2022年C++学习笔记
第一节 C++编写动态库
1.1 编写库代码
动态加载不需要.h和.lib文件,只需要.dll文件,同时知道所要使用的函数的参数类型以及返回值类型。
1.1.1 代码编写
案例代码:OperationFolder.cpp
#include案例代码:OperationFolder.h
#pragma once
#ifdef OPERATIONFOLDER_EXPORTS
#define OPERATIONFOLDER_API _declspec(dllexport)
#else
#define OPERATIONFOLDER_API _declspec(dllimport)
#endif
#include 1.2 静态加载dll
1.2.1 将编译生成的dll文件,.h文件,.lib文件拷贝到引用的目录下。
1.3 修改代码实现编写动态库
动态库就是说,无需.h和.lib文件,只需要.dll文件,同时知道所要使用的函数的参数类型以及返回值类型,依旧以1.2节的DLL为例。不过要稍做修改。这个时候我在原来的MyDll项目中改变了如下文件
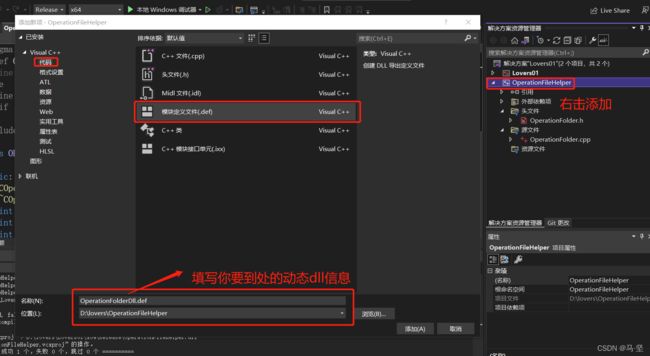
OperationFolderDll.def
LIBRARY "OperationFolder"
EXPORTS
getInstance
如果没有EXPORTS后面的代码会出现,找不到的问题。原因由于C++的编译方式考虑了函数重载,所以对函数名进行了新的修饰,产生了所谓的破坏性命名。这样实际上,我们在exe中调用的函数名字就是已经被修饰过的,所以我们直接按照原来的函数名自然就找不到了!
OperationFolderHelper.h
#pragma once
#include OperationFolderHelper.cpp
#include "OperationFolderHelper.h"
#include "OperationFolder.h"
COperationFolderHelper* getInstance()
{
return new COperationFolder();
}
OperationFolder.h
#pragma once
#include OperationFolder.cpp
#includemain.cpp
#include函数指针:如果在程序中定义了一个函数,那么在编译时系统就会为这个函数代码分配一段存储空间,这段存储空间的首地址称为这个函数的地址。而且函数名表示的就是这个地址。既然是地址我们就可以定义一个指针变量来存放,这个指针变量就叫作函数指针变量,简称函数指针。函数指针是指向函数的指针,而指针函数是返回值是指针的函数。指针函数定义:int *fun(int x); 函数指针定义:int (*f)(int); typedef void(*Func)(void) 是函数指针的类型定义,作用是声明一个 void(*)() 类型的函数指针 Func.
