Datawhale 《动手学深度学习》(二)
动手学深度学习(二)
- Day 3
-
- 过拟合&欠拟合及其解决方案
-
- 一些概念
- 高维线性回归实验从零开始的实现
- 丢弃法
- 梯度消失&梯度爆炸
-
- 一些理论
- Kaggle房价预测实战
- 循环神经网络进阶
-
- 代码实现
- Day 4
-
- 机器翻译及相关技术
-
- 定义
- 代码实现
- 注意力机制与Seq2seq模型
-
- 注意力机制框架
- 点积注意力
- 多层感知机注意力
- Seq2seq模型
- Transformer
-
- 结构
- 代码实现
- Day 5
-
- 卷积神经网络基础
-
- 二维卷积层
- 填充和步幅
- 多输入通道和多输出通道
- 简洁实现
- 池化
- IeNet
-
- 代码实现
- 卷积神经网络进阶
-
- 深度卷积神经网络(AlexNet)
- 使用重复元素的网络(VGG)
- ⽹络中的⽹络(NiN)
- 代码实现
Day 3
过拟合&欠拟合及其解决方案
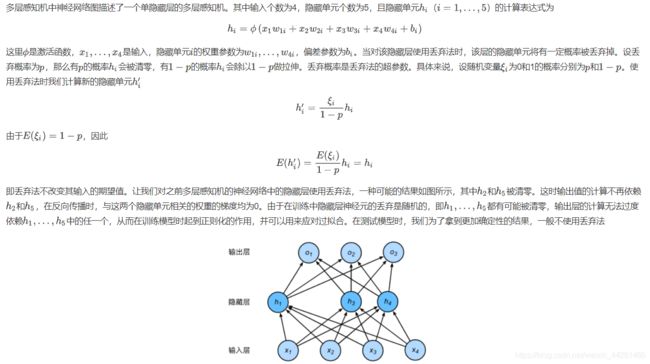
一些概念
- 训练误差(training error)
模型在训练数据集上表现出的误差。 - 泛化误差(generalization error)
模型在任意一个测试数据样本上表现出的误差的期望,并常常通过测试数据集上的误差来近似。
计算训练误差和泛化误差可以使用损失函数,例如线性回归用到的平方损失函数和softmax回归用到的交叉熵损失函数。
- K折交叉验证
把原始训练数据集分割成K个不重合的子数据集,然后做K次模型训练和验证。每一次使用一个子数据集验证模型,并使用其他K-1个子数据集来训练模型。在这K次训练和验证中,每次用来验证模型的子数据集都不同。最后,对这K次训练误差和验证误差分别求平均。 - 过拟合和欠拟合
模型无法得到较低的训练误差——欠拟合(underfitting)
模型的训练误差远小于它在测试数据集上的误差——过拟合(overfitting)
如果训练数据集中样本数过少,特别是比模型参数数量(按元素计)更少时,过拟合更容易发生。此外,泛化误差不会随训练数据集里样本数量增加而增大。因此,在计算资源允许的范围之内,我们通常希望训练数据集大一些,特别是在模型复杂度较高时,例如层数较多的深度学习模型。
正则化通过为模型损失函数添加惩罚项使学出的模型参数值较小,是应对过拟合的常用手段。
高维线性回归实验从零开始的实现
%matplotlib inline
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
import sys
sys.path.append("/home/kesci/input")
import d2lzh1981 as d2l
n_train, n_test, num_inputs = 20, 100, 200
true_w, true_b = torch.ones(num_inputs, 1) * 0.01, 0.05
features = torch.randn((n_train + n_test, num_inputs))
labels = torch.matmul(features, true_w) + true_b
labels += torch.tensor(np.random.normal(0, 0.01, size=labels.size()), dtype=torch.float)
train_features, test_features = features[:n_train, :], features[n_train:, :]
train_labels, test_labels = labels[:n_train], labels[n_train:]
def init_params():
w = torch.randn((num_inputs, 1), requires_grad=True)
b = torch.zeros(1, requires_grad=True)
return [w, b]
def l2_penalty(w):
return (w**2).sum() / 2
batch_size, num_epochs, lr = 1, 100, 0.003
net, loss = d2l.linreg, d2l.squared_loss
dataset = torch.utils.data.TensorDataset(train_features, train_labels)
train_iter = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size, shuffle=True)
def fit_and_plot(lambd):
w, b = init_params()
train_ls, test_ls = [], []
for _ in range(num_epochs):
for X, y in train_iter:
# 添加了L2范数惩罚项
l = loss(net(X, w, b), y) + lambd * l2_penalty(w)
l = l.sum()
if w.grad is not None:
w.grad.data.zero_()
b.grad.data.zero_()
l.backward()
d2l.sgd([w, b], lr, batch_size)
train_ls.append(loss(net(train_features, w, b), train_labels).mean().item())
test_ls.append(loss(net(test_features, w, b), test_labels).mean().item())
d2l.semilogy(range(1, num_epochs + 1), train_ls, 'epochs', 'loss',
range(1, num_epochs + 1), test_ls, ['train', 'test'])
print('L2 norm of w:', w.norm().item())
使用权重衰减
fit_and_plot(lambd=3)
简洁实现
def fit_and_plot_pytorch(wd):
# 对权重参数衰减。权重名称一般是以weight结尾
net = nn.Linear(num_inputs, 1)
nn.init.normal_(net.weight, mean=0, std=1)
nn.init.normal_(net.bias, mean=0, std=1)
optimizer_w = torch.optim.SGD(params=[net.weight], lr=lr, weight_decay=wd) # 对权重参数衰减
optimizer_b = torch.optim.SGD(params=[net.bias], lr=lr) # 不对偏差参数衰减
train_ls, test_ls = [], []
for _ in range(num_epochs):
for X, y in train_iter:
l = loss(net(X), y).mean()
optimizer_w.zero_grad()
optimizer_b.zero_grad()
l.backward()
# 对两个optimizer实例分别调用step函数,从而分别更新权重和偏差
optimizer_w.step()
