最大堆和最小堆和平衡二叉树_最小堆二叉树
最大堆和最小堆和平衡二叉树
A Min Heap Binary Tree is a Binary Tree where the root node has the minimum key in the tree.
最小堆二叉树是二叉树,其中根节点在树中具有最小密钥。
The above definition holds true for all sub-trees in the tree. This is called the Min Heap property.
上面的定义对于树中的所有子树都适用。 这称为“ 最小堆”属性。
Almost every node other than the last two layers must have two children. That is, this is almost a complete binary tree, with the exception of the last 2 layers.
除了最后两层以外,几乎每个节点都必须有两个子节点。 也就是说,除了最后两层外,这几乎是完整的二叉树。
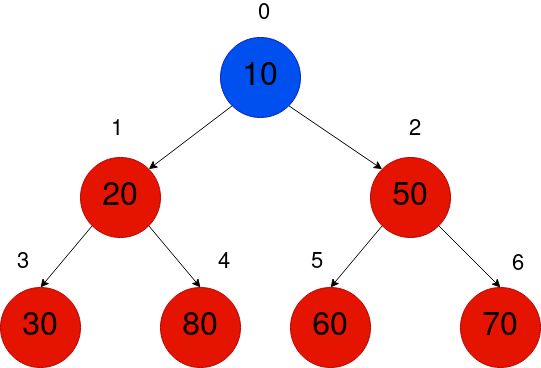
The below tree is an example of a min heap binary tree since the above two properties hold.
由于上面的两个属性成立,因此下面的树是最小堆二叉树的示例。
Now that we’ve covered what a min heap tree is, let’s look at how we can represent it.
现在我们已经了解了最小堆树是什么,让我们看看如何表示它。
最小堆树的表示 (Representation of a Min Heap Tree)
A Min Heap Binary Tree is commonly represented as an array, which is indexed according to the below format:
最小堆二叉树通常表示为数组,并根据以下格式进行索引:
| Current Node | arr[i] |
| Parent Node | arr[(i-1)/2] |
| Left Child | arr[(2*i) + 1] |
| Right Child | arr[(2*i )+ 2] |
| 当前节点 | arr[i] |
| 父节点 | arr[(i-1)/2] |
| 左子 | arr[(2*i) + 1] |
| 合适的孩子 | arr[(2*i )+ 2] |
The root of the whole tree is at arr[0].
整个树的根位于arr[0] 。
We will use the indexing as shown in the below figure. It’s not very hard to find the pattern here, which will match with the above table.
我们将使用下图所示的索引。 在此处找到与上表匹配的模式不是很困难。
This indexing follows a Level Order Traversal of the Binary Tree, so a Binary Heap array is a Binary Tree using a level order traversal.
该索引遵循二进制树的级别顺序遍历 ,因此,二进制堆数组是使用级别顺序遍历的二进制树。
The above figure shows the array representation of the Min Heap Tree.
上图显示了最小堆树的数组表示形式。
Now that we’ve covered the concepts, let’s move onto implementing this in C!
现在我们已经涵盖了概念,让我们继续使用C来实现它!
实施最小堆树 (Implementing a Min Heap Tree)
We will use the array representation to build the tree. Let’s start writing the structure for the Min Heap.
我们将使用数组表示法来构建树。 让我们开始编写Min Heap的结构。
typedef struct MinHeap MinHeap;
struct MinHeap {
int* arr;
// Current Size of the Heap
int size;
// Maximum capacity of the heap
int capacity;
};
We’ll have an array of elements, and a size, which gets updated as elements are being inserted or deleted.
我们将有一个元素数组和一个大小,该大小会随着元素的插入或删除而更新。
The array also has a capacity, which indicates the maximum size of the array.
阵列还具有容量,该容量指示阵列的最大大小。
There are a few functions that we need to write to indicate that we are representing a Min Heap Tree, like finding the parent, and the children.
我们需要编写一些函数来表示我们正在代表最小堆树,例如查找父级和子级。
int parent(int i) {
// Get the index of the parent
return (i - 1) / 2;
}
int left_child(int i) {
return (2*i + 1);
}
int right_child(int i) {
return (2*i + 2);
}
int get_min(MinHeap* heap) {
// Return the root node element,
// since that's the minimum, by the min-heap
// property
return heap->arr[0];
}
We’ll write functions to initialize and free the heap.
