MyBatis框架----多表查询与动态sql
目录
1.多表查询
1.1多对一
(1) 第一种方式 通过链表查询。
(2)第二种方式 通过嵌套查询。----两次查询。
1.2 一对多
2.动态SQL
(1)if和where一起用
(2) [choose when otherwise] 和where
(3)set标签---修改部分字段
(4) foreach 批量处理
1.多表查询
1.1多对一
例子: 根据学生id查询学生信息与班级信息
(1) 第一种方式 通过链表查询。
1. 创建两张具有逻辑外键或物理外键的数据表
2. 常见数据表对应的实体类
班级实体类:
public class Cls {
private Integer id;
private String cname;
public Cls() {
}
public Cls(Integer id, String cname) {
this.id = id;
this.cname = cname;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getCname() {
return cname;
}
public void setCname(String cname) {
this.cname = cname;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Cls{" +
"id=" + id +
", cname='" + cname + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
学生实体类:
public class Stu {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String classid;
//学生类里面需要创建一个班级类的实体类!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
private Cls cls;
public Stu() {
}
public Stu(Integer id, String name, String classid, Cls cls) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.classid = classid;
this.cls = cls;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getClassid() {
return classid;
}
public void setClassid(String classid) {
this.classid = classid;
}
public Cls getCls() {
return cls;
}
public void setCls(Cls cls) {
this.cls = cls;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Stu{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", classid='" + classid + '\'' +
", cls=" + cls +
'}';
}
}
3.创建学生dao层接口并定义方法
public interface StuDao {
Stu selectstuandclassbystuid(int id);
}4.在映射文件中写对应的dao接口方法中的sql语句
5.在配置文件中注册映射文件并测试
注册:
测试:
@Test
public void test01() throws IOException {
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory =new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StuDao stuDao = session.getMapper(StuDao.class);
Stu stu = stuDao.selectstuandclassbystuid(1001);
System.out.println(stu);
}结果:
(2)第二种方式 通过嵌套查询。----两次查询。
1. 在学生映射文件中写对应的dao接口方法中的sql语句
2. 在班级映射文件中写根据班级id查找班级信息的sql语句
3.在配置文件中注册两张表的映射文件 并测试
注册:
测试:
@Test
public void test01()throws IOException {
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory =new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StuDao stuDao = session.getMapper(StuDao.class);
Stu stu = stuDao.selectstuandclassbystuid(1001);
System.out.println(stu);
}1.2 一对多
例:根据班级id查找班级信息以及班级内所有学生
1. 使用上例多对一的数据表
2.创建数据表对应的实体类
学生类:
public class Stu {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String classid;
public Stu() {
}
public Stu(Integer id, String name, String classid) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.classid = classid;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getClassid() {
return classid;
}
public void setClassid(String classid) {
this.classid = classid;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Stu{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", classid='" + classid + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
班级类:
public class Cls {
private Integer id;
private String cname;
//班级中有很多学生 所以需要创建一个学生类的集合
private List stus;
public Cls() {
}
public Cls(Integer id, String cname, List stus) {
this.id = id;
