正文之前
毕业答辩的时候,答辩老师说我的最大的问题就是没有和大数据扯上关系。所以后面就要想方设法扯点关系上去。被逼无奈的我。只能继续开始琢磨Hadoop了。以前其实我是想做的。。但是ubuntu上的Hadoop一度坑的我想死。。所以就没有继续了。。。现在只能重操旧业了。。
正文
1:安装Homebrew
这个是Mac上安装软件的神器。。。贼鸡儿好用。。。谁用谁知道!
Homebrew的官方网站
安装Homebrew的方法,命令行键入下面的命令:
/usr/bin/ruby -e "$(curl -fsSLhttps://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)"
ps:homebrew常用shell命
- 查看brew的帮助
brew -help - 安装软件
brew install hadoop - 卸载软件
brew uninstall hadoop - 搜索软件
brew search hadoop - 查看已经安装的软件
brew list
*更新软件brew update - 更新某具体软件
brew upgrade hadoop
2:ssh登录本地
首先在系统里打开远程登录:
1:首先生成ssh公钥,终端命令代码如下
ssh-keygen -t rsa -P ""
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
如果提示缺少文件的话,那就创建个文件好了。不过应该不会。。我是先创建然后再操作的。。
2:接下来进行测试登录本地是否成功,在 Terminal 里输入以下代码查看能不能免密 ssh 到 localhost:
ssh localhost
3:登录成功显示结果如下:
3:安装Hadoop
3.1 : 输入以下代码,自动安装hadoop:
brew install hadoop
ps:通过Homebrew安装软件后,软件目录一般位于/usr/local/Cellar,并软件目录里面带有版本号. 如图我的hadoop安装目录如下:
4:测试Hadoop是否安装成功
Hadoop有三种安装模式:单机模式,伪分布式模式,分布式模式 分布式模式需要在多台电脑上面测试,这里只测试 伪分布式模式
4.1:测试伪分布式模式
测试为分布模式前,需要修改相关的5个配置文件,把homebrew默认的单机模式修改成伪分布式模式
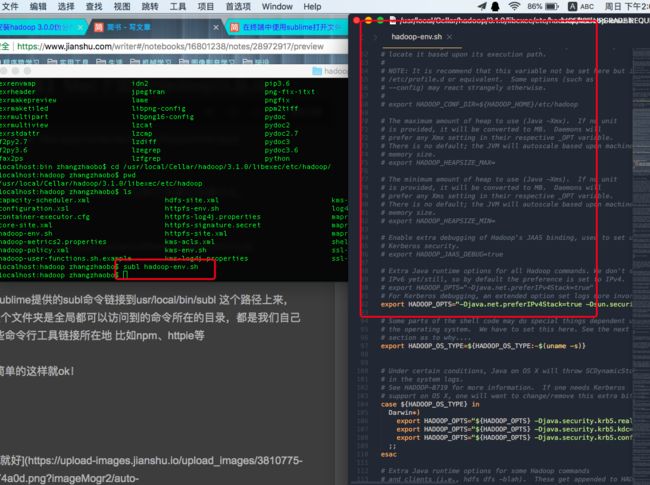
可以使用nano或者vim进行配置文件的修改,我这里使用sublime文本编辑器修改,方便省事儿。另外就是在sublime里面经常没法找到那些隐藏文件夹下的文件。所以这里我提供一个好办法,用命令行启动sublime!逼格满满还好用!
sublime 提供命令行的工具叫subs,路径在:
/Applications/Sublime\ Text.app/Contents/SharedSupport/bin/subl
使用ln命令
ln命令是做文件链接用的,不恰当的例子可以称之为建立快捷方式。
ln /Applications/Sublime\ Text.app/Contents/SharedSupport/bin/subl /usr/local/bin/subl
如上命令是将sublime提供的subl命令链接到usr/local/bin/subl 这个路径上来,usr/local/bin 这个文件夹是全局都可以访问到的命令所在的目录,都是我们自己下载安装的一些命令行工具链接所在地 比如npm、httpie等
搞完了之后,简单的这样就ok!
