一、核心配置文件
一个项目中 application.yml 和 application.properties 只能有一个。
(一)application.properties
# 设置内嵌Tomcat端口号
server.port = 8081
#设置上下文根
server.servlet.context-path = /springboot(二)application.yml
YML文件格式是YAML (YAML Aint Markup Language)编写的文件格式,YAML是一种直观的能够被电脑识别的的数据数据序列化格式,并且容易被人类阅读, 容易和脚本语言交互的,可以被支持YAML. YML文件是以数据为核心的,比传统的xml方式更加简洁。
server:
port: 8081
servlet:
context-path: 二、获取SpringBoot自定义配置的字段
(一)通过 @Value 注解读取自定义配置字段
配置 application.properties
# 设置内嵌Tomcat端口号
server.port = 8081
#设置上下文根
server.servlet.context-path = /springboot
school.name = binSchool
websit=http://bninecoding.com使用 @Value("${school.name}")
@Value(${school.name})
private String schoolName;(二)将自定义配置映射成对象
涉及注解:
@Component // 将此类交给spring容器进行管理
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "school")
@Autowired配置 application.properties
server.servlet.context-path = /springboot
school.name = binSchool
school.websit = binSchool
abc.name = binSchool
abc.websit = binSchool创建 school 类:
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "school")
public class School {
private String name;
private String websit;
public String getName() {
retutrn name;
}
public void setname(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
...
}因为@Component这样做之后已经将 school 类加载到 spring 容器里了,所以使用时可以使用 @Autowired 注入进来:
public class IndexController {
@Autowired
private School school;
@RequestMapping(value = "/say")
public @responseBody String say() {
return "school.name=" + school.getName() + "---school.websit=" + school.getWebsit;
}
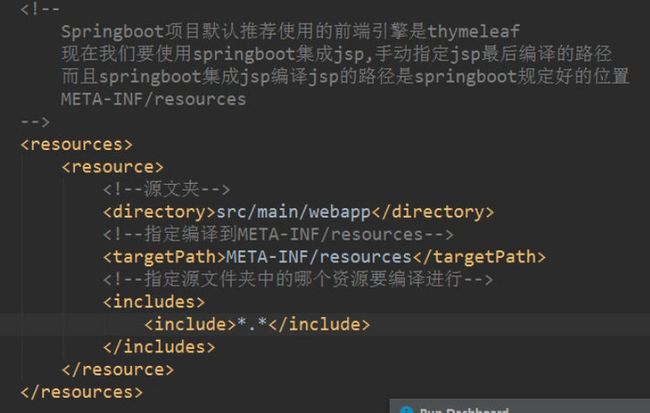
}三、SpringBoot集成jsp
(一)环境集成
配置视图解析器, application.properties :
spring.mvc.view.prefix = /
spring.mvc.view.suffix = .jsp(二)使用 jsp
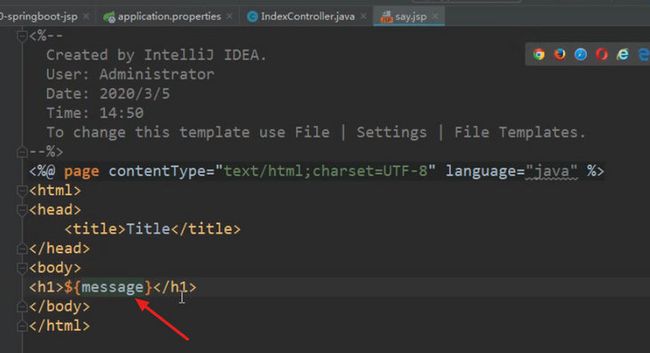
注:请教了做前后端的同学,现在基本不用 jsp 了,jsp 是后端做前端的问题,现在都交给前端做了,也就是迁到Vue了。
1. 配置接口
@RequestMapping(value = "/say")
public ModelAndView say() {
ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView();
mv.addObject("message","Hello,SpringBoot");
mv.setViewName("say");
return mv;
}2. 创建页面
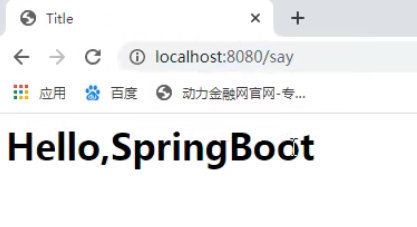
访问新创建的页面:
四、集成 Mybatis
MyBatis 是一款优秀的持久层框架,它支持自定义 SQL、存储过程以及高级映射。MyBatis 免除了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码以及设置参数和获取结果集的工作。MyBatis 可以通过简单的 XML 或注解来配置和映射原始类型、接口和 Java POJO(Plain Old Java Objects,普通老式 Java 对象)为数据库中的记录。
(一)添加Mybatis依赖,MySQL驱动(略)
(二)Mybatis Generator 自动生成代码(略)
在 renren-fast 项目中可以使用 renren-fast-generate 自动生成前后端的代码。
(三)Dao和Mapper
使用MyBatis开发Dao,通常有两个方法,即原始Dao开发方法和Mapper动态代理开发方法。
DAO层叫数据访问层,全称为data access object,属于一种比较底层,比较基础的操作,具体到对于某个表的增删改查,也就是说某个DAO一定是和数据库的某一张表一一对应的,其中封装了增删改查基本操作,建议DAO只做原子操作,增删改查。
Service层叫服务层,被称为服务,粗略的理解就是对一个或多个DAO进行的再次封装,封装成一个服务,所以这里也就不会是一个原子操作了,需要事物控制。
使用mapper代理的方法来开发dao时,程序员只需要干两件事即可,比使用原始Dao开发更加:
1、编写mapper.xml映射文件
2、编写mapper接口(相当于dao接口)
五、SpringBoot 常用注解
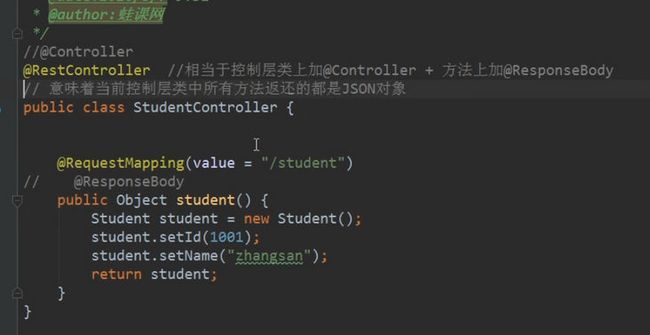
@RestController
相当于控制层类上加 @Controller + 所有方法上加 @ResponseBody。
意味着当前控制层类中所有方法返回的都是JSON对象
@RequestMapping
@RequestMapping = @GetMapping + @PostMapping
- @PostMapping :增加数据 使用
- @DeleteMapping:删除数据 使用
- @PutMapping : 修改数据 使用
- @GetMapping : 查询数据 使用
那每一个接口都要区分 增删改查 吗?
工作中没有明确要求,用哪个都行,平时用得最多的是 Post
六、RESTful
REST 英文:Representational State Transfer ,它是一种架构设计的风格,但它并不是标准,它只是提出了一组客户端和服务器交互式的架构理念和设计原则,基于这种理念和原则设计的接口可以更简洁,更有层次。
任何的技术都可以实现这个理念,如果一个架构符合REST原则,就称它为RESTFul架构,RESTful中path尽量使用名词,不要使用动词。
比如我们要访问一个 http 接口: http://localhost:8080/boot/or...
采用RESTFul风格则 http 地址为: http://localhost:8080/boot/or...