optimizer_b.step()
train_ls.append(loss(net(train_features), train_labels).mean().item())
test_ls.append(loss(net(test_features), test_labels).mean().item())
d2l.semilogy(range(1, num_epochs + 1), train_ls, 'epochs', 'loss',
range(1, num_epochs + 1), test_ls, ['train', 'test'])
print('L2 norm of w:', net.weight.data.norm().item())
fit_and_plot_pytorch(0)
丢弃法
%matplotlib inline
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
import sys
sys.path.append("/home/kesci/input")
import d2lzh1981 as d2l
def dropout(X, drop_prob):
X = X.float()
assert 0 <= drop_prob <= 1
keep_prob = 1 - drop_prob
# 这种情况下把全部元素都丢弃
if keep_prob == 0:
return torch.zeros_like(X)
mask = (torch.rand(X.shape) < keep_prob).float()
return mask * X / keep_prob
X = torch.arange(16).view(2, 8)
dropout(X, 0)
dropout(X, 0.5)
dropout(X, 1.0)
# 参数的初始化
num_inputs, num_outputs, num_hiddens1, num_hiddens2 = 784, 10, 256, 256
W1 = torch.tensor(np.random.normal(0, 0.01, size=(num_inputs, num_hiddens1)), dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
b1 = torch.zeros(num_hiddens1, requires_grad=True)
W2 = torch.tensor(np.random.normal(0, 0.01, size=(num_hiddens1, num_hiddens2)), dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
b2 = torch.zeros(num_hiddens2, requires_grad=True)
W3 = torch.tensor(np.random.normal(0, 0.01, size=(num_hiddens2, num_outputs)), dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
b3 = torch.zeros(num_outputs, requires_grad=True)
params = [W1, b1, W2, b2, W3, b3]
drop_prob1, drop_prob2 = 0.2, 0.5
def net(X, is_training=True):
X = X.view(-1, num_inputs)
H1 = (torch.matmul(X, W1) + b1).relu()
if is_training: # 只在训练模型时使用丢弃法
H1 = dropout(H1, drop_prob1) # 在第一层全连接后添加丢弃层
H2 = (torch.matmul(H1, W2) + b2).relu()
if is_training:
H2 = dropout(H2, drop_prob2) # 在第二层全连接后添加丢弃层
return torch.matmul(H2, W3) + b3
def evaluate_accuracy(data_iter, net):
acc_sum, n = 0.0, 0
for X, y in data_iter:
if isinstance(net, torch.nn.Module):
net.eval() # 评估模式, 这会关闭dropout
acc_sum += (net(X).argmax(dim=1) == y).float().sum().item()
net.train() # 改回训练模式
else: # 自定义的模型
if('is_training' in net.__code__.co_varnames): # 如果有is_training这个参数
# 将is_training设置成False
acc_sum += (net(X, is_training=False).argmax(dim=1) == y).float().sum().item()
else:
acc_sum += (net(X).argmax(dim=1) == y).float().sum().item()
n += y.shape[0]
return acc_sum / n
num_epochs, lr, batch_size = 5, 100.0, 256 # 这里的学习率设置的很大,原因与之前相同。
loss = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size, root='/home/kesci/input/FashionMNIST2065')
d2l.train_ch3(
net,
train_iter,
test_iter,
loss,
num_epochs,
batch_size,
params,
lr)
简洁实现
net = nn.Sequential(
d2l.FlattenLayer(),
nn.Linear(num_inputs, num_hiddens1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(drop_prob1),
nn.Linear(num_hiddens1, num_hiddens2),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(drop_prob2),
nn.Linear(num_hiddens2, 10)
)
for param in net.parameters():
nn.init.normal_(param, mean=0, std=0.01)
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.5)
d2l.train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, num_epochs, batch_size, None, None, optimizer)
梯度消失&梯度爆炸
一些理论
Kaggle房价预测实战
matplotlib inline
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import sys
