array.length-1 ? array.length-1 : s2+gap-1;
}
//只有一段了
while(s1 < array.length && s1 <= e1){
temp[k++] = array[s1++];
}
for (int i = 0; i < temp.length; i++) {
array[i] = temp[i];
}
}
public static void mergeSort2(int[] array){
for (int gap = 1; gap < array.length; gap*=2) {
merge(array,gap);
}
}
时间复杂度与空间复杂度
计算运行时间的小妙招
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
insertSort(array);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - begin);
买七送一(基数排序)
基数排序又叫“桶子排序”