前言
前一段时间,我们试着用C语言实现了数据结构中的顺序表,单链表,双向循环链表。今天我们再用C语言来实现另一种特殊的线性结构:栈
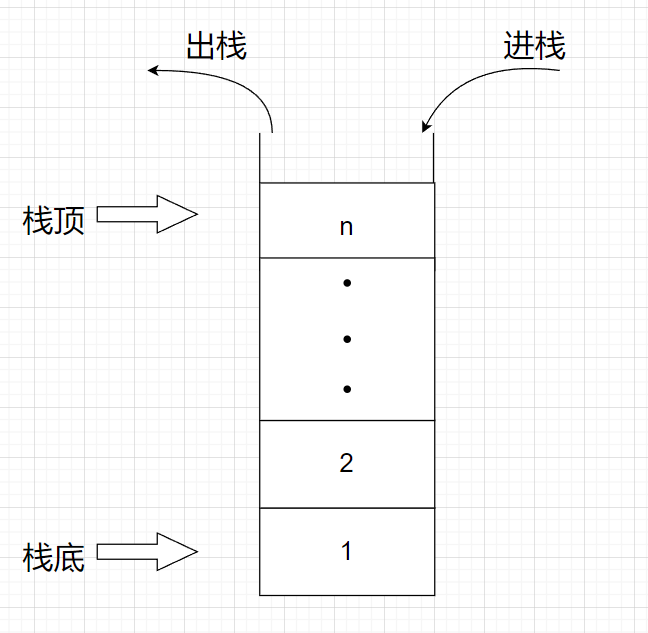
一. 什么是栈
栈(stack)又名堆栈,它是一种运算受限的线性表。限定仅在表尾进行插入和删除操作的线性表。这一端被称为栈顶,相对地,把另一端称为栈底。向一个栈插入新元素又称作进栈、入栈或压栈,它是把新元素放到栈顶元素的上面,使之成为新的栈顶元素;从一个栈删除元素又称作出栈或退栈,它是把栈顶元素删除掉,使其相邻的元素成为新的栈顶元素。
类似于步枪的子弹夹,后进去的子弹先发射出来以后,前面的子弹才可以发射。
二. 使用什么来实现栈
前一段时间,我们学习了两种线性表,一种是顺序表,一种是链表,那么对于栈我们该用哪一个来实现比较好呢
首先我们来对比一下线性表和链表
| 不同点 | 顺序表 | 链表 |
|---|---|---|
| 存储空间上 | 物理上一定连续 | 逻辑上连续,但物理上不一定连续 |
| 随机访问 | 可以直接访问任何元素 | 必须从头节点开始往后寻找 |
| 任意位置插入或删除元素 | 要搬移其他的元素,效率低。 | 只需要修改节点的指针指向,效率高 |
| 插入 | 动态顺序表,当空间不够时需要扩容 | 无容量概念,需要就申请,不用就释放 |
| 应用场景 | 元素高效存储,并且需要频繁访问 | 需要在任意位置插入或者删除频繁 |
综合以上来看,我认为实现一个栈,使用顺序表比较好。
1.栈是先进后出,使用顺序表,在元素出栈后更容易找到新的栈顶。
2.顺序表CPU高速缓存命中率高,可以减少CPU去内存拿数据的次数,速度快,效率高。
三. 栈的实现
3.1 头文件
1.包含的标准库
#include#include #include //C语言中的bool类型需要这个头文件 #include
2.定义结构体
typedef int STDateType;//栈中元素的数据类型
typedef struct Stack
{
STDateType* a; //顺序表
int top; //栈顶
int capacity; //栈的容量
}Stack;
3.函数的声明
void StackInti(Stack* ps); // 栈的初始化 void StackDestory(Stack* ps); // 栈的销毁 void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDateType x); // 入栈 void StackPop(Stack* ps); // 出栈 bool StackEmpty(Stack* ps); // 判断栈是否为空 STDateType StackTop(Stack* ps); // 取栈顶元素
3.2 函数实现
1. 栈的初始化
我们用assert(断言),防止ps为空指针。
void StackInti(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = 0;
ps->top = 0;
}
2. 栈的销毁
释放顺序表。
void StackDestory(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->capacity = 0;
ps->top = 0;
}
3.入栈
void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDateType x)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->top == ps->capacity) //判断容量是否足够
{
int newCapcity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
ps->a = (int*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(int) * newCapcity);
if (ps->a == NULL)
{
printf("ralloc error");
exit(-1);
}
ps->capacity = newCapcity;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
4. 出栈
void StackPop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0); //空栈不能被删除
ps->top--;
}
5. 判断栈是否为空
bool StackEmpty(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0; // 如果为空则返回true,否则返回false
}
6. 取栈顶元素
STDateType StackTop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);//空栈不能被删除
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
这样我们就实现了一个简单的栈
3.3 完整代码
#include#include #include #include typedef int STDateType; typedef struct Stack { STDateType* a; int top; int capacity; }Stack; void StackInti(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); ps->a = NULL; ps->capacity = 0; ps->top = 0; } void StackDestory(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); free(ps->a); ps->capacity = 0; ps->top = 0; } void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDateType x) { assert(ps); if (ps->top == ps->capacity) { int newCapcity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2; ps->a = (int*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(int) * newCapcity); if (ps->a == NULL) { printf("ralloc error"); exit(-1); } ps->capacity = newCapcity; } ps->a[ps->top] = x; ps->top++; } void StackPop(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); assert(ps->top > 0); ps->top--; } bool StackEmpty(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); return ps->top == 0; } STDateType StackTop(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); assert(ps->top > 0); return ps->a[ps->top - 1]; }
四. 栈的用处
我们好不容易实现了一个栈,接下来我们来做个题看看栈有什么用吧。
题目描述
给定一个只包括 ‘(’,’)’,’{’,’}’,’[’,’]’ 的字符串 s ,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
基础框架
C语言的基础框架如下
bool isValid(char * s){
}
解题思路
左括号一定要和右括号对齐,非常满足栈的特性
我们可以将所有的左括号存入一个栈中。
然后遇到右括号,就出栈,判断是否匹配。
直到栈为空且字符串中的括号也遍历完了,那么所有括号就正确的匹配了。
代码详解
// 1.因为C语言并没有现成的栈,所以我们需要自己造轮子,先写个栈再说
typedef char STDateType; // 更改数据类型为char
typedef struct Stack
{
STDateType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}Stack;
void StackInti(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = 0;
ps->top = 0;
}
void StackDestory(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->capacity = 0;
ps->top = 0;
}
void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDateType x)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
int newCapcity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
ps->a = (int*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(int) * newCapcity);
if (ps->a == NULL)
{
printf("ralloc error");
exit(-1);
}
ps->capacity = newCapcity;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
void StackPop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
ps->top--;
}
bool StackEmpty(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
STDateType StackTop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
bool isValid(char * s){
Stack a;
StackInti(&a);
while(*s)
{
if (*s == '(' || *s == '[' || *s == '{') //入栈
{
StackPush(&a, *s);
}
else //出栈
{
if(StackEmpty(&a)) //右括号多一个的情况
{
return false;
}
char tmp = StackTop(&a);
StackPop(&a);
if ((*s == ')' && tmp != '(')
||(*s == ']' && tmp != '[')
||(*s == '}' && tmp != '{') )
{
return false;
}
}
s++;
}
return StackEmpty(&a); //防止出现多一个左括号的情况
}
到此这篇关于C语言实现栈的示例详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关C语言 栈内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!