openCV调用YOLOv5 ONNX模型
导出U版YOLOv5的ONNX模型,openCV直接读取会失败,原因在于Pytorch2ONNX不支持对slice对象赋值,需要更改下列两个地方代码:
yolov5/models/common.py
class Focus(nn.Module):
# Focus wh information into c-space
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, p=None, g=1, act=True): # ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, padding, groups
super(Focus, self).__init__()
self.conv = Conv(c1 * 4, c2, k, s, p, g, act)
# self.contract = Contract(gain=2)
def forward(self, x): # x(b,c,w,h) -> y(b,4c,w/2,h/2)
return self.conv(torch.cat([x[..., ::2, ::2], x[..., 1::2, ::2], x[..., ::2, 1::2], x[..., 1::2, 1::2]], 1))
# return self.conv(self.contract(x))
更改为:
class Focus(nn.Module):
# Focus wh information into c-space
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, p=None, g=1, act=True): # ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, padding, groups
super(Focus, self).__init__()
self.conv = Conv(c1 * 4, c2, k, s, p, g, act)
# self.contract = Contract(gain=2)
def forward(self, x): # x(b,c,w,h) -> y(b,4c,w/2,h/2)
# return self.conv(torch.cat([x[..., ::2, ::2], x[..., 1::2, ::2], x[..., ::2, 1::2], x[..., 1::2, 1::2]], 1))
N, C, H, W = x.size() # assert (H / s == 0) and (W / s == 0), 'Indivisible gain'
s = 2
x = x.view(N, C, H // s, s, W // s, s) # x(1,64,40,2,40,2)
x = x.permute(0, 3, 5, 1, 2, 4).contiguous() # x(1,2,2,64,40,40)
y = x.view(N, C * s * s, H // s, W // s) # x(1,256,40,40)
return self.conv(y)具体原因可看博客2021.03.11更新 c++下使用opencv部署yolov5模型(一)_爱晚乏客游的博客-CSDN博客和Pytorch转ONNX-实战篇2(实战踩坑总结) - 知乎,这里不做过多解释
yolov5/models/yolo.py
class Detect(nn.Module):
stride = None # strides computed during build
export = False # onnx export
def __init__(self, nc=80, anchors=(), ch=()): # detection layer
super(Detect, self).__init__()
self.nc = nc # number of classes
self.no = nc + 5 # number of outputs per anchor
self.nl = len(anchors) # number of detection layers
self.na = len(anchors[0]) // 2 # number of anchors
self.grid = [torch.zeros(1)] * self.nl # init grid
a = torch.tensor(anchors).float().view(self.nl, -1, 2)
self.register_buffer('anchors', a) # shape(nl,na,2)
self.register_buffer('anchor_grid', a.clone().view(self.nl, 1, -1, 1, 1, 2)) # shape(nl,1,na,1,1,2)
self.m = nn.ModuleList(nn.Conv2d(x, self.no * self.na, 1) for x in ch) # output conv
def forward(self, x):
# x = x.copy() # for profiling
z = [] # inference output
self.training |= self.export
for i in range(self.nl):
x[i] = self.m[i](x[i]) # conv
bs, _, ny, nx = x[i].shape # x(bs,255,20,20) to x(bs,3,20,20,85)
x[i] = x[i].view(bs, self.na, self.no, ny, nx).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous()
x[i] = x[i].view(bs * self.na * ny * nx, self.no).contiguous()
return torch.cat(x)
# if not self.training: # inference
# if self.grid[i].shape[2:4] != x[i].shape[2:4]:
# self.grid[i] = self._make_grid(nx, ny).to(x[i].device)
#
# y = x[i].sigmoid()
# y[..., 0:2] = (y[..., 0:2] * 2. - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy
# y[..., 2:4] = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] # wh
# z.append(y.view(bs, -1, self.no))
#
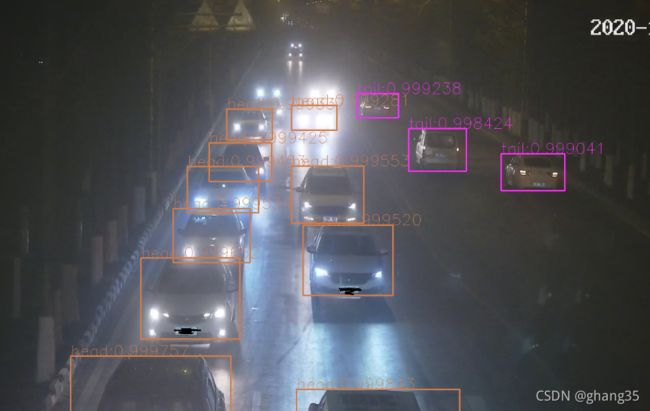
# return x if self.training else (torch.cat(z, 1), x)更改完成之后,使用netron查看导出的onnx模型,可发现上述操作把YOLO层的三个输出合并为一个输出,格式类似yolov4的格式。
python
import netron
netron.start("best.onnx")接下来就是使用openCV调用导出的onnx,本文使用的openCV版本为4.5.1,使用4.4版本的可能会出现错误。代码参考了博客2021.09.02更新说明 c++下使用opencv部署yolov5模型 (三)_爱晚乏客游的博客-CSDN博客,我也是依葫芦画瓢
yolo5.h
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
using namespace dnn;
using namespace std;
struct Output {
int id;//结果类别id
float confidence;//结果置信度
cv::Rect box;//矩形框
};
class YOLO
{
public:
YOLO() {};
bool readModel(Net &net, string &netPath, bool isCuda = false);
bool Detect(cv::Mat &SrcImg, cv::dnn::Net &net, std::vector yolo5.cpp
#include "yolo5.h"
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
bool YOLO::readModel(Net & net, string & netPath, bool isCuda)
{
try {
net = readNetFromONNX(netPath);
}
catch (const std::exception&) {
return false;
}
//cuda
if (isCuda) {