第二节 C++对文件的基本操作
2.1 使用C++代码创建文件夹。
2.1.1 使用direct.h头文件中的mkdir创建文件夹和io.h中的_access判断是否存在目标文件夹。
创建文件夹代码
#include第三节 C++项目工程配置
3.1 保证生成的.dll和.lib以及.h到指定的文件夹
假设代码目录如下
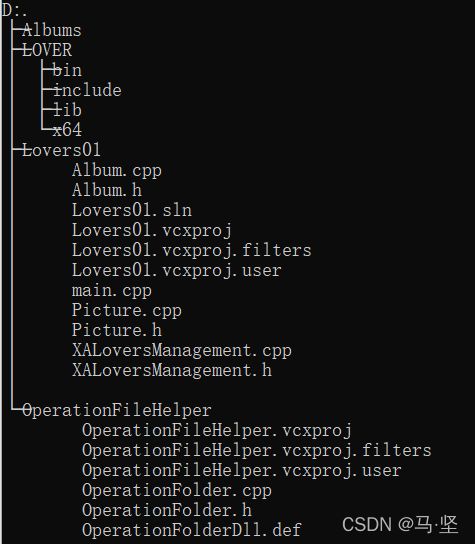
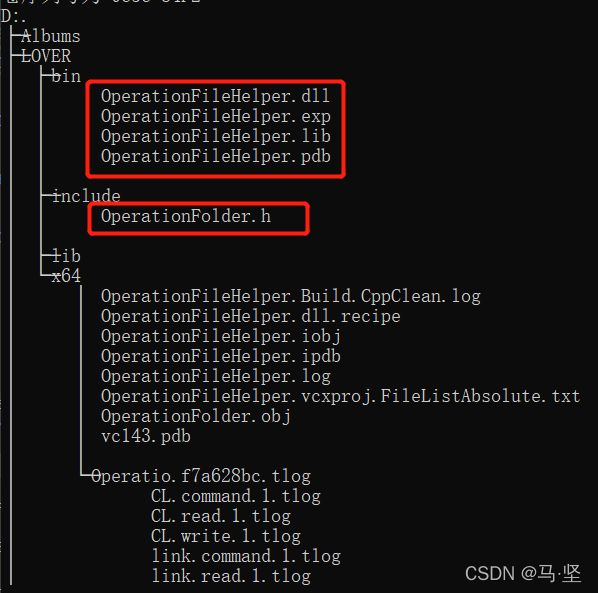
说明:代码位于OPerationFileHelper文件夹下,目的将生成的dll和lib文件放入到LOVER\bin\目录下,将.h文件放入到LOVER/include文件下。中间文件放入到x64文件夹下。
3.1.1 配置项目的输出目录,使得生成的dll和lib文件放入到LOVER\bin\目录下。
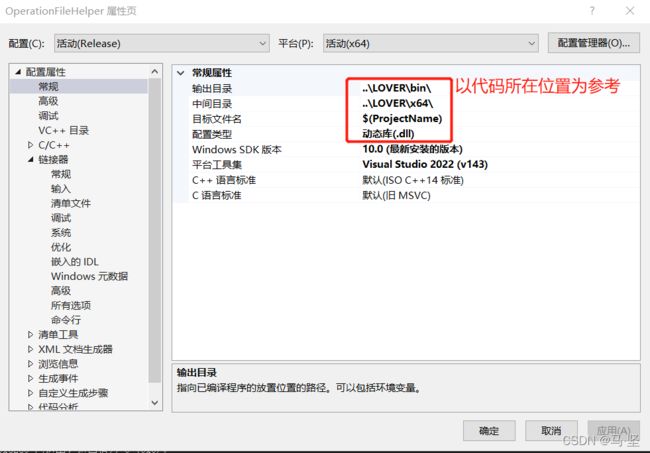
输出的目录填写后,会将dll生成到该目录下
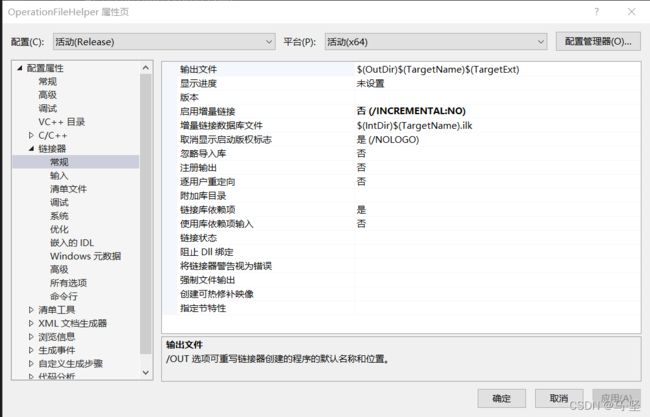
