【模拟退火】CF2C Commentator problem
文章目录
- 题目描述
- 输入格式
- 输出格式
-
- 具体思路
- 代码实现
题目描述
The Olympic Games in Bercouver are in full swing now. Here everyone has their own objectives: sportsmen compete for medals, and sport commentators compete for more convenient positions to give a running commentary. Today the main sport events take place at three round stadiums, and the commentator’s objective is to choose the best point of observation, that is to say the point from where all the three stadiums can be observed. As all the sport competitions are of the same importance, the stadiums should be observed at the same angle. If the number of points meeting the conditions is more than one, the point with the maximum angle of observation is prefered.
Would you, please, help the famous Berland commentator G. Berniev to find the best point of observation. It should be noted, that the stadiums do not hide each other, the commentator can easily see one stadium through the other.
输入格式
The input data consists of three lines, each of them describes the position of one stadium. The lines have the format x , y , r {x,y,r} x,y,r , where ( x , y {x,y} x,y ) are the coordinates of the stadium’s center ( − 1 0 3 < = x , y < = 1 0 3 ) { ( -10^3 <= x,y<=10^3 )} (−103<=x,y<=103) , and r ( 1 < = r < = 1 0 3 ) {r(1<=r<=10^3)} r(1<=r<=103) is its radius. All the numbers in the input data are integer, stadiums do not have common points, and their centers are not on the same line.
输出格式
Print the coordinates of the required point with five digits after the decimal point. If there is no answer meeting the conditions, the program shouldn’t print anything. The output data should be left blank.
具体思路
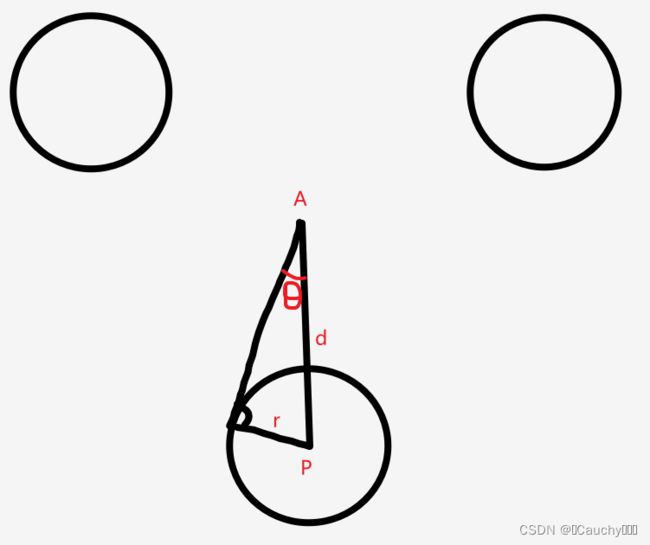
题意: 要求找到一个点,使得到三个圆的两切线张角相同,取最大张角的那个点输出,没有则不输出。
既然是模拟退火,那主要的就是两个部分:
- 估价函数
- 参数配置
那么对于评估函数的选定为:
-
1 s i n θ {\frac{1}{sinθ}} sinθ1 的 “方差”
- 1 s i n θ {\frac{1}{sinθ}} sinθ1 = 距离 / {/} / 半径
- “方差” :类似方差的思想,在此表现为 ∑ Δ 2 {\sumΔ^2} ∑Δ2
具体实现:
double evaluation(node &A) {
double t[3], delta[3], res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
t[i] = distance(A, p[i]) / p[i].r;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
delta[i] = t[i] - t[(i + 1) % 3];
res += delta[i] * delta[i];
}
return res * 1e9;
}
参数配置有如下:
- 初始温度的设定( T = 1 0 5 {T = 10^5} T=105 )
- 降温梯度的设定( Δ = 0.996 {Δ=0.996} Δ=0.996 )
- 极小量( e p s = 1 e − 14 {eps=1e^{-14}} eps=1e−14 )
- 判等极小常量( 1 e − 5 {1e^{-5}} 1e−5 )
- 评估函数中返回值适配常量( 1 0 9 {10^9} 109 )
- 模拟退火次数常量( 300 {300} 300 )
- 随机步长(
((rand() << 1) - RAND_MAX) * T) - M e t r o p o l i s {Metropolis} Metropolis 准则概率 p = {p = } p=
exp(-delta / T) * RAND_MAX > 1.0 * rand()
调参过程是很美妙(痛苦)的,不信你看
不过为了洛谷 AC 时刻的 还是很值得的。
那么附上全部代码:
代码实现
- 众所周知,
rand()是个玄学 - 实验得: 1 / 2 {1 / 2} 1/2 的概率通过
#include