线性表
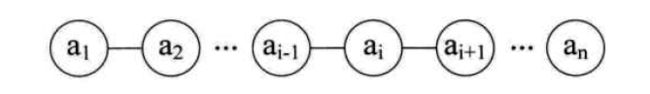
a1是a2的前驱,a2是a1的后继;首节点a1没有前驱,尾节an没有后继。
线性表有两种存储结构
-
顺序存储结构
-
链式存储结构
顺序存储结构
优:随机读取效率高
缺:插入删除效率低
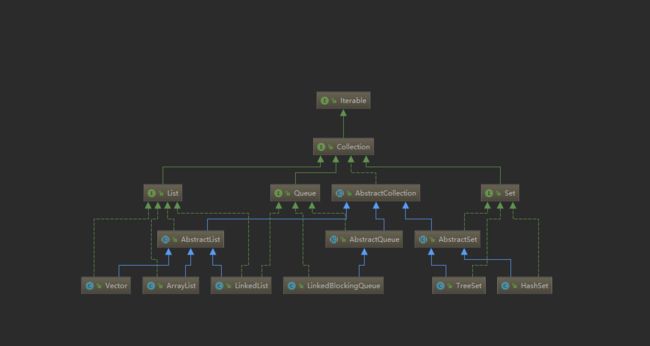
ArrayList
ArrayList容器是数组,对ArrayList的操作其实就是就是对数组的操作,但是ArrayList还有自动扩容机制。由于是数组结构,所以随机读取速度非常快,而插入删除会导致数组扩容或者拷贝所以速度较慢,不适合插入删除频繁的场景。
// 首次扩容的最小容量
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
private int size;
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
return elementData(index);
}
public E set(int index, E element) {
rangeCheck(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue;
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
自动扩容
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
/**
* The maximum size of array to allocate.
* Some VMs reserve some header words in an array.
* Attempts to allocate larger arrays may result in
* OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit
*/
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
/**
* Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the
* number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
链式存储结构
优:删除和插入效率高
缺:查询效率低
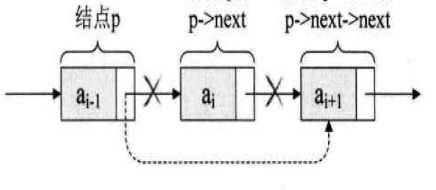
单向链表
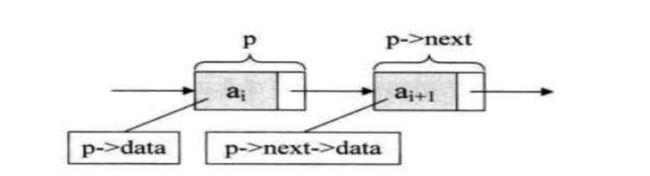
线性表的链式存储结构的特点是用一组任意的存储单元存储线性表的数据元素,这组存储单元可以是连续的,也可以是不连续的
- 插入节点
Node e = new Node();
e.next = p.next;
p.next = e;
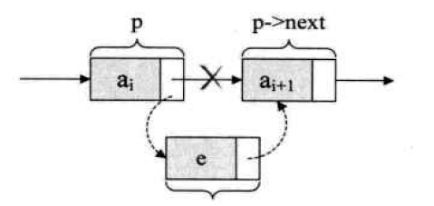
- 删除节点
p.next = p.next.next
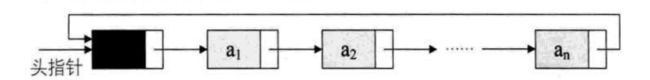
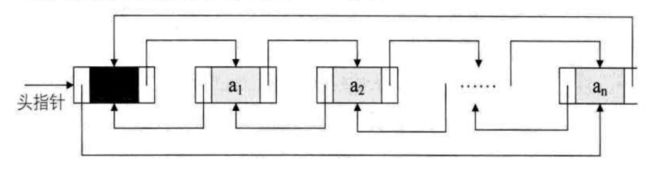
双向循环链表
循环链表:将单链表中终端结点的指针端由空指针改为指向头结点,就使整个单链表形成一个环,这种头尾相连的单链表称为单循环链表,简称循环链表
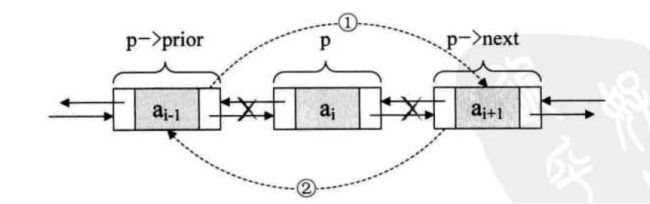
双向循环链表是单向循环链表的每个结点中,再设置一个指向其前驱结点的指针域
- 插入
s.next = p.next;
s.pre = p;
p.next.pre = s;
p.next = s;
- 删除
p.pre.next = p.next;
p.next.pre = p.pre;
LinkedList
LinkedList使用双向链表实现,获取给定位置的元素的查找较单向链表更快(双向遍历)。由于是链表结构所以插入删除操作速度快,根据位置查找元素速度慢。
//java.util.LinkedList
private static class Node {
E item;
Node next;
Node prev;
Node(Node prev, E element, Node next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
transient Node first;
transient Node last;
private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node f = first;
final Node newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);
first = newNode;
if (f == null)
last = newNode;
else
f.prev = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node l = last;
final Node newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
void linkBefore(E e, Node succ) {
// assert succ != null;
final Node pred = succ.prev;
final Node newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
private E unlinkFirst(Node f) {
// assert f == first && f != null;
final E element = f.item;
final Node next = f.next;
f.item = null;
f.next = null; // help GC
first = next;
if (next == null)
last = null;
else
next.prev = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
private E unlinkLast(Node l) {
// assert l == last && l != null;
final E element = l.item;
final Node prev = l.prev;
l.item = null;
l.prev = null; // help GC
last = prev;
if (prev == null)
first = null;
else
prev.next = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
E unlink(Node x) {
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node next = x.next;
final Node prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
public E getFirst() {
final Node f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item;
}
Node node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}