Java集合
集合框架图
java.lang.Iterable : 实现这个接口允许对象成为 "foreach" 语句的目标
| |方法
| |------- Iterator iterator() 返回一个在一组 T 类型的元素上进行迭代的迭代器
|
|子类
|--- java.util.Collection Collection 层次结构 中的根接口。
| | Collection 表示一组对象,这些对象也称为 collection 的元素
| |
| |
| |子类
| |-------- java.util.List
| | |
| | |------- java.util.ArrayList实现类
| | |------- java.util.LinkedList实现类
| | |------- java.util.Vector实现类
| | | |子类
| | | |------- java.util.Stack
| |子类
| |-------- java.util.Queue
| | |子类
| | |------ java.util.Deque
| | | |实现类
| | | |---- java.util.LinkedList
| |
| | 子类
| |-------- java.util.Set
| | |------- java.util.HashSet实现类
| | |------- java.util.TreeSet
| | |实现NavigableSet,NavigableSet继承SortedSet,SortedSet继承Set
| | |------- java.util.LinkedHashSet实现类并继承HashSet
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
java.util.Map
|
|------ java.util.HashMap实现类
|
|------ java.util.Hashtable实现类
| |子类
| |------ java.util.Properties
|
|
|--- java.util.SortedMap子类
| |子类
| |-------- java.util.NavigableMap
| | |实现类
| | |------- java.util.TreeMap
|
|
|--- java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap子类
| |实现类
| |-------- java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap
Iterator:迭代器,它是Java集合的顶层接口(不包括 map 系列的集合,Map接口 是 map 系列集合的顶层接口)。
Collection接口是集合类的根接口,Java中没有提供这个接口的直接的实现类。但是却让其被继承。Collection继承的是类 Iterable,Iterable里面封装了 Iterator 接口。所以只要实现了只要实现了Iterable接口的类,就可以使用Iterator迭代器。Collections中containsAll,contains,removeAll,remove是根据equals方法定义的。
List、Set和Queue继承Collection。
Map是Java.util包中的另一个接口,它和Collection接口没有关系,是相互独立的,但是都属于集合类的一部分。Map包含了key-value对。Map不能包含重复的key,但是可以包含相同的value。
HashMap和Hashtable实现接口Map,SortedMap和ConcurrentMap继承接口Map。
List接口特点
1、有序的 collection。
2、可以对列表中每个元素的插入位置进行精确地控制。
3、可以根据元素的索引访问元素,并搜索列表中的元素。
4、列表通常允许重复的元素。
5、允许存在 null 元素。
6、实现List接口的常用类有LinkedList、ArrayList、Vector和Stack。
List排序
1、按照自然顺序排序 : sort( List
自然顺序: 实现Comparable接口才能自然排序。 java.lang.Comparable
public int compareTo( T o ) 如果该对象小于、等于或大于指定对象,则分别返回负整数、零或正整数。
package ecut.collection;
// 声明 java.lang.Comparable 接口时, 表示类型参数 ( "形参")
// 在 实现接口 时, 也是类型参数 ( "实参" )
public class Panda implements Comparable{
private Integer id;
private String name;
public Panda(Integer id, String name) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
//确定比较规则,Integer id比较时不能用==,应该用equals方法
@Override
public int compareTo( Panda another ) {
if( this.id != null && another.id != null ) {
return this.id - another.id ; // this.id 和 another.id 不能是负数
/*
if( this.id < another.id ){
return -1 ;
} else if( this.id.equals( another.id ) ) {
return 0 ;
} else {
return 1 ;
}
*/
}
return 0;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "(id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ")";
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
} package ecut.collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class SortListTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add( new Panda( 100 , "桂花" ) );
list.add( new Panda( 88 , "花菜" ) );
list.add( new Panda( 200 , "团团" ) );
list.add( new Panda( 99 , "圆圆" ) );
System.out.println( list );
Collections.sort( list );//列表中的所有元素都必须实现 Comparable 接口。
System.out.println( list );//重写了toString方法,因此可以直接输出。
}
} 运行结果如下:
[(id=100, name=桂花), (id=88, name=花菜), (id=200, name=团团), (id=99, name=圆圆)]
[(id=88, name=花菜), (id=99, name=圆圆), (id=100, name=桂花), (id=200, name=团团)]2、按照比较器进行排序: sort(List
比较器: java.util.Comparator
int compare ( T o1 , T o2 ) 比较用来排序的两个参数:根据第一个参数小于、等于或大于第二个参数分别返回负整数、零或正整数。
package ecut.collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
public class SortListTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList<>(); // "菱形"语法
list.add( new Panda( 100 , "桂花" ) );
list.add( new Panda( 88 , "花菜" ) );
list.add( new Panda( 200 , "团团" ) );
list.add( new Panda( 99 , "圆圆" ) );
System.out.println( list );
// 创建一个用来比较 Panda 类型对象的 比较器 ( 裁判 )
Comparator c = new Comparator(){
@Override
public int compare(Panda o1, Panda o2) {
if( o1 != null && o2 != null ) {
String name1 = o1.getName() ;
String name2 = o2.getName();
if( name1 != null ){
// String 类实现了 Comparable 接口的 compareTo 方法
return name1.compareTo( name2 );
}
}
return 0;
}
};//Comparator是接口因此要用匿名内部类实现抽象的方法
Collections.sort( list , c ); // 根据给定的比较器来排序
System.out.println( list );
}
} 运行结果如下:
[(id=100, name=桂花), (id=88, name=花菜), (id=200, name=团团), (id=99, name=圆圆)]
[(id=200, name=团团), (id=99, name=圆圆), (id=100, name=桂花), (id=88, name=花菜)]List接口主要实现类
1、java.util.ArrayList
- ArrayList 内部基于 数组 存储 各个元素。
- 所谓大小可变数组,是指当 数组容量不足以存放新的元素时,创建新数组,并将原数组中的内容复制过来。
ArrayList类的add方法测试案例:
package ecut.collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ArrayListTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] x = { 1 , 2 };
System.out.println( Arrays.toString( x ) );
// x.length = 10 ; // The final field x.length cannot be assigned
// x[ 2 ] = 3 ; // ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>(0); // JDK 1.7 开始支持 "菱形" 语法
