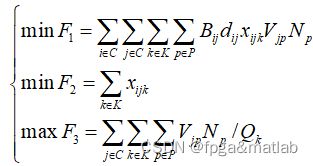【配送优化】基于PSO算法的有效空间模型的配送优化MATLAB仿真
1.软件版本
MATLAB2013b
2.本算法理论知识
步骤一:建模的前提假设
·不考虑堵车情况;
·不考虑汽车可能发送故障的情况;
·根据你的任务要求,成本因素仅考虑汽油,而对于同一汽车,即为最短路径和装载;
·不考虑装货和卸货导致的时间成本因素;
·不考虑天气等任何客观干扰因素;
·对于装载率,由于您提供的数据货物质量未知,这里仅考虑体积,不考虑质量,也不考虑不同货物在同一卡车中的具体的位置摆放需求,即以装载率最大化为目标,在单个货物不可切割的前提下,尽可能多的放货物,而不考虑上下,前后,左右的摆放问题。
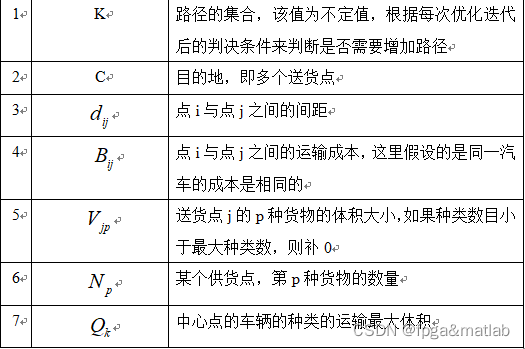
步骤二:所用的参数
步骤三:优化目标函数
这里,我们的优化目标函数为:
这里的函数含义是:
成本最低;
路径综合最短;
每条线路的装载率最大;
3.部分源码
clc;
clear;
close all;
warning off;
addpath 'func\'
%%
%参数的初始化
%算法的初始化参数
%算法的初始化参数
sel = 3;%选择三种卡车
Rr = 0.1; %挥发度系数
Iter = 80; %算法迭代次数
Num_ann = 30; %蚂蚁数目
Importance= 12; %重要度系数
%卡车的初始化参数
%卡车的初始化参数
if sel == 1
Lcar = 4.85; %集装箱的长
Wcar = 2.42; %集装箱的宽
Hcar = 2.15; %集装箱的高
Qv = Lcar*Wcar*Hcar;%卡车的装货体积
Lf = 8; %卡车每公里油耗
end
if sel == 2
Lcar = 9.5; %集装箱的长
Wcar = 2.3; %集装箱的宽
Hcar = 2.53; %集装箱的高
Qv = Lcar*Wcar*Hcar;%卡车的装货体积
Lf = 8; %卡车每公里油耗
end
if sel == 3
Lcar = 12.18; %集装箱的长
Wcar = 2.4; %集装箱的宽
Hcar = 1.95; %集装箱的高
Qv = Lcar*Wcar*Hcar;%卡车的装货体积
Lf = 8; %卡车每公里油耗
end
lemda = 0.95; %卡车装货率
%坐标点
%坐标点
C0=[ 0 0 %x[10202]
8.51 8.19 %x[10291]
8.69 9.01 %x[10295]
7.29 8.01 %x[10233]
7.3 7.95 %x[10183]
9.56 8.59 %x[10034]
9.56 9.14 %x[10207]
9.14 9.16 %x[10612]
7.84 9.18 %x[10237]
9.46 9.94 %x[10605]
8.84 9.84 %x[10203]
6.84 9.84 %x[10070]
7.27 10.02 %x[10090]
10.26 10.64 %x[10063]
7.97 10.67 %x[10992]
5.41 10.87 %x[10253]
10.66 11.33 %x[10281]
11.22 11.15 %x[10025]
11.48 11.04 %x[10776]
9.52 11.57 %x[10073]
7.61 11.73 %x[10309]
11.06 12.18 %x[10874]
8.69 12.71 %x[10262]
8.69 12.71 %x[10874]
8.96 13.18 %x[10369]
10.68 12.88 %x[10494]
10.88 13.64 %x[10514]
10.18 13.74 %x[10232]
7.36 15.8 %x[10367]
5.07 16.42 %x[10244]
14.58 11.04 %x[10468]
14.18 8.59 %x[10945]
14.64 7.54 %x[10118]
12.04 6.64 %x[10040]
31.88 17.84 %x[10016]
37.98 12.94 %x[10248]
45.08 2.38 %x[10061]
10.68 11.4 %x[10264]
10.96 12.28 %x[10161]
7.97 10.68 %x[10151]
];
%部分坐标值中没有提供,所以这里以你提供的坐标值为准给出频数
C_f=[1 %x[10202]
1 %x[10291]
