机器学习(五)Python+OpenCV+dlib实现人脸识别
Python+OpenCV+dlib实现人脸识别
IDE:Jupyter Notebook(Anaconda3)
Python版本:Python 3.8
本机环境:Windows 10
〇、原理概览
调用dlib库来进行人脸识别,调用预测器 “shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat”进行68点标定人脸,并用opencv的库函数来进行简单的图像处理
一·、Windows系统安装OpenCV和dlib库
- 打开Anaconda Prompt命令框,输入
python -V得到当前的python版本
-
使用命令安装opencv:
pip install opencv_python -
在dlib官网下载对应python版本的dlib
这里提供两个比较普遍的
dlib版本包python3.8的链接:
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1kLn0uEqO5xinuTMZzk3fFA
提取码:kh99python3.7的链接:
https://pan.baidu.com/s/14cxfDkC2dODyncLAZ3bwaQ
提取码:w8hp本连接出自https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_56102526/article/details/121119472平行叶子的博客
-
输入
pip install dlib -版本报名.whl来安装dlib,比如我要安装上面下载的python3.8的dlib包:pip install dlib-19.19.0-cp38-cp38-win_amd64.whl
二、人脸识别
使用jupyter notebook创建新项目,输入下列代码,实现最基本的人脸识别
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Wed Oct 27 03:15:10 2021
@author: GT72VR
"""
import numpy as np
import cv2
import dlib
import os
import sys
import random
# dlib预测器
detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector()
predictor = dlib.shape_predictor('shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat')
ok = True
# 打开摄像头 参数为输入流,可以为摄像头或视频文件
camera = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
#如果打开不了摄像头可以使用下面函数对视频进行人脸采集
#camera = cv2.VideoCapture('video.mp4')
while ok:
# 读取摄像头中的图像,ok为是否读取成功的判断参数
ok, img = camera.read()
# 转换成灰度图像
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
rects = detector(img_gray, 0)
for i in range(len(rects)):
landmarks = np.matrix([[p.x, p.y] for p in predictor(img, rects[i]).parts()])
# 画特征点
for idx, point in enumerate(landmarks):
# 68点的坐标
pos = (point[0, 0], point[0, 1])
# 利用cv2.circle给每个特征点画一个圈,共68个
cv2.circle(img, pos, 1, color=(0, 255, 0))
# 利用cv2.putText输出1-68
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX
cv2.putText(img, str(idx + 1), pos, font, 0.3, (0, 0, 255), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.imshow('video', img)
k = cv2.waitKey(1)
if k == 27: # 按下ESC退出
break
camera.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
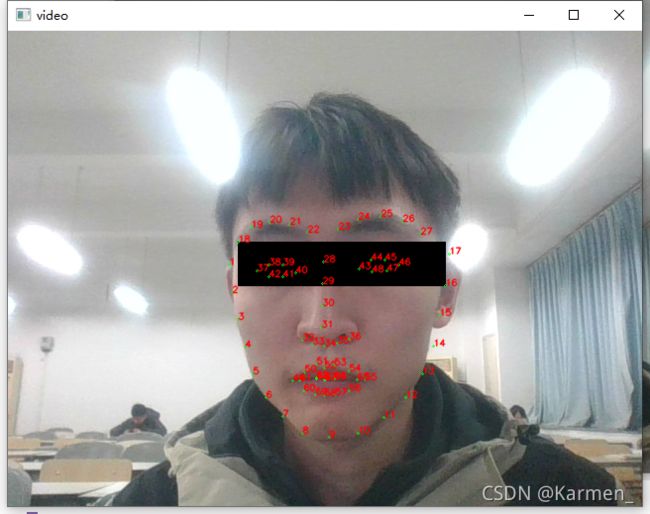
点击运行,等待片刻后会在菜单栏中出现一个新窗口,点开得到:
人长得不够帅,这里使用了
cv2.rectangle函数给自己简单打了个码
三、打上马赛克
实现人脸识别是不够好玩的,我们要整点节目效果,就像现在一些市面上的美颜相机的动态滤镜一样,可以给自己添加一副墨镜啥的
- 将下列画图代码添加到源文件中,可以就放在定义点坐标之后
# 画眼镜
cv2.circle(img, (point_list[41][0], point_list[41][1]), int(3 * size), (0, 0, 0), -1) #-1表示实心圆,墨镜打底
cv2.circle(img, (point_list[41][0], point_list[41][1]), int(3 * size), (255, 255, 255), 10) #10表示边框宽度有10个像素点,用来画边框
cv2.circle(img, (point_list[46][0], point_list[46][1]), int(3 * size), (0, 0, 0), -1)
cv2.circle(img, (point_list[46][0], point_list[46][1]), int(3 * size), (255, 255, 255), 10)
# 画眼镜框
cv2.line(img, point_39, point_42, (0, 0, 0), 4)
- 运行,得到以下效果
-
全部代码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ Created on Wed Oct 27 03:15:10 2021 @author: GT72VR """ import numpy as np import cv2 import dlib import os import sys import random # dlib预测器 detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector() predictor = dlib.shape_predictor('shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat') ok = True # 打开摄像头 参数为输入流,可以为摄像头或视频文件 camera = cv2.VideoCapture(0) #camera = cv2.VideoCapture('video.mp4') while ok: # 读取摄像头中的图像,ok为是否读取成功的判断参数 ok, img = camera.read() # 转换成灰度图像 img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) rects = detector(img_gray, 0) for i in range(len(rects)): landmarks = np.matrix([[p.x, p.y] for p in predictor(img, rects[i]).parts()]) # 矩阵转为列表 point_list=landmarks.getA() # 点坐标 point_37 = (point_list[37][0],point_list[37][1]) point_38 = (point_list[38][0], point_list[38][1]) # 比例系数,37,38两点距离 size = (pow(pow(point_38[1] - point_37[1], 2) + pow(point_38[0] - point_37[0], 2), 0.5)) # 点坐标 point_39 = (point_list[39][0], point_list[39][1]) point_42 = (point_list[42][0], point_list[42][1]) # 画眼镜 cv2.circle(img, (point_list[41][0], point_list[41][1]), int(3 * size), (0, 0, 0), -1) cv2.circle(img, (point_list[41][0], point_list[41][1]), int(3 * size), (255, 255, 255), 10) cv2.circle(img, (point_list[46][0], point_list[46][1]), int(3 * size), (0, 0, 0), -1) cv2.circle(img, (point_list[46][0], point_list[46][1]), int(3 * size), (255, 255, 255), 10) # 画眼镜框 cv2.line(img, point_39, point_42, (0, 0, 0), 4) # 画特征点 for idx, point in enumerate(landmarks): # 68点的坐标 pos = (point[0, 0], point[0, 1]) # 利用cv2.circle给每个特征点画一个圈,共68个 cv2.circle(img, pos, 1, color=(0, 255, 0)) # 利用cv2.putText输出1-68 font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX cv2.putText(img, str(idx + 1), pos, font, 0.3, (0, 0, 255), 1, cv2.LINE_AA) cv2.imshow('video', img) k = cv2.waitKey(1) if k == 27: # 按下ESC退出 break camera.release() cv2.destroyAllWindows()
四、总结
通过学习数据库shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat,python能够使用仅仅几十行代码就能完成一个简单的人脸数据采集,并结合Opencv图像编程可以将采集内容更加直观地呈现在我们的面前,还可以使用cv2的画图函数对采集到的人脸进行简单的图像处理,拿来整活儿。
五、参考文章
平行叶子: python3+opencv3.4+dlib库编程实现人脸特征点标定
一只特立独行的猪: python+opencv+dlib实现人脸识别
醉意丶千层梦: 基于OpenCv+Python+Dlib实现简单人脸数据采集