一 autoreleasepool到底是啥?
使用 clang -rewrite-objc main.m将OC代码转为main.cpp文件
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
// insert code here...
NSLog(@"Hello, World!");
}
return 0;
}
打开cpp代码随后我们可以搜索到对应的
extern "C" __declspec(dllimport) void * objc_autoreleasePoolPush(void);
extern "C" __declspec(dllimport) void objc_autoreleasePoolPop(void *);
struct __AtAutoreleasePool {
__AtAutoreleasePool() {atautoreleasepoolobj = objc_autoreleasePoolPush();}
~__AtAutoreleasePool() {objc_autoreleasePoolPop(atautoreleasepoolobj);}
void * atautoreleasepoolobj;
};
二 objc_autoreleasePoolPush和objc_autoreleasePoolPop又是什么呢?
查看objc源代码下的Object.mm文件我们可以找打如下class:
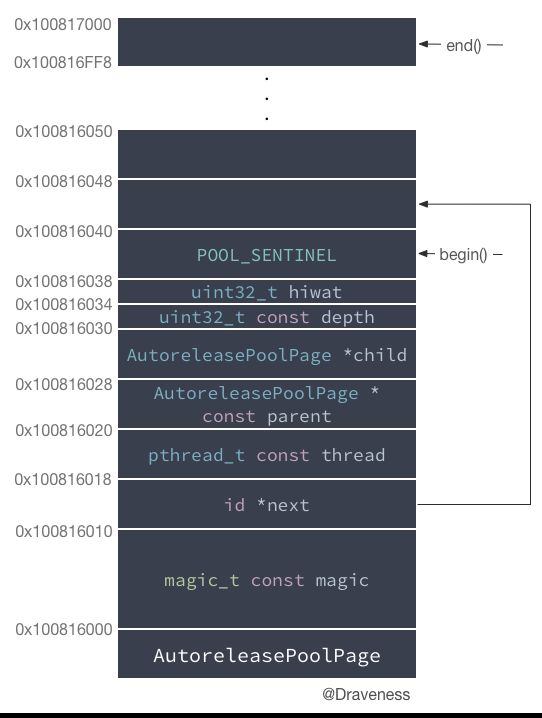
class AutoreleasePoolPage
{
// EMPTY_POOL_PLACEHOLDER is stored in TLS when exactly one pool is
// pushed and it has never contained any objects. This saves memory
// when the top level (i.e. libdispatch) pushes and pops pools but
// never uses them.
# define EMPTY_POOL_PLACEHOLDER ((id*)1)
# define POOL_BOUNDARY nil
static pthread_key_t const key = AUTORELEASE_POOL_KEY;
static uint8_t const SCRIBBLE = 0xA3; // 0xA3A3A3A3 after releasing
static size_t const SIZE =
#if PROTECT_AUTORELEASEPOOL
PAGE_MAX_SIZE; // must be multiple of vm page size
#else
PAGE_MAX_SIZE; // size and alignment, power of 2
#endif
static size_t const COUNT = SIZE / sizeof(id);
magic_t const magic;
id *next;
pthread_t const thread;
AutoreleasePoolPage * const parent;
AutoreleasePoolPage *child;
uint32_t const depth;
uint32_t hiwat;
……
AutoreleasePoolPage(AutoreleasePoolPage *newParent)
: magic(), next(begin()), thread(pthread_self()),
parent(newParent), child(nil),
depth(parent ? 1+parent->depth : 0),
hiwat(parent ? parent->hiwat : 0)
{
if (parent) {
parent->check();
assert(!parent->child);
parent->unprotect();
parent->child = this;
parent->protect();
}
protect();
}
~AutoreleasePoolPage()
{
check();
unprotect();
assert(empty());
// Not recursive: we don't want to blow out the stack
// if a thread accumulates a stupendous amount of garbage
assert(!child);
}
……
总体我们可以看出AutoreleasePoolPage是一个双向链表结构,每一个autorelease pool是由多个Page组成
static size_t const COUNT = SIZE / sizeof(id);
具体计算根据平台架构而定
#define I386_PGBYTES 4096 /* bytes per 80386 page */
#define I386_PGSHIFT 12 /* bitshift for pages */
#define PAGE_SIZE I386_PGBYTES
#define PAGE_SHIFT I386_PGSHIFT
#define PAGE_MASK (PAGE_SIZE - 1)
#define PAGE_MAX_SHIFT PAGE_SHIFT
#define PAGE_MAX_SIZE PAGE_SIZE
#define PAGE_MAX_MASK PAGE_MASK
总数几次宏跳转之后可以看到AutoreleasePoolPage大小是 4096
大致了解了自动释池的数据结构我们来看看它创建过程中发生了什么吧。
三
autoreleasepool的创建
在我们简单的调用@autoreleasepool{}的时候系统为我们先调用了
void *
objc_autoreleasePoolPush(void)
{
return AutoreleasePoolPage::push();
}
展开push就是
static inline void *push()
{
id *dest;
if (DebugPoolAllocation) {
// Each autorelease pool starts on a new pool page.
dest = autoreleaseNewPage(POOL_BOUNDARY);
} else {
dest = autoreleaseFast(POOL_BOUNDARY);
}
assert(dest == EMPTY_POOL_PLACEHOLDER || *dest == POOL_BOUNDARY);
return dest;
}
push就是简单的开启必要的检测,通过之后就是autoreleaseFast这个函数了
static inline id *autoreleaseFast(id obj)
{
AutoreleasePoolPage *page = hotPage();
if (page && !page->full()) {
return page->add(obj);
} else if (page) {
return autoreleaseFullPage(obj, page);
} else {
return autoreleaseNoPage(obj);
}
}
从autoreleaseFast这个函数就是我们自动释放池的核心逻辑
1 获取当前最顶部的page,也就是hotPage
2 page页存&&还没有存满(4096)则可以继续add关联object
3 存page && 当前page已满, 则会调用autoreleaseFullPage,去查找child下非fullPage去关联对象。假如最终查找不到,则会创建新的page,并将其设置为hotPage,同时调用add添加关联object
static __attribute__((noinline))
id *autoreleaseFullPage(id obj, AutoreleasePoolPage *page)
{
// The hot page is full.
// Step to the next non-full page, adding a new page if necessary.
// Then add the object to that page.
assert(page == hotPage());
assert(page->full() || DebugPoolAllocation);
do {
if (page->child) page = page->child;
else page = new AutoreleasePoolPage(page);
} while (page->full());
setHotPage(page);
return page->add(obj);
}
4 不存在page则去创建page
static __attribute__((noinline))
id *autoreleaseNoPage(id obj)
{
// "No page" could mean no pool has been pushed
// or an empty placeholder pool has been pushed and has no contents yet
assert(!hotPage());
bool pushExtraBoundary = false;
if (haveEmptyPoolPlaceholder()) {
// We are pushing a second pool over the empty placeholder pool
// or pushing the first object into the empty placeholder pool.
// Before doing that, push a pool boundary on behalf of the pool
// that is currently represented by the empty placeholder.
pushExtraBoundary = true;
}
else if (obj != POOL_BOUNDARY && DebugMissingPools) {
// We are pushing an object with no pool in place,
// and no-pool debugging was requested by environment.
_objc_inform("MISSING POOLS: (%p) Object %p of class %s "
"autoreleased with no pool in place - "
"just leaking - break on "
"objc_autoreleaseNoPool() to debug",
pthread_self(), (void*)obj, object_getClassName(obj));
objc_autoreleaseNoPool(obj);
return nil;
}
else if (obj == POOL_BOUNDARY && !DebugPoolAllocation) {
// We are pushing a pool with no pool in place,
// and alloc-per-pool debugging was not requested.
// Install and return the empty pool placeholder.
return setEmptyPoolPlaceholder();
}
// We are pushing an object or a non-placeholder'd pool.
// Install the first page.
AutoreleasePoolPage *page = new AutoreleasePoolPage(nil);
setHotPage(page);
// Push a boundary on behalf of the previously-placeholder'd pool.
if (pushExtraBoundary) {
page->add(POOL_BOUNDARY);
}
// Push the requested object or pool.
return page->add(obj);
}
走到这一步也代表的是首次pushpage,或者创建新的page。主要有两个动作
1 初始化新Page,add 关联object
2 push一个nil座位占位座位哨兵
每次push,在生成新的page时都会有个POOL_SETING哨兵先被push进去占位
四 对象是如何加到autoreleasepool中去的
简略看了autoreleasepool的创建过程,那么我们的对象是如何被添加进自动释放池的呢?