sys.path.append("/home/kesci/input")
import d2lzh1981 as d2l
print(torch.__version__)
torch.set_default_tensor_type(torch.FloatTensor)
获取数据集
test_data = pd.read_csv("/home/kesci/input/houseprices2807/house-prices-advanced-regression-techniques/test.csv")
train_data = pd.read_csv("/home/kesci/input/houseprices2807/house-prices-advanced-regression-techniques/train.csv")
预处理数据
numeric_features = all_features.dtypes[all_features.dtypes != 'object'].index
all_features[numeric_features] = all_features[numeric_features].apply(
lambda x: (x - x.mean()) / (x.std()))
# 标准化后,每个数值特征的均值变为0,所以可以直接用0来替换缺失值
all_features[numeric_features] = all_features[numeric_features].fillna(0)
# dummy_na=True将缺失值也当作合法的特征值并为其创建指示特征
all_features = pd.get_dummies(all_features, dummy_na=True)
all_features.shape
n_train = train_data.shape[0]
train_features = torch.tensor(all_features[:n_train].values, dtype=torch.float)
test_features = torch.tensor(all_features[n_train:].values, dtype=torch.float)
train_labels = torch.tensor(train_data.SalePrice.values, dtype=torch.float).view(-1, 1)
训练模型
loss = torch.nn.MSELoss()
def get_net(feature_num):
net = nn.Linear(feature_num, 1)
for param in net.parameters():
nn.init.normal_(param, mean=0, std=0.01)
return net
def log_rmse(net, features, labels):
with torch.no_grad():
# 将小于1的值设成1,使得取对数时数值更稳定
clipped_preds = torch.max(net(features), torch.tensor(1.0))
rmse = torch.sqrt(2 * loss(clipped_preds.log(), labels.log()).mean())
return rmse.item()
def train(net, train_features, train_labels, test_features, test_labels,
num_epochs, learning_rate, weight_decay, batch_size):
train_ls, test_ls = [], []
dataset = torch.utils.data.TensorDataset(train_features, train_labels)
train_iter = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size, shuffle=True)
# 这里使用了Adam优化算法
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(params=net.parameters(), lr=learning_rate, weight_decay=weight_decay)
net = net.float()
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for X, y in train_iter:
l = loss(net(X.float()), y.float())
optimizer.zero_grad()
l.backward()
optimizer.step()
train_ls.append(log_rmse(net, train_features, train_labels))
if test_labels is not None:
test_ls.append(log_rmse(net, test_features, test_labels))
return train_ls, test_ls
K折交叉验证
def get_k_fold_data(k, i, X, y):
# 返回第i折交叉验证时所需要的训练和验证数据
assert k > 1
fold_size = X.shape[0] // k
X_train, y_train = None, None
for j in range(k):
idx = slice(j * fold_size, (j + 1) * fold_size)
X_part, y_part = X[idx, :], y[idx]
if j == i:
X_valid, y_valid = X_part, y_part
elif X_train is None:
X_train, y_train = X_part, y_part
else:
X_train = torch.cat((X_train, X_part), dim=0)
y_train = torch.cat((y_train, y_part), dim=0)
return X_train, y_train, X_valid, y_valid
def k_fold(k, X_train, y_train, num_epochs,
learning_rate, weight_decay, batch_size):
train_l_sum, valid_l_sum = 0, 0
for i in range(k):
data = get_k_fold_data(k, i, X_train, y_train)
net = get_net(X_train.shape[1])
train_ls, valid_ls = train(net, *data, num_epochs, learning_rate,
weight_decay, batch_size)
train_l_sum += train_ls[-1]
valid_l_sum += valid_ls[-1]
if i == 0:
d2l.semilogy(range(1, num_epochs + 1), train_ls, 'epochs', 'rmse',
range(1, num_epochs + 1), valid_ls,
['train', 'valid'])
print('fold %d, train rmse %f, valid rmse %f' % (i, train_ls[-1], valid_ls[-1]))
return train_l_sum / k, valid_l_sum / k
模型选择
k, num_epochs, lr, weight_decay, batch_size = 5, 100, 5, 0, 64
train_l, valid_l = k_fold(k, train_features, train_labels, num_epochs, lr, weight_decay, batch_size)
print('%d-fold validation: avg train rmse %f, avg valid rmse %f' % (k, train_l, valid_l))
模型预测
def train_and_pred(train_features, test_features, train_labels, test_data,
num_epochs, lr, weight_decay, batch_size):
net = get_net(train_features.shape[1])
train_ls, _ = train(net, train_features, train_labels, None, None,
num_epochs, lr, weight_decay, batch_size)
d2l.semilogy(range(1, num_epochs + 1), train_ls, 'epochs', 'rmse')
print('train rmse %f' % train_ls[-1])
preds = net(test_features).detach().numpy()
test_data['SalePrice'] = pd.Series(preds.reshape(1, -1)[0])
submission = pd.concat([test_data['Id'], test_data['SalePrice']], axis=1)
submission.to_csv('./submission.csv', index=False)
# sample_submission_data = pd.read_csv("../input/house-prices-advanced-regression-techniques/sample_submission.csv")
train_and_pred(train_features, test_features, train_labels, test_data, num_epochs, lr, weight_decay, batch_size)
循环神经网络进阶
代码实现
同文章一
Day 4
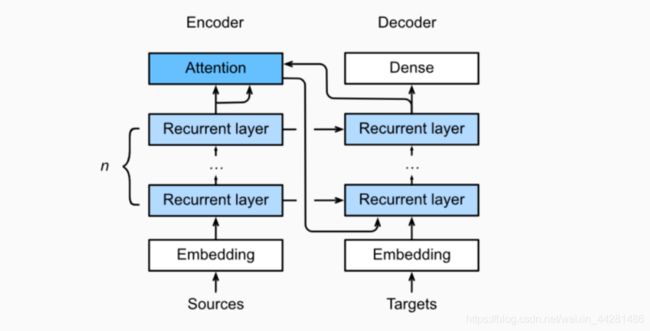
机器翻译及相关技术
定义
机器翻译(MT):将一段文本从一种语言自动翻译为另一种语言,用神经网络解决这个问题通常称为神经机器翻译(NMT)。 主要特征:输出是单词序列而不是单个单词。 输出序列的长度可能与源序列的长度不同。
代码实现
import os
os.listdir('/home/kesci/input/')
import sys
sys.path.append('/home/kesci/input/d2l9528/')
import collections
import d2l
import zipfile
from d2l.data.base import Vocab
import time
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.utils import data
from torch import optim
with open('/home/kesci/input/fraeng6506/fra.txt', 'r') as f:
raw_text = f.read()
print(raw_text[0:1000])
def preprocess_raw(text):
text = text.replace('\u202f', ' ').replace('\xa0', ' ')
out = ''
for i, char in enumerate(text.lower()):
if char in (',', '!', '.') and i > 0 and text[i-1] != ' ':
out += ' '
out += char
return out
text = preprocess_raw(raw_text)
print(text[0:1000])
num_examples = 50000
source, target = [], []
for i, line in enumerate(text.split('\n')):
if i > num_examples:
break
parts = line.split('\t')
if len(parts) >= 2:
source.append(parts[0].split(' '))
target.append(parts[1].split(' '))
source[0:3], target[0:3]
d2l.set_figsize()
d2l.plt.hist([[len(l) for l in source], [len(l) for l in target]],label=['source', 'target'])
d2l.plt.legend(loc='upper right');
def build_vocab(tokens):
tokens = [token for line in tokens for token in line]
return d2l.data.base.Vocab(tokens, min_freq=3, use_special_tokens=True)
src_vocab = build_vocab(source)
len(src_vocab)
def pad(line, max_len, padding_token):
if len(line) > max_len:
return line[:max_len]
return line + [padding_token] * (max_len - len(line))
pad(src_vocab[source[0]], 10, src_vocab.pad)
def build_array(lines, vocab, max_len, is_source):
lines = [vocab[line] for line in lines]
if not is_source:
lines = [[vocab.bos] + line + [vocab.eos] for line in lines]
array = torch.tensor([pad(line, max_len, vocab.pad) for line in lines])
valid_len = (array != vocab.pad).sum(1) #第一个维度
return array, valid_len
def load_data_nmt(batch_size, max_len): # This function is saved in d2l.