下面进行文件修改,修改路径为:
修改core-site.xml(位置 etc/hadoop/),改参数如下:
hadoop.tmp.dir
/usr/local/Cellar/hadoop/hdfs/tmp
A base for other temporary directories
fs.default.name
hdfs://localhost:9000
.修改mapred-site.xml (位置 etc/hadoop/),改参数如下:
如果文件后缀是 .xml.example,改为 .xml。
mapred.job.tracker
localhost:9010
mapreduce.framework.name
yarn
变量mapred.job.tracker 保存了JobTracker的位置,因为只有MapReduce组件需要知道这个位置,所以它出现在mapred-site.xml文件中。
修改hdfs-site.xml(位置 etc/hadoop/),改参数如下:
dfs.replication
1
变量dfs.replication指定了每个HDFS数据库的复制次数。 通常为3, 由于我们只有一台主机和一个伪分布式模式的DataNode,将此值修改为1。
修改yarn-site.xml(位置 etc/hadoop/),改参数如下:
yarn.nodemanager.aux-services
mapreduce_shuffle
修改hadoop-env.sh(位置 etc/hadoop/),改参数如下:然后开启hadoop-env.sh里的注释
#
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
# or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
# distributed with this work for additional information
# regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
# to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
# "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
# with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# Set Hadoop-specific environment variables here.
##
## THIS FILE ACTS AS THE MASTER FILE FOR ALL HADOOP PROJECTS.
## SETTINGS HERE WILL BE READ BY ALL HADOOP COMMANDS. THEREFORE,
## ONE CAN USE THIS FILE TO SET YARN, HDFS, AND MAPREDUCE
## CONFIGURATION OPTIONS INSTEAD OF xxx-env.sh.
##
## Precedence rules:
##
## {yarn-env.sh|hdfs-env.sh} > hadoop-env.sh > hard-coded defaults
##
## {YARN_xyz|HDFS_xyz} > HADOOP_xyz > hard-coded defaults
##
# Many of the options here are built from the perspective that users
# may want to provide OVERWRITING values on the command line.
# For example:
#
# JAVA_HOME=/usr/java/testing hdfs dfs -ls
#
# Therefore, the vast majority (BUT NOT ALL!) of these defaults
# are configured for substitution and not append. If append
# is preferable, modify this file accordingly.
###
# Generic settings for HADOOP
###
# Technically, the only required environment variable is JAVA_HOME.
# All others are optional. However, the defaults are probably not
# preferred. Many sites configure these options outside of Hadoop,
# such as in /etc/profile.d
# The java implementation to use. By default, this environment
# variable is REQUIRED on ALL platforms except OS X!
export JAVA_HOME=/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_172.jdk/Contents/Home
# Location of Hadoop. By default, Hadoop will attempt to determine
# this location based upon its execution path.
# export HADOOP_HOME=
# Location of Hadoop's configuration information. i.e., where this
# file is living. If this is not defined, Hadoop will attempt to
# locate it based upon its execution path.
#
# NOTE: It is recommend that this variable not be set here but in
# /etc/profile.d or equivalent. Some options (such as
# --config) may react strangely otherwise.
#
# export HADOOP_CONF_DIR=${HADOOP_HOME}/etc/hadoop
# The maximum amount of heap to use (Java -Xmx). If no unit
# is provided, it will be converted to MB. Daemons will
# prefer any Xmx setting in their respective _OPT variable.
# There is no default; the JVM will autoscale based upon machine
# memory size.
# export HADOOP_HEAPSIZE_MAX=
# The minimum amount of heap to use (Java -Xms). If no unit
# is provided, it will be converted to MB. Daemons will
# prefer any Xms setting in their respective _OPT variable.
# There is no default; the JVM will autoscale based upon machine
# memory size.
# export HADOOP_HEAPSIZE_MIN=
# Enable extra debugging of Hadoop's JAAS binding, used to set up
# Kerberos security.
# export HADOOP_JAAS_DEBUG=true
# Extra Java runtime options for all Hadoop commands. We don't support
# IPv6 yet/still, so by default the preference is set to IPv4.
# export HADOOP_OPTS="-Djava.net.preferIPv4Stack=true"
# For Kerberos debugging, an extended option set logs more invormation
export HADOOP_OPTS="-Djava.net.preferIPv4Stack=true -Dsun.security.krb5.debug=true -Dsun.security.spnego.debug"
# Some parts of the shell code may do special things dependent upon
# the operating system. We have to set this here. See the next
# section as to why....
export HADOOP_OS_TYPE=${HADOOP_OS_TYPE:-$(uname -s)}
# Under certain conditions, Java on OS X will throw SCDynamicStore errors
# in the system logs.
# See HADOOP-8719 for more information. If one needs Kerberos
# support on OS X, one will want to change/remove this extra bit.
case ${HADOOP_OS_TYPE} in
Darwin*)
export HADOOP_OPTS="${HADOOP_OPTS} -Djava.security.krb5.realm= "
export HADOOP_OPTS="${HADOOP_OPTS} -Djava.security.krb5.kdc= "
export HADOOP_OPTS="${HADOOP_OPTS} -Djava.security.krb5.conf= "
;;
esac
# Extra Java runtime options for some Hadoop commands
# and clients (i.e., hdfs dfs -blah). These get appended to HADOOP_OPTS for
# such commands. In most cases, # this should be left empty and
# let users supply it on the command line.
# export HADOOP_CLIENT_OPTS=""
#
# A note about classpaths.
#
# By default, Apache Hadoop overrides Java's CLASSPATH
# environment variable. It is configured such
# that it sarts out blank with new entries added after passing
# a series of checks (file/dir exists, not already listed aka
# de-deduplication). During de-depulication, wildcards and/or
# directories are *NOT* expanded to keep it simple. Therefore,
# if the computed classpath has two specific mentions of
# awesome-methods-1.0.jar, only the first one added will be seen.
# If two directories are in the classpath that both contain
# awesome-methods-1.0.jar, then Java will pick up both versions.
# An additional, custom CLASSPATH. Site-wide configs should be
# handled via the shellprofile functionality, utilizing the
# hadoop_add_classpath function for greater control and much
# harder for apps/end-users to accidentally override.
# Similarly, end users should utilize ${HOME}/.hadooprc .
# This variable should ideally only be used as a short-cut,
# interactive way for temporary additions on the command line.
# export HADOOP_CLASSPATH="/some/cool/path/on/your/machine"
# Should HADOOP_CLASSPATH be first in the official CLASSPATH?
# export HADOOP_USER_CLASSPATH_FIRST="yes"
# If HADOOP_USE_CLIENT_CLASSLOADER is set, the classpath along
# with the main jar are handled by a separate isolated
# client classloader when 'hadoop jar', 'yarn jar', or 'mapred job'
# is utilized. If it is set, HADOOP_CLASSPATH and
# HADOOP_USER_CLASSPATH_FIRST are ignored.
# export HADOOP_USE_CLIENT_CLASSLOADER=true
# HADOOP_CLIENT_CLASSLOADER_SYSTEM_CLASSES overrides the default definition of
# system classes for the client classloader when HADOOP_USE_CLIENT_CLASSLOADER
# is enabled. Names ending in '.' (period) are treated as package names, and
# names starting with a '-' are treated as negative matches. For example,
# export HADOOP_CLIENT_CLASSLOADER_SYSTEM_CLASSES="-org.apache.hadoop.UserClass,java.,javax.,org.apache.hadoop."
# Enable optional, bundled Hadoop features
# This is a comma delimited list. It may NOT be overridden via .hadooprc
# Entries may be added/removed as needed.
# export HADOOP_OPTIONAL_TOOLS="hadoop-openstack,hadoop-aliyun,hadoop-azure,hadoop-azure-datalake,hadoop-aws,hadoop-kafka"
###
# Options for remote shell connectivity
###
# There are some optional components of hadoop that allow for
# command and control of remote hosts. For example,
# start-dfs.sh will attempt to bring up all NNs, DNS, etc.
# Options to pass to SSH when one of the "log into a host and
# start/stop daemons" scripts is executed
# export HADOOP_SSH_OPTS="-o BatchMode=yes -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no -o ConnectTimeout=10s"
# The built-in ssh handler will limit itself to 10 simultaneous connections.
# For pdsh users, this sets the fanout size ( -f )
# Change this to increase/decrease as necessary.
# export HADOOP_SSH_PARALLEL=10
# Filename which contains all of the hosts for any remote execution
# helper scripts # such as workers.sh, start-dfs.sh, etc.
# export HADOOP_WORKERS="${HADOOP_CONF_DIR}/workers"
###
# Options for all daemons
###
#
#
# Many options may also be specified as Java properties. It is
# very common, and in many cases, desirable, to hard-set these
# in daemon _OPTS variables. Where applicable, the appropriate
# Java property is also identified. Note that many are re-used
# or set differently in certain contexts (e.g., secure vs
# non-secure)
#
# Where (primarily) daemon log files are stored.
# ${HADOOP_HOME}/logs by default.
# Java property: hadoop.log.dir
# export HADOOP_LOG_DIR=${HADOOP_HOME}/logs
# A string representing this instance of hadoop. $USER by default.
# This is used in writing log and pid files, so keep that in mind!
# Java property: hadoop.id.str
# export HADOOP_IDENT_STRING=$USER
# How many seconds to pause after stopping a daemon
# export HADOOP_STOP_TIMEOUT=5
# Where pid files are stored. /tmp by default.
# export HADOOP_PID_DIR=/tmp
# Default log4j setting for interactive commands
# Java property: hadoop.root.logger
# export HADOOP_ROOT_LOGGER=INFO,console
# Default log4j setting for daemons spawned explicitly by
# --daemon option of hadoop, hdfs, mapred and yarn command.
# Java property: hadoop.root.logger
# export HADOOP_DAEMON_ROOT_LOGGER=INFO,RFA
# Default log level and output location for security-related messages.
# You will almost certainly want to change this on a per-daemon basis via
# the Java property (i.e., -Dhadoop.security.logger=foo). (Note that the
# defaults for the NN and 2NN override this by default.)
# Java property: hadoop.security.logger
# export HADOOP_SECURITY_LOGGER=INFO,NullAppender
# Default process priority level
# Note that sub-processes will also run at this level!
# export HADOOP_NICENESS=0
# Default name for the service level authorization file
# Java property: hadoop.policy.file
# export HADOOP_POLICYFILE="hadoop-policy.xml"
#
# NOTE: this is not used by default! <-----
# You can define variables right here and then re-use them later on.
# For example, it is common to use the same garbage collection settings
# for all the daemons. So one could define:
#
# export HADOOP_GC_SETTINGS="-verbose:gc -XX:+PrintGCDetails -XX:+PrintGCTimeStamps -XX:+PrintGCDateStamps"
#
# .. and then use it as per the b option under the namenode.
###
# Secure/privileged execution
###
#
# Out of the box, Hadoop uses jsvc from Apache Commons to launch daemons
# on privileged ports. This functionality can be replaced by providing
# custom functions. See hadoop-functions.sh for more information.
#
# The jsvc implementation to use. Jsvc is required to run secure datanodes
# that bind to privileged ports to provide authentication of data transfer
# protocol. Jsvc is not required if SASL is configured for authentication of
# data transfer protocol using non-privileged ports.
# export JSVC_HOME=/usr/bin
#
# This directory contains pids for secure and privileged processes.
#export HADOOP_SECURE_PID_DIR=${HADOOP_PID_DIR}
#
# This directory contains the logs for secure and privileged processes.
# Java property: hadoop.log.dir
# export HADOOP_SECURE_LOG=${HADOOP_LOG_DIR}
#
# When running a secure daemon, the default value of HADOOP_IDENT_STRING
# ends up being a bit bogus. Therefore, by default, the code will
# replace HADOOP_IDENT_STRING with HADOOP_xx_SECURE_USER. If one wants
# to keep HADOOP_IDENT_STRING untouched, then uncomment this line.
# export HADOOP_SECURE_IDENT_PRESERVE="true"
###
# NameNode specific parameters
###
# Default log level and output location for file system related change
# messages. For non-namenode daemons, the Java property must be set in
# the appropriate _OPTS if one wants something other than INFO,NullAppender
# Java property: hdfs.audit.logger
# export HDFS_AUDIT_LOGGER=INFO,NullAppender
# Specify the JVM options to be used when starting the NameNode.
# These options will be appended to the options specified as HADOOP_OPTS
# and therefore may override any similar flags set in HADOOP_OPTS
#
# a) Set JMX options
# export HDFS_NAMENODE_OPTS="-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote=true -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.authenticate=false -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl=false -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port=1026"
#
# b) Set garbage collection logs
# export HDFS_NAMENODE_OPTS="${HADOOP_GC_SETTINGS} -Xloggc:${HADOOP_LOG_DIR}/gc-rm.log-$(date +'%Y%m%d%H%M')"
#
# c) ... or set them directly
# export HDFS_NAMENODE_OPTS="-verbose:gc -XX:+PrintGCDetails -XX:+PrintGCTimeStamps -XX:+PrintGCDateStamps -Xloggc:${HADOOP_LOG_DIR}/gc-rm.log-$(date +'%Y%m%d%H%M')"