设置输出的dll和exe的路径,通过设置链接器+常规中的输出文件来实现。
 设置输出的lib的路径,通过设置链接器+高级中的导入库(其实是导出的)来实现。
设置输出的lib的路径,通过设置链接器+高级中的导入库(其实是导出的)来实现。
3.1.2 配置项目的生成事件,将.h文件拷贝到LOVER/bin目录中。
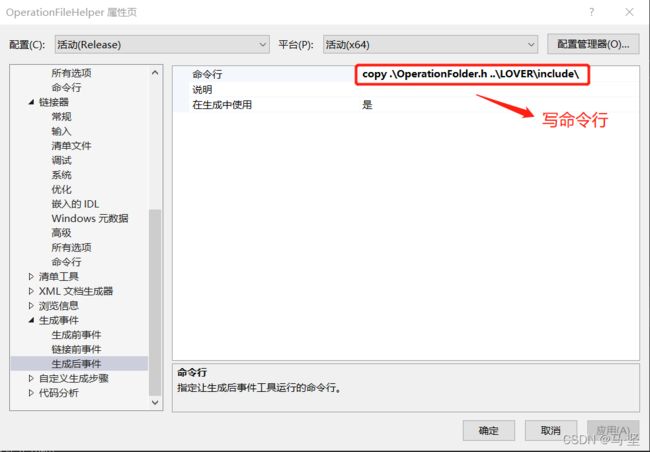
经过如上配置后,点击生成项目,生成目录如下。可以发现成功生成。
3.2 使用dll工程配置
3.2.1 目录说明
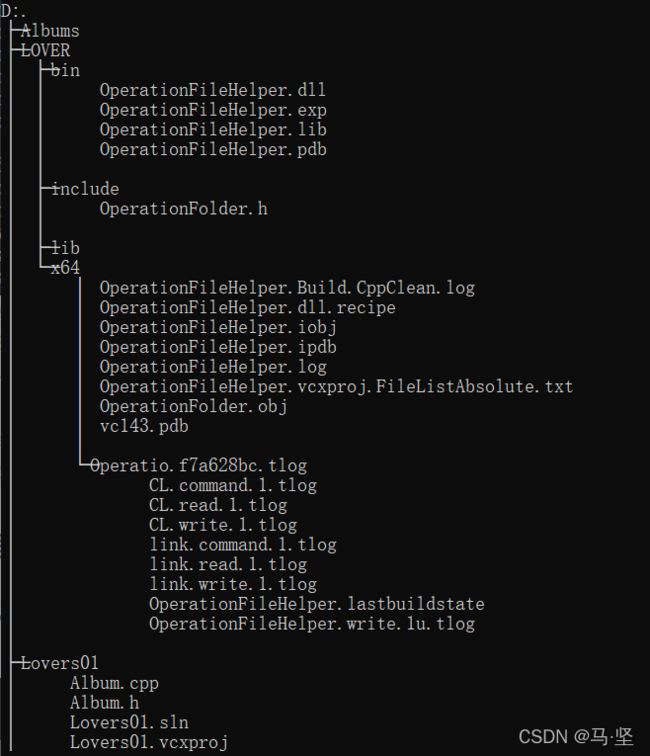
如上图所示,工程Lovers01需要调用LOVER/bin/目录下的OperationFolderHelper.dll文件,需要的配置如下
3.2.2 配置步骤
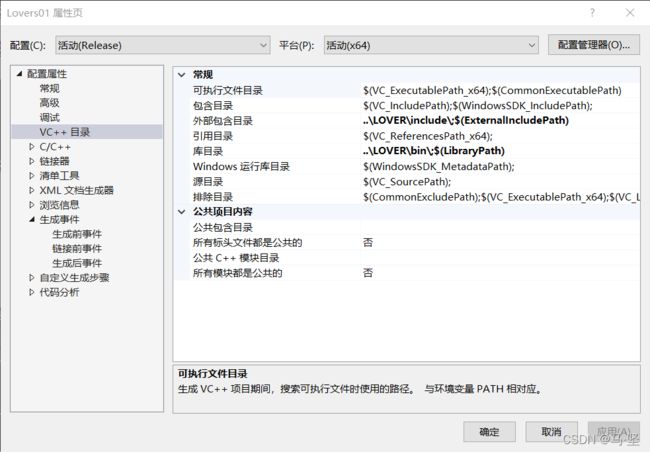
第一步,配置VC++目录。
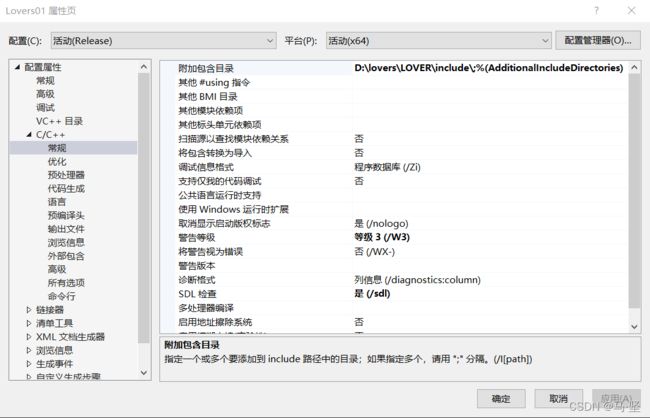
