TensorFlow多任务学习以及验证码识别
一、TensorFlow多任务学习
Multi-task Learning交替训练示意图:
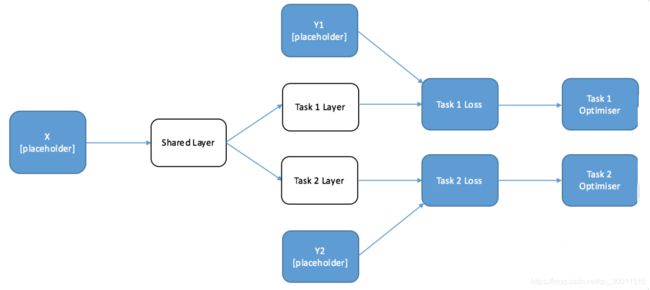
Multi-task Learning – 联合训练示意图:
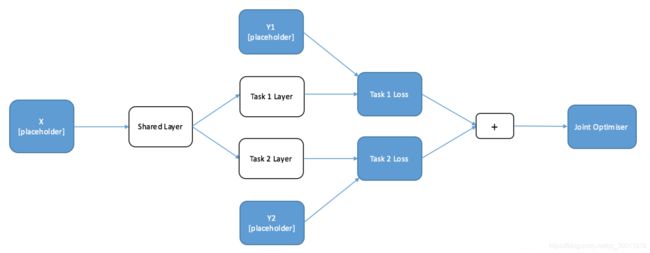
二、TensorFlow验证码识别
验证码生成代码示例:
# 验证码生成库
from captcha.image import ImageCaptcha # pip install captcha
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import random
import sys
number = ['0','1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9']
# alphabet = ['a','b','c','d','e','f','g','h','i','j','k','l','m','n','o','p','q','r','s','t','u','v','w','x','y','z']
# ALPHABET = ['A','B','C','D','E','F','G','H','I','J','K','L','M','N','O','P','Q','R','S','T','U','V','W','X','Y','Z']
def random_captcha_text(char_set=number, captcha_size=4):
# 验证码列表
captcha_text = []
for i in range(captcha_size):
#随机选择
c = random.choice(char_set)
#加入验证码列表
captcha_text.append(c)
return captcha_text
# 生成字符对应的验证码
def gen_captcha_text_and_image():
image = ImageCaptcha()
#获得随机生成的验证码
captcha_text = random_captcha_text()
#把验证码列表转为字符串
captcha_text = ''.join(captcha_text)
#生成验证码
captcha = image.generate(captcha_text)
image.write(captcha_text, 'captcha/images/' + captcha_text + '.jpg') # 写到文件
#数量少于10000,因为重名
num = 10000
if __name__ == '__main__':
for i in range(num):
gen_captcha_text_and_image()
sys.stdout.write('\r>> Creating image %d/%d' % (i+1, num))
sys.stdout.flush()
sys.stdout.write('\n')
sys.stdout.flush()
print("生成完毕")
生成tfrecord文件代码示例:
import tensorflow as tf
import os
import random
import math
import sys
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
# In[2]:
#验证集数量
_NUM_TEST = 500
#随机种子
_RANDOM_SEED = 0
#数据集路径
DATASET_DIR = "D:/Tensorflow/captcha/images/"
#tfrecord文件存放路径
TFRECORD_DIR = "D:/Tensorflow/captcha/"
#判断tfrecord文件是否存在
def _dataset_exists(dataset_dir):
for split_name in ['train', 'test']:
output_filename = os.path.join(dataset_dir,split_name + '.tfrecords')
if not tf.gfile.Exists(output_filename):
return False
return True
#获取所有验证码图片
def _get_filenames_and_classes(dataset_dir):
photo_filenames = []
for filename in os.listdir(dataset_dir):
#获取文件路径
path = os.path.join(dataset_dir, filename)
photo_filenames.append(path)
return photo_filenames
def int64_feature(values):
if not isinstance(values, (tuple, list)):
values = [values]
return tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=values))
def bytes_feature(values):
return tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[values]))
def image_to_tfexample(image_data, label0, label1, label2, label3):
#Abstract base class for protocol messages.
return tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature={
'image': bytes_feature(image_data),
'label0': int64_feature(label0),
'label1': int64_feature(label1),
'label2': int64_feature(label2),
'label3': int64_feature(label3),
}))
#把数据转为TFRecord格式
def _convert_dataset(split_name, filenames, dataset_dir):
assert split_name in ['train', 'test']
with tf.Session() as sess:
#定义tfrecord文件的路径+名字
output_filename = os.path.join(TFRECORD_DIR,split_name + '.tfrecords')
with tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(output_filename) as tfrecord_writer:
for i,filename in enumerate(filenames):
try:
sys.stdout.write('\r>> Converting image %d/%d' % (i+1, len(filenames)))
sys.stdout.flush()
#读取图片
image_data = Image.open(filename)
#根据模型的结构resize
image_data = image_data.resize((224, 224))
#灰度化
image_data = np.array(image_data.convert('L'))
#将图片转化为bytes
image_data = image_data.tobytes()
#获取label
labels = filename.split('/')[-1][0:4]
num_labels = []
for j in range(4):
num_labels.append(int(labels[j]))
#生成protocol数据类型
example = image_to_tfexample(image_data, num_labels[0], num_labels[1], num_labels[2], num_labels[3])
tfrecord_writer.write(example.SerializeToString())
except IOError as e:
print('Could not read:',filename)
print('Error:',e)
print('Skip it\n')
sys.stdout.write('\n')
sys.stdout.flush()
#判断tfrecord文件是否存在
if _dataset_exists(TFRECORD_DIR):
print('tfcecord文件已存在')
else:
#获得所有图片
photo_filenames = _get_filenames_and_classes(DATASET_DIR)
#把数据切分为训练集和测试集,并打乱
random.seed(_RANDOM_SEED)
random.shuffle(photo_filenames)
training_filenames = photo_filenames[_NUM_TEST:]
testing_filenames = photo_filenames[:_NUM_TEST]
#数据转换
_convert_dataset('train', training_filenames, DATASET_DIR)
_convert_dataset('test', testing_filenames, DATASET_DIR)
print('生成tfcecord文件')
验证码识别代码示例:
import os
import tensorflow as tf
from PIL import Image
from nets import nets_factory
import numpy as np
# In[2]:
# 不同字符数量
CHAR_SET_LEN = 10
# 图片高度
IMAGE_HEIGHT = 60
# 图片宽度
IMAGE_WIDTH = 160
# 批次
BATCH_SIZE = 25
# tfrecord文件存放路径
TFRECORD_FILE = "D:/Tensorflow/captcha/train.tfrecords"
# placeholder
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 224, 224])
y0 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None])
y1 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None])
y2 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None])
y3 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None])
# 学习率
lr = tf.Variable(0.003, dtype=tf.float32)
# 从tfrecord读出数据
def read_and_decode(filename):
# 根据文件名生成一个队列
filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer([filename])
reader = tf.TFRecordReader()
# 返回文件名和文件
_, serialized_example = reader.read(filename_queue)
features = tf.parse_single_example(serialized_example,
features={
'image' : tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string),
'label0': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
'label1': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
'label2': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
'label3': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
})
# 获取图片数据
image = tf.decode_raw(features['image'], tf.uint8)
# tf.train.shuffle_batch必须确定shape
image = tf.reshape(image, [224, 224])
# 图片预处理
image = tf.cast(image, tf.float32) / 255.0
image = tf.subtract(image, 0.5)
image = tf.multiply(image, 2.0)
# 获取label
label0 = tf.cast(features['label0'], tf.int32)
label1 = tf.cast(features['label1'], tf.int32)
label2 = tf.cast(features['label2'], tf.int32)
label3 = tf.cast(features['label3'], tf.int32)
return image, label0, label1, label2, label3
# In[3]:
# 获取图片数据和标签
image, label0, label1, label2, label3 = read_and_decode(TFRECORD_FILE)
#使用shuffle_batch可以随机打乱
image_batch, label_batch0, label_batch1, label_batch2, label_batch3 = tf.train.shuffle_batch(
[image, label0, label1, label2, label3], batch_size = BATCH_SIZE,
capacity = 50000, min_after_dequeue=10000, num_threads=1)
#定义网络结构
train_network_fn = nets_factory.get_network_fn(
'alexnet_v2',
num_classes=CHAR_SET_LEN,
weight_decay=0.0005,
is_training=True)
with tf.Session() as sess:
# inputs: a tensor of size [batch_size, height, width, channels]
X = tf.reshape(x, [BATCH_SIZE, 224, 224, 1])
# 数据输入网络得到输出值
logits0,logits1,logits2,logits3,end_points = train_network_fn(X)
# 把标签转成one_hot的形式
one_hot_labels0 = tf.one_hot(indices=tf.cast(y0, tf.int32), depth=CHAR_SET_LEN)
one_hot_labels1 = tf.one_hot(indices=tf.cast(y1, tf.int32), depth=CHAR_SET_LEN)
one_hot_labels2 = tf.one_hot(indices=tf.cast(y2, tf.int32), depth=CHAR_SET_LEN)
one_hot_labels3 = tf.one_hot(indices=tf.cast(y3, tf.int32), depth=CHAR_SET_LEN)
# 计算loss
loss0 = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits0,labels=one_hot_labels0))
loss1 = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits1,labels=one_hot_labels1))
loss2 = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits2,labels=one_hot_labels2))
loss3 = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits3,labels=one_hot_labels3))
# 计算总的loss
total_loss = (loss0+loss1+loss2+loss3)/4.0
# 优化total_loss
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=lr).minimize(total_loss)
# 计算准确率
correct_prediction0 = tf.equal(tf.argmax(one_hot_labels0,1),tf.argmax(logits0,1))
accuracy0 = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction0,tf.float32))
correct_prediction1 = tf.equal(tf.argmax(one_hot_labels1,1),tf.argmax(logits1,1))
accuracy1 = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction1,tf.float32))
correct_prediction2 = tf.equal(tf.argmax(one_hot_labels2,1),tf.argmax(logits2,1))
accuracy2 = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction2,tf.float32))
correct_prediction3 = tf.equal(tf.argmax(one_hot_labels3,1),tf.argmax(logits3,1))
accuracy3 = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction3,tf.float32))
# 用于保存模型
saver = tf.train.Saver()
# 初始化
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
# 创建一个协调器,管理线程
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
# 启动QueueRunner, 此时文件名队列已经进队
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess, coord=coord)
for i in range(6001):
# 获取一个批次的数据和标签
b_image, b_label0, b_label1 ,b_label2 ,b_label3 = sess.run([image_batch, label_batch0, label_batch1, label_batch2, label_batch3])
# 优化模型
sess.run(optimizer, feed_dict={
x: b_image, y0:b_label0, y1: b_label1, y2: b_label2, y3: b_label3})
# 每迭代20次计算一次loss和准确率
if i % 20 == 0:
# 每迭代2000次降低一次学习率
if i%2000 == 0:
sess.run(tf.assign(lr, lr/3))
acc0,acc1,acc2,acc3,loss_ = sess.run([accuracy0,accuracy1,accuracy2,accuracy3,total_loss],feed_dict={
x: b_image,
y0: b_label0,
y1: b_label1,
y2: b_label2,
y3: b_label3})
learning_rate = sess.run(lr)
print ("Iter:%d Loss:%.3f Accuracy:%.2f,%.2f,%.2f,%.2f Learning_rate:%.4f" % (i,loss_,acc0,acc1,acc2,acc3,learning_rate))
# 保存模型
# if acc0 > 0.90 and acc1 > 0.90 and acc2 > 0.90 and acc3 > 0.90:
if i==6000:
saver.save(sess, "./captcha/models/crack_captcha.model", global_step=i)
break
# 通知其他线程关闭
coord.request_stop()
# 其他所有线程关闭之后,这一函数才能返回
coord.join(threads)