# this is the default:
# export HDFS_NAMENODE_OPTS="-Dhadoop.security.logger=INFO,RFAS"
###
# SecondaryNameNode specific parameters
###
# Specify the JVM options to be used when starting the SecondaryNameNode.
# These options will be appended to the options specified as HADOOP_OPTS
# and therefore may override any similar flags set in HADOOP_OPTS
#
# This is the default:
# export HDFS_SECONDARYNAMENODE_OPTS="-Dhadoop.security.logger=INFO,RFAS"
###
# DataNode specific parameters
###
# Specify the JVM options to be used when starting the DataNode.
# These options will be appended to the options specified as HADOOP_OPTS
# and therefore may override any similar flags set in HADOOP_OPTS
#
# This is the default:
# export HDFS_DATANODE_OPTS="-Dhadoop.security.logger=ERROR,RFAS"
# On secure datanodes, user to run the datanode as after dropping privileges.
# This **MUST** be uncommented to enable secure HDFS if using privileged ports
# to provide authentication of data transfer protocol. This **MUST NOT** be
# defined if SASL is configured for authentication of data transfer protocol
# using non-privileged ports.
# This will replace the hadoop.id.str Java property in secure mode.
# export HDFS_DATANODE_SECURE_USER=hdfs
# Supplemental options for secure datanodes
# By default, Hadoop uses jsvc which needs to know to launch a
# server jvm.
# export HDFS_DATANODE_SECURE_EXTRA_OPTS="-jvm server"
###
# NFS3 Gateway specific parameters
###
# Specify the JVM options to be used when starting the NFS3 Gateway.
# These options will be appended to the options specified as HADOOP_OPTS
# and therefore may override any similar flags set in HADOOP_OPTS
#
# export HDFS_NFS3_OPTS=""
# Specify the JVM options to be used when starting the Hadoop portmapper.
# These options will be appended to the options specified as HADOOP_OPTS
# and therefore may override any similar flags set in HADOOP_OPTS
#
# export HDFS_PORTMAP_OPTS="-Xmx512m"
# Supplemental options for priviliged gateways
# By default, Hadoop uses jsvc which needs to know to launch a
# server jvm.
# export HDFS_NFS3_SECURE_EXTRA_OPTS="-jvm server"
# On privileged gateways, user to run the gateway as after dropping privileges
# This will replace the hadoop.id.str Java property in secure mode.
# export HDFS_NFS3_SECURE_USER=nfsserver
###
# ZKFailoverController specific parameters
###
# Specify the JVM options to be used when starting the ZKFailoverController.
# These options will be appended to the options specified as HADOOP_OPTS
# and therefore may override any similar flags set in HADOOP_OPTS
#
# export HDFS_ZKFC_OPTS=""
###
# QuorumJournalNode specific parameters
###
# Specify the JVM options to be used when starting the QuorumJournalNode.