我们将编写函数来初始化和释放堆。
MinHeap* init_minheap(int capacity) {
MinHeap* minheap = (MinHeap*) calloc (1, sizeof(MinHeap));
minheap->arr = (int*) calloc (capacity, sizeof(int));
minheap->capacity = capacity;
minheap->size = 0;
return minheap;
}
void free_minheap(MinHeap* heap) {
if (!heap)
return;
free(heap->arr);
free(heap);
}
With that covered, let’s now move on to how we can insert elements!
讲完这些后,让我们继续介绍如何插入元素!
插入最小堆 (Inserting onto the Min Heap)
The insertion algorithm is simple. This inserts an element into the tree.
插入算法很简单。 这会将元素插入树中。
Breaking down the algorithm:
分解算法:
- First, always insert at the bottom of the tree. The initial position of the inserted element is at the last level. 首先,请始终插入树的底部。 插入元素的初始位置在最后一层。
- We will now need to update the position of this element so that the min-heap property is satisfied. 现在,我们将需要更新此元素的位置,以便满足min-heap属性。
- Since the root node of every sub-tree must be the minimum, check the sub-tree of its immediate parent. 由于每个子树的根节点必须是最小的,因此请检查其直接父级的子树。
- If the parent is greater than this inserted element, we need to update its position by swapping it. 如果父级大于此插入的元素,则需要通过交换来更新其位置。
- But we are not yet done, since the min-heap property may be violated of the updated node’s sub-tree! 但是我们还没有完成,因为min-heap属性可能会违反更新节点的子树!
- We need to keep swapping until we reach the root node, after which we are done. 我们需要继续交换,直到到达根节点为止。
To understand this procedure, let’s take an example.
为了理解此过程,我们举一个例子。
Consider the tree below, having only one element.
考虑下面的树,它只有一个元素。
Let’s insert the element 40. Since there is only one element, it inserts to the bottom, and we observe that the min-heap property is satisfies, since 10 < 40. So there is no need to swap.
让我们插入元素40。由于只有一个元素,因此它插入到底部,并且我们观察到min-heap属性满足,因为10 <40。因此不需要交换。
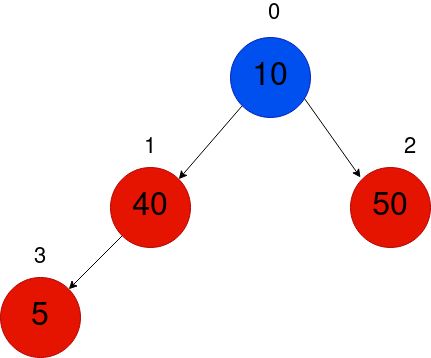
Next, we’ll insert 50. A similar procedure follows.
接下来,我们将插入50。遵循类似的过程。
Next, we’ll insert 5. So now, we first insert to the bottom of the tree, at index 3.
接下来,我们将插入5。因此,现在,我们首先在树的底部插入索引3。
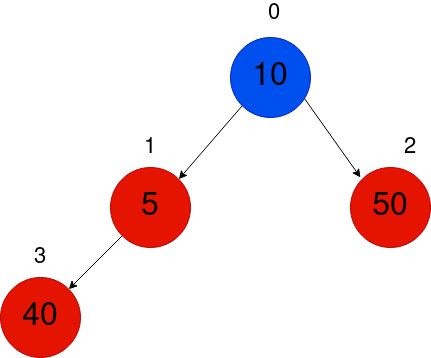
The min heap property is violated for the sub-tree 1-3, and therefore, for the whole tree. So, we must keep swapping with the parent until we reach the root.
对于子树1-3,因此对于整个树,都违反了min heap属性。 因此,我们必须继续与父交换,直到到达根为止。
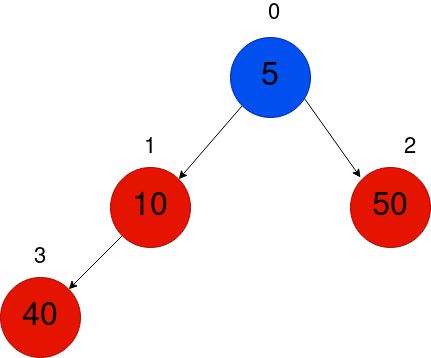
So, we need one more swap, since again, the min-heap property is violated for the sub-tree rooted at node 0.