src_vocab, tgt_vocab = build_vocab(source), build_vocab(target)
src_array, src_valid_len = build_array(source, src_vocab, max_len, True)
tgt_array, tgt_valid_len = build_array(target, tgt_vocab, max_len, False)
train_data = data.TensorDataset(src_array, src_valid_len, tgt_array, tgt_valid_len)
train_iter = data.DataLoader(train_data, batch_size, shuffle=True)
return src_vocab, tgt_vocab, train_iter
src_vocab, tgt_vocab, train_iter = load_data_nmt(batch_size=2, max_len=8)
for X, X_valid_len, Y, Y_valid_len, in train_iter:
print('X =', X.type(torch.int32), '\nValid lengths for X =', X_valid_len,
'\nY =', Y.type(torch.int32), '\nValid lengths for Y =', Y_valid_len)
break
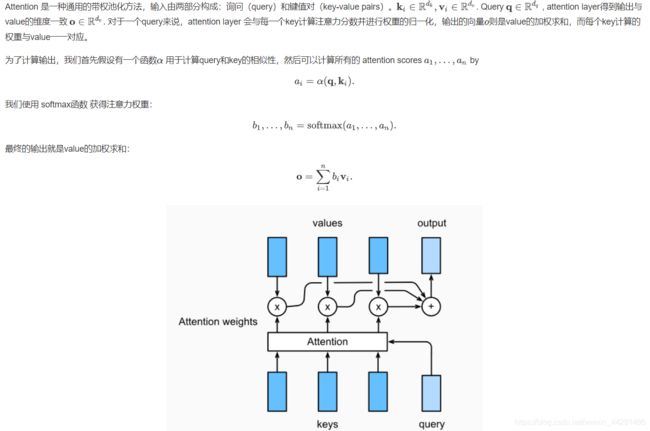
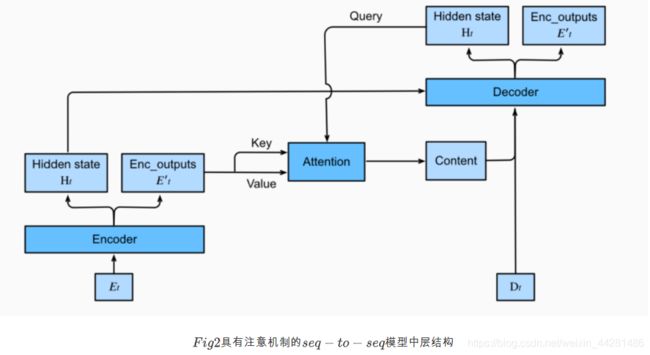
注意力机制与Seq2seq模型
注意力机制框架
点积注意力
# Save to the d2l package.
class DotProductAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dropout, **kwargs):
super(DotProductAttention, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
# query: (batch_size, #queries, d)
# key: (batch_size, #kv_pairs, d)
# value: (batch_size, #kv_pairs, dim_v)
# valid_length: either (batch_size, ) or (batch_size, xx)
def forward(self, query, key, value, valid_length=None):
d = query.shape[-1]
# set transpose_b=True to swap the last two dimensions of key
scores = torch.bmm(query, key.transpose(1,2)) / math.sqrt(d)
attention_weights = self.dropout(masked_softmax(scores, valid_length))
print("attention_weight\n",attention_weights)
return torch.bmm(attention_weights, value)
多层感知机注意力
# Save to the d2l package.
class MLPAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, units,ipt_dim,dropout, **kwargs):
super(MLPAttention, self).__init__(**kwargs)
# Use flatten=True to keep query's and key's 3-D shapes.
self.W_k = nn.Linear(ipt_dim, units, bias=False)
self.W_q = nn.Linear(ipt_dim, units, bias=False)
self.v = nn.Linear(units, 1, bias=False)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
def forward(self, query, key, value, valid_length):
query, key = self.W_k(query), self.W_q(key)
#print("size",query.size(),key.size())