# These options will be appended to the options specified as HADOOP_OPTS
# and therefore may override any similar flags set in HADOOP_OPTS
#
# export HDFS_JOURNALNODE_OPTS=""
###
# HDFS Balancer specific parameters
###
# Specify the JVM options to be used when starting the HDFS Balancer.
# These options will be appended to the options specified as HADOOP_OPTS
# and therefore may override any similar flags set in HADOOP_OPTS
#
# export HDFS_BALANCER_OPTS=""
###
# HDFS Mover specific parameters
###
# Specify the JVM options to be used when starting the HDFS Mover.
# These options will be appended to the options specified as HADOOP_OPTS
# and therefore may override any similar flags set in HADOOP_OPTS
#
# export HDFS_MOVER_OPTS=""
###
# Router-based HDFS Federation specific parameters
# Specify the JVM options to be used when starting the RBF Routers.
# These options will be appended to the options specified as HADOOP_OPTS
# and therefore may override any similar flags set in HADOOP_OPTS
#
# export HDFS_DFSROUTER_OPTS=""
###
###
# Advanced Users Only!
###
#
# When building Hadoop, one can add the class paths to the commands
# via this special env var:
# export HADOOP_ENABLE_BUILD_PATHS="true"
#
# To prevent accidents, shell commands be (superficially) locked
# to only allow certain users to execute certain subcommands.
# It uses the format of (command)_(subcommand)_USER.
#
# For example, to limit who can execute the namenode command,
# export HDFS_NAMENODE_USER=hdfs
这里记得要改掉Java的位置啊!!!
export JAVA_HOME=/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_172.jdk/Contents/Home
4.2:运行hadoop以及查看远端
第一步:进入文件夹(重要重要重要:后续所有操作一定要先进入当前hadoop文件夹)
cd /usr/local/Cellar/hadoop/3.0.0
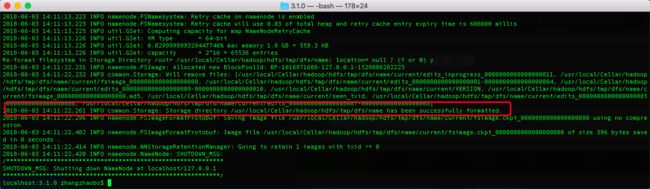
第二步:格式化文件系统(是对namenode进行初始化):
./bin/hdfs namenode -format
启动 NameNode 和 DataNode:
./sbin/start-dfs.sh
localhost:3.1.0 zhangzhaobo$ ./sbin/start-dfs.sh
Starting namenodes on [localhost]
Starting datanodes
Starting secondary namenodes [localhost]
2018-06-03 14:12:02,890 WARN util.NativeCodeLoader: Unable to load native-hadoop library for your platform... using builtin-java classes where applicable
localhost:3.1.0 zhangzhaobo$
报错没关系。。随它去~
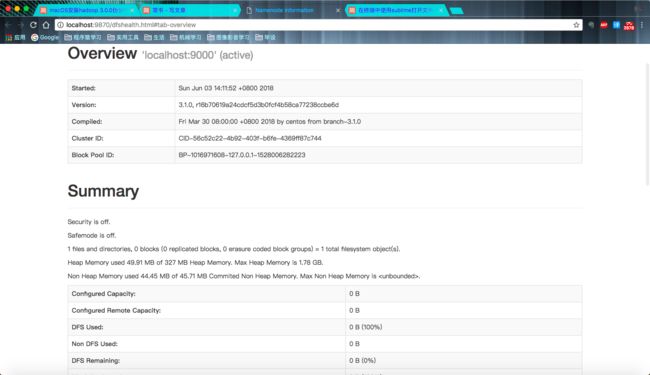
现在可以直接看到Overview 界面了:
http://localhost:9870 Overview
让 HDFS 可以被用来执行 MapReduce jobs:
./bin/hdfs dfs -mkdir /user
./bin/hdfs dfs -mkdir /user/input
localhost:3.1.0 zhangzhaobo$ ./bin/hdfs dfs -mkdir /user
2018-06-03 14:13:45,029 WARN util.NativeCodeLoader: Unable to load native-hadoop library for your platform... using builtin-java classes where applicable
localhost:3.1.0 zhangzhaobo$ ./bin/hdfs dfs -mkdir /user/input
2018-06-03 14:13:51,659 WARN util.NativeCodeLoader: Unable to load native-hadoop library for your platform... using builtin-java classes where applicable
localhost:3.1.0 zhangzhaobo$
把input改成你想要命名的任意子文件夹名字即可,这里我选择命名input.