因此,我们需要再进行一次交换,因为同样,对于以节点0为根的子树,min-heap属性被违反了。
Alright. Now that we have visualized it, let’s write it down!
好的。 现在我们已经可视化了,让我们写下来吧!
MinHeap* insert_minheap(MinHeap* heap, int element) {
// Inserts an element to the min heap
// We first add it to the bottom (last level)
// of the tree, and keep swapping with it's parent
// if it is lesser than it. We keep doing that until
// we reach the root node. So, we will have inserted the
// element in it's proper position to preserve the min heap property
if (heap->size == heap->capacity) {
fprintf(stderr, "Cannot insert %d. Heap is already full!\n", element);
return heap;
}
// We can add it. Increase the size and add it to the end
heap->size++;
heap->arr[heap->size - 1] = element;
// Keep swapping until we reach the root
int curr = heap->size - 1;
// As long as you aren't in the root node, and while the
// parent of the last element is greater than it
while (curr > 0 && heap->arr[parent(curr)] > heap->arr[curr]) {
// Swap
int temp = heap->arr[parent(curr)];
heap->arr[parent(curr)] = heap->arr[curr];
heap->arr[curr] = temp;
// Update the current index of element
curr = parent(curr);
}
return heap;
}
We’ll now implement the deletion method.
现在,我们将实现删除方法。
从最小堆中删除 (Delete from the Min Heap)
Before we look at deleting an element any index, since the min-heap is very closely associated with the root, we will look at deleting the root first.
在考虑删除任何索引元素之前,由于min-heap与根紧密相关,因此我们将首先考虑删除根。
To delete the minimum element (i.e the root), we will do the following:
要删除最小元素(即根),我们将执行以下操作:
- Update the root as the last element of the array (tree) 将根更新为数组(树)的最后一个元素
- We will now remove the last element at the bottom. This is similar to swapping and deleting at the end! Only because we don’t care about the root value anymore, we simply update it instead. 现在,我们将删除底部的最后一个元素。 这类似于最后交换和删除! 只是因为我们不再关心根值,我们才更新它。
- The problem again is that we need to maintain the min-heap property. 再次出现的问题是,我们需要维护min-heap属性。
- So we must ensure that the whole tree maintains this property. We will use a function called
heapify()to do this for us. 因此,我们必须确保整个树都保留此属性。 我们将使用一个称为heapify()的函数来为我们执行此操作。
So, we know that the deletion method will be complete after we do the heapify() method as well.
因此,我们知道删除方法也将在完成heapify()方法之后完成。
MinHeap* delete_minimum(MinHeap* heap) {
// Deletes the minimum element, at the root
if (!heap || heap->size == 0)
return heap;
int size = heap->size;
int last_element = heap->arr[size-1];
// Update root value with the last element
heap->arr[0] = last_element;
// Now remove the last element, by decreasing the size
heap->size--;
size--;
// We need to call heapify(), to maintain the min-heap
// property
heap = heapify(heap, 0);
return heap;
}
heapify()过程 (The heapify() procedure)
This function takes in an element index index, and maintains the min heap property, by swapping with the smallest element of its immediate sub-tree.
此函数通过交换其直接子树的最小元素来获取元素索引index ,并维护min heap属性。
The resulting tree will satisfy the min-heap property.
生成的树将满足min-heap属性。
This involves finding the minimum element of the sub-tree and performing a swap with the current element.
这涉及找到子树的最小元素,并与当前元素进行交换。
After this, we still need to make sure the entire tree satisfies this. So, we need to recursively call the procedure on the smallest element, until we reach the root!
此后,我们仍然需要确保整个树都满足此要求。 因此,我们需要递归地调用最小元素上的过程,直到到达根为止!
