Windows 下OpenGL的基本安装与配置(基于Visual Studio 2019 与 MinGW)
MinGW的安装
1.首先我们下载相应的MinGW安装文件, 可以通过下载相对应的架构和相应的环境的压缩文件或者在线安装。在这里我选择的是在线安装的安装程序。
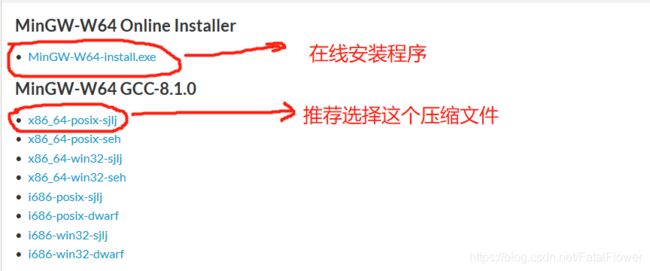
如果你下载的是压缩包的形式(.7z), 请将它解压缩到你想安装的位置, 然后设置相应的环境变量。
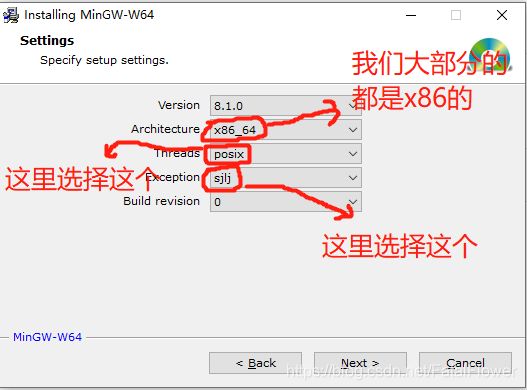
若果你选择在线安装, 则直接点击安装程序(.msi), 点击“Next”, 按照下图的选项配置, 点击“Next”, 之后选择你的安装路径, 点击“Next”, 等待下载相关的文件, 完成安装。
- 设置环境变量:右击“此电脑”——>“属性”——>“高级系统设置”——>"环境变量“。在“系统变量”寻找Path变量, 点击“编辑”——>“新建”, 将安装路径下的“bin”目录的绝对路径复制到新建的变量内, 点击“确定”, 完成环境变量的设置。如果设置成功, 按下“win + R”输入CMD输入“gcc --version”应当能够看到对应的版本信息。
安装OpenGL
按下“Win + R”, 输入“dxdiag”, 点击左上角的“呈现”, 查看当前显卡的版本, 下载对应的驱动。如果你电脑的“C:\Windows\System32\”下已经有“opengl32.dll和glu32.dll”, 那么你可以跳过这一步。
OpenGL下载地址
CMake
在下载对应的GLFW源代码后,首先对其进行解压缩。 我们需要使用CMake工具来生成对应的库文件, 首先我们需要下载CMake, Cmake下载地址。下载相应的安装文件(.msi 大概25MB左右), 运行它安装CMake。
我们直接点击“Next”, 接受相应的许可协议, 点击Next。
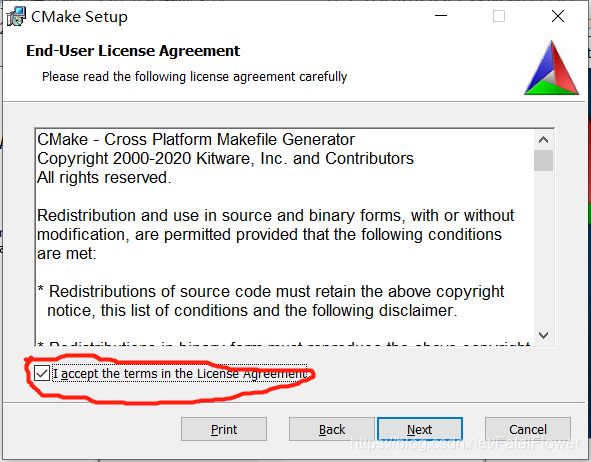
在这里推荐选择第二项, 以便之后的使用。
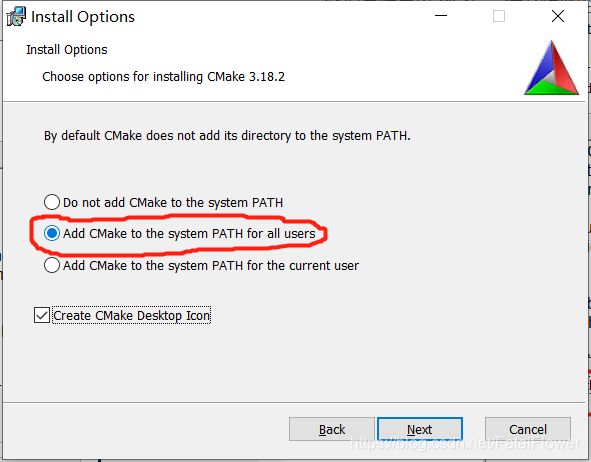
选择安装路径
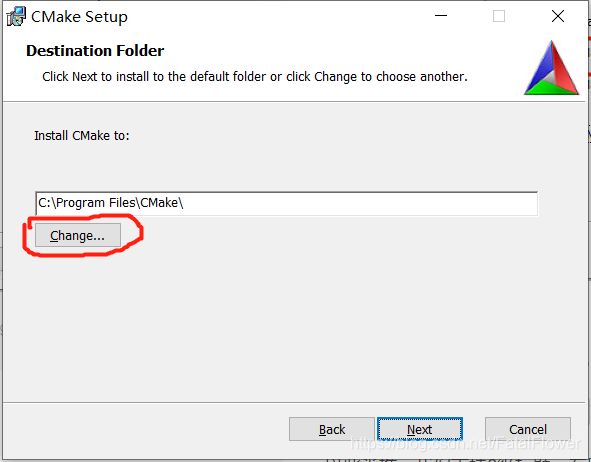
点击“Install”开始安装
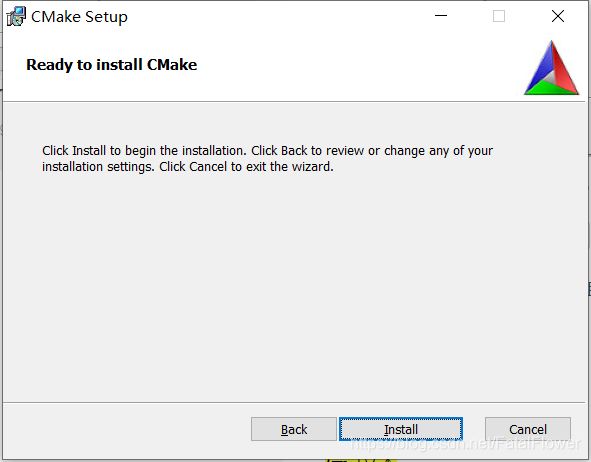
等待安装完成, 至此, CMake的安装结束。
FreeGLUT
FreeGLUT是OpenGL Utility Toolkit(GLUT)库的开源替代方案。GLUT(以及FreeGLUT)允许用户在广泛的平台上创建和管理包含OpenGL上下文的窗口,还可以读取鼠标,键盘和操纵杆功能。FreeGLUT旨在完全替代GLUT,并且仅有几处区别。
由于GLUT陷入停滞,因此FreeGLUT正在开发中,以改进该工具包。它根据MIT许可证发布。
- 下载对应的FreeGLUT
- 进入解压缩后的FreeGLUT文件夹, 你应当能看到里面的CMakeLists.txt文件
- 打开“cmd”,以管理员身份运行。
- 执行生成Makefile的指令
cmake -G "MinGW Makefiles" -S . -B . -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=安装路径\x86_64-w64-mingw32最后的"-DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX"参数的值应当与你MinGW的安装路径一致。
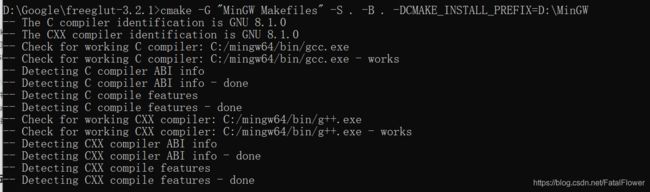
执行之后, 如果你已经安装了OpenGL, 那么不出错的话你应当能够在你的FreeGLUT文件夹下看到对应的Makefile文件。 - 让我们Make它!在FreeGLUT文件夹下已经产生了Makefile文件, 我们接下来要做的就是生成可执行文件然后安装到我们的MinGW中。在FreeGLUT文件夹下输入
mingw32-make install实现安装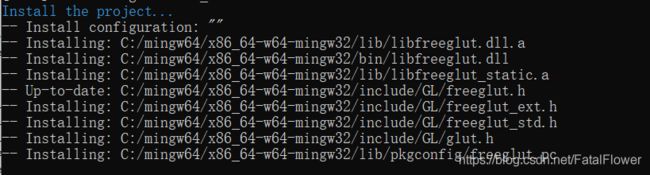
如果最后你看到了这样的内容, 那么恭喜你, 你已经把FreeGLUT安装到你的MinGW中了, 它已经自动把需要的include文件、lib文件以及bin文件复制到你的MinGW中了(在 freeglut 3.0.0以上的版本中, 可能不会安装"glut.h"库文件)。最后, 让我们来测试一下。
编写一个FreeGLUT的C程序example.c, 源代码如下:
/*
* GL01Hello.cpp: Test OpenGL C/C++ Setup
*/
#include 执行一下指令
gcc -c -o example.o example.c
gcc -o example.exe example.o -lfreeglut -lopengl32 -Wl,--subsystem,windows
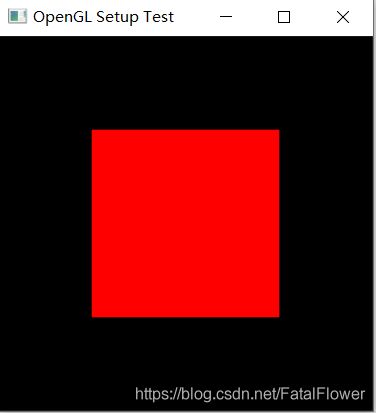
运行生成的example.exe文件, 你应该可以看到以下界面:
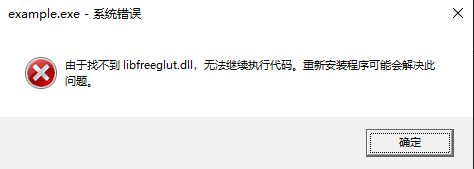
如果你看到以下这种错误, 那么你可能需要将“x86_64-w64-mingw32\bin”目录下的“libfreeglut.dll”文件复制到MinGW安装目录下的"bin"目录下。
GLEW
- 下载GLEW, GLEW下载, 解压缩到指定目录
- 进入GLEW目录, 进入“build\cmake”, 你将会看到“CMakeLisits.txt”文件。
- 打开“cmd”,以管理员身份运行。
- 在输入
cmake -G "MinGW Makefiles“” -S . -B . -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=MinGW安装路径\x86_64-w64-mingw32。 - 最后你应当能够在GLEW的目录下看到生成的Makefile文件。
- 生成相应的GLEW库文件
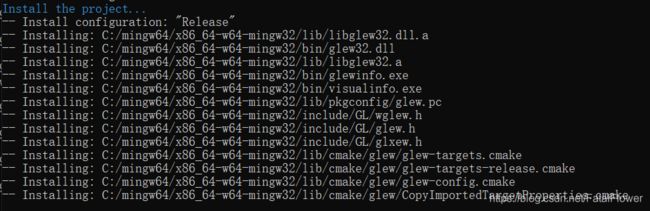
mingw32-make all - 将生成的GLEW库文件安装到我们的MinGW中,
mingw32-make install
GLFW
GLFW是一个专门针对OpenGL的C语言库,它提供了一些渲染物体所需的最低限度的接口。它允许用户创建OpenGL上下文,定义窗口参数以及处理用户输入。我们需要先下载它GLFW官网下载,它对应的源代码。当然你可以选择直接下载对应的已经编译好的库文件, 下载源代码来构建库文件是为了更好的适合每个人的电脑。

使用CMake的GUI界面可以很简单的完成生成Makefile的任务, 但是我们在这里使用命令行的方式来执行, 一是为了更具普遍性, 二是为了之后的安装。
- 我们进入解压缩后的GLFW文件夹, 你应该能够看到CmakeLists.txt文件。
- 打开“cmd”,以管理员身份运行。
- 在输入
cmake -G "MinGW Makefiles“” -S . -B . -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=MinGW安装路径\x86_64-w64-mingw32。 - 最后你应当能够在GLFW的目录下看到生成的Makefile文件。
- 生成相应的GLFW库文件
mingw32-make all - 将生成的GLFW库文件安装到我们的MinGW中,
mingw32-make install
不出意外的话, 你看到的应该是以下的界面
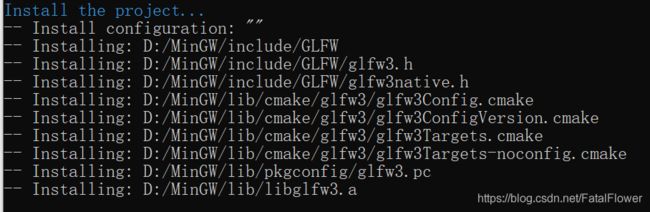
恭喜你, 你已经完成了GLFW的安装, 你应当能在你的MinGW目录下的“include”文件夹下看到相关的头文件。
编写一个简单的OpenGL程序 HelloOpenGL.cpp
// CPP program to render a triangle using Shaders
#include 将文件保存为HelloOpenGL.cpp,输入以下命令:
g++ HelloOpenGL.cpp -o HelloOpenGL.exe -lopengl32 -lglew32 -lfreeglut -lglu32
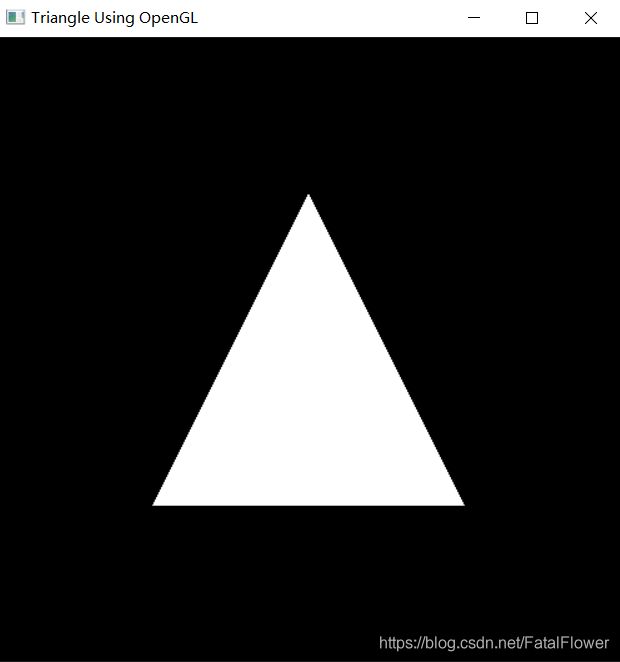
运行HelloOpenGL.exe, 你应当看到以下图形
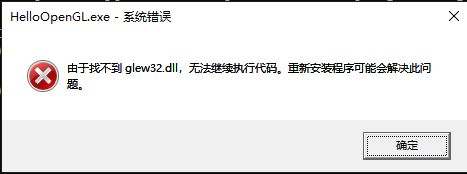
如果你看到以下这种错误, 那么你可能需要将“x86_64-w64-mingw32\bin”目录下的“glew32.dll”文件复制到MinGW安装目录下的"bin"目录下。
GLAD
由于OpenGL驱动版本众多,它大多数函数的位置都无法在编译时确定下来,需要在运行时查询。所以任务就落在了开发者身上,开发者需要在运行时获取函数地址并将其保存在一个函数指针中供以后使用。这种方式十分麻烦, 所幸我们有GLAD来帮助我们解决这个问题。
- 配置GLAD库:打开GLAD在线服务,将语言(Language)设置为C/C++,在API选项中,选择3.3以上的OpenGL(gl)版本。之后将模式(Profile)设置为Core,并且保证生成加载器(Generate a loader)的选项是选中的。GLAD现在应该提供给你了一个zip压缩文件,包含两个头文件目录,和一个glad.c文件。
- 我们可以将glad.c生成lib文件和include文件下的头文件放入MinGW中, 以便每次都能够加载对应文件。首先将include目录下的头文件放入MinGW的"x86_64-w64-mingw32\include"目录下, 随后生成lib文件的命令如下:
gcc -c -o glad.o glad.c
ar cr libglad.a glad.o
将生成的“libglad.a”库文件放入MinGW的"x86_64-w64-mingw32\lib"目录下, 以便之后的使用。之后, 我们只需要在编译时加入相对应的链接库即可。编译的命令如下:
g++ ***.cpp -o ***.exe -lopengl32 -lglu32 -lglfw3 -lglew32 -lgdi32 -lglad
gcc ***.cpp -o ***.exe -lopengl32 -lglu32 -lglfw3 -lglew32 -lgdi32 -lglad
Visual Studio 的配置
-
关于Visual Studio的安装, 相信网上有许多的教程, 再次就不再赘述了。
-
首先, 我们需要使用CMake工具生成我们的glfw3.lib库文件, 打开CMake的GUI界面, 选择已经解压缩的glfw源文件, 选择生成项目的目标目录, 点击“configure”,选择生成的项目类型, 这里我们选择“Visual Studio”类型的。.
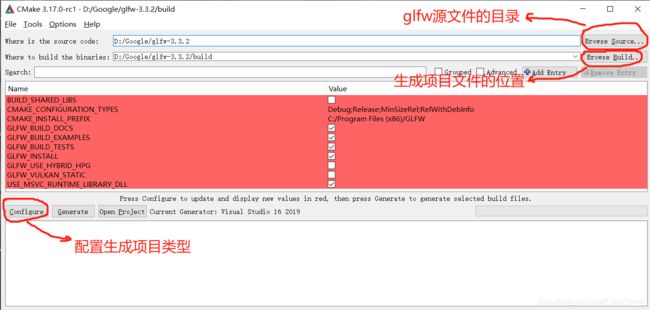
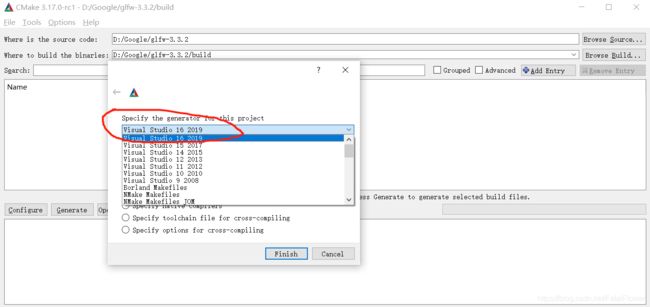
点击“finish”,等待配置完成之后, 再点击“Generate”生成对应的项目文件。
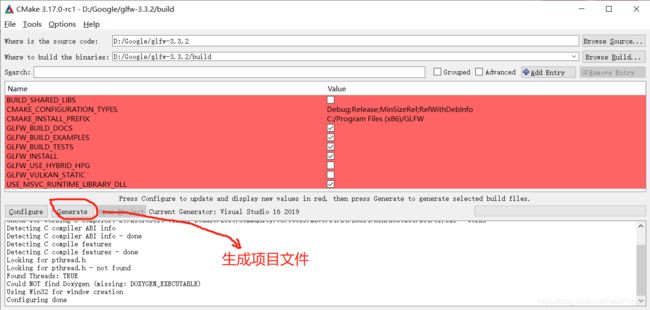
打开项目的生成路径, 你将会看到“GLFW.sln”的文件, 双击打开它。点击“Visual Studio”上方的“生成”——>"生成解决方案“, 最终的lib库文件将会在“src/Debug”目录下。
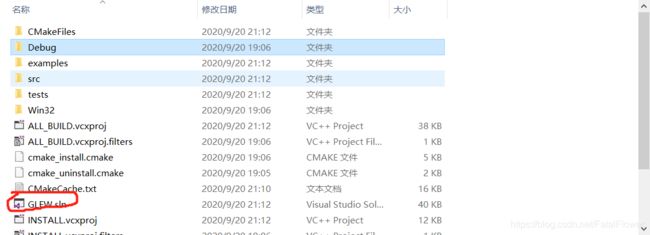
-
将对应的glad.c文件转变为对应的lib文件, 以便使用。打开Visual Studio, 创建一个glad静态库项目,在该项目路径下创建“include”, 将glad.zip内的“include”内的内容复制到项目下的“include”目录下, 将glad.c的内容复制到glad.cpp文件中, 在glad.cpp的第一行添加“#include “pch.h””,将下载的glad压缩文件内的include目录复制到项目的目录下, 点击“项目”——>"glad属性“——>"C/C++“——>"常规“”, 将"附加包含目录“设置为之前我们项目下的“include”目录。

点击“确定”。
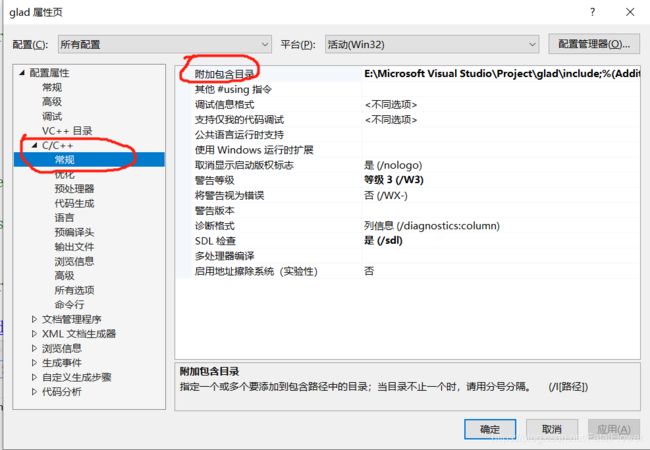
点击上方的“生成”——>“生成解决方案”。我们将在项目路径下的“Debug”路径下看到我们生成的glid.lib文件。 -
