第四周:cnn卷积神经网络
1.正向传播
1.1输入层
每一张图应该是是m*n的二维数组的形式呈现在我们眼前,但现在我们把它打平:二维展开变成一维,本来该是原图中一列中的下一列,我们把这下一列不放在下面了,直接连着上一列,这样每张图片的数据就变成一维了。
把无数张打平的图片数据拿来训练,进行paraRounds次训练,每次训练选择batch张图(batch列)拿来训练,每张图进行训练epoch次。
1.2卷积层
下图的步长为2(注:不是代码里步长,代码里的步长为1)
![]()
代码表示卷积如下:
/**
***********************
* Compute the convolution output according to the output of the last layer.
*
* @param paraLastLayer
* the last layer.
* @param paraLayer
* the current layer.
***********************
*/
private void setConvolutionOutput(final CnnLayer paraLayer, final CnnLayer paraLastLayer) {
// int mapNum = paraLayer.getOutMapNum();
final int lastMapNum = paraLastLayer.getOutMapNum();
// Attention: paraLayer.getOutMapNum() may not be right.
for (int j = 0; j < paraLayer.getOutMapNum(); j++) {
//当前层的为paraLayer.getOutMapNum()个二维矩阵
double[][] tempSumMatrix = null;
for (int i = 0; i < lastMapNum; i++) {
//当前层的上一层为paraLastLayer.getOutMapNum()个二维矩阵
double[][] lastMap = paraLastLayer.getMap(i);
double[][] kernel = paraLayer.getKernel(i, j);
if (tempSumMatrix == null) {
// On the first map.
tempSumMatrix = MathUtils.convnValid(lastMap, kernel);
} else {
// Sum up convolution maps
tempSumMatrix = MathUtils.matrixOp(MathUtils.convnValid(lastMap, kernel),
tempSumMatrix, null, null, MathUtils.plus);
} // Of if
} // Of for i
// Activation.
final double bias = paraLayer.getBias(j);
tempSumMatrix = MathUtils.matrixOp(tempSumMatrix, new Operator() {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2469461972825890810L;
@Override
public double process(double value) {
return MathUtils.sigmod(value + bias);//sigmoid函数处理,1/(1+e^(-z))
}
});
paraLayer.setMapValue(j, tempSumMatrix);
} // Of for j
}// Of setConvolutionOutput
MathUtils.convnValid:
/**
***********************
* Convolution operation, from a given matrix and a kernel, sliding and sum
* to obtain the result matrix. It is used in forward.
***********************
*/
public static double[][] convnValid(final double[][] matrix, double[][] kernel) {
// kernel = rot180(kernel);
int m = matrix.length;
int n = matrix[0].length;
final int km = kernel.length;
final int kn = kernel[0].length;
int kns = n - kn + 1;
final int kms = m - km + 1;
final double[][] outMatrix = new double[kms][kns];
for (int i = 0; i < kms; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < kns; j++) {
double sum = 0.0;
for (int ki = 0; ki < km; ki++) {
for (int kj = 0; kj < kn; kj++)
sum += matrix[i + ki][j + kj] * kernel[ki][kj];//步长为1
}
outMatrix[i][j] = sum;
}
}
return outMatrix;
}// Of convnValid
注:进行了对上一层卷积完的结果要进行激活函数处理,这里的激活函数选的是sigmoid, 1 / ( 1 + e − z ) 1/(1+e^{-z}) 1/(1+e−z)
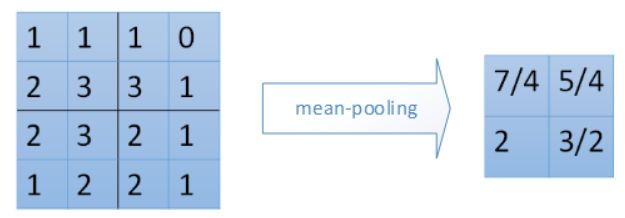
1.3 池化层
1.3.1平均池化
/**
***********************
* Compute the convolution output according to the output of the last layer.
*
* @param paraLastLayer
* the last layer.
* @param paraLayer
* the current layer.
***********************
*/
private void setSampOutput(final CnnLayer paraLayer, final CnnLayer paraLastLayer) {
// int tempLastMapNum = paraLastLayer.getOutMapNum();
// Attention: paraLayer.outMapNum may not be right.
for (int i = 0; i < paraLayer.outMapNum; i++) {
int templastMapNum=paraLastLayer.outMapNum;
double[][] lastMap = paraLastLayer.getMap(i);
Size scaleSize = paraLayer.getScaleSize();
double[][] sampMatrix = MathUtils.scaleMatrix(lastMap, scaleSize);
paraLayer.setMapValue(i, sampMatrix);
} // Of for i
}// Of setSampOutput
MathUtils.scaleMatrix:
/**
***********************
* Scale the matrix.
***********************
*/
public static double[][] scaleMatrix(final double[][] matrix, final Size scale) {
int m = matrix.length;
int n = matrix[0].length;
final int sm = m / scale.width;
final int sn = n / scale.height;
final double[][] outMatrix = new double[sm][sn];
if (sm * scale.width != m || sn * scale.height != n)
throw new RuntimeException("scale matrix");
final int size = scale.width * scale.height;
for (int i = 0; i < sm; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < sn; j++) {
double sum = 0.0;
for (int si = i * scale.width; si < (i + 1) * scale.width; si++) {
for (int sj = j * scale.height; sj < (j + 1) * scale.height; sj++) {
sum += matrix[si][sj];
} // Of for sj
} // Of for si
//池化,区域取平均数
outMatrix[i][j] = sum / size;
} // Of for j
} // Of for i
return outMatrix;
}// Of scaleMatrix
1.3.2最大池化
1.4输出层
输出层同样用卷积,用和上一层尺寸同样大小的kernel对上层的二维数组进行卷积运算,上一层第i个二维数组和输出层的第j个二维数组之间有自己的kernel。
代码中输出层为10个一维数组,假如当一维数组O_i位置装的是1(其他的位置装的是0),则卷积完成后,从0~9中分出的类是O_i(0<=O_i<=9)。
2.反向传播
2.1输出层的梯度
输出层误差对上一层的输出结果梯度为( ∂ E r r o r i ∂ N e t o i \frac{\partial Error_{i}}{\partial Net_{oi}} ∂Netoi∂Errori): t e m p O u t M a p s [ m ] ⋅ ( 1 − t e m p O u t M a p s [ m ] ) ⋅ ( t e m p O u t M a p s [ m ] − t e m p T a r g e t [ m ] ) tempOutMaps[m] \cdot(1 - tempOutMaps[m]) \cdot ( tempOutMaps[m]-tempTarget[m] ) tempOutMaps[m]⋅(1−tempOutMaps[m])⋅(tempOutMaps[m]−tempTarget[m]),因为:

误差对输出层第i个输出的梯度为: ∂ E r r o r i ∂ O u t o i ⋅ ∂ O u t o i ∂ N e t o i \frac{\partial Error_{i}}{\partial Out_{oi}} \cdot \frac{\partial Out_{oi}}{\partial Net_{oi}} ∂Outoi∂Errori⋅∂Netoi∂Outoi
-
∂ E r r o r i ∂ O u t o i : \frac{\partial Error_{i}}{\partial Out_{oi}}: ∂Outoi∂Errori:
E r r o r i = 1 2 ( t a r g e t i − O u t o i ) ˙ 2 Error_{i}=\frac{1}{2}\dot{(target_{i}-Out_{oi})}^2 Errori=21(targeti−Outoi)˙2
∂ E r r o r i ∂ O u t o i = 2 ⋅ 1 2 ⋅ ( t a r g e t o i − O u t o i ) ⋅ ( − 1 ) = − ( t a r g e t o i − O u t o i ) \frac{\partial Error_{i}}{\partial Out_{oi}}=2\cdot \frac{1}{2}\cdot\left ( target_{oi} -Out_{oi}\right ) \cdot (-1)=-( target_{oi} -Out_{oi}) ∂Outoi∂Errori=2⋅21⋅(targetoi−Outoi)⋅(−1)=−(targetoi−Outoi) -
∂ O u t o i ∂ N e t o i \frac{\partial Out_{oi}}{\partial Net_{oi}} ∂Netoi∂Outoi
O u t o i = 1 1 + e − N e t o i Out_{oi}=\frac{1}{1+e^{-Net_{oi}}} Outoi=1+e−Netoi1
∂ O u t o i ∂ N e t o i = ( O u t o i ) ⋅ ( 1 − O u t o i ) \frac{\partial Out_{oi}}{\partial Net_{oi}} =(Out_{oi})\cdot (1-Out_{oi}) ∂Netoi∂Outoi=(Outoi)⋅(1−Outoi)java代码为:
/**
***********************
* Set errors of a sampling layer.