MinHeap* heapify(MinHeap* heap, int index) {
// Rearranges the heap as to maintain
// the min-heap property
if (heap->size <= 1)
return heap;
int left = left_child(index);
int right = right_child(index);
// Variable to get the smallest element of the subtree
// of an element an index
int smallest = index;
// If the left child is smaller than this element, it is
// the smallest
if (left < heap->size && heap->arr[left] < heap->arr[index])
smallest = left;
// Similarly for the right, but we are updating the smallest element
// so that it will definitely give the least element of the subtree
if (right < heap->size && heap->arr[right] < heap->arr[smallest])
smallest = right;
// Now if the current element is not the smallest,
// swap with the current element. The min heap property
// is now satisfied for this subtree. We now need to
// recursively keep doing this until we reach the root node,
// the point at which there will be no change!
if (smallest != index)
{
int temp = heap->arr[index];
heap->arr[index] = heap->arr[smallest];
heap->arr[smallest] = temp;
heap = heapify(heap, smallest);
}
return heap;
}
We can now extend this delete_minimum() function, to delete any element.
现在,我们可以扩展此delete_minimum()函数,以删除任何元素。
删除任意元素 (Deleting an Arbitrary Element)
This involves only setting the desired element to the minimum possible value, that will be get_min() - 1, since it must be lesser than the current minimum.
这仅涉及将所需元素设置为可能的最小值,即get_min() - 1 ,因为它必须小于当前的最小值。
We will now keep swapping until we update the position so that the new root is this element.
现在,我们将继续交换直到更新位置,以便新的根成为该元素。
Now, we’re back at our old delete_minimum() function! We can simply delete the new root!
现在,我们回到旧的delete_minimum()函数! 我们可以简单地删除新的根目录!
With this, our entire deletion procedure will look like this:
这样,我们的整个删除过程将如下所示:
MinHeap* delete_element(MinHeap* heap, int index) {
// Deletes an element, indexed by index
// Ensure that it's lesser than the current root
heap->arr[index] = get_min(heap) - 1;
// Now keep swapping, until we update the tree
int curr = index;
while (curr > 0 && heap->arr[parent(curr)] > heap->arr[curr]) {
int temp = heap->arr[parent(curr)];
heap->arr[parent(curr)] = heap->arr[curr];
heap->arr[curr] = temp;
curr = parent(curr);
}
// Now simply delete the minimum element
heap = delete_minimum(heap);
return heap;
}
Phew! We’re finally done. I’ll now show you the entire code until now, along with the print() function, to visualize the tree.
! 我们终于完成了。 现在,直到现在为止,我将向您展示整个代码以及print()函数,以可视化该树。
完整代码 (The Complete Code)
#include
#include
typedef struct MinHeap MinHeap;
struct MinHeap {
int* arr;
// Current Size of the Heap
int size;
// Maximum capacity of the heap
int capacity;
};
int parent(int i) {
// Get the index of the parent
return (i - 1) / 2;
}
int left_child(int i) {
return (2*i + 1);
}
int right_child(int i) {
return (2*i + 2);
}
int get_min(MinHeap* heap) {
// Return the root node element,
// since that's the minimum
return heap->arr[0];
}
MinHeap* init_minheap(int capacity) {
MinHeap* minheap = (MinHeap*) calloc (1, sizeof(MinHeap));
minheap->arr = (int*) calloc (capacity, sizeof(int));
minheap->capacity = capacity;
minheap->size = 0;
return minheap;
}
MinHeap* insert_minheap(MinHeap* heap, int element) {
// Inserts an element to the min heap
// We first add it to the bottom (last level)
// of the tree, and keep swapping with it's parent
// if it is lesser than it. We keep doing that until
// we reach the root node. So, we will have inserted the
// element in it's proper position to preserve the min heap property
if (heap->size == heap->capacity) {
fprintf(stderr, "Cannot insert %d. Heap is already full!\n", element);
return heap;
}
// We can add it. Increase the size and add it to the end
heap->size++;
heap->arr[heap->size - 1] = element;
// Keep swapping until we reach the root
int curr = heap->size - 1;
// As long as you aren't in the root node, and while the
// parent of the last element is greater than it
while (curr > 0 && heap->arr[parent(curr)] > heap->arr[curr]) {
// Swap
int temp = heap->arr[parent(curr)];
heap->arr[parent(curr)] = heap->arr[curr];
heap->arr[curr] = temp;
// Update the current index of element
curr = parent(curr);
}
return heap;
}
MinHeap* heapify(MinHeap* heap, int index) {
// Rearranges the heap as to maintain
// the min-heap property
if (heap->size <= 1)
return heap;
int left = left_child(index);
int right = right_child(index);
// Variable to get the smallest element of the subtree
// of an element an index
int smallest = index;
// If the left child is smaller than this element, it is
// the smallest
if (left < heap->size && heap->arr[left] < heap->arr[index])
smallest = left;
// Similarly for the right, but we are updating the smallest element
// so that it will definitely give the least element of the subtree
if (right < heap->size && heap->arr[right] < heap->arr[smallest])
smallest = right;
// Now if the current element is not the smallest,
// swap with the current element. The min heap property
// is now satisfied for this subtree. We now need to
// recursively keep doing this until we reach the root node,
// the point at which there will be no change!
if (smallest != index)
{
int temp = heap->arr[index];
heap->arr[index] = heap->arr[smallest];
heap->arr[smallest] = temp;
heap = heapify(heap, smallest);
}
return heap;
}
MinHeap* delete_minimum(MinHeap* heap) {
// Deletes the minimum element, at the root
if (!heap || heap->size == 0)
return heap;
int size = heap->size;
int last_element = heap->arr[size-1];
// Update root value with the last element
heap->arr[0] = last_element;
// Now remove the last element, by decreasing the size
heap->size--;
size--;
// We need to call heapify(), to maintain the min-heap
// property
heap = heapify(heap, 0);
return heap;
}
MinHeap* delete_element(MinHeap* heap, int index) {
// Deletes an element, indexed by index
// Ensure that it's lesser than the current root
heap->arr[index] = get_min(heap) - 1;
// Now keep swapping, until we update the tree
int curr = index;
while (curr > 0 && heap->arr[parent(curr)] > heap->arr[curr]) {
int temp = heap->arr[parent(curr)];
heap->arr[parent(curr)] = heap->arr[curr];
heap->arr[curr] = temp;
curr = parent(curr);
}
// Now simply delete the minimum element
heap = delete_minimum(heap);
return heap;
}
void print_heap(MinHeap* heap) {
// Simply print the array. This is an
// inorder traversal of the tree
printf("Min Heap:\n");
for (int i=0; isize; i++) {
printf("%d -> ", heap->arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
void free_minheap(MinHeap* heap) {
if (!heap)
return;
free(heap->arr);
free(heap);
}
int main() {
// Capacity of 10 elements
MinHeap* heap = init_minheap(10);
insert_minheap(heap, 40);
insert_minheap(heap, 50);
insert_minheap(heap, 5);
print_heap(heap);
// Delete the heap->arr[1] (50)
delete_element(heap, 1);
print_heap(heap);
free_minheap(heap);
return 0;
}
Output
输出量
Min Heap:
5 -> 50 -> 40 ->
Min Heap:
5 -> 40 ->
实施的时间复杂度 (Time Complexity of Implementation)
The time complexities of the above procedures are mentioned below:
上述过程的时间复杂度如下:
| Function | Time Complexity |
get_min() |
O(1) |
insert_minheap() |
O(logN) |
delete_minimum() |
Same as insert – O(logN) |
heapify() |
O(logN) |
delete_element() |
O(logN) |
| 功能 | 时间复杂度 |
get_min() |
O(1) |
insert_minheap() |
O(logN) |
delete_minimum() |
与插入相同– O(logN) |
heapify() |
O(logN) |
delete_element() |
O(logN) |
下载代码 (Download the Code)
You can download the complete code as a Github Gist that I have uploaded. If you have any queries regarding this, do ask them in the comment section below!
您可以下载完整的代码作为我上传的Github Gist 。 如果对此有任何疑问,请在下面的评论部分中提问!
结论 (Conclusion)
In this article, we learned how we can represent a Min Heap Binary Tree, and also look at an implementation in C.
在本文中,我们学习了如何表示Min Heap Binary Tree,以及如何用C实现。
参考资料 (References)
- An illustration of Heaps, from Cormen 堆的插图,来自Cormen
- Wikipedia article on Binary Heaps 维基百科有关二进制堆的文章
翻译自: https://www.journaldev.com/36805/min-heap-binary-tree
最大堆和最小堆和平衡二叉树