+ (id)autorelease {
return (id)self;
}
// Replaced by ObjectAlloc
- (id)autorelease {
return ((id)self)->rootAutorelease();
}
展开rootAutorelease函数
// Base autorelease implementation, ignoring overrides.
inline id
objc_object::rootAutorelease()
{
if (isTaggedPointer()) return (id)this;
if (prepareOptimizedReturn(ReturnAtPlus1)) return (id)this;
return rootAutorelease2();
}
__attribute__((noinline,used))
id
objc_object::rootAutorelease2()
{
assert(!isTaggedPointer());
return AutoreleasePoolPage::autorelease((id)this);
}
public:
static inline id autorelease(id obj)
{
assert(obj);
assert(!obj->isTaggedPointer());
id *dest __unused = autoreleaseFast(obj);
assert(!dest || dest == EMPTY_POOL_PLACEHOLDER || *dest == obj);
return obj;
}
最终我们通过rootAutorelease2()找到了我们位置的object_object是通过自身将自己加入自动释放池,同时返回自身的
此处注意一个问题isTaggedPointer()这个判断,由于taggedPointer类型是内存和数据一体,因此才脱离自动释放池管理
五 对象是如何从autoreleasepool中移出的
object被add进自动释放池后,系统会根据当前的状况来自行决定何时释放内存(runloop相关),我们今天先只关注内部pop释放的过程
void
objc_autoreleasePoolPop(void *ctxt)
{
AutoreleasePoolPage::pop(ctxt);
}
展开pop()后我们看到一大坨
static inline void pop(void *token)
{
AutoreleasePoolPage *page;
id *stop;
if (token == (void*)EMPTY_POOL_PLACEHOLDER) {
// Popping the top-level placeholder pool.
if (hotPage()) {
// Pool was used. Pop its contents normally.
// Pool pages remain allocated for re-use as usual.
pop(coldPage()->begin());
} else {
// Pool was never used. Clear the placeholder.
setHotPage(nil);
}
return;
}
page = pageForPointer(token);
stop = (id *)token;
if (*stop != POOL_BOUNDARY) {
if (stop == page->begin() && !page->parent) {
// Start of coldest page may correctly not be POOL_BOUNDARY:
// 1. top-level pool is popped, leaving the cold page in place
// 2. an object is autoreleased with no pool
} else {
// Error. For bincompat purposes this is not
// fatal in executables built with old SDKs.
return badPop(token);
}
}
if (PrintPoolHiwat) printHiwat();
page->releaseUntil(stop);
// memory: delete empty children
if (DebugPoolAllocation && page->empty()) {
// special case: delete everything during page-per-pool debugging
AutoreleasePoolPage *parent = page->parent;
page->kill();
setHotPage(parent);
} else if (DebugMissingPools && page->empty() && !page->parent) {
// special case: delete everything for pop(top)
// when debugging missing autorelease pools
page->kill();
setHotPage(nil);
}
else if (page->child) {
// hysteresis: keep one empty child if page is more than half full
if (page->lessThanHalfFull()) {
page->child->kill();
}
else if (page->child->child) {
page->child->child->kill();
}
}
}
static void init()
{
int r __unused = pthread_key_init_np(AutoreleasePoolPage::key,
AutoreleasePoolPage::tls_dealloc);
assert(r == 0);
}
void print()
{
_objc_inform("[%p] ................ PAGE %s %s %s", this,
full() ? "(full)" : "",
this == hotPage() ? "(hot)" : "",
this == coldPage() ? "(cold)" : "");
check(false);
for (id *p = begin(); p < next; p++) {
if (*p == POOL_BOUNDARY) {
_objc_inform("[%p] ################ POOL %p", p, p);
} else {
_objc_inform("[%p] %#16lx %s",
p, (unsigned long)*p, object_getClassName(*p));
}
}
}
1 page是双向链表,查找hotPage的parent也就是coldPage,循环递归的方式依次pop出coldPage
2 对PointerPage的释放,查找出
3 releaseUntil内部进行清理,memset,同时调用objc->release()达到释放
void releaseUntil(id *stop)
{
// Not recursive: we don't want to blow out the stack
// if a thread accumulates a stupendous amount of garbage
while (this->next != stop) {
// Restart from hotPage() every time, in case -release
// autoreleased more objects
AutoreleasePoolPage *page = hotPage();
// fixme I think this `while` can be `if`, but I can't prove it
while (page->empty()) {
page = page->parent;
setHotPage(page);
}
page->unprotect();
id obj = *--page->next;
memset((void*)page->next, SCRIBBLE, sizeof(*page->next));
page->protect();
if (obj != POOL_BOUNDARY) {
objc_release(obj);
}
}
setHotPage(this);
#if DEBUG
// we expect any children to be completely empty
for (AutoreleasePoolPage *page = child; page; page = page->child) {
assert(page->empty());
}
#endif
}
``