System.out.println( list ); // list.toString(),list重写了toString方法,因此可以直接输出。
list.add( "hello" );
System.out.println( list );
}
} 源码:
/**
* 向列表的尾部添加指定的元素(可选操作)。
*
* @param e 要添加到列表的元素
* @return true (根据 Collection.add(E) 的规定)
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}运行结果如下:
[1, 2]
[]
[hello]add()方法开销为分摊的常数,添加n个元素需要O(n)的时间。其他的方法运行时间为线性。每个ArrayList实例都有一个容量(Capactity),即用于存储元素的数组的大小。这个容量可随着不断添加新元素而自动增加,但是增长算法并没有定义。当需要插入大量元素时,在插入之前可以调用ensureCapacity()方法来增加ArrayList容量已提高插入效率确保容量可用后在末尾添加指定元素。
ArrayList类的remove方法测试案例:
package ecut.collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArrayListTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add( 2 ); // auto-boxing : 2 ---> Integer.valueOf( 2 )
list.add( 200 ) ;
list.add( 2 ) ;
list.add( 20 );
System.out.println( list );
// T remove( int index ) 是 List 接口定义的方法
Integer removed = list.remove( 2 ); // 根据索引删除,而不是根据 Integer 对象删除
System.out.println( "被删除的元素:" + removed );
System.out.println( list );
Object o = 2 ; // auto-boxing
// boolean remove( Object o ) 是 Collection 接口定义的方法
boolean result = list.remove( o ) ; // 根据元素来删除
System.out.println( result );
System.out.println( list );
}
} 运行结果如下:
[2, 200, 2, 20]
被删除的元素:2
[2, 200, 20]
true
[200, 20]自动装箱将基本数据类型包装成Integer对象放入list里。T remove(int index):删除的是下标位置的对象并返回(List接口中定义的方法),boolean remove(Object o):删除对象(Colletion接口中都有的)。
2、java.util.LinkedList
- 内部基于链表实现,增删快、迭代快,随机访问能力较差。
- 链表中的每个节点都是 LinkedList.Node 类型的对象。
- LinkedList提供额外的get、remove、insert方法在LinkedList的首部或尾部。
- 这些操作使LinkedList可被用作堆栈(stack),队列(queue)或双向队列(deque)。
- LinkedList没有同步方法。如果多个线程想访问同一个List,则必须自己实现访问同步。
LinkedList类的add方法测试案例:
package ecut.collection;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class LinkedListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add( "猴哥" );
list.add( "二师兄" );
list.add( "老沙" );
System.out.println( list );
System.out.println( list.get( 2 ) );
list.add( 1 , "白龙马" );
System.out.println( list );
}
} 源码:
private static class Node {
E item; // 表示当前节点存放的数据
Node next; // 指向下一个节点的指针
Node previous; // 指向前一个节点的指针
Node(Node previous, E element, Node next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.previous = previous;
}
}
/**
* 将指定元素添加到此列表的结尾。
*
*
* 此方法等效于{@link #addLast}.
*
* @param 要添加到此列表的元素
* @return {@code true} (根据 Collection.add(E) 的规定)
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node l = last;
final Node newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
运行结果如下:
[猴哥, 二师兄, 老沙]
老沙
[猴哥, 白龙马, 二师兄, 老沙]add方法调用linkLast 方法去实现,找到最后的节点,创建新的节点以最后的节点为前节点,新节点作为最后的节点。 list.get( 2 )链表没有索引的说法,不是直接访问2的位置而是实际遍历整个链表去查找,因此随机访问能力较差。插入和删除的效率比较高。
3、java.util.Vector
- 内部也是用数组存放元素。
- 与 ArrayList 不同的是 扩容方式不同,Vector 每次增长的容量是固定的,大部分方法都被 synchronized 关键字修饰。
- Vector 是线程安全的。
Vector类的测试案例:
package ecut.collection;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Vector;
public class VectorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个 Vector 实例,其初始容量为 10 ,容量的增量为 5
Vector v = new Vector<>( 10 , 5 );
v.add( "hello" );
v.addElement( "world" );
System.out.println( v );
v.add( 1 , "你好" );
System.out.println( v );
v.insertElementAt( "世界" , 2 );
System.out.println( v );
Enumeration e = v.elements();//类似迭代器
while( e.hasMoreElements() ) {
String s = e.nextElement();
System.out.println( s );
}
}
} 源码:
/**
* 使用指定的初始容量和容量增量构造一个空的向量。
*
* @param initialCapacity 向量的初始容量
* @param capacityIncrement 当向量溢出时容量增加的量
* @throws IllegalArgumentException 如果指定的初始容量为负数
*/
public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement;
}运行结果如下:
[hello, world]
[hello, 你好, world]
[hello, 你好, 世界, world]
hello
你好
世界
world4、java.util.Stack
- 表示堆栈。
- 栈的特点: 后进先出。
Stack类的测试案例:
package ecut.collection;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
System.out.println( stack.empty() );
stack.push( "first" );
stack.push( "second" );
stack.push( "third" );
System.out.println( stack );
String top = stack.peek();
System.out.println( "top : " + top );
System.out.println( stack );
top = stack.pop();
System.out.println( "top : " + top );
System.out.println( stack );
System.out.println( stack.empty() );
int index = stack.search( "first" ); // 返回对象在堆栈中的位置,以 1 为基数(只有jdbc和stack.search以 1 为基数)
System.out.println( index );
}
} 运行结果如下:
true
[first, second, third]
top : third
[first, second, third]
top : third
[first, second]
false
2Queue接口特点
1、先进先出 ( FIFO , First In , First Out )。
2、Queue接口子类Deque的实现类LinkedList。
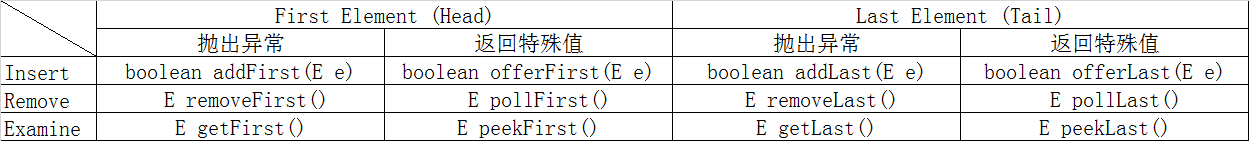
3、除了基本的 Collection 操作外,队列还提供其他的插入、提取和检查操作。每个方法都存在两种形式:一种抛出异常(操作失败时),另一种返回一个特殊值(null 或 false,具体取决于操作)。
Queue类可能会抛出异常的测试案例:
package ecut.collection;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class QueueTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue queue= new LinkedList<>();
queue.add( "林冲" );
queue.add( "晁盖" );
queue.add( "武松" );
System.out.println( queue );
//queue.clear();
//当无法获取到元素时,element 方法抛出 NoSuchElementException
String head = queue.element() ; // 获取队列头部的元素,但不删除