***********************
*/
private boolean setOutputLayerErrors(Instance paraRecord) {
CnnLayer tempOutputLayer = layerBuilder.getOutputLayer();
int tempMapNum = tempOutputLayer.getOutMapNum();
double[] tempTarget = new double[tempMapNum];
double[] tempOutMaps = new double[tempMapNum];
for (int m = 0; m < tempMapNum; m++) {
double[][] outmap = tempOutputLayer.getMap(m);
tempOutMaps[m] = outmap[0][0];
} // Of for m
int tempLabel = paraRecord.getLabel().intValue();
tempTarget[tempLabel] = 1;
// Log.i(record.getLable() + "outmaps:" +
// Util.fomart(outmaps)
// + Arrays.toString(target));
for (int m = 0; m < tempMapNum; m++) {
tempOutputLayer.setError(m, 0, 0,
tempOutMaps[m] * (1 - tempOutMaps[m]) * (tempTarget[m] - tempOutMaps[m]));//源代码是这个,但我觉得应该是tempOutMaps[m] * (1 - tempOutMaps[m]) * (tempTarget[m] - tempOutMaps[m])*(-1));
} // Of for m
return tempLabel == MathUtils.getMaxIndex(tempOutMaps);
}// Of setOutputLayerErrors
2.2卷积层上一层的误差梯度(代码中是采样层的误差梯度)
该代码中采样层下一层是卷积层,采样层是被卷积的,应该参考卷积层反向传播,采样层的误差=采样层下一层的误差维度扩大后*采样层与下一层的kernel的转置
详情原理查看:链接
2.2.1求平均池化层的误差梯度
卷积层上一层的是池化层,由卷积层的误差梯度推导它的上一层(池化层)的梯度,所以是求池化层的误差梯度。
2.2.1.1kernel转180后相乘(因为要用下一层的扩大的误差与kernel转180后相乘,得到当前层的误差(Error))
/**
***********************
* Rotate the matrix 180 degrees.
* paralayer到nextlayer的kernel旋转180度
***********************
*/
public static double[][] rot180(double[][] matrix) {
matrix = cloneMatrix(matrix);
int m = matrix.length;
int n = matrix[0].length;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n / 2; j++) {
double tmp = matrix[i][j];
matrix[i][j] = matrix[i][n - 1 - j];
matrix[i][n - 1 - j] = tmp;
}
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
for (int i = 0; i < m / 2; i++) {
double tmp = matrix[i][j];
matrix[i][j] = matrix[m - 1 - i][j];
matrix[m - 1 - i][j] = tmp;
}
}
return matrix;
}// Of rot180
2.2.1.2(1)将下一层误差矩阵维度扩大(2)下一层的扩大的误差与kernel转180后相乘,得到当前层的误差(具体推到可看参考博客)
/**
***********************
* Convolution full to obtain a bigger size. It is used in back-propagation.
* double[][] matrix:下一层的误差
* double[][] kernel:采样层到池化层的误差
***********************
*/
public static double[][] convnFull(double[][] matrix, final double[][] kernel) {
int m = matrix.length;
int n = matrix[0].length;
final int km = kernel.length;
final int kn = kernel[0].length;
final double[][] extendMatrix = new double[m + 2 * (km - 1)][n + 2 * (kn - 1)];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
//扩大下一层误差矩阵维度
extendMatrix[i + km - 1][j + kn - 1] = matrix[i][j];
} // Of for j
} // Of for i
//下一层的扩大的误差与kernel转180后相乘,获得当前层误差
return convnValid(extendMatrix, kernel);
}// Of convnFull
/**
***********************
* Convolution operation, from a given matrix and a kernel, sliding and sum
* to obtain the result matrix. It is used in forward.
* 下一层的扩大的误差与kernel转180后相乘,更新当前层误差
***********************
*/
public static double[][] convnValid(final double[][] matrix, double[][] kernel) {
// kernel = rot180(kernel);
int m = matrix.length;
int n = matrix[0].length;
final int km = kernel.length;
final int kn = kernel[0].length;
int kns = n - kn + 1;
final int kms = m - km + 1;
final double[][] outMatrix = new double[kms][kns];
for (int i = 0; i < kms; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < kns; j++) {
double sum = 0.0;
for (int ki = 0; ki < km; ki++) {
for (int kj = 0; kj < kn; kj++)
sum += matrix[i + ki][j + kj] * kernel[ki][kj];
}
outMatrix[i][j] = sum;
}
}
return outMatrix;
}// Of convnValid
2.2.2最大池化的误差
2.3池化层的上一层的误差梯度(代码中是卷积层的误差梯度)
代码中的池化层的上一层是卷积层,所以是求卷积层的误差梯度
详情原理查看:链接
该卷积层的下一层为采样层,该卷积层被采样,应参考采样反向传播,卷积层的误差梯度=采样层误差扩大后*卷积层的sigmoid函数导数
计算当前卷积层的误差:
- 下一层(采样层)的误差扩大后(注释:这里对采样层误差的扩大和网上有点不一样,网上其他的博客写:平均池化的误差扩大是通过将每个池化层的误差在扩大后的每个scale(采样区间)平均,但这里的代码是直接把误差放到扩大后的相应的位置)
- 当前层对sigmoid求导
- 当前卷积的误差= ( O u t o i ) ⋅ ( 1 − O u t o i ) ∗ e r r o r = 当 前 层 对 s i g m o i d 求 导 ⋅ 下 一 层 的 误 差 (Out_{oi})\cdot(1-Out_{oi})*error=当前层对sigmoid求导 \cdot下一层的误差 (Outoi)⋅(1−Outoi)∗error=当前层对sigmoid求导⋅下一层的误差
/**
***********************
* Set errors of a Convolution layer.
