相比于range,list等简易单词,enumerate仅凭外形都不太让人愿意用。事实上,enumerate还是很好用的。
- enumerate()是python的内置函数、适用于python2.x和python3.x
- enumerate在字典上是枚举、列举的意思
- enumerate参数为可遍历/可迭代的对象(如列表、字符串)
- enumerate多用于在for循环中得到计数,利用它可以同时获得索引和值,即需要index和value值的时候可以使用enumerate
- enumerate()返回的是一个enumerate对象
python中最常用的数据结构就是list,处理list中每个元素,通常都用for循环搞定。
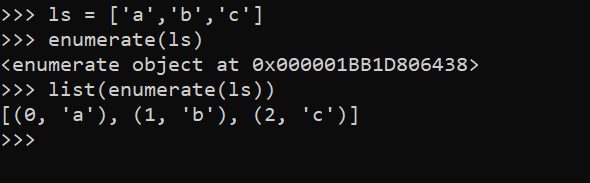
我们先看,加入了enumerate之后,list的变化:
多了一个索引,同时还能读取到元素。这个特性有什么应用呢?看一段代码:
ls = ['a', 'b', 'c']
# method 1
for i in range(len(ls)):
print(i, end=' ')
print(ls[i])
# method 2
for s in ls:
print(ls.index(s), end=' ')
print(s)
# method 3
for i, s in enumerate(ls):
print(i, end=' ')
print(s)
一看方法3就能更简便地访问到索引i和对应的元素s。
而且,用enumerate会显得代码更加高级~
enumerate的使用:
例如:已知lst = [1,2,3,4,5,6],要求输出:
0,1
1,2
2,3
3,4
4,5
5,6
>>> lst = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
>>> for index,value in enumerate(lst):
print ('%s,%s' % (index,value))
0,1
1,2
2,3
3,4
4,5
5,6
#指定索引从1开始
>>> lst = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
>>> for index,value in enumerate(lst,1):
print ('%s,%s' % (index,value))
1,1
2,2
3,3
4,4
5,5
6,6
#指定索引从3开始
>>> for index,value in enumerate(lst,3):
print ('%s,%s' % (index,value))
3,1
4,2
5,3
6,4
7,5
8,6
补充:
如果要统计文件的行数,可以这样写:
count = len(open(filepath, 'r').readlines())
这种方法简单,但是可能比较慢,当文件比较大时甚至不能工作。
可以利用enumerate():
count = 0 for index, line in enumerate(open(filepath,'r')): count += 1
到此这篇关于Python中的枚举函数enumerate()的具体用法的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Python enumerate内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!