System.out.println( head );
System.out.println( queue );
//queue.clear();
//当无法获取到元素时,remove 方法抛出 NoSuchElementException
head = queue.remove(); // 获取并移除队列头部元素
System.out.println( head );
System.out.println( queue );
}
} 运行结果如下:
[林冲, 晁盖, 武松]
林冲
[林冲, 晁盖, 武松]
林冲
[晁盖, 武松]add(e)插入,remove()移除,element()检查当无法获取到元素时,方法抛出 NoSuchElementException异常。
Queue类返回一个特殊值的测试案例:
package ecut.collection;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class QueueTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue queue= new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer( "林冲" );
queue.offer( "晁盖" );
queue.offer( "武松" );
System.out.println( queue );
queue.clear();
// 当无法获取元素时,返回 null,不会抛出异常
String head = queue.peek() ; // 获取队列头部的元素,但不删除
System.out.println( head );
System.out.println( queue );
// 当无法获取元素时,返回 null,不会抛出异常
head = queue.poll(); // 获取并移除队列头部元素
System.out.println( head );
System.out.println( queue );
}
} 运行结果如下:
[林冲, 晁盖, 武松]
null
[]
null
[]offer(e)插入,poll()移除,peek()检查当无法获取元素时,返回 null,不会抛出异常。
Queue接口主要实现类
1、java.util.Deque
- 一个线性 collection,支持在两端插入和移除元素。
- 此接口定义在双端队列两端访问元素的方法。提供插入、移除和检查元素的方法。每种方法都存在两种形式:一种形式在操作失败时抛出异常,另一种形式返回一个特殊值(null 或 false,具体取决于操作),共12个方法。
- 在将双端队列用作队列时,将得到 FIFO(先进先出)行为。
- 继承Queue的6个方法以及和栈的3个方法,共21个方法需了解。
- 方法:
由于继承了Queue,所以Deque拥有Queue的方法,因此以下方法等价:
add(e) <--> addLast(e)
offer(e) <--> offerLast(e)
remove() <--> removeFirst()
poll() <--> pollFirst()
element() <--> getFirst()
peek() <--> peekFirst()
也可以用于Stack,因此以下方法等价:
push(e) <--> addFirst(e)
pop() <--> removeFirst()
peek() <--> peekFirst()
Deque测试案例:
package ecut.collection;
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class DequeTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 以 输出 deque 的字符串形式 的 "左侧" 为头
Deque deque = new LinkedList<>();
//将指定的元素插入此双端队列的末尾
deque.offerLast( "曹操" ) ;
deque.offerLast( "曹丕" );
deque.offerLast( "曹爽" );
deque.offerLast( "司马炎" );
System.out.println( deque );
//获取并移除此双端队列的第一个元素;如果此双端队列为空,则返回 null。
String head = deque.pollFirst();
System.out.println( "移除队列头: " + head );
System.out.println( deque );
head = deque.pollFirst();
System.out.println( "移除队列头: " + head );
System.out.println( deque );
head = deque.pollFirst();
System.out.println( "移除队列头: " + head );
System.out.println( deque );
}
} 运行结果如下:
[曹操, 曹丕, 曹爽, 司马炎]
移除队列头: 曹操
[曹丕, 曹爽, 司马炎]
移除队列头: 曹丕
[曹爽, 司马炎]
移除队列头: 曹爽
[司马炎]offerLast插入的元素作为最后一个
运行过程:
曹操
曹操, 曹丕
曹操, 曹丕, 曹爽
曹操, 曹丕, 曹爽, 司马炎
以 输出 deque 的字符串形式 的 "左侧" 为头(第一个进入的元素)
Deque测试案例:
package ecut.collection;
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class DequeTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 以 输出 deque 的字符串形式 的 "右侧" 为头
Deque deque = new LinkedList<>();
//将指定的元素插入此双端队列的开头
deque.offerFirst( "曹操" ) ;
deque.offerFirst( "曹丕" );
deque.offerFirst( "曹爽" );
deque.offerFirst( "司马炎" );
System.out.println( deque );
//获取并移除此双端队列的最后一个元素;如果此双端队列为空,则返回 null。
String head = deque.pollLast();
System.out.println( "移除队列头: " + head );
System.out.println( deque );
head = deque.pollLast();
System.out.println( "移除队列头: " + head );
System.out.println( deque );
head = deque.pollLast();
System.out.println( "移除队列头: " + head );
System.out.println( deque );
}
} 运行结果如下:
[司马炎, 曹爽, 曹丕, 曹操]
移除队列头: 曹操
[司马炎, 曹爽, 曹丕]
移除队列头: 曹丕
[司马炎, 曹爽]
移除队列头: 曹爽
[司马炎]offerFirst插入的元素作为第一个
运行过程:
曹操
曹丕, 曹操
曹爽, 曹丕, 曹操
司马炎, 曹爽, 曹丕, 曹操
以 输出 deque 的字符串形式 的 "右侧" 为头(第一个进入的元素)
2、java.util.LinkedList
- 内部基于链表实现,增删快、迭代快,随机访问能力较差。
- 链表中的每个节点都是 LinkedList.Node 类型的对象。
- LinkedList提供额外的get、remove、insert方法在LinkedList的首部或尾部。
- 这些操作使LinkedList可被用作堆栈(stack),队列(queue)或双向队列(deque)。双端队列也可用作 LIFO(后进先出)堆栈。
- LinkedList没有同步方法。如果多个线程想访问同一个List,则必须自己实现访问同步。
LinkedList 当作 "栈" 来使用测试案例:
package ecut.collection;
import java.util.LinkedList;
/**
* 将 LinkedList 当作 "栈" 来使用
* 栈: 后进先出 ( Last In , First Out , LIFO )
*/
public class LinkedListStackTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList s = new LinkedList<>();
s.push( "Java" );
s.push( "C++" );
s.push( "Go" );
System.out.println( s );
String top = s.peek() ; // 检查栈顶元素 ( 只获取不删除 )
System.out.println( top );
System.out.println( s );
top = s.pop(); // 弹出栈顶元素 ( 获取并移除 )
System.out.println( top );
System.out.println( s );
top = s.pop(); // 弹出栈顶元素 ( 获取并移除 )
System.out.println( top );
System.out.println( s );
top = s.pop(); // 弹出栈顶元素 ( 获取并移除 )
System.out.println( top );
System.out.println( s );
}
} 运行结果如下:
[Go, C++, Java]
Go
[Go, C++, Java]
Go
[C++, Java]
C++
[Java]
Java
[]Set接口特点
1、最接近数学中的 "集" 的概念。
2、元素不重复 ( 必须通过元素的 equals 方法来判断是否存在重复元素 )。
3、并且最多包含一个 null 元素(可能有限制)。
Set接口主要实现类
1、java.util.HashSet
- 由 哈希表(实际上是一个 HashMap 实例)支持。
- 元素可以是 null。
- 元素存放的位置跟添加顺序无关 ( 元素存放的位置 跟 element.hashCode() 有关 )。
- 不支持排序(根据hashcode来确定位置的,所以位置不能改变,因此不支持排序)。
HashSet测试案例:
package ecut.collection;
import java.util.HashSet;
public class HashSetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet set = new HashSet<>();
set.add( "张三丰" );
set.add( "张翠山" );
set.add( "殷素素" );
set.add( "张无忌" );
set.add( "谢逊" );
set.add( "赵敏" );
set.add( "张三丰" );
set.add( null );
System.out.println( set );
}
} 源码:
private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();
public boolean add(E e) {
return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}HashMap实现的因为key 不能重复因此Set元素不重复,value为固定的PRESENT。
运行结果如下:
[null, 殷素素, 张翠山, 张三丰, 谢逊, 赵敏, 张无忌]2、Java.util.TreeSet
- NavigableSet
的实现类,NavigableSet 继承SortedSet ,SortedSet 继承Set 。 - TreeSet基于 TreeMap 来实现TreeMap 内部是基于 红黑树( Red-Black tree)。
- SortedSet是有顺序因此TreeSet有顺序 ( 根据元素的自然顺序,元素得实现Comparable接口或比较器排序后存放元素)。
- 元素不可以是 null(每添加一个元素都得进行一次排序调用compareTo方法,一次不能为null)。
- 元素存放的位置 跟 添加顺序无关。
TreeSet测试案例:
package ecut.collection;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class TreeSetTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 如果构造方法没有指定比较器,则根据元素的 自然顺序 排序
// java.lang.String 支持 自然比较
TreeSet ts = new TreeSet<>();
ts.add( "张三丰" );
ts.add( "张翠山" );
ts.add( "殷素素" );
ts.add( "张无忌" );
ts.add( "谢逊" );
ts.add( "赵敏" );
ts.add( "张三丰" );
System.out.println( ts );
}
} 源码:
public TreeSet() {
this(new TreeMap());
} 实际上是创建一个TreeMap,因此TreeSet的元素和treeMap的key特点一样。
运行结果如下:
[张三丰, 张无忌, 张翠山, 殷素素, 谢逊, 赵敏]3、java.util.LinkedHashSet
- 继承HashSet和LinkedList相似。
- 内部是基于链表。
- 不能重复。
Map接口特点
1、将键映射到值的对象 ( Map 集合中存放的是 key-value 对 ( Map.Entry ) )。
2、一个映射不能包含重复的键 ( Map 集合中的 key 不能重复 )。
3、每个键最多只能映射到一个值 ( Map 集合中的 key 只能对应一个 值 )。
4、几乎所有的map都具有三个视图所有的 key 组成的 Set 集合,所有的 value 组成的 Collection 集合和所有的 entry 对应的 Set 集合
Map接口主要方法
V put( K key, V value ) : 将指定的值(value)与此映射中的指定键(key)关联。
V get( Object key ) : 返回指定键所映射的值;如果此映射不包含该键的映射关系,则返回 null。
boolean containsKey(Object key): 如果此映射包含指定键的映射关系,则返回 true。
boolean containsValue(Object value):如果此映射将一个或多个键映射到指定值,则返回 true。。
void clear(): 从此映射中移除所有映射关系(可选操作)。
boolean isEmpty(): 如果此映射未包含键-值映射关系,则返回 true。
int size() :返回此映射中的键-值映射关系数。
V remove(Object key):如果存在一个键的映射关系,则将其从此映射中移除(可选操作)。
void putAll( Map m ) :从指定映射中将所有映射关系复制到此映射中(可选操作)。
Set
Collection
Set
Map接口主要方法的测试案例:
package ecut.collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class MapTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
//以前与 key 关联的值,如果没有针对 key 的映射关系,则返回 null。
Integer value = map.put( "Java从入门到精通" , 98 );
System.out.println( "value : " + value );
// 将指定的值(value)与此映射中的指定键(key)关联
value = map.put( "Java从入门到精通" , 108 );
System.out.println( "value : " + value );
// 返回指定键所映射的值;如果此映射不包含该键的映射关系,则返回 null
System.out.println( map.get( "Java从入门到精通" ) );
System.out.println( map.containsKey( "Java从入门到精通" ) );
System.out.println( map.containsKey( "Oracle从入门到精通" ) );
System.out.println( map.containsValue( 108 ) );
map.put( "C++大学教程" , 108 );
map.put( "A语言大学教程" , 108 );
System.out.println( map );
}
} 运行结果如下:
value : null
value : 98
108
true
false
true
{Java从入门到精通=108, A语言大学教程=108, C++大学教程=108}Map接口主要方法的测试案例:
package ecut.collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class MapTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// map 变量的值 不是 null
// map 集合中没有放入 任何键值对时,isEmpty 返回 true
Map map = new HashMap<>();
System.out.println( "size : " + map.size() + " , isEmpty : " + map.isEmpty() );
map.put( "软件工程" , 500 );
map.put( "通信工程" , 200 );
map.put( "土木工程" , 100 );
System.out.println( "size : " + map.size() + " , isEmpty : " + map.isEmpty() );
System.out.println( map );
// 删除指定的 key 对应的 key-value 对,并返回 该 key 对应的 value
Integer value = map.remove( "土木工程" );
System.out.println( value );
System.out.println( map );
map.clear();
System.out.println( "size : " + map.size() + " , isEmpty : " + map.isEmpty() );
map.put( "信息科学技术" , 100 );
Map m = new HashMap<>();
m.put( "幼儿教育" , 5000 );
m.put( "信息科学技术" , 150 );
System.out.println( m );
map.putAll( m );
System.out.println( map );
}
} 运行结果如下:
size : 0 , isEmpty : true
size : 3 , isEmpty : false
{通信工程=200, 土木工程=100, 软件工程=500}
100
{通信工程=200, 软件工程=500}
size : 0 , isEmpty : true
{信息科学技术=150, 幼儿教育=5000}
{信息科学技术=150, 幼儿教育=5000}Map接口主要方法的测试案例:
package ecut.collection;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* keySet()
* values()
* entrySet()
*/
public class MapTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put( "软件工程" , 500 );
map.put( "通信工程" , 200 );
map.put( "土木工程" , 100 );
map.put( "幼儿教育" , 300 );
map.put( "护士护理" , 600 );
// 返回此映射中包含的键的 Set 视图
Set keys = map.keySet(); // 所有的 key 组成的 Set 集合
for( String key : keys ) {
Integer value = map.get( key );
System.out.println( key + " : " + value );
}
System.out.println( "~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~" );
// 返回此映射中包含的值的 Collection 视图
Collection values = map.values();
for( Integer v : values ) {
System.out.println( v );
}
System.out.println( "~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~" );
// 返回此映射中包含的映射关系的 Set 视图
Set< Map.Entry > entries = map.entrySet();
for( Map.Entry entry : entries ){
System.out.println( entry.getKey() + " : " + entry.getValue() );
}
}
} 运行结果如下:
通信工程 : 200
土木工程 : 100
护士护理 : 600
软件工程 : 500
幼儿教育 : 300
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
200
100
600
500
300
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
通信工程 : 200
土木工程 : 100
护士护理 : 600
软件工程 : 500
幼儿教育 : 300HashCode测试案例:
package ecut.collection;
/**
* 对于 Object # hashCode()
*
* 1、由 Object 类定义的 hashCode 方法确实会针对不同的对象返回不同的整数。
* (这一般是通过将该对象的内部地址转换成一个整数来实现的,但是 JavaTM 编程语言不需要这种实现技巧。)
*
* 2、这个整数 与 System.identityHashCode 的返回值相同
*
* 3、这个整数的意义: Identity Hash Code ( 相当于 每个 对象的 身份证编号 )
*
* 4、Object 提供 hashCode 方法是为了提高哈希表(例如 java.util.Hashtable 提供的哈希表)的性能
*
* 5、这个整数 在第一次 访问时 才触发产生
*
*/
public class IdentityHashCodeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 数组也是引用类型变量
int[] a = new int[ 10 ];
int[] b = new int[10] ;
//返回该对象的哈希码值。
System.out.println( "a : " + a.hashCode() );
System.out.println( "b : " + b.hashCode() );
//这个整数 与 System.identityHashCode 的返回值相同
System.out.println( "b : " + System.identityHashCode( b ) );
System.out.println( "a : " + System.identityHashCode( a ) );
}
}运行结果如下:
a : 366712642
b : 1829164700
b : 1829164700
a : 366712642Map接口主要实现类
1、java.util.HashMap
- key 允许为 null , value 也允许为 null
- 不保证映射的顺序,特别是它不保证该顺序恒久不变
HashMap测试案例:
package ecut.collection;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.HashMap;
/***
* hashCode 相同的字符串:
* 重地 - 通话
* 方面 - 树人
* 玉班 - 王环 - 牛顿
* 王八 - 玌兌
* 东理 - 两猎 - 二晶 - 伍囗 - 住仙
* 东华 - 世合
* 德鹏 - 恢覚
* 农丰 - 儿女
* 掌门 - 文境 - 方創
*/
public class MapHelper {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap map = new HashMap( 1 );
//根据传入的 HashMap 实例获取其内部的 哈希表 的容量
int c = capacity( map );
System.out.println( "容量: " + c );
map.put( "掌门" , "张三丰" );
map.put( "方創" , "大众创业万众等死" );
map.put( "农丰" , "三轮车" );
map.put( "儿女" , "张无忌" );
map.put( "重地" , "仓库重地" );
map.put( "通话" , "通话记录");
map.put( null , null );
//显示给定 HashMap 实例内部的 哈希表中存储的数据 (只处理到链表层次)
show( map );
c = capacity( map );
System.out.println( "容量: " + c );
String key = "儿女" ;
//计算指定的 key 在给定的 map 集合中的位置(在哈希表中的索引)
int p = position(map, key );
System.out.println( key + "在哈希表中的位置: " + p );
key = null ;
p = position(map, key);
System.out.println( key + "在哈希表中的位置: " + p );
}
private static Class hashMapClass ;
private static Field tableField;
private static Method hashMethod ;
static {
hashMapClass = HashMap.class;
try {
// 通过反射来获得 HashMap 内部的 table 属性
tableField = hashMapClass.getDeclaredField( "table" );
// 让本来因为被封装而不能访问的 table 能够被访问
tableField.setAccessible( true );
// 通过反射获得 HashMap 内部的 hash 方法
hashMethod = hashMapClass.getDeclaredMethod( "hash" , Object.class );
// 让本来因为封装而不能访问的 hash 方法能够被访问
hashMethod.setAccessible( true );
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
System.out.println( "在 " + hashMapClass.getName() + " 中未找到 table 属性 : " + e.getMessage() );
} catch (SecurityException e) {
System.out.println( "无法访问 " + hashMapClass.getName() + " 的 table 属性 : " + e.getMessage() );
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
System.out.println( "在 " + hashMapClass.getName() + " 累中未找到 hash 方法 : " + e.getMessage() );
}
}
/**
* 计算指定的 key 在给定的 map 集合中的位置(在哈希表中的索引)
* @param map
* @param key
* @return
*/
public static int position( HashMap map , Object key ) {
int position = -1 ;
//获取 哈希表的容量
int capacity = capacity( map );
// 根据 键 计算哈希值
int hash = hash( map , key );
// 根据 HashMap 中的实现思路,计算 键 的存储位置
position = ( capacity - 1 ) & hash ;
return position ;
}
/**
* 计算指定的 key 的 hash 值
* @param map
* @param key
*/
public static int hash( HashMap map , Object key ) {
int hash = -1 ;
try {
// 通过反射调用 HashMap 中的 hash 方法
Object h = hashMethod.invoke( map , key );
if( h != null ) {
// 判断 h 是否是 int 类型 或 Integer 类型
if( h.getClass() == Integer.class || h.getClass() == int.class ) {
hash = Integer.class.cast( h ) ; // 通过反射方法,实现强制类型转换
}
}
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return hash ;
}
/**
* 根据传入的 HashMap 实例获取其内部的 哈希表 的容量
* @param map
*/
public static int capacity( HashMap map ) {
int capacity = 0 ;
try {
// 获得给定的 map 实例 中的 table 属性的值 (获取到哈希表)
Object value = tableField.get( map );
if( value != null ){
Class valueClass = value.getClass(); // 获得 table 属性的 值 的类型
if( valueClass.isArray() ){ // 如果是个数组
capacity = Array.getLength( value ); // 获取数组长度 (获取哈希表的长度)
}
}
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return capacity ;
}
/**
* 显示给定 HashMap 实例内部的 哈希表中存储的数据 (只处理到链表层次)
* @param map
*/
public static void show( HashMap map ) {
try {
// 从参数传入的 map 实例中获得 该实例中的 table 属性的值
Object value = tableField.get( map );
if( value != null ){
Class valueClass = value.getClass(); // 获得 table 属性的 值 的类型
if( valueClass.isArray() ){ // 如果是个数组
System.out.println( "HashMap 实例中的哈希表:" );
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer();
// 遍历数组
for( int i = 0 , n = Array.getLength( value ) ; i < n ; i++ ){
buffer.setLength( 0 );
Object e = Array.get( value , i ) ; // 从数组中获取 下标是 i 的元素
if( e != null ){
buffer.append( i ) ;
buffer.append( " : " );
// 获得 当前循环取得的 元素的类型
Class eClass = e.getClass();
Field hashField = eClass.getDeclaredField( "hash" ); // 获得 eClass 中 名称是 hash 的属性
hashField.setAccessible(true);
buffer.append( "[ " );
Field keyField = eClass.getDeclaredField( "key" ); // 获得 eClass 中 名称是 key 的属性
keyField.setAccessible(true);
Field valueField = eClass.getDeclaredField( "value" ); // 获得 eClass 中 名称是 key 的属性
valueField.setAccessible(true);
Field nextField = eClass.getDeclaredField( "next" ); // 获得 eClass 中 名称是 key 的属性
nextField.setAccessible(true);
Object hash = hashField.get( e );
buffer.append( "<");
buffer.append( hash );
buffer.append( ">" );
Object k = keyField.get( e );
buffer.append( k );
buffer.append( "=" );
Object v = valueField.get( e );
buffer.append( v );
Object next = nextField.get( e );
while( next != null ) {
buffer.append( " , " );
hash = hashField.get( e );
k = keyField.get( next );
v = valueField.get( next );
buffer.append( "<");
buffer.append( hash );
buffer.append( ">" );
buffer.append( k );
buffer.append( "=" );
buffer.append( v );
next = nextField.get( next ) ; // 继续获得下一个节点
}
buffer.append( " ]" );
} else {
buffer.append( i );
buffer.append( " : [ empty ]" );
}
System.out.println( buffer.toString() );
}// end of for loop
}
} else {
System.out.println( "null");
}
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SecurityException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} package ecut.collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class HashMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap map = new HashMap<>( 20 , 0.8F );
/**
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
this.threshold = tableSizeFor( initialCapacity );
**/
// 因为 HashMap 内部用 哈希表来存储 键值对
// 并且 HashMap 采用 key 的hashCode 来确定 键值对 在哈希表中的位置
// 因此,添加键值对的顺序,跟它们在哈希表中的存放位置可能不同
map.put( "软件工程" , 500 );
map.put( "通信工程" , 200 );
map.put( "土木工程" , 100 );
map.put( "幼儿教育" , 300 );
map.put( "护士护理" , 600 );
map.put( "东理" , 600 );
map.put( "两猎" , 600 );
map.put( "二晶" , 600 );
map.put( "伍囗" , 600 );
map.put( "住仙" , 600 );
System.out.println( map );
int capacity = MapHelper.capacity( map );
System.out.println( "HashMap实例内部的哈希表的长度: " + capacity );
int index = MapHelper.position( map , "护士护理" );
System.out.println( "元素在哈希表中的存放位置: " + index );
MapHelper.show( map );
}
} 运行结果如下:
{东理=600, 两猎=600, 二晶=600, 伍囗=600, 住仙=600, 土木工程=100, 软件工程=500, 幼儿教育=300, 通信工程=200, 护士护理=600}
HashMap实例内部的哈希表的长度: 32
元素在哈希表中的存放位置: 24
HashMap 实例中的哈希表:
0 : [ empty ]
1 : [ empty ]
2 : [ empty ]
3 : [ <649571>东理=600 , <649571>两猎=600 , <649571>二晶=600 , <649571>伍囗=600 , <649571>住仙=600 ]
4 : [ empty ]
5 : [ empty ]
6 : [ <690577222>土木工程=100 ]
7 : [ empty ]
8 : [ empty ]
9 : [ empty ]
10 : [ <1114081802>软件工程=500 ]
11 : [ empty ]
12 : [ empty ]
13 : [ <741421005>幼儿教育=300 ]
14 : [ empty ]
15 : [ empty ]
16 : [ empty ]
17 : [ empty ]
18 : [ empty ]
19 : [ empty ]
20 : [ empty ]
21 : [ <1119401141>通信工程=200 ]
22 : [ empty ]
23 : [ empty ]
24 : [ <774976728>护士护理=600 ]
25 : [ empty ]
26 : [ empty ]
27 : [ empty ]
28 : [ empty ]
29 : [ empty ]
30 : [ empty ]
31 : [ empty ]2、java.util.Hashtable
- Properties类继承了Hashtable。
- 实现一个哈希表,该哈希表将键映射到相应的值
- 几乎所有的方法都是线程安全的
- Hashtable 的 key 和 value 都不能为 null
Hashtable测试案例:
package ecut.collection;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Hashtable;
/**
* 一个 Map 接口的实现类的自我修养:
* 1、将键映射到值的对象 ( Map 集合中存放的是 key-value 对 ( Map.Entry ) )
2、一个映射不能包含重复的键 ( Map 集合中的 key 不能重复 )
3、每个键最多只能映射到一个值 ( Map 集合中的 key 只能对应一个 值 )
Hashtable 的特点:
1、key 和 value 都不能为 null
2、几乎所有的方法都是线程安全的( 几乎所有的方法都被 synchronized 修饰 )
*/
public class HashtableTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hashtable ht = new Hashtable<>();
//ht.put(null, null);//抛出NullPointerException,key 和 value 都不能为 null
ht.put( "罗玉凤" , 250 );
ht.put( "罗玉龙" , 500 );
System.out.println( ht ); // ht.toString()
System.out.println( ht.get( "罗玉龙" ) );
Enumeration keys = ht.keys();
while( keys.hasMoreElements() ){
String key = keys.nextElement();
Integer value = ht.get( key );
System.out.println( key + " : " + value );
}
}
} Enumeration接口的功能与 Iterator 接口的功能是重复的。此外,Iterator 接口添加了一个可选的移除操作,并使用较短的方法名。新的实现应该优先考虑使用 Iterator 接口而不是 Enumeration 接口。
运行结果如下:
{罗玉龙=500, 罗玉凤=250}
500
罗玉龙 : 500
罗玉凤 : 2503、java.util.Properties:Hashtable的子类,表示属性集
- Properties 可保存在流中或从流中加载。
- 属性列表中每个键及其对应值都是一个字符串,应该用 setProperty 和 getProperty 方法来 操作属性 ,而不是使用 put 和 get。
Properties测试案例:
package ecut.collection;
import java.util.Properties;
public class PropertiesTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Properties props = new Properties();
// props.put(key, value) ;
props.setProperty( "driver", "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" );
props.setProperty( "url" , "jdbc:msyql://127.0.0.1:3306/ecut" );
// props.get(key);
String d = props.getProperty( "driver" );
System.out.println( d );
String user = props.getProperty( "user" );
System.out.println( user );
// 当指定的属性名在集合中不存在时,使用 第二个参数 当作默认值返回
user = props.getProperty( "user" , "root" );
System.out.println( user );
}
}运行结果如下:
com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
null
rootProperties测试案例:
jdbc.url = jdbc:oracle:thin:@127.0.0.1:1521:ecut
jdbc.driver = oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver
jdbc.user = ecut
jdbc.password = ecut2017package ecut.collection;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* 1、从类路径下获得任意资源对应的输入流
* 2、用 Properties 加载 属性文件 ( 以 .properties 为后缀,其中的内容形式是 key = value )
*/
public class PropertiesTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Properties props = new Properties();
System.out.println( "属性个数: " + props.size() );
//任何一个类型都可以通过.class来获得自己的类型对应Class 对象
Class c = PropertiesTest2.class ;// 通过 java.lang.Class 类的 getResourceAsStream 方法获得指定资源名称对应的输入流
// 如果仅仅指定的是 文件名,则该文件必须跟 当前类在同一个包
// 如果在 文件名之前使用了 / 则表示 从 当前的 类路径 的根路径开始寻找
InputStream inStream = c.getResourceAsStream( "/jdbc.properties" ) ;
try {
props.load( inStream ); // 从指定的流中读取 属性 ,并加入到 属性集合 中
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println( "加载失败: " + e.getMessage() );
} catch( NullPointerException e ) {
System.err.println( "未找到文件: " + e.getMessage() );
}
if( props.size() > 0 ) {
System.out.println( props.getProperty( "jdbc.url" ) );
System.out.println( props.getProperty( "jdbc.driver" ) );
System.out.println( props.getProperty( "jdbc.user" ) );
System.out.println( props.getProperty( "jdbc.password" ) );
}
}
}运行结果如下:
属性个数: 0
jdbc:oracle:thin:@127.0.0.1:1521:ecut
oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver
ecut
ecut2017HashMap 和 Hashtable 的相同点
1、内部都是基于 哈希表 存储数据(内部都有数组table,HashTable是Entry[] table,HashMap是Node
2、HashMap 和 Hashtable 的迭代器 都是 快速失败 ( fail-fast ) 的
HashMap 和 Hashtable 的区别
1、用来确定元素在哈希表中的位置的方式不同:
HashMap 根据 key.hashCode() 重新计算一个值:
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}static final int hash( Object key ) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : ( h = key.hashCode() ) ^ ( h >>> 16 );
}然后再根据这个值来确定元素在哈希表中的位置:
部分源码
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node[] tab; Node p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
.................................. 源码if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)转换:
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); int n = table.length ;
int hash = hash( key ) ;
table[ ( n - 1) & hash ] = newNode( hash, key, value, null ) ; // 不是源码 ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Hashtable 中的实现:
部分源码:
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
//确保value 不能为空
if (value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
// 确保key不在哈希表
Entry tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
...................................... int hash = key.hashCode(); // key 必须不能为 null,不然抛出空指针异常
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;2、HashMap 不支持线程安全的 ( 所有的方法都没有 synchronized 修饰 )。
Hashtable 支持线程安全的 ( 几乎所有的方法都被 synchronized 修饰 )。
3、HashMap 的迭代器是 快速失败 ( fail-fast ) 的 , Hashtable 的迭代器是 也是 快速失败 ( fail-fast ) 的,
但是 由 Hashtable 的 键 ( keys() ) 和 元素 ( elements() ) 方法返回的 Enumeration 不 是快速失败的,是安全失败。
注意,迭代器的快速失败行为不能得到保证,一般来说,存在非同步的并发修改时,不可能作出任何坚决的保证。快速失败迭代器尽最大努力抛出 ConcurrentModificationException(此异常不一定抛出)。
快速失败测试案例:
package ecut.collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class FailFastTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
map.put( "炒粉" , 3 );
map.put( "炒面" , 5 );
map.put( "包子" , 1 );
map.put( "皮蛋瘦肉粥" , 2 );
Set keySet = map.keySet();
Iterator itor = keySet.iterator();
while( itor.hasNext() ){
String key = itor.next() ;
Integer value = map.get( key );
System.out.println( key + " : " + value );
// map.put( "罗玉凤" , 250 ); // 尽最大可能抛出 ConcurrentModificationException
// map.remove( "包子" ); // 尽最大可能抛出 ConcurrentModificationException
if( key.equals( "包子" )){
itor.remove(); // 不抛出 ConcurrentModificationException
}
}
System.out.println( "~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~" );
itor = keySet.iterator();
while (itor.hasNext()) {
String key = itor.next();
Integer value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key + " : " + value);
}
}
} 运行结果如下:
包子 : 1
炒粉 : 3
炒面 : 5
皮蛋瘦肉粥 : 2
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
炒粉 : 3
炒面 : 5
皮蛋瘦肉粥 : 2添加和移除元素触发了因快速失败抛出的异常ConcurrentModificationException,是因为我们在使用迭代器对map里的元素进行迭代的时候,对map的结构进行了修改,map发生更改,迭代器是不允许的。
快速失败:我们正在使用迭代器对可以获得迭代器的集合(map不能获得迭代器但是对应的keyset视图可以获得迭代器),keyset对他进行的迭代的是,如果同时对他进行修改,map的结构发生改变,触发异常ConcurrentModificationException,称之为快速失败。要避免则只能使用迭代器本身的 remove 方法或 add 方法。
安全失败测试案例:
package ecut.collection;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Hashtable;
public class FailSafeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hashtable table = new Hashtable<>(); //Alt+Shift+R快速修改某个变量的名称
table.put( "炒粉" , 3 );
table.put( "炒面" , 5 );
table.put( "包子" , 1 );
table.put( "皮蛋瘦肉粥" , 2 );
Enumeration keys = table.keys();
while( keys.hasMoreElements() ){
String key = keys.nextElement();
Integer value = table.get( key );
System.out.println( key + " : " + value );
table.put( "拌面" , 3 );
}
System.out.println( "~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~" );
keys = table.keys();
while( keys.hasMoreElements() ){
String key = keys.nextElement();
Integer value = table.get( key );
System.out.println( key + " : " + value );
}
}
} 运行结果如下:
包子 : 1
炒粉 : 3
拌面 : 3
炒面 : 5
皮蛋瘦肉粥 : 2
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
包子 : 1
炒粉 : 3
拌面 : 3
炒面 : 5
皮蛋瘦肉粥 : 2次要的区别:
4、父类不同: Hashtable 的 父类 Dictionary ,而 HashMap 的父类是 AbstractMap。
5、对 键集、值集、键值对集 的处理方式不同:
HashMap 和 Hashtable 都具有:
Set
Collection
Set
Hashtable 还具有:
Enumeration
Enumeration
6、因为 Hashtable 是线程安全的,因此 在 单线程环 境下比 HashMap 要慢。
7、HashMap允许存在一个为null的key,多个为null的value 。Hashtable的key和value都不允许为null。
SortedMap接口特点
1、进一步提供关于键的总体排序 的 Map。该映射是根据其键的自然顺序进行排序的,或者根据通常在创建有序映射时提供的 Comparator 进行排序。
2、对有序映射的 collection 视图(由 entrySet、keySet 和 values 方法返回)进行迭代时,此顺序就会反映出来。
3、要采用此排序方式,还需要提供一些其他操作(此接口是 SortedSet 的对应映射)。
SortedMap接口主要实现类
1、java.util.TreeMap
- NavigableMap类继承了SortedMap,TreeMap实现了NavigableMap。
- 基于红黑树( Red-Black tree )来实现 Map 集合 ( 同时实现了 NavigableMap 、SortedMap )。
- 该映射根据其键 ( key ,得实现Comparable接口,支持自然排序) 的自然顺序进行排序,或者根据创建映射时提供的 Comparator 进行排序,具体取决于使用的构造方法。
- TreeMap 的 key 不可以为 null ,而 value 可以为 null。
- TreeMap 中的键值对根据 键来排序 ( 根据自然顺序 或 比较器排序)。
TreeMap测试案例:
package ecut.collection;
public class Fox implements Comparable {
private Integer id ; // 对象标识符 ( Object Identifier )
private String name ;
public Fox(Integer id, String name) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Fox o) {
if( this.id != null && o.id != null ) {
if( this.id > o.id ){
return 1 ;
} else if( this.id == o.id ){
return 0 ;
} else {
return -1 ;
}
}
return 0;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "[id=" + id + ", name=" + name + "]";
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
} package ecut.collection;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class TreeMapTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建 TreeMap 对象时,如果没有指定比较器,则默认按照 key 的 自然顺序排序
TreeMap tm = new TreeMap<>();
Fox fox1 = new Fox( 100 , "妲己" );
tm.put( fox1 , 1.0 );
Fox fox2 = new Fox( 200 , "褒姒" );
tm.put( fox2 , 0.8 );
System.out.println( tm );
Fox fox3 = new Fox( 150 , "金角大王他干娘" );
tm.put( fox3 , 100.0 );
System.out.println( tm );
}
} 运行结果如下:
{[id=100, name=妲己]=1.0, [id=200, name=褒姒]=0.8}
{[id=100, name=妲己]=1.0, [id=150, name=金角大王他干娘]=100.0, [id=200, name=褒姒]=0.8}TreeMap测试案例:
package ecut.collection;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class TreeMapTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Comparator c = new Comparator(){
@Override
public int compare( Fox o1, Fox o2 ) {
if( o1 != null && o2 != null && o1.getName() != null && o2.getName() != null ){
String name1 = o1.getName() ;
String name2 = o2.getName() ;
return name1.compareTo( name2 ) ;
}
return 0;
}
};
// 创建 TreeMap 对象时,指定比较器,则按照 比较器 排序
TreeMap tm = new TreeMap<>( c );
Fox fox3 = new Fox( 150 , "金角大王他干娘" );
tm.put( fox3 , 100.0 );
System.out.println( tm );
Fox fox2 = new Fox( 200 , "褒姒" );
tm.put( fox2 , 0.8 );
System.out.println( tm );
Fox fox1 = new Fox( 100 , "妲己" );
tm.put( fox1 , 1.0 );
System.out.println( tm );
}
} 运行结果如下:
{[id=150, name=金角大王他干娘]=100.0}
{[id=200, name=褒姒]=0.8, [id=150, name=金角大王他干娘]=100.0}
{[id=100, name=妲己]=1.0, [id=200, name=褒姒]=0.8, [id=150, name=金角大王他干娘]=100.0}ConcurrentMap接口特点
1、,它可以处理并发访问。
2、ConcurrentMap除了继承自java.util.Map的方法,还有一些自己的原子方法。
ConcurrentMap接口主要实现类
1、java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap
- ConcurrentMap接口的的实现类。
- ConcurrentHashMap 是 安全失败 ( fail-safe )。
- ConcurrentHashMap 为了提高并发性能而出现的map集合,支持完全的并发操作,默认支持16个线程。
- 不会 抛出
ConcurrentModificationException,因此不保证数据的一致性。
ConcurrentHashMap测试案例:
package ecut.collection;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
/**
* ConcurrentHashMap 是 安全失败 ( fail-safe )
* ConcurrentHashMap 支持完全的并发操作
*/
public class ConcurrentHashMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConcurrentHashMap map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
map.put( "炒粉" , 3 );
map.put( "炒面" , 5 );
map.put( "包子" , 1 );
map.put( "皮蛋瘦肉粥" , 2 );
Set< Map.Entry > entrySet = map.entrySet();
Iterator< Map.Entry > itor = entrySet.iterator();
while( itor.hasNext() ){
Map.Entry entry = itor.next();
System.out.println( entry.getKey() + " : " + entry.getValue() );
map.put( "拌面" , 3 );
}
System.out.println( "~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~" );
Enumeration keys = map.keys();
while( keys.hasMoreElements() ){
String key = keys.nextElement();
Integer value = map.get( key );
System.out.println( key + " : " + value );
map.remove( "拌面" );
}
}
} 运行结果如下:
包子 : 1
炒粉 : 3
拌面 : 3
炒面 : 5
皮蛋瘦肉粥 : 2
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
包子 : 1
炒粉 : 3
炒面 : 5
皮蛋瘦肉粥 : 2转载请于明显处标明出处
http://www.cnblogs.com/AmyZheng/p/8463722.html