(一)原始HTTP解析参数的写法
@RequestMapping(value = "/student")
public Object student(Integer id, Integer age) {
Student stuent = new Student();
student.setId(id);
student.setAge(age);
return student;
}然后访问地址: localhost:8080/student?id=1001&age=23
(二)RESTful写法
@PathVariable : 路径变量,取路径里的值
@RequestMapping(value = "/student/detail/{id}/{age}")
public Object student(@PathVariable("id") Integer id,
@PathVariable("age") Integer age) {
Map retMap = new HashMap<>();
retMap.put("id",id);
retMap.put("age",age);
return retMap;
} 访问地址: localhost:8080/student/detail/1010/28
可以发现: RESTful更安全了一点,如果不是开发者,调用方不知道参数是什么意思。
但使用 RESTful 还会存在问题:
@RequestMapping(value = "/student/detail/{id}/{age}")
public Object student(@PathVariable("id") Integer id,
@PathVariable("age") Integer age) {
Map retMap = new HashMap<>();
retMap.put("id",id);
retMap.put("age",age);
return retMap;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/student/detail/{id}/{status}")
public Object student(@PathVariable("id") Integer id,
@PathVariable("status") Integer status) {
Map retMap = new HashMap<>();
retMap.put("id",id);
retMap.put("status", status);
return retMap;
} 以上代码 student1 和 student2 会出现请求路径迷糊的错误,
比如请求路径: localhost:8080/student/detail/1010/28
因为没有明确指明变量名,所以也无法知晓这个请求是连向 id-age 还是 id-status。
通常在 RESTful风格中方法的请求方式会按 增删改查 的请求方式来区分,比如可以这么修改:
// @RequestMapping(value = "/student/detail/{id}/{age}")
@GetMapping(value = "/student/detail/{id}/{age}")
public Object student(@PathVariable("id") Integer id,
@PathVariable("age") Integer age) {
Map retMap = new HashMap<>();
retMap.put("id",id);
retMap.put("age",age);
return retMap;
}
/// @RequestMapping(value = "/student/detail/{id}/{status}")
@DeleteMapping(value = "/student/detail/{id}/{status}")
public Object student(@PathVariable("id") Integer id,
@PathVariable("status") Integer status) {
Map retMap = new HashMap<>();
retMap.put("id",id);
retMap.put("status", status);
return retMap;
} 如果两个都是GET请求,那就根据请求的意思修改path路径。
RESTful 经常出现上面路径重复的问题,解决方式有:
- 修改请求方式
- 修改path路径
RESTful 小结
项目中用不用 RESTful 基本不是你能决定的,项目如果采用 RESTful,那你就用 RESTful,项目不用你也用不了。
七、Redis
(一)什么时候需要用Redis呢?
- 不需要实时更新但是又极其消耗数据库的数据。比如网站上商品销售排行榜,这种数据一天统计一次就可以了,用户不会关注其是否是实时的。
- 需要实时更新,但是更新频率不高的数据。比如一个用户的订单列表,他肯定希望能够实时看到自己下的订单,但是大部分用户不会频繁下单。
- 在某个时刻访问量极大而且更新也很频繁的数据。这种数据有一个很典型的例子就是秒杀,在秒杀那一刻,可能有N倍于平时的流量进来,系统压力会很大。但是这种数据使用的缓存不能和普通缓存一样,这种缓存必须保证不丢失,否则会有大问题。
一般地,Redis可以用来作为MySQL的缓存层。为什么MySQL最好有缓存层呢?
想象一下这样的场景:在一个多人在线的游戏里,排行榜、好友关系、队列等直接关系数据的情景下,如果直接和MySQL正面交手,大量的数据请求可能会让MySQL疲惫不堪,甚至过量的请求将会击穿数据库,导致整个数据服务中断,数据库性能的瓶颈将掣肘业务的开发;那么如果通过Redis来做数据缓存,将大大减小查询数据的压力。在这种架子里,当我们在业务层有数据查询需求时,先到Redis缓存中查询,如果查不到,再到MySQL数据库中查询,同时将查到的数据更新到Redis里;当我们在业务层有修改插入数据需求时,直接向MySQL发起请求,同时更新Redis缓存。
(二)配置 redis
application.properties配置:
# 设置redis配置信息
spring.redis.host = 192.168.154.128
spring.redis.port = 6379
spring.redis.password = 123456(三)使用redis
// 使用redis业务逻辑
@Controller
public class StudentController {
@Autowired
private StudentService studentService;
@RequestMapping(value = "/put")
public @ResponseBody Object put(String key, string value) {
studentService.put(key,value);
return "值已成功放入redis"
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/get")
public String get() {
String count = studentService.get("count");
return "数据count为:" + count;
}
}
@Service
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Override
public void put(String key, String value) {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key,value);
}
@Override
public String get(String key) {
String count = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key)
return count;
}
}