启动 ResourceManager 和 NodeManager:
./sbin/start-yarn.sh
localhost:3.1.0 zhangzhaobo$ ./sbin/start-yarn.sh
Starting resourcemanager
Starting nodemanagers
localhost:3.1.0 zhangzhaobo$
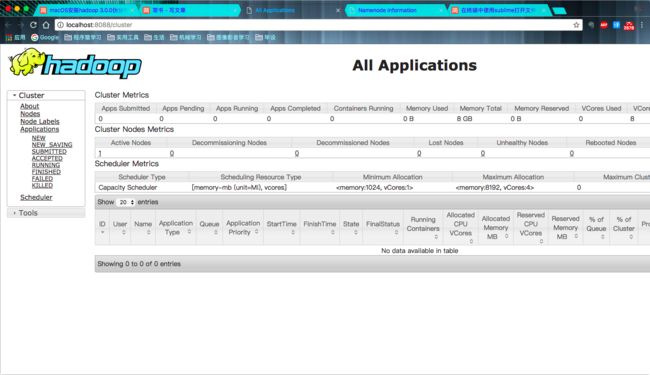
现在你就可以看到All Applications 界面了:
http://localhost:8088 All Applications
上面大部分内容来自的两位优秀程序猿同学。。。通报下:
macOS安装hadoop 3.0.0伪分布式教程
在终端中使用sublime打开文件
OK!下面进入深化拓展!!
首先就是可能因为安装Java的时候默认安装了一些版本。。所以会有一些奇形怪状的错误出来。。这里介绍下如何查看版本以及改变版本:
首先输入代码看看你把 Java 装到哪里了 :
/usr/libexec/java_home
输入代码:
java -version
如果已经装了Java,你会看到类似酱紫结果:
localhost:3.1.0 zhangzhaobo$ java -version
java version "1.8.0_172"
Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_172-b11)
Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.172-b11, mixed mode)
如果没有 ,用 Homebrew 安装了 Java8,老铁, 求你一定要加那个8.。不然9的话别怪我没警告你!
brew cask install java8
如果你本来就安装了Java9 其实也没关系,一起装了就好了!!你看我的:
一起装了之后,你只要告诉系统,我要的默认Java是哪个就ok了!这个时候输入如下命令:
subl ~/.bash_profile
然后开始编辑
基本上按照我这个就没啥错误了。。
export JAVA_HOME_9=/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk-9.0.1.jdk/Contents/Home
export JAVA_HOME_8=/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_172.jdk/Contents/Home
export JAVA_HOME=$JAVA_HOME_8
alias jdk8='export JAVA_HOME=$JAVA_HOME_8'
alias jdk9='export JAVA_HOME=$JAVA_HOME_9'
然后你再去那个地方改一下:
没错,就是这里!!
修改hadoop-env.sh(位置 etc/hadoop/),改参数如下:然后开启hadoop-env.sh里的注释,JAVA_HOME那儿改成后来的这个就ok了!然后你就发现啥事没有了。。不然你在8088那个网址肯定出错。。。
正文之后
溜了溜了。今晚健身完回去好好学习。。把ubuntu和Raspberry都搭个Hadoop,做个小集群。。。哇咔咔!毕设完成有望啊!!!