5 %x[10295]
1 %x[10233]
1 %x[10183]
4 %x[10034]
4 %x[10207]
1 %x[10612]
3 %x[10237]
1 %x[10605]
6 %x[10203]
4 %x[10070]
2 %x[10090]
3 %x[10063]
2 %x[10992]
2 %x[10253]
2 %x[10281]
4 %x[10025]
1 %x[10776]
3 %x[10073]
6 %x[10309]
4 %x[10874]
3 %x[10262]
4 %x[10874]
5 %x[10369]
4 %x[10494]
4 %x[10514]
1 %x[10232]
4 %x[10367]
2 %x[10244]
1 %x[10468]
4 %x[10945]
6 %x[10118]
2 %x[10040]
2 %x[10016]
4 %x[10248]
2 %x[10061]
2 %x[10264]
1 %x[10161]
1 %x[10151]
];
C = func_pos(C0,C_f);
%每个点的货物体积和不同类别的数量
%x[10202]%x[10291]%x[10295]%x[10233]%x[10183]%x[10034]%x[10207]%x[10612]%x[10237]%x[10605]
%x[10203]%x[10070]%x[10090]%x[10063]%x[10992]%x[10253]%x[10281]%x[10025]%x[10776]%x[10073]
%x[10309]%x[10874]%x[10262]%x[10874]%x[10369]%x[10494]%x[10514]%x[10232]%x[10367]%x[10244]
%x[10468]%x[10945]%x[10118]%x[10040]%x[10016]%x[10248]%x[10061]%x[10264]%x[10161]%x[10151]
Infors = func_V();
for i = 1:length(Infors)
Nums{i} = Infors{i}(:,4);
V1{i} = (Infors{i}(:,1).*Infors{i}(:,2)).*Infors{i}(:,3)/1000/1000/1000;
end
%映射表
B = func_maps(C_f);
%计算规模和权值的初始值
[SCALEs,Wsd]=func_w(C);
%中心和每个供货点之间连接能节省的距离
Save_d = func_save_d(SCALEs,Wsd);
LOADs = 0;
Eer = 1./Wsd; %启发常系数
Tau = ones(SCALEs,SCALEs);
Save_roads = zeros(Num_ann,SCALEs+20);%生成路的径
Iteration = 1;
Best_roads = [Iter,SCALEs+20]; %各代最佳路线
Best_roads_Lens = inf.*ones(Iter,1); %各代最佳路线的长度
Best_roads_Lens_avgs = zeros(Iter,1); %各代路线的平均长度
%进行蚁群+PSO算法
while (Iteration <= Iter)
disp('当前迭代次数')
Iteration
%产生随机变量作为初始化粒子
Save_roads(:,1) = randint(Num_ann,1,[1,1]);
%按如下的规则进行循环历遍
for i=1:Num_ann
%指定随机性
RandStream.setDefaultStream(RandStream('mt19937ar','seed',Iteration*i));
Will_walks = Save_roads(i,:);
Will_walks = Will_walks(Will_walks>0);
Will_walks2 = setdiff(1:SCALEs,Will_walks);
c_temp = length(Will_walks2);
Jer=1;
while Jer <= SCALEs
if isempty(Will_walks2) == 0
%按照规则选下一个供货点或者是回到中心
for k=1:length(Will_walks2)
x(k) = (Tau(Will_walks(end),Will_walks2(k))) *...
(Eer(Will_walks(end),Will_walks2(k))) *...
