备战蓝桥杯大赛:Python必刷题单之语法基础
1. 入门训练
A + B 问题
题目链接
a, b = map(int, input().split())
print(a + b)
圆的面积
题目链接
import math
r = int(input())
area = math.pi * r * r
print("%.7f" % area)
数学函数相关内容
序列求和
题目链接
# 等差数列求和,注意数据范围和整除
n = int(input())
ans = (1 + n) * n // 2
print(ans)
闰年判断
题目链接
y = int(input())
if y % 400 == 0 or y % 4 == 0 and y % 100 != 0:
print("yes")
else:
print("no")
阶乘计算
题目链接
n = int(input())
f = 1
for i in range(1, n + 1):
f *= i
print(f)
Fibonacci数列
题目链接
n = int(input())
# 列表初始化,多申请10个空间防止越界
a = [1] * (n + 10)
for i in range(3, n + 1):
a[i] = (a[i - 1] + a[i - 2]) % 10007
print(a[n])
2. 基础练习
调和数列问题
题目链接
while True:
x = float(input())
if x > 0:
sum = 0
n = 1
while sum < x:
sum += 1 / (n + 1)
n += 1
print("%d card(s)" % (n - 1))
else:
break
时间转换
题目链接
n = int(input())
h = n // 3600
m = n % 3600 // 60
s = n % 3600 % 60
print("%d:%d:%d" % (h, m, s))
特殊的数字
题目链接
for n in range(100, 1000):
o = n % 10
t = n // 10 % 10
h = n // 100
if o ** 3 + t ** 3 + h ** 3 == n:
print(n)
查找整数
题目链接
n = int(input())
a = list(map(int, input().split()))
x = int(input())
for i in range(n):
if a[i] == x:
print(i + 1)
break;
else:
print(-1)
Python列表相关内容
数列特征
题目链接
n = int(input())
a = list(map(int, input().split()))
print(max(a))
print(min(a))
print(sum(a))
数列排序
题目链接
n = int(input())
a = list(map(int, input().split()))
a.sort()
for x in a:
print(x, end = " ")
交换Easy
题目链接
n, m = map(int, input().split())
a = list(map(int, input().split()))
for i in range(m):
x, y = map(int, input().split())
a[x - 1], a[y - 1] = a[y - 1], a[x - 1]
for x in a:
print(x)
Huffuman树
题目链接
n = int(input())
a = list(map(int, input().split()))
ans = 0
while len(a) > 1:
a.sort()
p = a[0] + a[1]
a.pop(0)
a.pop(0)
a.append(p)
ans += p
print(ans)
矩形相交面积
题目链接
算法思想
相交矩形左边的 x x x坐标 = 两个矩形左边 x x x的最大值
相交矩形右边的 x x x坐标 = 两个矩形右边 x x x的最小值
相交矩形下边的 y y y坐标 = 两个矩形下边 x x x的最大值
相交矩形上边的 y y y坐标 = 两个矩形上边 y y y的最小值
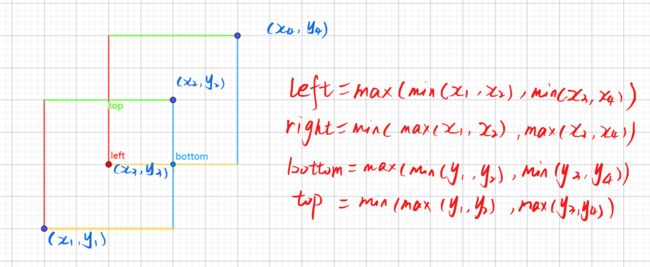
x1,y1,x2,y2 = list(map(float, input().split()))
x3,y3,x4,y4 = list(map(float, input().split()))
# 相交矩形左右两边的x坐标
left = max(min(x1, x2), min(x3, x4))
right = min(max(x1, x2), max(x3, x4))
# 相交矩形上下两边的y坐标
bottom = max(min(y1, y2), min(y3, y4))
top = min(max(y1, y2), max(y3, y4))
if left >= right or bottom >= top :
print("0.00")
else:
area = (right - left ) * (top - bottom)
print("%.2f" % area)
龟兔赛跑预测
题目链接
v1,v2,t,s,l = map(int, input().split())
s1 = 0
s2 = 0
t1 = 0
t2 = l // v2
while s1 < l:
if s1 - s2 >= t:
s2 += v2 * s
t1 += s
else:
s1 += v1
s2 += v2
t1 += 1
if t1 > t2:
print("T")
elif t1 < t2:
print("R")
else:
print("D")
print(min(t1, t2))
十进制转十六进制
题目链接
n = int(input())
s = format(n, "X")
print(s)
- format函数相关内容
- 字符串format函数相关内容
十六进制转十进制
题目链接
s = input()
d = int(s, 16)
print(d)
Python进制转换相关内容
十六进制转八进制
题目链接
n = int(input())
for i in range(n):
s = input()
# 将十六进制转十进制
d = int(s, 16)
# 将十进制转八进制
s = format(d, "o")
print(s)
01字串
题目链接
for i in range(32):
s = format(i,"0>5b")
print(s)
最长字符串
题目链接
a = input().split()
maxn = 0
ans = ""
for x in a:
if len(x) > maxn:
maxn = len(x)
