梯度下降法及其模拟
梯度下降法(Gradient Descent)
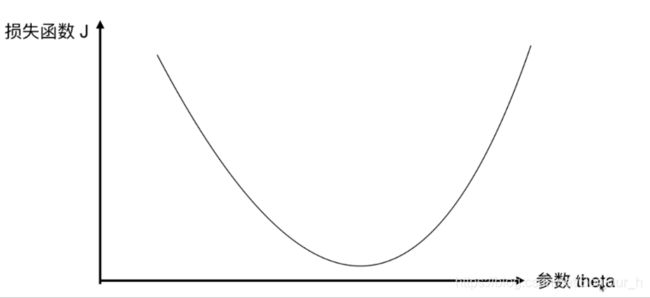
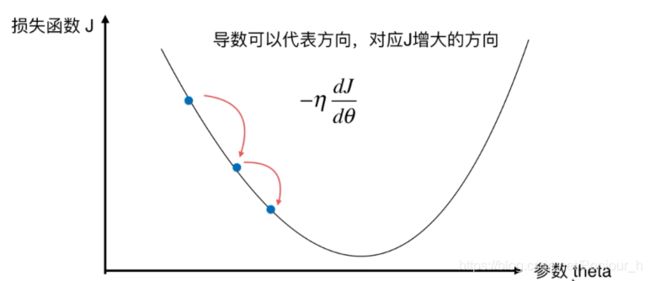
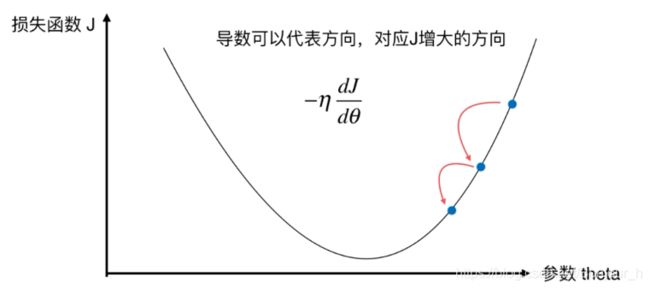
根据高等数学的知识,图中曲线上点的位置应当沿着 d J d Θ \frac{dJ}{d\Theta } dΘdJ的值减小的方向移动。设有一个 η \eta η>0, − η -\eta −η<0,此时 Θ \Theta Θ就会变成 Θ − η d J d Θ \Theta-\eta\frac{dJ}{d\Theta } Θ−ηdΘdJ。 η \eta η表示蓝色点移动的速度
-
η \eta η称为学习率(learning rate)
-
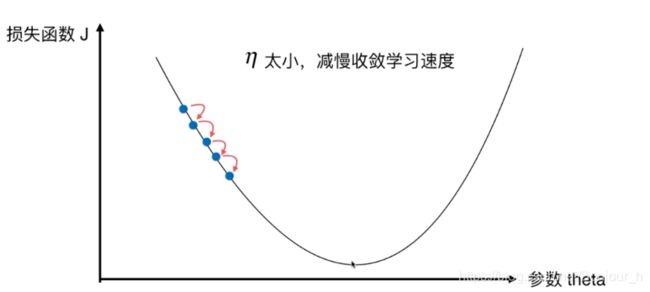
η \eta η的取值影响获得最优解的速度
-
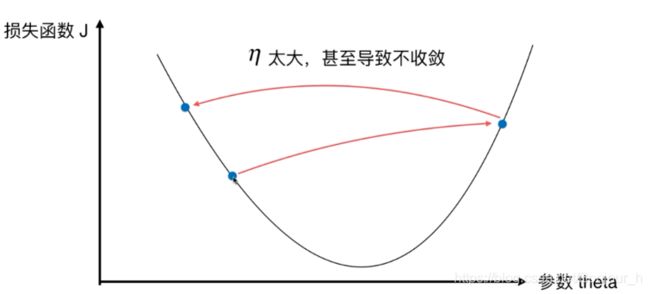
η \eta η取值不合适,甚至得不到最优解
-
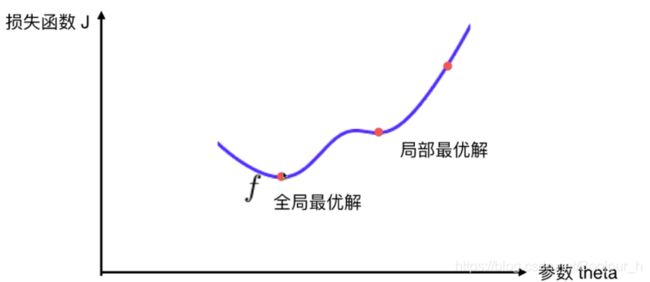
并不是所有的函数都有唯一的极值点
- 多次运行,随机化初始点
- 梯度下降法的初始点也是一个超参数
### 梯度下降法模拟
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plot_x = np.linspace(-1,6,141)#在x轴上-1到6中等间距取140个点,加上头尾一共有141个点
plot_x
输出:array([-1. , -0.95, -0.9 , -0.85, -0.8 , -0.75, -0.7 , -0.65, -0.6 ,
-0.55, -0.5 , -0.45, -0.4 , -0.35, -0.3 , -0.25, -0.2 , -0.15,
-0.1 , -0.05, 0. , 0.05, 0.1 , 0.15, 0.2 , 0.25, 0.3 ,
0.35, 0.4 , 0.45, 0.5 , 0.55, 0.6 , 0.65, 0.7 , 0.75,
0.8 , 0.85, 0.9 , 0.95, 1. , 1.05, 1.1 , 1.15, 1.2 ,
1.25, 1.3 , 1.35, 1.4 , 1.45, 1.5 , 1.55, 1.6 , 1.65,
1.7 , 1.75, 1.8 , 1.85, 1.9 , 1.95, 2. , 2.05, 2.1 ,
2.15, 2.2 , 2.25, 2.3 , 2.35, 2.4 , 2.45, 2.5 , 2.55,
2.6 , 2.65, 2.7 , 2.75, 2.8 , 2.85, 2.9 , 2.95, 3. ,
3.05, 3.1 , 3.15, 3.2 , 3.25, 3.3 , 3.35, 3.4 , 3.45,
3.5 , 3.55, 3.6 , 3.65, 3.7 , 3.75, 3.8 , 3.85, 3.9 ,
3.95, 4. , 4.05, 4.1 , 4.15, 4.2 , 4.25, 4.3 , 4.35,
4.4 , 4.45, 4.5 , 4.55, 4.6 , 4.65, 4.7 , 4.75, 4.8 ,
4.85, 4.9 , 4.95, 5. , 5.05, 5.1 , 5.15, 5.2 , 5.25,
5.3 , 5.35, 5.4 , 5.45, 5.5 , 5.55, 5.6 , 5.65, 5.7 ,
5.75, 5.8 , 5.85, 5.9 , 5.95, 6. ])
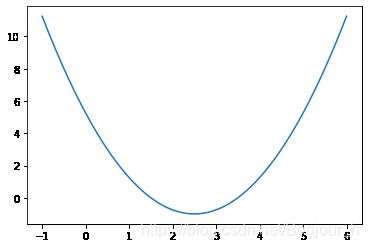
plot_y = (plot_x-2.5)**2 - 1#损失函数
plt.plot(plot_x,plot_y)
plt.show()
def dJ(theta):#计算损失函数的倒数
return 2*(theta - 2.5)
def J(theta):#求theta对应值的损失函数
return (theta-2.5)**2 - 1
eta = 0.1
epsilon = 1e-8#设定一个精度
theta = 0.0
while True:
gradient = dJ(theta)
last_theta = theta
theta = theta - eta * gradient
if(abs(J(theta) - J(last_theta)) < epsilon):
break
print(theta)
print(J(theta))
print(dJ(theta))
输出:
2.499891109642585
-0.99999998814289
-0.0002177807148298072
解析theta是如何获得的
theta = 0.0
theta_history = [theta]
while True:
gradient = dJ(theta)
last_theta = theta
theta = theta - eta * gradient
theta_history.append(theta)
if(abs(J(theta) - J(last_theta)) < epsilon):#保证损失函数J的值是减小的
break
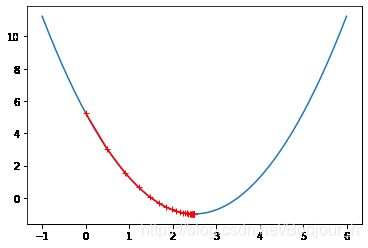
plt.plot(plot_x,J(plot_x))
plt.plot(np.array(theta_history),J(np.array(theta_history)),color='r',marker='+')
plt.show()
len(theta_history)
输出:46
对代码进行封装
def gradient_descent(initial_theta,eta,epsilon=1e-8):
theta = initial_theta
theta_history.append(initial_theta)
while True:
gradient = dJ(theta)
last_theta = theta
theta = theta - eta * gradient
theta_history.append(theta)
if(abs(J(theta) - J(last_theta)) < epsilon):
break
def plot_theta_history():
plt.plot(plot_x,J(plot_x))
plt.plot(np.array(theta_history),J(np.array(theta_history)),color='r',marker='+')
plt.show()
eta = 0.01
theta_history = []
gradient_descent(0.,eta)
plot_theta_history()
len(theta_history)
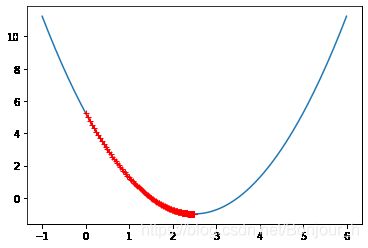
eta = 0.001
theta_history = []
gradient_descent(0.,eta)
plot_theta_history()
len(theta_history)
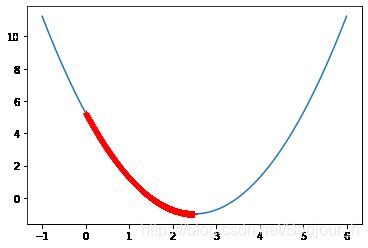
eta = 0.8
theta_history = []
gradient_descent(0.,eta)
plot_theta_history()
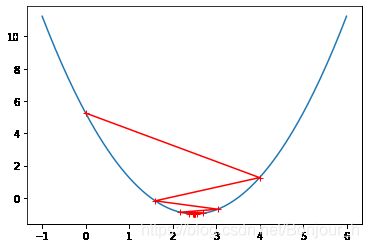
eta = 1.1#eta过大,导致损失函数的值变大
theta_history = []
gradient_descent(0.,eta)
plot_theta_history()
报错:OverflowError: (34, 'Result too large')