(Save_d(Will_walks(end),Will_walks2(k))^2);
end
Pers = rand(1,1);
if Pers < 0.1
choices = find(max(x));
else
x = x/(sum(x));
xcum = cumsum(x);
choices = find(xcum>=rand(1,1));
end
%以下是对每个供货点进行供货的装载情况的计算
if isempty(choices) == 1
choices = 1;
%计算当前供货点的物件数量和体积
INDs = choices;
INDs2 = INDs;
LOADs = LOADs + V1{INDs2}(choices);
else
INDs = Will_walks2(choices(1));
%对当前点下的情况进行装货
INDs2 = B(INDs,2);
%计算当前点种的货物的种类
ZL = length(V1{INDs2});
%%产生一组概率进行选择货物,如果装载满足需求,则继续装,否则不装
%NNS = floor(ZL*rand(1,1)) + 1;
NNS = 1;
for NNS = 1:ZL
CC = Nums{INDs2}(NNS);
while CC > 0
Vtmp = V1{INDs2}(NNS);%选择的货物的体积大小
%然后进行装载
LOADs = LOADs + Vtmp;
%存货数量减1
CC = CC-1;
Nums{INDs2}(NNS) = CC;
end
end
end
%计算装载率
if LOADs <= lemda*Qv
WW(i,Iteration) = LOADs/(lemda*Qv);%记录当前的装载率值
end
if LOADs > lemda*Qv%装满则返回
choices = 1;
Jer = Jer-1;
LOADs = 0;
Save_roads(i,length(Will_walks)+1) = choices(1);
else
Save_roads(i,length(Will_walks)+1) = Will_walks2(choices(1));
end
end
Will_walks = Save_roads(i,:);
Will_walks = Will_walks(Will_walks>0);
Will_walks2 = setdiff(1:SCALEs,Will_walks);
x = [];
if Will_walks(end) > 1 | Will_walks(end) < 1
Save_roads(i,1:(length(Will_walks)+1))=[Will_walks,1];
end
Jer=Jer+1;
end
LOADs=0;
end
L = zeros(Num_ann,1);
for i=1:Num_ann
tmpsss = Save_roads(i,:);
R = tmpsss(tmpsss>0);
for j=1:(length(R)-1)
L(i) = L(i) + Wsd(R(j),R(j+1));
end
end
Best_roads_Lens(Iteration) = min(L);
pos = find(L==Best_roads_Lens(Iteration));
Best_roads(Iteration,1:length(Save_roads(pos(1),:))) = Save_roads(pos(1),:);
SELS = find(Best_roads(Iteration,:)==1);
Best_save = [];
Best_save2 = 0;
for Si=1:(length(SELS)-1)
YBEST = Best_roads(Iteration,SELS(Si):SELS(Si+1));
al = length(YBEST);
T = zeros((length(SELS)-1),1);
for Sj=1:(al-1)
T(Si)=T(Si)+Wsd(YBEST(Sj),YBEST(Sj+1));
end
for Sp=2:(al-1)
for Sq=(Sp+1):(al-1)
DD = YBEST;
temp1 = DD(Sp);
temp2 = DD(Sq);
DD(Sp) = temp2;
DD(Sq) = temp1;
TT = zeros(1);
for Sj=1:(al-1)
TT = TT + Wsd(DD(Sj),DD(Sj+1));
end
if TT=2
YBEST = YBEST(2:al);
end
Best_save = [Best_save,YBEST];
Best_save2= Best_save2+T(Si);
end
Best_roads_Lens(Iteration) = Best_save2;
Best_roads(Iteration,1:length(Best_save)) = Best_save;
Best_save = [];
Best_save2 = 0;
Best_roads_Lens_avgs(Iteration) = mean(L);
LOADs = 0;
Iteration = Iteration+1;
Delta_Tau=zeros(SCALEs,SCALEs);
for i=1:Num_ann
MM = Save_roads(i,:);
R = MM(MM>0);
for j=1:(length(R)-1)
Delta_Tau(R(j),R(j+1))=Delta_Tau(R(j),R(j+1))+Importance/L(i);
end
end
Tau = (1-Rr).*Tau+Delta_Tau;
%清零
Save_roads = zeros(Num_ann,SCALEs);
end
%优化结果
Pos = find(Best_roads_Lens==min(Best_roads_Lens));
best_route = Best_roads(Pos(1),:);
best_route = best_route(best_route>0);
for i = 1:Iter
Load_rate(i) = mean(WW(:,i));
end
%装载率的变化
%装载率的变化
disp('装载率:');
Load_rate(end)
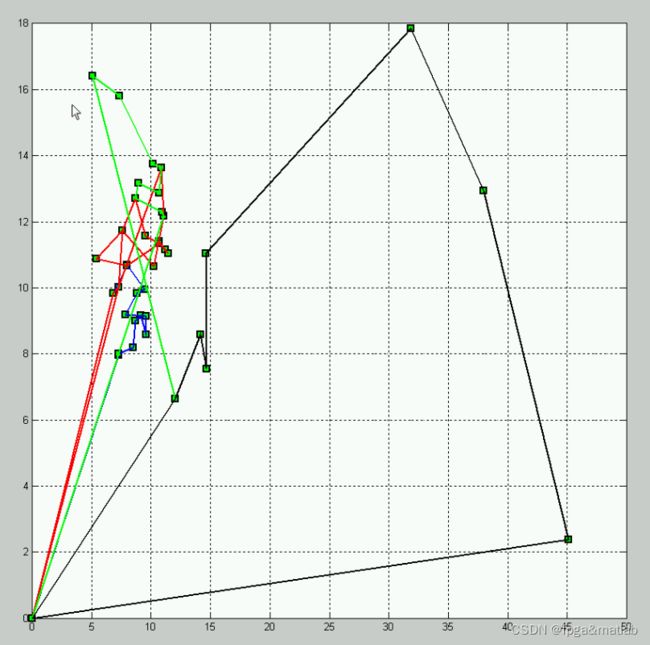
%画出循环路径
%画出循环路径
VV = find(best_route == 1);
Color = ['b';'r';'g';'k';'m';'c';'y'];
figure;
plot([C(best_route,1)],[C(best_route,2)],'ms','LineWidth',2,'MarkerEdgeColor','k','MarkerFaceColor','g');
hold on;
for i = 1:length(VV)-1
if i <= 7
tmp = num2str(Color(i));
plot([C(best_route(VV(i):VV(i+1)),1)],[C(best_route(VV(i):VV(i+1)),2)],tmp,'LineWidth',2)
hold on;
end
if i>7 & i<=14
tmp = [num2str(Color(i-7)),'--'];
plot([C(best_route(VV(i):VV(i+1)),1)],[C(best_route(VV(i):VV(i+1)),2)],tmp,'LineWidth',2)
hold on;
end
if i>14 & i<=21
tmp = [num2str(Color(i-7)),'-.'];
plot([C(best_route(VV(i):VV(i+1)),1)],[C(best_route(VV(i):VV(i+1)),2)],tmp,'LineWidth',2)
hold on;
end
end
grid on;
axis square;
disp('所有的供货循环路径为:');
for i = 1:length(VV)-1
fprintf('%d : ',i);
for j = 1:length([best_route(VV(i):VV(i+1))])
tmps = [best_route(VV(i):VV(i+1))];
if j == length([best_route(VV(i):VV(i+1))])
fprintf('%d',tmps(j));
else
fprintf('%d -> ',tmps(j));
end
end
fprintf('\n\n');
end
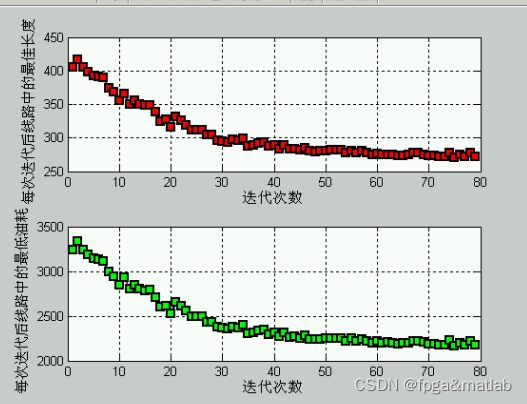
%线路长度的变化
%线路长度的变化
figure;
subplot(211);
plot(Best_roads_Lens_avgs(2:end),'bs-','LineWidth',2,'MarkerEdgeColor','k','MarkerFaceColor','r');
grid on;
xlabel('迭代次数');
ylabel('每次迭代后线路中的最佳长度');
subplot(212);
plot(Lf*Best_roads_Lens_avgs(2:end),'bs-','LineWidth',2,'MarkerEdgeColor','k','MarkerFaceColor','g');
grid on;
xlabel('迭代次数');
ylabel('每次迭代后线路中的最低油耗');
4.仿真分析
5.参考文献
A06-08