只谈谈,不全覆盖
简单介绍重入锁
ReentrantLock为并发包多数的类提供底层应用。重要性不言而喻,重入锁实现的基石就是AbstractQueuedSynchronizer。所以把AbstractQueuedSynchronizer研究透,就可以摸清重入锁是如何实现的。
ReentrantLock的Sync内部类继承了AbstractQueuedSynchronizer,ReentrantLock的非公平锁与公平锁都继承了Sync
- 公平锁
先判断如果当前线程之前的节点没有排队的线程(hasQueuedPredecessors, 就是要乖乖的按顺序排队),则当前线程可以获取锁,否则插入队尾等待唤醒。 - 非公平锁
上来就先抢占锁,如果抢占不到再去尝试获取锁(nonfairTryAcquire,各种抢占谁抢到算谁的),如果获取不到,则插入队尾等待唤醒。
拿公平锁举例
通过一段代码,阐述下,ReentrantLock的公平锁是如果做到线程同步的。
public void lockT() {
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(true); // 公平锁
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { // 模拟5个线程执行
singleThreadPool.execute(() -> {
lock.lock(); // 上锁
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
lock.unlock(); // 解锁
});
}
singleThreadPool.shutdown();
}
- 等待队列节点类
static final class Node {
// 共享模式节点
static final Node SHARED = new Node();
// 独占模式节点
static final Node EXCLUSIVE = null;
// 表示线程已被取消
static final int CANCELLED = 1;
// 表示后续线程需要唤醒(线程可被唤醒的标识)
static final int SIGNAL = -1;
// 表示线程正在等待条件
static final int CONDITION = -2;
// 传播等待状态,表示无条件传播(执行)
static final int PROPAGATE = -3;
// 对于正常同步节点,此字段初始化为0,对于条件节点初始化值应该是 CONDITION -2。waitStatus 对应以上状态值(CANCELLED、SIGNAL 、CONDITION、PROPAGATE)。
volatile int waitStatus;
// 当前节点的前一个节点
volatile Node prev;
// 当前节点的后一个节点
volatile Node next;
// 正在排队的线程节点。在构造时初始化,并在使用后清除
volatile Thread thread;
// 链接下一个正在等待条件的节点,或者指定值为 SHARED 的节点。因为条件队列只有当持有独占模式下时才能被访问,我们只需要一个简单的链队列去保持正在等待条件的节点。他们在这个队列中转换成重新获取(re-acquire)节点。并且条件只能为独占,所以我们使用这个属性来保存特殊的值,表示为一个共享模式
Node nextWaiter;
// 如果节点在共享模式下等待,则返回 true
final boolean isShared() {
return nextWaiter == SHARED;
}
// 返回前一个节点,或者如果为空抛出空指针异常。当前一个不为空时可以使用。
final Node predecessor() throws NullPointerException {
Node p = prev;
if (p == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
else
return p;
}
Node() { // Used to establish initial head or SHARED marker
}
Node(Thread thread, Node mode) { // Used by addWaiter 使用的等待模式
this.nextWaiter = mode;
this.thread = thread;
}
Node(Thread thread, int waitStatus) { // Used by Condition 使用的等待状态
this.waitStatus = waitStatus;
this.thread = thread;
}
}
- 上锁
public void lock() {
sync.lock();
}
final void lock() {
acquire(1);
}
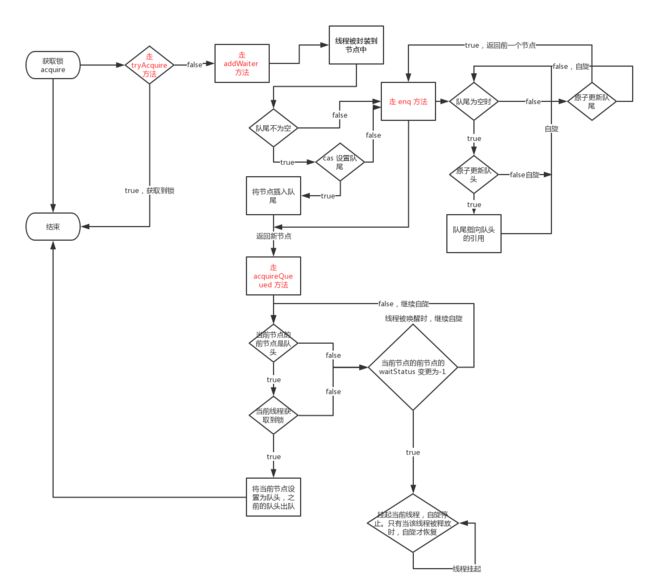
public final void acquire(int arg) {
// 尝试获取锁失败,并且成功加入等待队列。线程自己中断。
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
- 首先尝试获取锁
tryAcquire
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); // 获取当前线程
int c = getState(); // 同步状态, 状态为0时表示锁空闲,当前线程可以获取锁
if (c == 0) {
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) { // 表示当前线程之前的线程是否有排队的,如果有跳出 if,没有就走原子更新状态从0变1.表示该锁已被占用
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current); // 设置独占线程所有者为当前线程
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) { // cpu 时间片,锁重入
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 每次公平锁都要进行这个判断。如果在当前线程之前有一个排队的线程返回true,如果当前线程在队列的头或者队列为空返回false
public final boolean hasQueuedPredecessors() {
// The correctness of this depends on head being initialized
// before tail and on head.next being accurate if the current
// thread is first in queue.
Node t = tail; // Read fields in reverse initialization order
Node h = head;
Node s;
return h != t &&
((s = h.next) == null || s.thread != Thread.currentThread()); // 首尾不相等 并且 s 为队头的下一个节点为空或者 s 的线程不等于当前线程
}
- 获取锁失败后,把当前线程组装成新的节点加入到等待队列中。
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
// 要添加等待队列的线程节点
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// 尝试把新的节点插入在队列的尾部
// pred 指向队尾
Node pred = tail;
// 如果队尾有值,则进行 cas 队尾替换,并移动上一个队尾的指针
if (pred != null) {
// 不为空时,新节点的前一个指向队尾,队尾的后一个节点指向新节点
node.prev = pred;
// 队尾原子替换
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
// 如果队尾为空或者队尾原子替换失败,则走 enq 方法
enq(node);
// 返回新节点
return node;
}
private Node enq(final Node node) { // final 类型的节点
// 自旋
for (;;) {
// t 指向队尾的引用
Node t = tail;
// 如果 t 为空必须要初始化一个空的队头
if (t == null) {
// 成功初始化一个空的队头
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
// 队尾指向空队头的引用
tail = head;
} else { // 如果 t 不为空,将节点插入队尾
// 参数节点的前一个值指向 t
node.prev = t;
// 进行尾部的原子替换,把 t 替换成 node
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
// 成功后,t 的下一个节点指向参数 node
t.next = node;
// 返回前一个节点
return t;
}
}
}
}
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
// 自旋
for (;;) {
// 获取前一个节点
final Node p = node.predecessor();
// 如果是队头并且重新尝试获取锁成功。 当前节点是否是重新获取锁时的当前线程??答案:是的
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
// 队头指向队头的下一个节点,使老队头出列(设置新队头,老队头出列),先进先出
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
// 如果 p 不是队头并且获取锁失败后阻塞当前线程,自旋阻塞
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
// 获取锁失败之后暂挂(阻塞)该线程
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
// 前节点的等待状态
int ws = pred.waitStatus;
// 前一个节点的等待状态为-1,表示当前线程可以安全的阻塞
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)
/*
* 前置节点已经是 SIGNAL 状态,所以当前线程可以被安全阻塞
*/
return true;
if (ws > 0) {
/*
* ws > 0 表示前节点已经被取消,跳过等待状态大于0的前节点并重试
*/
do {
// 跳过状态大于0的节点
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node;
} else {
/*
* 等待状态必须为0或者为 PROPAGATE。我们需要一个等待状态变为 signal,这时还没有阻塞。调用者需要重试,确保它在阻塞前不能获取锁
*/
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL); // 把前一个节点的状态由0或者 PROPAGATE 变为 SIGNAL
}
return false;
}
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
// 挂起(阻塞)当前线程
LockSupport.park(this);
return Thread.interrupted();
}
上锁总结
至此关于重入锁上锁部分的源码分析完毕。其实很简单,并发时只有当线程获取到锁时,才能进行之后的逻辑操作,如果线程没有获取到锁时,则会被加入双向链表中。公平锁获取锁时每次会通过hasQueuedPredecessors方法判断当前线程是否为排队的第一个线程(fifo先进先出)。
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
tryAcquire()
hasQueuedPredecessors()
compareAndSetState()
setExclusiveOwnerThread()
getExclusiveOwnerThread()
addWaiter()
compareAndSetTail()
enq()
acquireQueued()
tryAcquire()
shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire()
parkAndCheckInterrupt()
cancelAcquire()
============
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
tryRelease()
setExclusiveOwnerThread()
setState()
unparkSuccessor()
compareAndSetWaitStatus()
unpark()