net.setPreferableBackend(cv::dnn::DNN_BACKEND_CUDA);
net.setPreferableTarget(cv::dnn::DNN_TARGET_CUDA);
}
//cpu
else {
net.setPreferableBackend(cv::dnn::DNN_BACKEND_DEFAULT);
net.setPreferableTarget(cv::dnn::DNN_TARGET_CPU);
}
return true;
}
bool YOLO::Detect(cv::Mat & SrcImg, cv::dnn::Net & net, std::vector& output)
{
Mat blob;
blobFromImage(SrcImg, blob, 1 / 255.0, cv::Size(netWidth, netHeight), Scalar(0, 0, 0), true, false);
net.setInput(blob);
vector netOutputImg;
net.forward(netOutputImg, net.getUnconnectedOutLayersNames());
vector classIds;//结果id数组
vector confidences;//结果每个id对应置信度数组
vector boxes;//每个id矩形框
float ratio_h = (float)SrcImg.rows / netHeight;
float ratio_w = (float)SrcImg.cols / netWidth;
int net_width = className.size() + 5; //输出的网络宽度是类别数+5
float* pdata = (float*)netOutputImg[0].data;
for (int stride = 0; stride < 3; stride++) { //stride
int grid_x = (int)(netWidth / netStride[stride]);
int grid_y = (int)(netHeight / netStride[stride]);
for (int anchor = 0; anchor < 3; anchor++) { //anchors
const float anchor_w = netAnchors[stride][anchor * 2];
const float anchor_h = netAnchors[stride][anchor * 2 + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < grid_x; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < grid_y; j++) {
float box_score = Sigmoid(pdata[4]);//获取每一行的box框中含有某个物体的概率
if (box_score > boxThreshold) {
cv::Mat scores(1, className.size(), CV_32FC1, pdata + 5);
Point classIdPoint;
double max_class_socre;
minMaxLoc(scores, 0, &max_class_socre, 0, &classIdPoint);
max_class_socre = Sigmoid((float)max_class_socre);
if (max_class_socre > boxThreshold) {
//rect [x,y,w,h]
float x = (Sigmoid(pdata[0]) * 2.f - 0.5f + j) * netStride[stride]; //x
float y = (Sigmoid(pdata[1]) * 2.f - 0.5f + i) * netStride[stride]; //y
float w = powf(Sigmoid(pdata[2]) * 2.f, 2.f) * anchor_w; //w
float h = powf(Sigmoid(pdata[3]) * 2.f, 2.f) * anchor_h; //h
int left = (x - 0.5*w)*ratio_w;
int top = (y - 0.5*h)*ratio_h;
classIds.push_back(classIdPoint.x);
confidences.push_back(max_class_socre);
boxes.push_back(Rect(left, top, int(w*ratio_w), int(h*ratio_h)));
}
}
pdata += net_width;//指针移到下一行
}
}
}
}
vector nms_result;
NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, classThreshold, nmsThreshold, nms_result);
for (int i = 0; i < nms_result.size(); i++) {
int idx = nms_result[i];
Output result;
result.id = classIds[idx];
result.confidence = confidences[idx];
result.box = boxes[idx];
output.push_back(result);
}
if (output.size())
return true;
else
return false;
}
void YOLO::drawPred(Mat &img, vector result, vector color) {
for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++)
{
int left, top;
left = result[i].box.x;
top = result[i].box.y;
int color_num = i;
rectangle(img, result[i].box, color[result[i].id], 2, 8);
string label = className[result[i].id] + ":" + to_string(result[i].confidence);
int baseLine;
Size labelSize = getTextSize(label, FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1, &baseLine);
top = max(top, labelSize.height);
putText(img, label, Point(left, top), FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, color[result[i].id], 1);
}
cv::resize(img, img, cv::Size(1400, 800));
imshow("test", img);
waitKey();
} main.cpp
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "yolo5.h"
using namespace cv;
using namespace cv::dnn;
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string img_path = "./test.jpg";
string model_path = "./best.onnx";
YOLO test;
Net net;
if (test.readModel(net, model_path, false)) {
cout << "read net ok!" << endl;
}
else {
return -1;
}
//生成随机颜色
vector color;
srand(time(0));
for (int i = 0; i < 80; i++) {
int b = rand() % 256;
int g = rand() % 256;
int r = rand() % 256;
color.push_back(Scalar(b, g, r));
}
vector result;
Mat img = imread(img_path);
if (test.Detect(img, net, result)) {
test.drawPred(img, result, color);
}
else {
cout << "Detect Failed!" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
我做了一个夜间车辆检测,下面贴出运行结果。感觉检测结果边框有点变形,回头再看看哪出错了。模型文件可在我的博客资源里下载yolov5夜间车辆检测模型-深度学习文档类资源-CSDN文库