this.cname = cname;
this.stus = stus;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getCname() {
return cname;
}
public void setCname(String cname) {
this.cname = cname;
}
public List getStus() {
return stus;
}
public void setStus(List stus) {
this.stus = stus;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Cls{" +
"id=" + id +
", cname='" + cname + '\'' +
", stus=" + stus +
'}';
}
}
3.创建班级dao接口
public interface ClsDao {
Cls selectclassandstubyclassid(int id);
}
4.在班级表的映射文件中写dao接口方法的对应sql
5.测试
@Test
public void test02()throws IOException{
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory =new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
ClsDao clsDao = session.getMapper(ClsDao.class);
Cls cls = clsDao.selectclassandstubyclassid(1);
System.out.println(cls);
}上述为第一种链表查询 第二种嵌套查询与多对一第二种相同 略
2.动态SQL
所谓动态sql 便是sql语句根据条件而发生改变。 一般用到的方法为:
| 元素 | 作用 | 描述 |
| if | 条件判断 | 但条件判断 |
| choos(when、otherwise) | 条件选择,相当Java when | 多条件分支判断 |
| where、set | 辅助 | 处理sql语句拼接问题 |
| foreache | 循环 | 循环 |
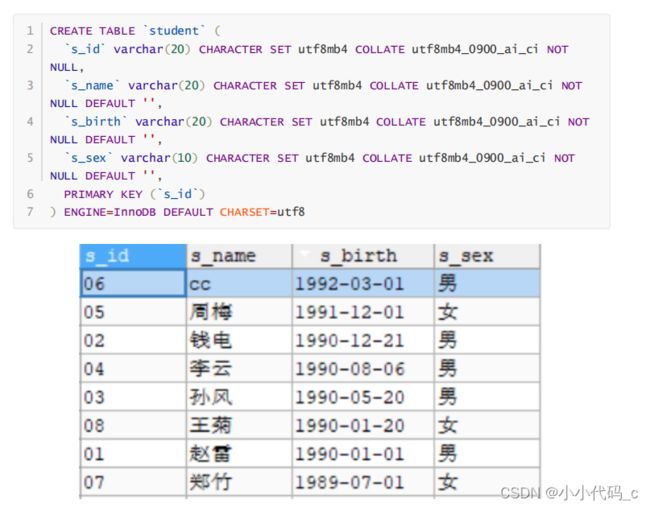
首先创建一个数据表 并存入数据
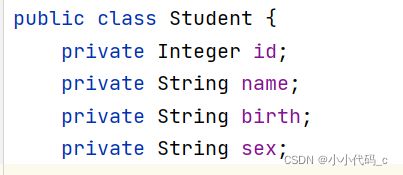
创建对应实体类与dao接口 并创建sql方法
(1)if和where一起用
测试:
@Test
public void test03()throws IOException{
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory =new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StudentDao studentDao = session.getMapper(StudentDao.class);
Map map = new HashMap();
//从网页中得到参数值 并且封装到map对象中。
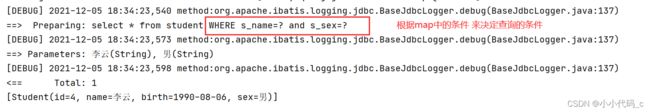
map.put("sname","李云");
map.put("ssex","男");
List list = studentDao.selectbysome(map);
System.out.println(list);
} (2) [choose when otherwise] 和where
根据 name和 sex 来查询数据 若name有数据则之按照name查询 若name没数据 则按照sex查询 若sex也没数据则查询id为1的学生
测试:
@Test
public void test05()throws IOException{
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory =new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StudentDao studentDao = session.getMapper(StudentDao.class);
Map map = new HashMap();
//从网页中得到参数值 并且封装到map对象中。
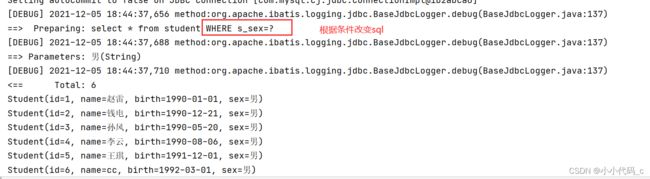
map.put("sex","男");
List list = studentDao.selectbysexorname(map);
System.out.println(list);
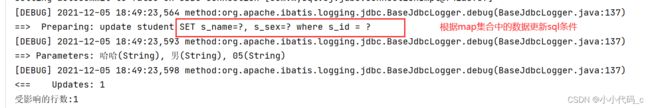
} (3)set标签---修改部分字段
update student
s_name=#{name},
s_birth=#{birth}
s_sex=#{sex}
where s_id = #{id}
测试:
@Test
public void test04()throws IOException{
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory =new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StudentDao studentDao = session.getMapper(StudentDao.class);
Map map = new HashMap();
//从网页中得到参数值 并且封装到map对象中。
map.put("id","05");
map.put("name","哈哈");
map.put("sex","男");
int i = studentDao.updateall(map);
System.out.println("受影响的行数:"+i);
session.commit();
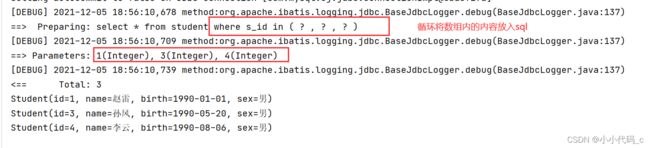
} (4) foreach 批量处理
查询id=01,02,03,04的学生。
测试:
@Test
public void test06()throws IOException{
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory =new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StudentDao studentDao = session.getMapper(StudentDao.class);
int[] ids = {1,3,4};
List list = studentDao.selectbysomeid(ids);
for(Student s:list){
System.out.println(s);
}
}
最后,mybatis框架的基本使用到此结束,感谢浏览 ^_^