ans = x
print(ans)
字符串对比
题目链接
a = input()
b = input()
if len(a) != len(b):
print(1)
elif a == b:
print(2)
elif a.lower() == b.lower():
print(3)
else:
print(4)
FJ的字符串
题目链接
n = int(input())
s = ""
for i in range(n):
# 拼接新字符串 = s + 新字母 + s
s = s + chr(ord("A") + i) + s
print(s)
Python ASCII码与字符相互转换
字母图形
题目链接
n, m = map(int, input().split())
a = [chr(i + ord("A")) for i in range(m)]
c = ord('A')
for i in range(n):
print("".join(a))
# 删除末尾字符
a.pop()
# 在头部插入新字符
c = c + 1
a.insert(0, chr(c))
回文数
题目链接
for i in range(1000, 10000):
s = str(i)
# 通过切片将字符串反转
if(s == s[::-1]):
print(s)
字符串切片相关内容
特殊回文数
题目链接
n = int(input())
for i in range(10000, 1000000):
s = str(i)
# 通过切片将字符串反转
if(s == s[::-1]):
a = [int(c) for c in s]
if sum(a) == n:
print(s)
判断质数
题目链接
n = int(input())
i = 2
while i * i <= n:
if n % i == 0:
print("No")
break
i += 1
else:
print("Yes")
计算质数因子
题目链接
n = int(input())
p = 2
while n > 1:
if n % p == 0:
print(p, end = " ")
while n % p == 0:
n //= p
else:
p += 1
数组输出
题目链接
a = []
for i in range(3):
a.append(list(map(int, input().split())))
ans = 0
x = 0
y = 0
for i in range(3):
for j in range(4):
if abs(a[i][j]) > ans:
ans = abs(a[i][j])
x = i
y = j
print(ans, x + 1, y + 1)
矩阵之和
题目链接
n, m = map(int, input().split())
# 读入a矩阵和b矩阵
a = []
b = []
for i in range(n):
a.append(list(map(int, input().split())))
for i in range(n):
b. append(list(map(int, input().split())))
# 初始化c矩阵
c = []
for i in range(n):
c.append([0] * m)
# 计算a+b
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
c[i][j] = a[i][j] + b[i][j]
# 输出矩阵之和
for i in range(n):
print(" ".join([str(x) for x in c[i]]))
分数统计
题目链接
n = int(input())
a = list(map(int, input().split()))
b = []
c = []
# 初始化各等级分数列表和人数
for i in range(5):
b.append([])
c.append(0)
for x in a:
if x >= 90:
level = 0
elif x >= 80:
level = 1
elif x >= 70:
level = 2
elif x >= 60:
level = 3
else:
level = 4
b[level].append(x) # 将分数添加到等级列表中
c[level] += 1 # 将等级人数增加1
# 输出各等级人数
print(" ".join([str(x) for x in c]))
# 输出人数最多的等级
maxn = max(c)
print(maxn)
# 从大到小输出分数
level = c.index(maxn)
b[level].sort(reverse=True)
print(" ".join([str(x) for x in b[level]]))
回形取数
题目链接
a = []
b = []
n, m = map(int, input().split())
# 读入序列
for i in range(n):
a.append(list(map(int, input().split())))
# 从r行、c列开始取数
r = 0
c = 0
b.append(a[r][c])
a[r][c] = -1
# 已取个数
cnt = 1
while cnt < n * m:
while r + 1 < n and a[r + 1][c] != -1:
r = r + 1
b.append(a[r][c])
a[r][c] = -1
cnt += 1
while c + 1 < m and a[r][c + 1] != -1:
c = c + 1
b.append(a[r][c])
a[r][c] = -1
cnt += 1
while r - 1 >= 0 and a[r - 1][c] != -1:
r = r - 1
b.append(a[r][c])
a[r][c] = -1
cnt += 1
while c - 1 >= 0 and a[r][c - 1] != -1:
c = c - 1
b.append(a[r][c])
a[r][c] = -1
cnt += 1
# 将b列表中的数字用空格连接起来,避免末尾有多余空格
print(" ".join([str(i) for i in b]))
芯片测试
题目链接
n = int(input())
a = []
# 初始化芯片状态
b = [0] * n
for i in range(n):
a.append(list(map(int, input().split())))
# 好芯片比坏芯片多,将真芯片标记为1
if sum(a[i]) > n // 2:
b[i] = 1
# 枚举每个芯片
for i in range(n):
# 跳过假芯片
if b[i] == 0:
continue;
# 对真芯片进行投票,如果超过半数则为真芯片
sum = 0
# 枚举每一列的测试情况
for j in range(n):
if a[j][i] == 1:
sum += 1
if sum > n // 2:
print(i + 1, end = " ")
不同单词个数统计
题目链接
a = input().split()
s = set(a)
print(len(s))
报时助手
题目链接
a = {0: 'zero', 1: 'one', 2: 'two', 3: 'three', 4: 'four', 5: 'five',
6:'six', 7: 'seven', 8: 'eight', 9: 'nine', 10: 'ten', 11:'eleven',
12: 'twelve', 13: 'thirteen', 14: 'fourteen', 15:'fifteen', 16: 'sixteen',
17: 'seventeen', 18: 'eighteen', 19:'nineteen', 20: 'twenty', 21: 'twenty one',
22: 'twenty two', 23: 'twenty three', 30: 'thirty', 40: 'forty', 50: 'fifty'}
h, m = map(int, input().split())
if m == 0:
print("%s o'clock" % a[h])
else:
print(a[h], end = " ")
if m <= 20 or m == 30 or m == 40 or m == 50:
print(a[m])
elif m < 30:
print(a[20] + " " + a[m - 20])
elif m < 40:
print(a[30] + " " + a[m - 30])
elif m < 50:
print(a[40] + " " + a[m - 40])
else:
print(a[50] + " " + a[m - 50])
寻找三位数
题目链接
def check(s):
if len(s) != 9:
return False
s = set(s)
return ('0' not in s) and len(s) == 9
for a in range(100, 1000):
b = a * 2
c = a * 3
s = str(a) + str(b) + str(c)
if check(s):
print(a, b, c)
数的读法
题目链接
a = { 0 : "ling", 1 : "yi", 2 : "er", 3 : "san", 4 : "si", 5 : "wu",
6 : "liu", 7 : "qi", 8 : "ba", 9 : "jiu", 10 : "yi shi" }
def work(n, allowZero):
# 千位
q = n // 1000
hasQ = 0
if q > 0:
# 千位不为0
print("%s qian" % a[q], end = " ")
hasQ = 1
allowZero = 1
# 百位
b = n // 100 % 10
hasB = 0
if b > 0:
# 百位不为0
if allowZero and not hasQ:
print("ling %s bai" % a[b], end = " ")
else:
print("%s bai" % a[b], end = " ")
hasB = 1
allowZero = 1
# 十位
s = n // 10 % 10
hasS = 0
if s > 0:
if allowZero and not hasB:
print("ling %s shi" % a[s], end = " ")
else:
# 特殊处理:当十位为1时
if s == 1:
print("shi", end = " ")
else:
print("%s shi" % a[s], end = " ")
hasS = 1
allowZero = 1
# 个位
g = n % 10
hasG = 0
if g > 0:
if allowZero and not hasS:
print("ling %s" % a[g], end = " ")
else:
print("%s" % a[g], end = " ")
hasG = 1
return (hasQ or hasB or hasS or hasG)
n = int(input())
# 处理超过亿位的数字
t = n // 100000000
hasY = work(t, 0)
if hasY:
print("yi", end = " ")
# 处理超过万位的数字
t = n // 10000 % 10000
hasW = work(t, hasY)
if hasW:
print("wan", end = " ")
# 处理最低4位数字
t = n % 10000
work(t, hasW)
Hanoi问题
题目链接
def hanoi(n, m):
if n <= m:
return 1
return hanoi(n - m, m) + 1 + hanoi(n - m, m)
n, m = map(int, input().split())
print(hanoi(n, m))
阿尔法乘积
题目链接
# 递归求解n的阿尔法乘积
def work(n):
if n < 10:
return n
# 拆位相乘
m = 1
while n != 0:
if n % 10 != 0:
m *= n % 10
n //= 10
return work(m)
n = int(input())
print(work(n)
递归倒置字符数组
题目链接
def reverse(s, L, R):
if L >= R:
print("")
return
# 交换L和R位置上的字符
s[L], s[R] = s[R], s[L]
print("".join(s))
reverse(s, L + 1, R - 1)
n, s = input().split()
n = int(n)
# 将s转为列表进行处理
a = list(s)
reverse(a, 0, len(s) - 1)
print("".join(a))
Sine之舞
题目链接
def A(k, n):
if k == n:
return "sin({})".format(n)
op = "-" if k % 2 else "+"
return "sin({}{}{})".format(k, op, A(k + 1, n))
def S(k, n):
if k == n:
return "{}+{}".format(A(1,1), n)
return "({}){}+{}".format(S(k + 1, n), A(1, n - k + 1), k)
n = int(input())
print(S(1, n))