第二步,配置C/C++常规
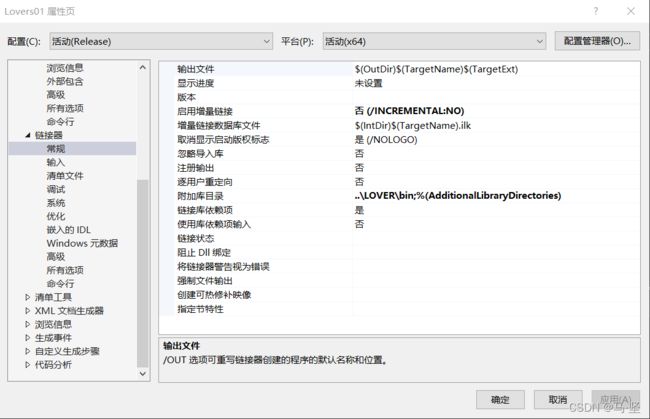
第三部 配置链接器+常规
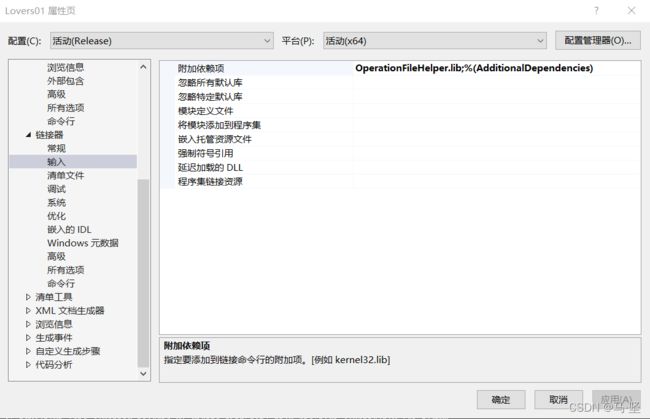
第四步 配置连接器+输入
第五步 总结备注
- 包含目录和附加包含目录(库目录和附加库目录)的区别
- 包含目录:修改了系统的include宏的值,是全局的;
- 附加包含目录:用于当前项目,对其他项目没有影响。
- 一般当需要对某工程添加这些目录时,通常情况下,都是在附加包含目录和附加库目录中添加的。添加方法如下
- 附加包含目录—添加工程的头文件目录:
- 项目->属性->配置属性->C/C+±>常规->附加包含目录:加上头文件的存放目录;
- 附加库目录—添加文件引用的lib静态库路径:
- 项目->属性->配置属性->链接器->常规->附加库目录:加上lib文件的存放目录;
- 附加依赖项—添加工程引用的lib文件名:
- 项目->属性->配置属性->链接器->输入->附加依赖项:加上lib文件名。
- 附加包含目录—添加工程的头文件目录: