c语言实现图的基本操作--邻接矩阵存储,c语言实现图的基本操作--邻接矩阵存储...
利用邻接矩阵容易判定任意两个顶点之间是否有边(或弧)相连,并容易求得各个顶点的度。
c语言代码实现如下:
#include
#include
#define MAX_VER_NUM 50
typedef char VertexType;
typedef enum
{
DG,UDG
}GraphType;
typedef struct
{
VertexType vexs[MAX_VER_NUM]; //顶点向量
int arcs[MAX_VER_NUM][MAX_VER_NUM]; //邻接矩阵
int vexnum,arcnum; //图的当前顶点数和弧数
GraphType type; //图的种类标志
}MGraph;
//根据名称得到指定顶点在顶点集合中的下标
//vex 顶点
//return 如果找到,则返回下标,否则,返回0
int getIndexOfVexs(char vex,MGraph *MG)
{
int i;
for(i=1;i<=MG->vexnum;i++)
{
if(MG->vexs[i]==vex)
{
return i;
}
}
return 0;
}
//创建邻接矩阵
void create_MG(MGraph *MG)
{
int i,j,k;
int v1,v2,type;
char c1,c2;
printf("Please input graph type DG(0) or UDG(1):");
scanf("%d",&type);
if(type==0)
{
MG->type=DG;
}
else if(type==1)
{
MG->type=UDG;
}
else
{
printf("Please input correct graph type DG(0) or UDG(1)!");
return;
}
printf("Please input vexnum:");
scanf("%d",&MG->vexnum);
printf("Please input arcnum:");
scanf("%d",&MG->arcnum);
getchar();
for(i=1;i<=MG->vexnum;i++)
{
printf("Please input %dth vex(char):",i);
scanf("%c",&MG->vexs[i]);
getchar();
}
//初始化邻接矩阵
for(i=1;i<=MG->vexnum;i++)
{
for (j=1;j<=MG->vexnum;j++)
{
MG->arcs[i][j]=0;
}
}
//输入边的信息,建立邻接矩阵
for(k=1;k<=MG->arcnum;k++)
{
printf("Please input %dth arc v1(char) v2(char):",k);
scanf("%c %c",&c1,&c2);
v1=getIndexOfVexs(c1,MG);
v2=getIndexOfVexs(c2,MG);
if(MG->type==-1)
{
MG->arcs[v1][v2]=MG->arcs[v2][v1]=1;
}
else
{
MG->arcs[v1][v2]=1;
}
getchar();
}
}
//打印邻接矩阵和顶点信息
void print_MG(MGraph MG)
{
int i,j;
if(MG.type==DG)
{
printf("Graph type: Direct graph\n");
}
else
{
printf("Graph type: Undirect graph\n");
}
printf("Graph vertex number: %d\n",MG.vexnum);
printf("Graph arc number: %d\n",MG.arcnum);
printf("Vertex set:");
for(i=1;i<=MG.vexnum;i++)
{
printf("%c",MG.vexs[i]);
}
printf("\nAdjacency Matrix:\n");
for(i=1;i<=MG.vexnum;i++)
{
for(j=1;j<=MG.vexnum;j++)
{
printf("%d",MG.arcs[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
//主函数
int main(void)
{
MGraph MG;
create_MG(&MG);
print_MG(MG);
return 0;
}
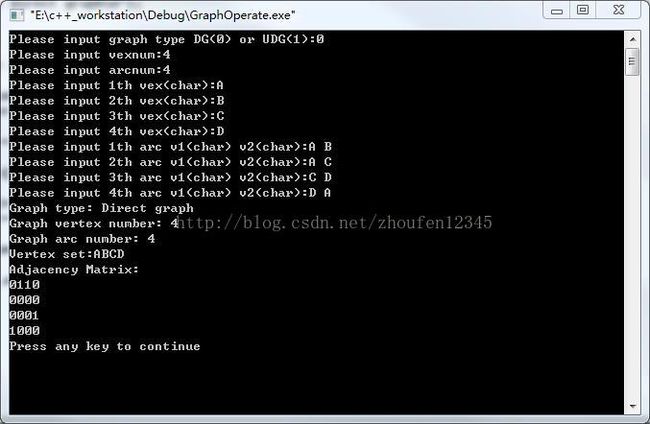
得到的结果如下图所示: