人工智能 | ShowMeAI资讯日报 #2022.06.13
ShowMeAI日报系列全新升级!覆盖AI人工智能 工具&框架 | 项目&代码 | 博文&分享 | 数据&资源 | 研究&论文 等方向。点击查看 历史文章列表,在公众号内订阅话题 #ShowMeAI资讯日报,可接收每日最新推送。点击 专题合辑&电子月刊 快速浏览各专题全集。点击 这里 回复关键字 日报 免费获取AI电子月刊与资料包。
1.工具&框架
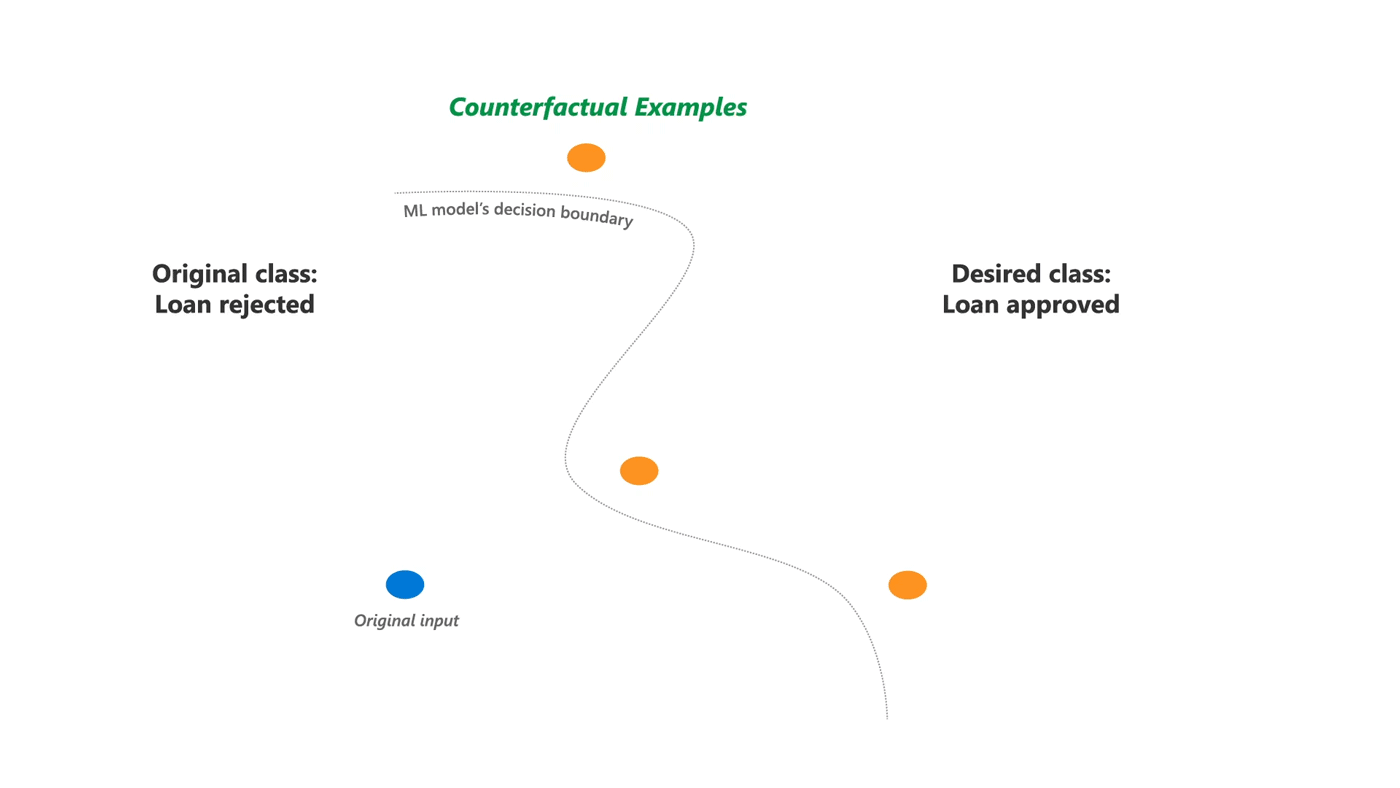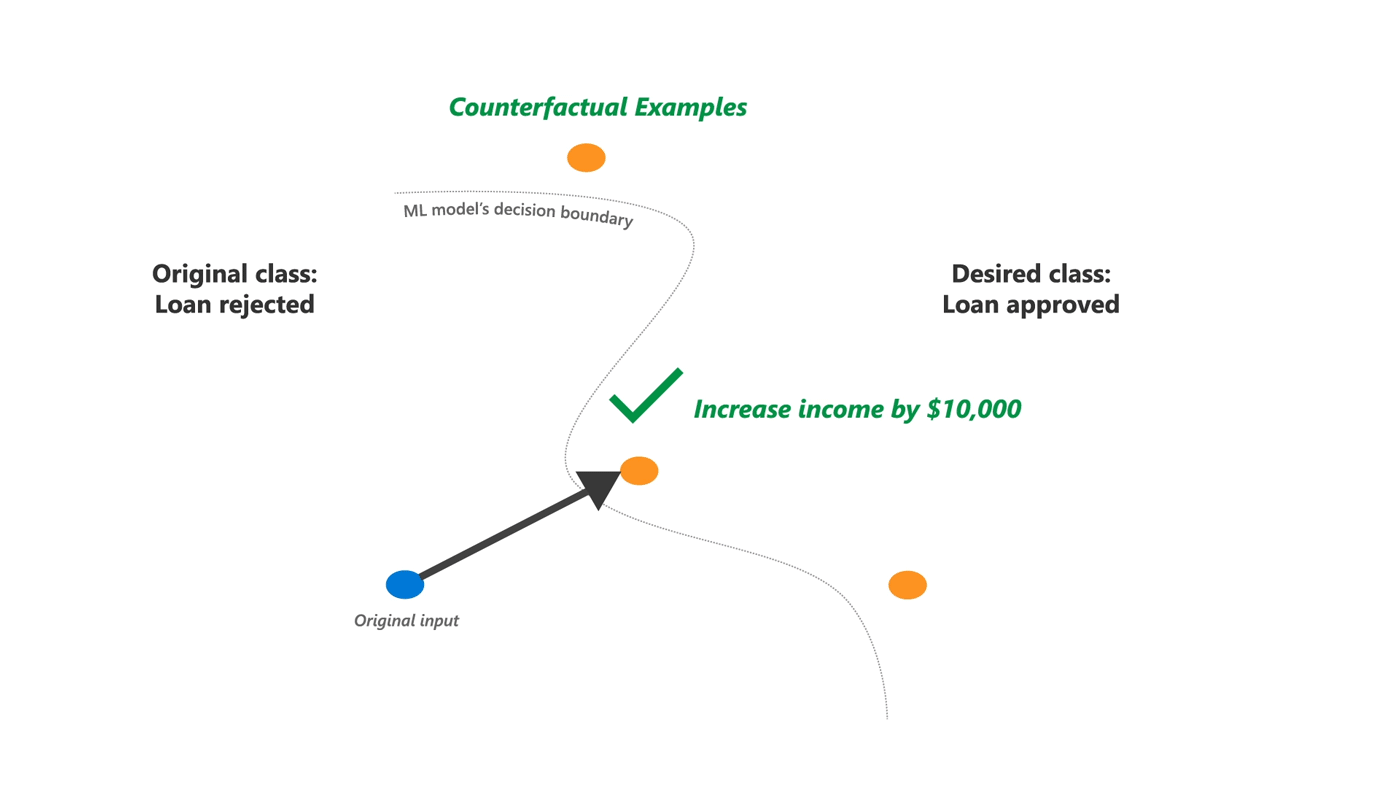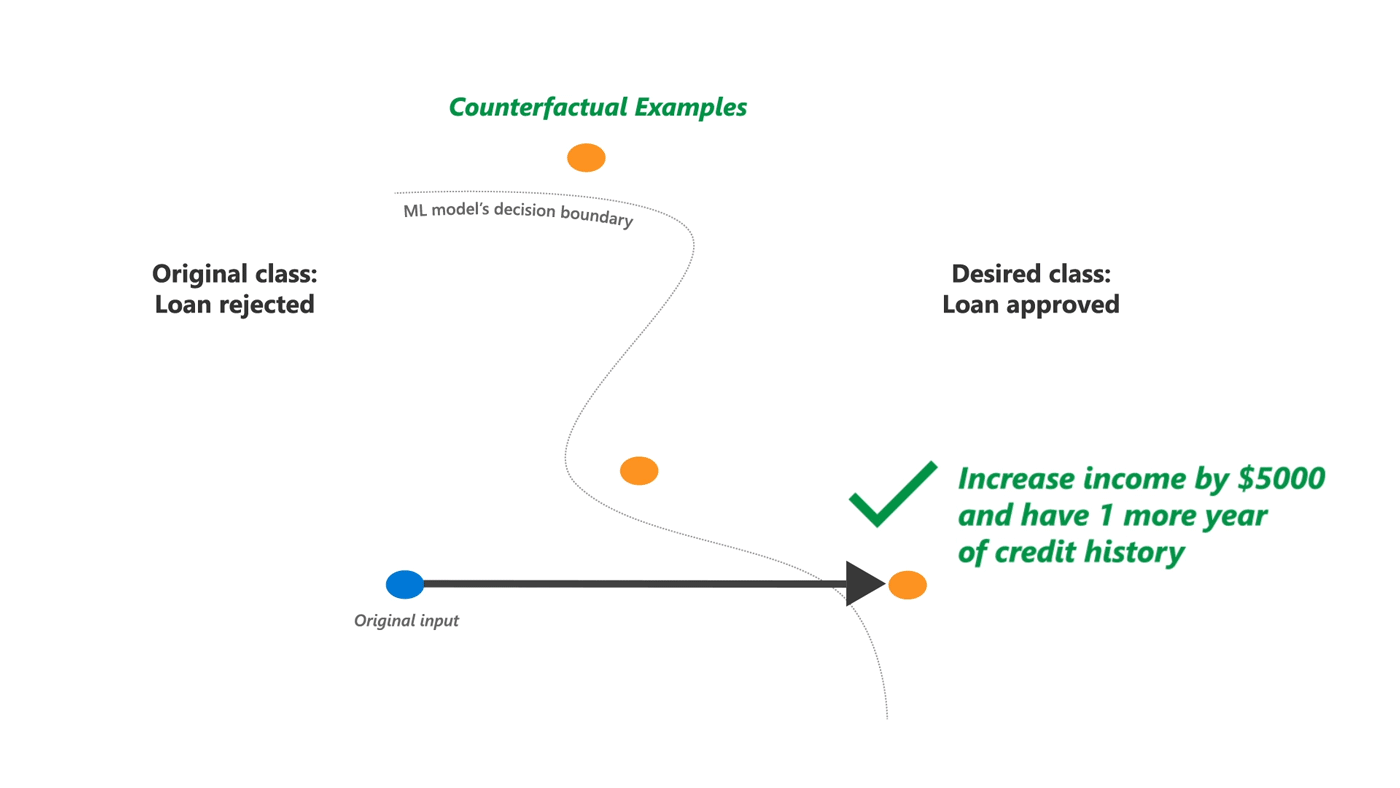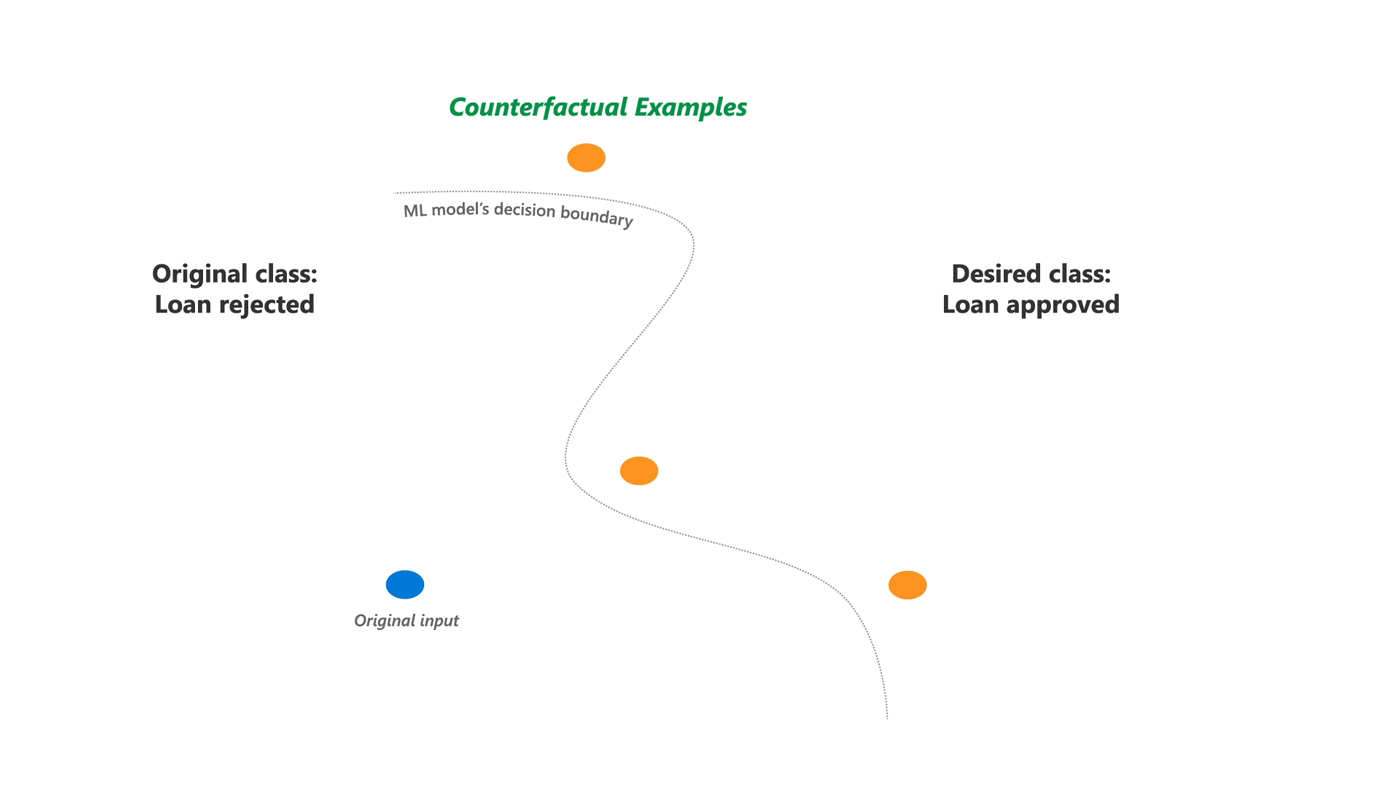
工具库:DiCE - 为机器学习模型生成多样化反事实解释
tags: [机器学习,反事实,解释]
‘DiCE - Generate Diverse Counterfactual Explanations for any machine learning model.’ by InterpretML
GitHub: https://github.com/interpretml/DiCE
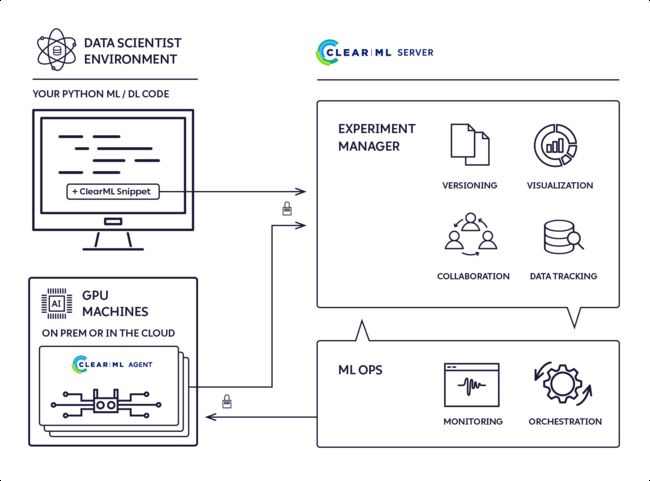
工具套件:Clearml - 用于简化机器学习工作流的工具套件
tags: [机器学习,工具套件,实验管理,运维,数据管理]
工具套件覆盖实验管理器,机器学习运维、数据管理等
‘ClearML - Auto-Magical Suite of tools to streamline your ML workflow Experiment Manager, ML-Ops and Data-Management’ by Allegro AI
GitHub: https://github.com/allegroai/clearml
工具库:river - Python在线机器学习库
tags: [机器学习,在线学习]
‘river - a Python library for online machine learning’ by OnlineML
GitHub: https://github.com/online-ml/river
工具库:ocotillo - 快速、准确、超简单的语音识别工具库
tags: [机器学习,人工智能,语音识别]
‘ocotillo - A fast, accurate and super simple speech recognition model - Performant and accurate speech recognition built on Pytorch’ by James Betker
GitHub: https://github.com/neonbjb/ocotillo
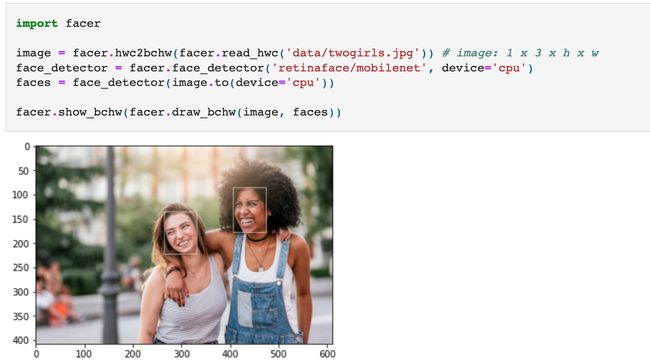
工具库:FACER - 基于最新人脸解析技术的人脸分析研究工具
tags: [人脸分析,人脸检测,人工智能,工具库]
‘FACER - Face analysis tools for modern research, equipped with state-of-the-art Face Parsing’ by FacePerceiver
GitHub: https://github.com/FacePerceiver/facer
工具:EasyNode - 简易的个人Linux服务器管理面板(基础探针+webssh终端)
tags: [管理面板,服务器,Linux,工具]
GitHub: https://github.com/chaos-zhu/easynode
2.项目&代码
项目实现:深度学习3D重构项目集
tags: [深度学习,3D重构]
‘3D-Reconstruction-with-Deep-Learning-Methods - List of projects for 3d reconstruction’ by Simon
GitHub: https://github.com/natowi/3D-Reconstruction-with-Deep-Learning-Methods
3.博文&分享
博文:DALL·E 2工作原理通俗解析《How DALL·E 2 Works》
Link: http://adityaramesh.com/posts/dalle2/dalle2.html
4.数据&资源
数据集:Bandai-Namco-Research-Motiondataset - Bandai Namco的人物动作数据集
tags: [任务动作,动作,数据集]
‘Bandai-Namco-Research-Motiondataset - This repository provides motion datasets collected by Bandai Namco Research Inc’ by Bandai Namco Research Inc.
GitHub: https://github.com/BandaiNamcoResearchInc/Bandai-Namco-Research-Motiondataset
资源列表:GEC Information - 语法纠错相关文献分类集锦
tags: [语法纠错,纠错,文献,资源集]
‘GEC Information - Repository to collect and categorize Grammatical Error Correction papers.’ by gotutiyan
GitHub: https://github.com/gotutiyan/GEC-Info
5.研究&论文
可以点击 这里 回复关键字 日报,免费获取整理好的6月论文合辑。
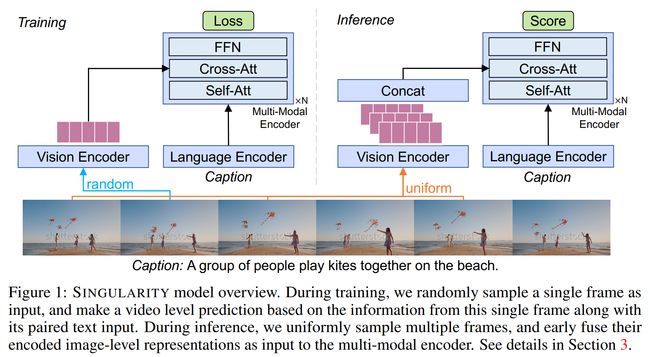
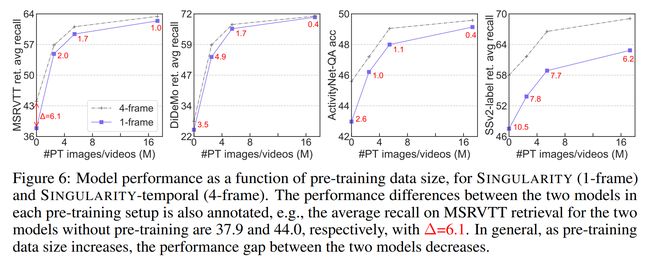
论文:Revealing Single Frame Bias for Video-and-Language Learning
论文标题:Revealing Single Frame Bias for Video-and-Language Learning
论文时间:7 Jun 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:Action Recognition,Fine-grained Action Recognition,Language Modelling,Question Answering,Text to Video Retrieval,Video Question Answering,Video Retrieval,动作识别,细粒度动作识别,语言建模,问答,文字转视频检索,视频问答,视频检索
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.03428
代码实现:https://github.com/jayleicn/singularity
论文作者:Jie Lei, Tamara L. Berg, Mohit Bansal
论文简介:Training an effective video-and-language model intuitively requires multiple frames as model inputs. / 直观地训练有效的视频和语言模型需要多帧作为模型输入。
论文摘要:Training an effective video-and-language model intuitively requires multiple frames as model inputs. However, it is unclear whether using multiple frames is beneficial to downstream tasks, and if yes, whether the performance gain is worth the drastically-increased computation and memory costs resulting from using more frames. In this work, we explore single-frame models for video-and-language learning. On a diverse set of video-and-language tasks (including text-to-video retrieval and video question answering), we show the surprising result that, with large-scale pre-training and a proper frame ensemble strategy at inference time, a single-frame trained model that does not consider temporal information can achieve better performance than existing methods that use multiple frames for training. This result reveals the existence of a strong “static appearance bias” in popular video-and-language datasets. Therefore, to allow for a more comprehensive evaluation of video-and-language models, we propose two new retrieval tasks based on existing fine-grained action recognition datasets that encourage temporal modeling. Our code is available at https://github.com/jayleicn/singularity
直观地训练一个有效的视频和语言模型需要多帧作为模型输入。然而,目前尚不清楚使用多帧是否有利于下游任务,如果是,性能增益是否值得因使用更多帧而大幅增加的计算和内存成本。在这项工作中,我们探索了视频和语言学习的单帧模型。在一组不同的视频和语言任务(包括文本到视频的检索和视频问答)中,我们展示了令人惊讶的结果,即通过大规模预训练和推理时适当的帧集成策略,一个不考虑时间信息的单帧训练模型可以比使用多帧训练的现有方法获得更好的性能。这一结果揭示了流行的视频和语言数据集中存在强烈的“静态外观偏差”。因此,为了对视频和语言模型进行更全面的评估,我们提出了两个基于现有细粒度动作识别数据集的新检索任务,这些数据集鼓励时间建模。我们的代码在 https://github.com/jayleicn/singularity
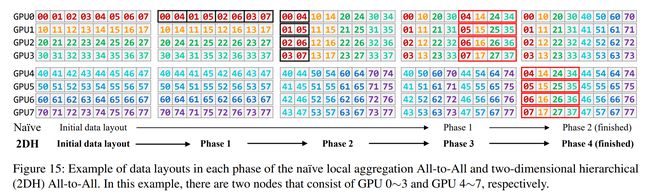
论文:Tutel: Adaptive Mixture-of-Experts at Scale
论文标题:Tutel: Adaptive Mixture-of-Experts at Scale
论文时间:7 Jun 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:Object Detection,物体检测
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.03382
代码实现:https://github.com/microsoft/Swin-Transformer , https://github.com/microsoft/tutel
论文作者:Changho Hwang, Wei Cui, Yifan Xiong, Ziyue Yang, Ze Liu, Han Hu, Zilong Wang, Rafael Salas, Jithin Jose, Prabhat Ram, Joe Chau, Peng Cheng, Fan Yang, Mao Yang, Yongqiang Xiong
论文简介:On effectiveness, the SwinV2-MoE model achieves superior accuracy in both pre-training and down-stream computer vision tasks such as COCO object detection than the counterpart dense model, indicating the readiness of Tutel for end-to-end real-world model training and inference. / 在有效性方面,SwinV2-MoE 模型在预训练和下游计算机视觉任务(如 COCO 对象检测)中实现了优于对应的密集模型的准确性,这表明 Tutel 已准备好进行端到端的真实-世界模型训练和推理。
论文摘要:In recent years, Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) has emerged as a promising technique for deep learning that can scale the model capacity to trillion-plus parameters while reducing the computing cost via sparse computation. While MoE opens a new frontier of exceedingly large models, its implementation over thousands of GPUs has been limited due to mismatch between the dynamic nature of MoE and static parallelism/pipelining of the system. We present Tutel, a highly scalable stack design and implementation for MoE with dynamically adaptive parallelism and pipelining. Tutel delivers adaptive parallelism switching and adaptive pipelining at runtime, which achieves up to 1.74x and 2.00x single MoE layer speedup, respectively. We also propose a novel two-dimensional hierarchical algorithm for MoE communication speedup that outperforms the previous state-of-the-art up to 20.7x over 2,048 GPUs. Aggregating all techniques, Tutel finally delivers 4.96x and 5.75x speedup of a single MoE layer on 16 GPUs and 2,048 GPUs, respectively, over Fairseq: Meta’s Facebook AI Research Sequence-to-Sequence Toolkit (Tutel is now partially adopted by Fairseq). Tutel source code is available in public: https://github.com/microsoft/tutel . Our evaluation shows that Tutel efficiently and effectively runs a real-world MoE-based model named SwinV2-MoE, built upon Swin Transformer V2, a state-of-the-art computer vision architecture. On efficiency, Tutel accelerates SwinV2-MoE, achieving up to 1.55x and 2.11x speedup in training and inference over Fairseq, respectively. On effectiveness, the SwinV2-MoE model achieves superior accuracy in both pre-training and down-stream computer vision tasks such as COCO object detection than the counterpart dense model, indicating the readiness of Tutel for end-to-end real-world model training and inference. SwinV2-MoE is open sourced in https://github.com/microsoft/Swin-Transformer
近年来,Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) 已成为一种很有前途的深度学习技术,它可以将模型容量扩展到万亿级以上的参数,同时通过稀疏计算降低计算成本。虽然 MoE 开辟了超大型模型的新前沿,但由于 MoE 的动态特性与系统的静态并行/流水线不匹配,其在数千个 GPU 上的实施受到了限制。我们介绍了 Tutel,这是一种用于 MoE 的高度可扩展的堆栈设计和实现,具有动态自适应并行性和流水线。 Tutel 在运行时提供自适应并行切换和自适应流水线,分别实现高达 1.74 倍和 2.00 倍的单 MoE 层加速。我们还提出了一种用于 MoE 通信加速的新型二维分层算法,该算法在 2,048 个 GPU 上的性能比以前的最新技术高出 20.7 倍。综合所有技术,Tutel 最终通过 Fairseq:Meta 的 Facebook AI Research Sequence-to-Sequence Toolkit(Tutel 现在部分被 Fairseq 采用)在 16 个 GPU 和 2,048 个 GPU 上分别提供了 4.96 倍和 5.75 倍的单个 MoE 层加速。 Tutel 源代码已公开:https://github.com/microsoft/tutel 。我们的评估表明,Tutel 高效且有效地运行了一个名为 SwinV2-MoE 的真实世界基于 MoE 的模型,该模型基于最先进的计算机视觉架构 Swin Transformer V2 构建。在效率方面,Tutel 加速了 SwinV2-MoE,在 Fairseq 上的训练和推理速度分别提高了 1.55 倍和 2.11 倍。在有效性方面,SwinV2-MoE 模型在预训练和下游计算机视觉任务(如 COCO 对象检测)中都比对应的密集模型实现了更高的准确性,这表明 Tutel 已准备好进行端到端的真实世界模型训练和推理。 SwinV2-MoE 在 https://github.com/microsoft/Swin-Transformer 中开源
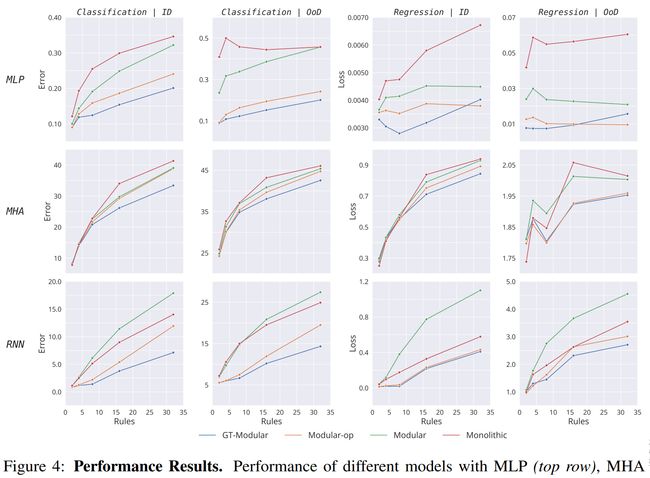
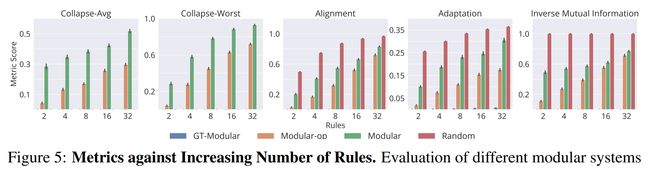
论文:Is a Modular Architecture Enough?
论文标题:Is a Modular Architecture Enough?
论文时间:6 Jun 2022
对应任务:Out-of-Distribution Generalization,分布外泛化
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.02713
代码实现:https://github.com/sarthmit/mod_arch
论文作者:Sarthak Mittal, Yoshua Bengio, Guillaume Lajoie
论文简介:Inspired from human cognition, machine learning systems are gradually revealing advantages of sparser and more modular architectures. / 受人类认知的启发,机器学习系统逐渐展现出更稀疏、更模块化架构的优势。
论文摘要:Inspired from human cognition, machine learning systems are gradually revealing advantages of sparser and more modular architectures. Recent work demonstrates that not only do some modular architectures generalize well, but they also lead to better out-of-distribution generalization, scaling properties, learning speed, and interpretability. A key intuition behind the success of such systems is that the data generating system for most real-world settings is considered to consist of sparsely interacting parts, and endowing models with similar inductive biases will be helpful. However, the field has been lacking in a rigorous quantitative assessment of such systems because these real-world data distributions are complex and unknown. In this work, we provide a thorough assessment of common modular architectures, through the lens of simple and known modular data distributions. We highlight the benefits of modularity and sparsity and reveal insights on the challenges faced while optimizing modular systems. In doing so, we propose evaluation metrics that highlight the benefits of modularity, the regimes in which these benefits are substantial, as well as the sub-optimality of current end-to-end learned modular systems as opposed to their claimed potential.
受人类认知的启发,机器学习系统逐渐展现出更稀疏、更模块化架构的优势。最近的工作表明,一些模块化架构不仅可以很好地泛化,而且还可以带来更好的分布外泛化、缩放属性、学习速度和可解释性。此类系统成功背后的一个关键直觉是,大多数现实世界设置的数据生成系统被认为由稀疏交互的部分组成,赋予模型类似的归纳偏差将是有帮助的。然而,该领域一直缺乏对此类系统的严格定量评估,因为这些现实世界的数据分布是复杂且未知的。在这项工作中,我们通过简单且已知的模块化数据分布的视角,对常见的模块化架构进行了全面评估。我们强调了模块化和稀疏性的好处,并揭示了在优化模块化系统时面临的挑战的见解。在这样做的过程中,我们提出了突出模块化好处的评估指标,这些好处是巨大的,以及当前端到端学习模块化系统的次优性,而不是它们声称的潜力。
论文:There is no data like more data – current status of machine learning datasets in remote sensing
论文标题:There is no data like more data – current status of machine learning datasets in remote sensing
论文时间:25 May 2021
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.11726
代码实现:https://github.com/Seyed-Ali-Ahmadi/Awesome_Benchmark_Satellite_Datasets , https://github.com/Seyed-Ali-Ahmadi/Awesome_Satellite_Benchmark_Datasets
论文作者:Michael Schmitt, Seyed Ali Ahmadi, Ronny Hänsch
论文简介:Annotated datasets have become one of the most crucial preconditions for the development and evaluation of machine learning-based methods designed for the automated interpretation of remote sensing data. / 带注释的数据集已成为开发和评估基于机器学习的方法的最重要的先决条件之一,这些方法旨在自动解释遥感数据。
论文摘要:Annotated datasets have become one of the most crucial preconditions for the development and evaluation of machine learning-based methods designed for the automated interpretation of remote sensing data. In this paper, we review the historic development of such datasets, discuss their features based on a few selected examples, and address open issues for future developments.
带注释的数据集已经成为开发和评估基于机器学习的遥感数据自动解释方法的最重要的先决条件之一。 在本文中,我们回顾了此类数据集的历史发展,基于几个选定的示例讨论了它们的特征,以及未来发展的未解决问题。
论文:Scaling Vision Transformers to Gigapixel Images via Hierarchical Self-Supervised Learning
论文标题:Scaling Vision Transformers to Gigapixel Images via Hierarchical Self-Supervised Learning
论文时间:CVPR 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:Self-Supervised Learning,Survival Prediction,自监督学习,生存预测
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.02647
代码实现:https://github.com/mahmoodlab/hipt
论文作者:Richard J. Chen, Chengkuan Chen, Yicong Li, Tiffany Y. Chen, Andrew D. Trister, Rahul G. Krishnan, Faisal Mahmood
论文简介:Vision Transformers (ViTs) and their multi-scale and hierarchical variations have been successful at capturing image representations but their use has been generally studied for low-resolution images (e. g. - 256x256, 384384). / 视觉Transformer(ViTs) 及其多尺度和分层变体已成功地捕获图像表示,但它们的使用通常被研究用于低分辨率图像(例如 - 256x256、384384)。
论文摘要:Vision Transformers (ViTs) and their multi-scale and hierarchical variations have been successful at capturing image representations but their use has been generally studied for low-resolution images (e.g. - 256x256, 384x384). For gigapixel whole-slide imaging (WSI) in computational pathology, WSIs can be as large as 150000x150000 pixels at 20X magnification and exhibit a hierarchical structure of visual tokens across varying resolutions: from 16x16 images capture spatial patterns among cells, to 4096x4096 images characterizing interactions within the tissue microenvironment. We introduce a new ViT architecture called the Hierarchical Image Pyramid Transformer (HIPT), which leverages the natural hierarchical structure inherent in WSIs using two levels of self-supervised learning to learn high-resolution image representations. HIPT is pretrained across 33 cancer types using 10,678 gigapixel WSIs, 408,218 4096x4096 images, and 104M 256x256 images. We benchmark HIPT representations on 9 slide-level tasks, and demonstrate that: 1) HIPT with hierarchical pretraining outperforms current state-of-the-art methods for cancer subtyping and survival prediction, 2) self-supervised ViTs are able to model important inductive biases about the hierarchical structure of phenotypes in the tumor microenvironment.
视觉Transformer(ViTs) 及其多尺度和分层变化已成功地捕获图像表示,但它们的使用通常被研究用于低分辨率图像(例如 - 256x256、384x384)。对于计算病理学中的千兆像素全载玻片成像 (WSI),WSI 可以在 20 倍放大倍率下高达 150000x150000 像素,并在不同分辨率下表现出视觉标记的层次结构:从 16x16 图像捕获细胞之间的空间模式,到 4096x4096 图像表征相互作用在组织微环境中。我们引入了一种新的 ViT 架构,称为分层图像金字塔变换器 (HIPT),它利用 WSI 中固有的自然分层结构,使用两个级别的自监督学习来学习高分辨率图像表示。 HIPT 使用 10,678 个千兆像素 WSI、408,218 个 4096x4096 图像和 104M 256x256 图像对 33 种癌症类型进行了预训练。我们在 9 个幻灯片级任务上对 HIPT 表示进行基准测试,并证明:1) 具有分层预训练的 HIPT 优于当前最先进的癌症分型和生存预测方法,2) 自监督 ViT 能够对重要的归纳建模关于肿瘤微环境中表型的层次结构的偏见。
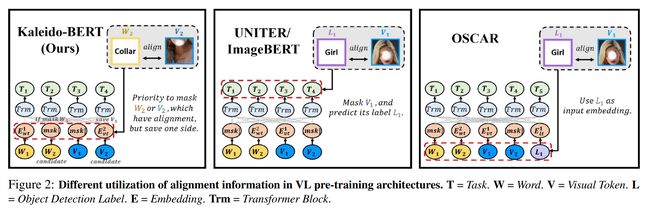
论文:Kaleido-BERT: Vision-Language Pre-training on Fashion Domain
论文标题:Kaleido-BERT: Vision-Language Pre-training on Fashion Domain
论文时间:CVPR 2021
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:Image Retrieval,图像检索
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.16110
代码实现:https://github.com/mczhuge/Kaleido-BERT
论文作者:Mingchen Zhuge, Dehong Gao, Deng-Ping Fan, Linbo Jin, Ben Chen, Haoming Zhou, Minghui Qiu, Ling Shao
论文简介:We present a new vision-language (VL) pre-training model dubbed Kaleido-BERT, which introduces a novel kaleido strategy for fashion cross-modality representations from transformers. / 我们提出了一种名为 Kaleido-BERT 的新视觉语言 (VL) 预训练模型,该模型引入了一种新颖的 kaleido 策略,用于从变形器中进行时尚跨模态表示。
论文摘要:We present a new vision-language (VL) pre-training model dubbed Kaleido-BERT, which introduces a novel kaleido strategy for fashion cross-modality representations from transformers. In contrast to random masking strategy of recent VL models, we design alignment guided masking to jointly focus more on image-text semantic relations. To this end, we carry out five novel tasks, i.e., rotation, jigsaw, camouflage, grey-to-color, and blank-to-color for self-supervised VL pre-training at patches of different scale. Kaleido-BERT is conceptually simple and easy to extend to the existing BERT framework, it attains new state-of-the-art results by large margins on four downstream tasks, including text retrieval (R@1: 4.03% absolute improvement), image retrieval (R@1: 7.13% abs imv.), category recognition (ACC: 3.28% abs imv.), and fashion captioning (Bleu4: 1.2 abs imv.). We validate the efficiency of Kaleido-BERT on a wide range of e-commerical websites, demonstrating its broader potential in real-world applications.
我们提出了一种新的视觉语言 (VL) 预训练模型,称为 Kaleido-BERT,它引入了一种新颖的 kaleido 策略,用于从变形器中进行时尚跨模态表示。与最近的 VL 模型的随机掩蔽策略相比,我们设计了对齐引导掩蔽,以共同更多地关注图像-文本语义关系。为此,我们执行了五项新颖的任务,即旋转、拼图、伪装、灰色到彩色和空白到彩色,用于在不同规模的子图块(patch)上进行自我监督的 VL 预训练。 Kaleido-BERT 在概念上很简单,很容易扩展到现有的 BERT 框架,它在四个下游任务上获得了新的最先进的结果,包括文本检索(R@1:4.03% 绝对改进)、图像检索(R@1:7.13% abs imv.)、类别识别(ACC:3.28% abs imv.)和时尚图文描述(Bleu4:1.2 abs imv.)。我们在广泛的电子商务网站上验证了 Kaleido-BERT 的效率,展示了其在实际应用中的更广泛潜力。
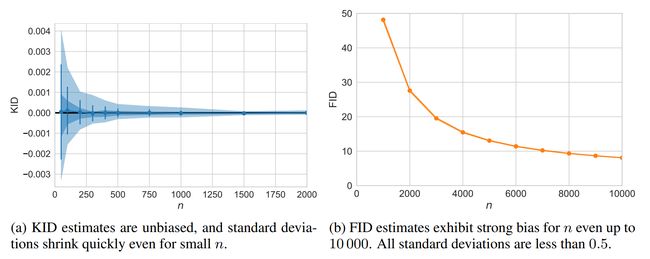
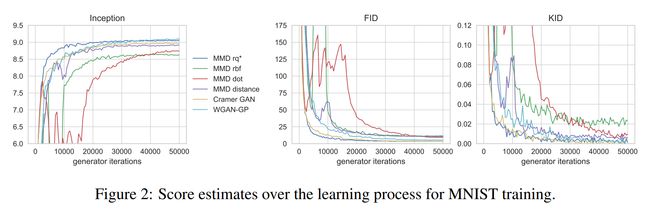
论文:Demystifying MMD GANs
论文标题:Demystifying MMD GANs
论文时间:ICLR 2018
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/1801.01401
代码实现:https://github.com/mbinkowski/MMD-GAN , https://github.com/NVlabs/eg3d , https://github.com/toshas/torch-fidelity , https://github.com/mbinkowski/DeepSpeechDistances , https://github.com/beresandras/gan-flavours-keras
论文作者:Mikołaj Bińkowski, Danica J. Sutherland, Michael Arbel, Arthur Gretton
论文简介:We investigate the training and performance of generative adversarial networks using the Maximum Mean Discrepancy (MMD) as critic, termed MMD GANs. / 我们使用最大均值差异(MMD)作为批评者(称为 MMD GAN)来研究生成对抗网络的训练和性能。
论文摘要:We investigate the training and performance of generative adversarial networks using the Maximum Mean Discrepancy (MMD) as critic, termed MMD GANs. As our main theoretical contribution, we clarify the situation with bias in GAN loss functions raised by recent work: we show that gradient estimators used in the optimization process for both MMD GANs and Wasserstein GANs are unbiased, but learning a discriminator based on samples leads to biased gradients for the generator parameters. We also discuss the issue of kernel choice for the MMD critic, and characterize the kernel corresponding to the energy distance used for the Cramer GAN critic. Being an integral probability metric, the MMD benefits from training strategies recently developed for Wasserstein GANs. In experiments, the MMD GAN is able to employ a smaller critic network than the Wasserstein GAN, resulting in a simpler and faster-training algorithm with matching performance. We also propose an improved measure of GAN convergence, the Kernel Inception Distance, and show how to use it to dynamically adapt learning rates during GAN training.
我们使用最大平均差异(MMD)作为评估准则,研究生成对抗网络的训练和性能,称为 MMD GAN。作为我们的主要理论贡献,我们澄清了最近工作提出的 GAN 损失函数中存在偏差的情况:我们证明了 MMD GAN 和 Wasserstein GAN 的优化过程中使用的梯度估计器是无偏的,但是基于样本学习判别器会导致生成器参数的偏置梯度。我们还讨论了 MMD 批评者的内核选择问题,并描述了与用于 Cramer GAN 批评者的能量距离相对应的内核。作为一个完整的概率度量,MMD 受益于最近为 Wasserstein GAN 开发的训练策略。在实验中,MMD GAN 能够使用比 Wasserstein GAN 更小的批评网络,从而产生更简单、更快的训练算法,并具有匹配的性能。我们还提出了一种改进的 GAN 收敛度量,即内核初始距离,并展示了如何在 GAN 训练期间使用它来动态调整学习率。
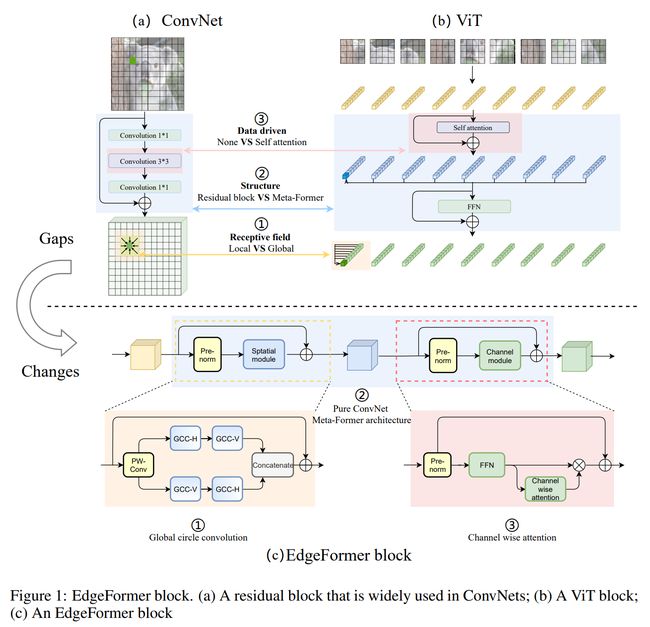
论文:EdgeFormer: Improving Light-weight ConvNets by Learning from Vision Transformers
论文标题:EdgeFormer: Improving Light-weight ConvNets by Learning from Vision Transformers
论文时间:8 Mar 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:Image Classification,Object Detection,Semantic Segmentation,图像分类,目标检测,语义分割
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.03952
代码实现:https://github.com/hkzhang91/edgeformer
论文作者:Haokui Zhang, Wenze Hu, Xiaoyu Wang
论文简介:Experiment results show that the proposed EdgeFormer achieves better performance than popular light-weight ConvNets and vision transformer based models in common vision tasks and datasets, while having fewer parameters and faster inference speed. / 实验结果表明,在常见的视觉任务和数据集中,所提出的 EdgeFormer 比流行的轻量级 ConvNets 和基于视觉变换器的模型具有更好的性能,同时具有更少的参数和更快的推理速度。
论文摘要:Recently, vision transformers started to show impressive results which outperform large convolution based models significantly. However, in the area of small models for mobile or resource constrained devices, ConvNet still has its own advantages in both performance and model complexity. We propose EdgeFormer, a pure ConvNet based backbone model that further strengthens these advantages by fusing the merits of vision transformers into ConvNets. Specifically, we propose global circular convolution (GCC) with position embeddings, a light-weight convolution op which boasts a global receptive field while producing location sensitive features as in local convolutions. We combine the GCCs and squeeze-exictation ops to form a meta-former like model block, which further has the attention mechanism like transformers. The aforementioned block can be used in plug-and-play manner to replace relevant blocks in ConvNets or transformers. Experiment results show that the proposed EdgeFormer achieves better performance than popular light-weight ConvNets and vision transformer based models in common vision tasks and datasets, while having fewer parameters and faster inference speed. For classification on ImageNet-1k, EdgeFormer achieves 78.6% top-1 accuracy with about 5.0 million parameters, saving 11% parameters and 13% computational cost but gaining 0.2% higher accuracy and 23% faster inference speed (on ARM based Rockchip RK3288) compared with MobileViT, and uses only 0.5 times parameters but gaining 2.7% accuracy compared with DeIT. On MS-COCO object detection and PASCAL VOC segmentation tasks, EdgeFormer also shows better performance. Code is available at https://github.com/hkzhang91/EdgeFormer
最近,视觉transformer开始显示出令人印象深刻的结果,其性能明显优于基于大型卷积的模型。然而,在移动或资源受限设备的小型模型领域,ConvNet 在性能和模型复杂度方面仍然具有自己的优势。我们提出了 EdgeFormer,这是一个纯基于 ConvNet 的骨干模型,通过将视觉转换器的优点融合到 ConvNet 中来进一步增强这些优势。具体来说,我们提出了带有位置嵌入的全局循环卷积(GCC),这是一种轻量级的卷积运算,它拥有全局感受野,同时产生与局部卷积一样的位置敏感特征。我们将 GCC 和挤压激发操作结合起来,形成一个类似于元模型的模型块,它还具有类似于transformer的注意力机制。上述块可以即插即用的方式使用,以替换 ConvNets 或变压器中的相关块。实验结果表明,在常见的视觉任务和数据集中,所提出的 EdgeFormer 比流行的轻量级 ConvNets 和基于视觉变换器的模型具有更好的性能,同时具有更少的参数和更快的推理速度。对于 ImageNet-1k 上的分类,EdgeFormer 在大约 500 万个参数的情况下实现了 78.6% 的 top-1 准确率,节省了 11% 的参数和 13% 的计算成本,但与(在基于 ARM 的 Rockchip RK3288 上)相比,准确率提高了 0.2%,推理速度提高了 23%与 MobileViT 相比,仅使用 0.5 倍的参数,但与 DeIT 相比获得了 2.7% 的准确度。在 MS-COCO 对象检测和 PASCAL VOC 分割任务上,EdgeFormer 也表现出更好的性能。代码可在 https://github.com/hkzhang91/EdgeFormer
我们是 ShowMeAI,致力于传播AI优质内容,分享行业解决方案,用知识加速每一次技术成长!点击查看 历史文章列表,在公众号内订阅话题 #ShowMeAI资讯日报,可接收每日最新推送。点击 专题合辑&电子月刊 快速浏览各专题全集。点击 这里 回复关键字 日报 免费获取AI电子月刊与资料包。
- 作者:韩信子@ShowMeAI
- 历史文章列表
- 专题合辑&电子月刊
- 声明:版权所有,转载请联系平台与作者并注明出处
- 欢迎回复,拜托点赞,留言推荐中有价值的文章、工具或建议,我们都会尽快回复哒~