***********************
*/
private void setConvolutionErrors(final CnnLayer paraLayer, final CnnLayer paraNextLayer) {
// System.out.println("setConvErrors");
for (int m = 0; m < paraLayer.getOutMapNum(); m++) {
Size tempScale = paraNextLayer.getScaleSize();
double[][] tempNextLayerErrors = paraNextLayer.getError(m);
double[][] tempMap = paraLayer.getMap(m);
//tempOutMatrix是当(out)*(1-Out_i),对应前面反向传播说过的delta{Out_oi}/delta{Net_oi}的梯度
double[][] tempOutMatrix = MathUtils.matrixOp(tempMap, MathUtils.cloneMatrix(tempMap),
null, MathUtils.one_value, MathUtils.multiply);
//MathUtils.kronecker(tempNextLayerErrors, tempScale)是将下一层的误差矩阵扩大,扩大后与上一层的矩阵相乘,得到当前层的误差
tempOutMatrix = MathUtils.matrixOp(tempOutMatrix,
MathUtils.kronecker(tempNextLayerErrors, tempScale), null, null,
MathUtils.multiply);
//更新当前层的误差
paraLayer.setError(m, tempOutMatrix);
// System.out.println("range check nextError");
if (!rangeCheck(tempNextLayerErrors, -10, 10)) {
System.out.println("setConvErrors, nextError out of range:\r\n"
+ Arrays.deepToString(tempNextLayerErrors));
System.out.println("the new errors are:\r\n" + Arrays.deepToString(tempOutMatrix));
System.exit(0);
} // Of if
if (!rangeCheck(tempOutMatrix, -10, 10)) {
System.out.println("setConvErrors, error out of range.");
System.exit(0);
} // Of if
} // Of for m
}// Of setConvolutionErrors
MathUtils.kronecker():
/**
***********************
* Extend the matrix to a bigger one (a number of times).
***********************
*/
public static double[][] kronecker(final double[][] matrix, final Size scale) {
final int m = matrix.length;
int n = matrix[0].length;
final double[][] outMatrix = new double[m * scale.width][n * scale.height];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
for (int ki = i * scale.width; ki < (i + 1) * scale.width; ki++) {
for (int kj = j * scale.height; kj < (j + 1) * scale.height; kj++) {
outMatrix[ki][kj] = matrix[i][j];
}
}
}
}
return outMatrix;
}// Of kronecker
3.更新
3.1 kernel
新的kernel (更新卷积层或输出层与他们上一层之间的kernel,代码里的输出层也是一种卷积层):第i层和第i+1层的某两个矩阵之间的kernel更新为:第i+1层的误差与第i层的矩阵做卷积。
代码如下:
/**
***********************
* Convolution operation, from a given matrix and a kernel, sliding and sum
* to obtain the result matrix. It is used in forward.
*
*
* final double[][] matrix:第i层的矩阵
* double[][] kernel:第i+1层的误差
***********************
*/
public static double[][] convnValid(final double[][] matrix, double[][] kernel) {
// kernel = rot180(kernel);
int m = matrix.length;
int n = matrix[0].length;
final int km = kernel.length;
final int kn = kernel[0].length;
int kns = n - kn + 1;
final int kms = m - km + 1;
final double[][] outMatrix = new double[kms][kns];
for (int i = 0; i < kms; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < kns; j++) {
double sum = 0.0;
for (int ki = 0; ki < km; ki++) {
for (int kj = 0; kj < kn; kj++)
sum += matrix[i + ki][j + kj] * kernel[ki][kj];
}
outMatrix[i][j] = sum;
}
}
return outMatrix;
}// Of convnValid
3.2更新偏置
/**
***********************
* Update bias.
***********************
*/
private void updateBias(final CnnLayer paraLayer, CnnLayer paraLastLayer) {
final double[][][][] errors = paraLayer.getErrors();
// int mapNum = paraLayer.getOutMapNum();
// Attention: getOutMapNum() may not be correct.
for (int j = 0; j < paraLayer.getOutMapNum(); j++) {
double[][] error = MathUtils.sum(errors, j);
double deltaBias = MathUtils.sum(error) / batchSize;
double bias = paraLayer.getBias(j) + ALPHA * deltaBias;
paraLayer.setBias(j, bias);
} // Of for j
}// Of updateBias
4.参考资料
- 源代码:https://blog.csdn.net/minfanphd/article/details/116976111
- CNN反向传播推导
- 卷积神经网络六之CNN反向传播计算过程
- 【Python实现卷积神经网络】:卷积层的正向传播与反向传播+python实现代码
CNN笔记:通俗理解卷积神经网络