# expand query to (batch_size, #querys, 1, units), and key to
# (batch_size, 1, #kv_pairs, units). Then plus them with broadcast.
features = query.unsqueeze(2) + key.unsqueeze(1)
#print("features:",features.size()) #--------------开启
scores = self.v(features).squeeze(-1)
attention_weights = self.dropout(masked_softmax(scores, valid_length))
return torch.bmm(attention_weights, value)
Seq2seq模型
import sys
sys.path.append('/home/kesci/input/d2len9900')
import d2l
class Seq2SeqAttentionDecoder(d2l.Decoder):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embed_size, num_hiddens, num_layers,
dropout=0, **kwargs):
super(Seq2SeqAttentionDecoder, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.attention_cell = MLPAttention(num_hiddens,num_hiddens, dropout)
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embed_size)
self.rnn = nn.LSTM(embed_size+ num_hiddens,num_hiddens, num_layers, dropout=dropout)
self.dense = nn.Linear(num_hiddens,vocab_size)
def init_state(self, enc_outputs, enc_valid_len, *args):
outputs, hidden_state = enc_outputs
# print("first:",outputs.size(),hidden_state[0].size(),hidden_state[1].size())
# Transpose outputs to (batch_size, seq_len, hidden_size)
return (outputs.permute(1,0,-1), hidden_state, enc_valid_len)
#outputs.swapaxes(0, 1)
def forward(self, X, state):
enc_outputs, hidden_state, enc_valid_len = state
#("X.size",X.size())
X = self.embedding(X).transpose(0,1)
# print("Xembeding.size2",X.size())
outputs = []
for l, x in enumerate(X):
# print(f"\n{l}-th token")
# print("x.first.size()",x.size())
# query shape: (batch_size, 1, hidden_size)
# select hidden state of the last rnn layer as query
query = hidden_state[0][-1].unsqueeze(1) # np.expand_dims(hidden_state[0][-1], axis=1)
# context has same shape as query
# print("query enc_outputs, enc_outputs:\n",query.size(), enc_outputs.size(), enc_outputs.size())
context = self.attention_cell(query, enc_outputs, enc_outputs, enc_valid_len)
# Concatenate on the feature dimension
# print("context.size:",context.size())
x = torch.cat((context, x.unsqueeze(1)), dim=-1)
# Reshape x to (1, batch_size, embed_size+hidden_size)
# print("rnn",x.size(), len(hidden_state))
out, hidden_state = self.rnn(x.transpose(0,1), hidden_state)
outputs.append(out)
outputs = self.dense(torch.cat(outputs, dim=0))
return outputs.transpose(0, 1), [enc_outputs, hidden_state,
enc_valid_len]
encoder = d2l.Seq2SeqEncoder(vocab_size=10, embed_size=8,
num_hiddens=16, num_layers=2)
# encoder.initialize()
decoder = Seq2SeqAttentionDecoder(vocab_size=10, embed_size=8,
num_hiddens=16, num_layers=2)
X = torch.zeros((4, 7),dtype=torch.long)
print("batch size=4\nseq_length=7\nhidden dim=16\nnum_layers=2\n")
print('encoder output size:', encoder(X)[0].size())
print('encoder hidden size:', encoder(X)[1][0].size())
print('encoder memory size:', encoder(X)[1][1].size())
state = decoder.init_state(encoder(X), None)
out, state = decoder(X, state)
out.shape, len(state), state[0].shape, len(state[1]), state[1][0].shape
训练
import zipfile
import torch
import requests
from io import BytesIO
from torch.utils import data
import sys
import collections
class Vocab(object): # This class is saved in d2l.
def __init__(self, tokens, min_freq=0, use_special_tokens=False):
# sort by frequency and token
counter = collections.Counter(tokens)
token_freqs = sorted(counter.items(), key=lambda x: x[0])
token_freqs.sort(key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
if use_special_tokens:
# padding, begin of sentence, end of sentence, unknown
self.pad, self.bos, self.eos, self.unk = (0, 1, 2, 3)
tokens = ['', '', '', '']
else:
self.unk = 0
tokens = ['']
tokens += [token for token, freq in token_freqs if freq >= min_freq]
self.idx_to_token = []
self.token_to_idx = dict()
for token in tokens:
self.idx_to_token.append(token)
self.token_to_idx[token] = len(self.idx_to_token) - 1
def __len__(self):
return len(self.idx_to_token)
def __getitem__(self, tokens):
if not isinstance(tokens, (list, tuple)):
return self.token_to_idx.get(tokens, self.unk)
else:
return [self.__getitem__(token) for token in tokens]
def to_tokens(self, indices):
if not isinstance(indices, (list, tuple)):
return self.idx_to_token[indices]
else:
return [self.idx_to_token[index] for index in indices]
def load_data_nmt(batch_size, max_len, num_examples=1000):
"""Download an NMT dataset, return its vocabulary and data iterator."""