创建一个新的空白C++项目, 在项目目录下创建目录“include”、“lib”,将我们之前的glfw的“include”头文件以及我们glad.zip文件内的“include”头文件放入我们的创建的“include”目录下,将我们之前得到的“glfw.lib”以及"glad.lib"放入我们创建的“lib”目录下, 点击上方的“项目”——>“属性”——>"Visual C++目录“, 将“包含目录”设置为我们项目下的“include”目录, 将“库目录”设置为我们创建的“lib”目录下。
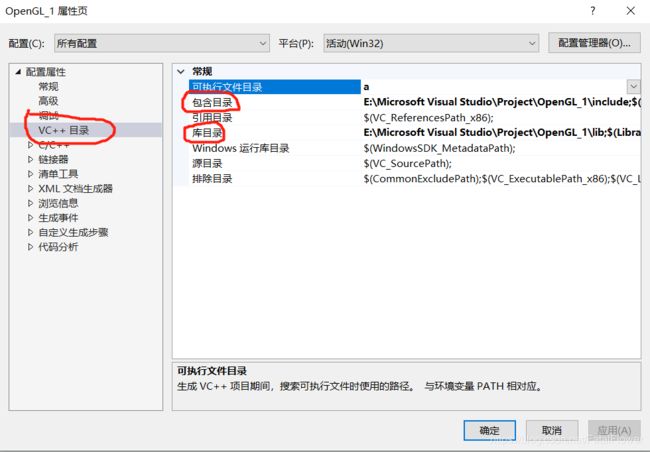
之后, 我们点击“链接器”——>“输入”, 在附加依赖项内输入“opengl32.lib”、以及你的glfw的库文件, 我这里的是glfw3.lib, 生成的glad库文件, 我这里的是glad.lib。opengl32.lib是Visual Studio SDK自带的一个库文件。
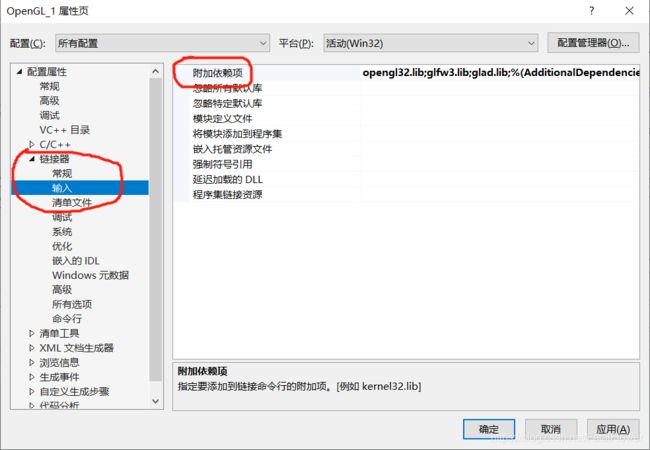
点击“确定”, 即可完成OpenGL的配置。
点击“本地Windows调试”即可运行你的OpenGL程序。为了能够正常运行你的程序, 在运行时请确保你的每个库都是基于相同位数的, X86对应的是32位的, 而X64对应的是64位的。
参考
[1]: https://medium.com/@bhargav.chippada/how-to-setup-opengl-on-mingw-w64-in-windows-10-64-bits-b77f350cea7e
[2]: https://www.transmissionzero.co.uk/computing/using-glut-with-mingw/
[3]: https://learnopengl-cn.github.io/01%20Getting%20started/02%20Creating%20a%20window/