# Download and preprocess
def preprocess_raw(text):
text = text.replace('\u202f', ' ').replace('\xa0', ' ')
out = ''
for i, char in enumerate(text.lower()):
if char in (',', '!', '.') and text[i-1] != ' ':
out += ' '
out += char
return out
with open('/home/kesci/input/fraeng6506/fra.txt', 'r') as f:
raw_text = f.read()
text = preprocess_raw(raw_text)
# Tokenize
source, target = [], []
for i, line in enumerate(text.split('\n')):
if i >= num_examples:
break
parts = line.split('\t')
if len(parts) >= 2:
source.append(parts[0].split(' '))
target.append(parts[1].split(' '))
# Build vocab
def build_vocab(tokens):
tokens = [token for line in tokens for token in line]
return Vocab(tokens, min_freq=3, use_special_tokens=True)
src_vocab, tgt_vocab = build_vocab(source), build_vocab(target)
# Convert to index arrays
def pad(line, max_len, padding_token):
if len(line) > max_len:
return line[:max_len]
return line + [padding_token] * (max_len - len(line))
def build_array(lines, vocab, max_len, is_source):
lines = [vocab[line] for line in lines]
if not is_source:
lines = [[vocab.bos] + line + [vocab.eos] for line in lines]
array = torch.tensor([pad(line, max_len, vocab.pad) for line in lines])
valid_len = (array != vocab.pad).sum(1)
return array, valid_len
src_vocab, tgt_vocab = build_vocab(source), build_vocab(target)
src_array, src_valid_len = build_array(source, src_vocab, max_len, True)
tgt_array, tgt_valid_len = build_array(target, tgt_vocab, max_len, False)
train_data = data.TensorDataset(src_array, src_valid_len, tgt_array, tgt_valid_len)
train_iter = data.DataLoader(train_data, batch_size, shuffle=True)
return src_vocab, tgt_vocab, train_iter
预测
for sentence in ['Go .', 'Good Night !', "I'm OK .", 'I won !']:
print(sentence + ' => ' + d2l.predict_s2s_ch9(
model, sentence, src_vocab, tgt_vocab, num_steps, ctx))
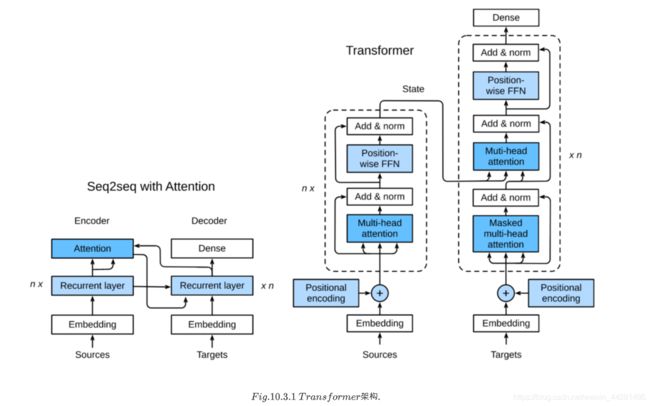
Transformer
结构
代码实现
import os
import math
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import sys
sys.path.append('/home/kesci/input/d2len9900')
import d2l
def SequenceMask(X, X_len,value=-1e6):
maxlen = X.size(1)
X_len = X_len.to(X.device)
#print(X.size(),torch.arange((maxlen),dtype=torch.float)[None, :],'\n',X_len[:, None] )
mask = torch.arange((maxlen), dtype=torch.float, device=X.device)
mask = mask[None, :] < X_len[:, None]
#print(mask)
X[~mask]=value
return X
def masked_softmax(X, valid_length):
# X: 3-D tensor, valid_length: 1-D or 2-D tensor
softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)
if valid_length is None:
return softmax(X)
else:
shape = X.shape
if valid_length.dim() == 1:
try:
valid_length = torch.FloatTensor(valid_length.numpy().repeat(shape[1], axis=0))#[2,2,3,3]
except:
valid_length = torch.FloatTensor(valid_length.cpu().numpy().repeat(shape[1], axis=0))#[2,2,3,3]
else:
valid_length = valid_length.reshape((-1,))
# fill masked elements with a large negative, whose exp is 0
X = SequenceMask(X.reshape((-1, shape[-1])), valid_length)
return softmax(X).reshape(shape)
# Save to the d2l package.
class DotProductAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dropout, **kwargs):
super(DotProductAttention, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
# query: (batch_size, #queries, d)
# key: (batch_size, #kv_pairs, d)
# value: (batch_size, #kv_pairs, dim_v)
# valid_length: either (batch_size, ) or (batch_size, xx)
def forward(self, query, key, value, valid_length=None):
d = query.shape[-1]
# set transpose_b=True to swap the last two dimensions of key
scores = torch.bmm(query, key.transpose(1,2)) / math.sqrt(d)
attention_weights = self.dropout(masked_softmax(scores, valid_length))
return torch.bmm(attention_weights, value)
class MultiHeadAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, num_heads, dropout, **kwargs):
super(MultiHeadAttention, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.attention = DotProductAttention(dropout)
self.W_q = nn.Linear(input_size, hidden_size, bias=False)
self.W_k = nn.Linear(input_size, hidden_size, bias=False)
self.W_v = nn.Linear(input_size, hidden_size, bias=False)
self.W_o = nn.Linear(hidden_size, hidden_size, bias=False)
def forward(self, query, key, value, valid_length):
# query, key, and value shape: (batch_size, seq_len, dim),
# where seq_len is the length of input sequence
# valid_length shape is either (batch_size, )
# or (batch_size, seq_len).
# Project and transpose query, key, and value from
# (batch_size, seq_len, hidden_size * num_heads) to
# (batch_size * num_heads, seq_len, hidden_size).
query = transpose_qkv(self.W_q(query), self.num_heads)
key = transpose_qkv(self.W_k(key), self.num_heads)
value = transpose_qkv(self.W_v(value), self.num_heads)
if valid_length is not None:
# Copy valid_length by num_heads times
device = valid_length.device
valid_length = valid_length.cpu().numpy() if valid_length.is_cuda else valid_length.numpy()
if valid_length.ndim == 1:
valid_length = torch.FloatTensor(np.tile(valid_length, self.num_heads))
else:
valid_length = torch.FloatTensor(np.tile(valid_length, (self.num_heads,1)))
valid_length = valid_length.to(device)
output = self.attention(query, key, value, valid_length)
output_concat = transpose_output(output, self.num_heads)
return self.W_o(output_concat)
def transpose_qkv(X, num_heads):
# Original X shape: (batch_size, seq_len, hidden_size * num_heads),
# -1 means inferring its value, after first reshape, X shape:
# (batch_size, seq_len, num_heads, hidden_size)
X = X.view(X.shape[0], X.shape[1], num_heads, -1)
# After transpose, X shape: (batch_size, num_heads, seq_len, hidden_size)
X = X.transpose(2, 1).contiguous()
# Merge the first two dimensions. Use reverse=True to infer shape from
# right to left.
# output shape: (batch_size * num_heads, seq_len, hidden_size)
output = X.view(-1, X.shape[2], X.shape[3])
return output
# Saved in the d2l package for later use
def transpose_output(X, num_heads):
# A reversed version of transpose_qkv
X = X.view(-1, num_heads, X.shape[1], X.shape[2])
X = X.transpose(2, 1).contiguous()
return X.view(X.shape[0], X.shape[1], -1)
class PositionWiseFFN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, ffn_hidden_size, hidden_size_out, **kwargs):
super(PositionWiseFFN, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.ffn_1 = nn.Linear(input_size, ffn_hidden_size)
self.ffn_2 = nn.Linear(ffn_hidden_size, hidden_size_out)
def forward(self, X):
return self.ffn_2(F.relu(self.ffn_1(X)))
Day 5
卷积神经网络基础
二维卷积层
填充和步幅
多输入通道和多输出通道
简洁实现
池化
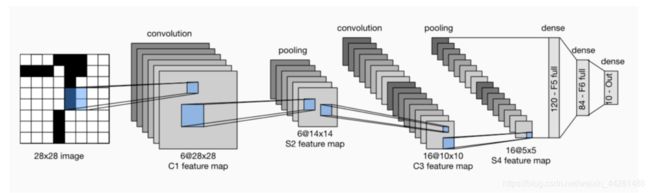
IeNet
代码实现
卷积神经网络进阶
深度卷积神经网络(AlexNet)
使用重复元素的网络(VGG)
⽹络中的⽹络(NiN)
代码实现
(最后部分内容稍后补充)