BN(Batch Normalization)详解,包含pytorch实现、numpy实现
起源
- 对于神经网络来说,如果每一层的数据分布都不一样,后一层的网络则需要去学习适应前一层的数据分布,这相当于去做了domian的adaptation,无疑增加了训练难度,尤其是网络越来越深的情况。
- BN的那篇论文中指出,不同层的数据分布会往激活函数的上限或者下限偏移。论文称这种偏移为internal Covariate Shift,internal指的是网络内部。BN就是为了解决偏移的,解决的方式也很简单,就是让每一层的分布都normalize到标准正太分布。
- 我们在图像预处理过程中通常会对图像进行标准化处理,也就是image normalization,使得每张输入图片的数据分布能够统均值为u,方差为h的分布。这样能够加速网络的收敛。但是当一张图片输入到神经网络经过卷积计算之后,这个分布就不会满足刚才经过image normalization操作之后的分布了,可能适应了新的数据分布规律,这个时候将数据接入激活函数中,很可能一些新的数据会落入激活函数的饱和区,导致神经网络训练的梯度消失。
步骤
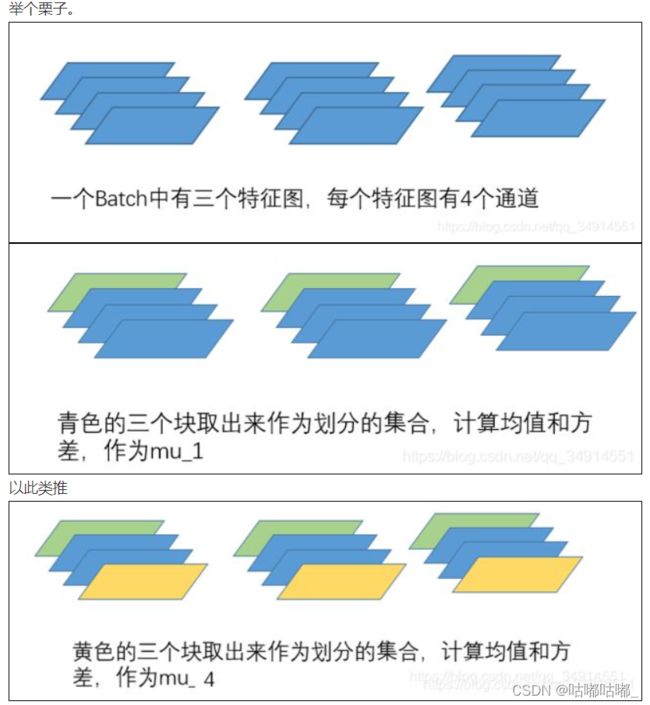
计算得到一个四维的向量,作为这个channel的均值,方差,然后在每个通道上分别用该点的像素值减均值除方差得到该点的像素值,此过程就是BN。最后将其接入到激活函数中。如下图:


pytorch实现
import torch
from torch import nn
# 一维BN
d1 = torch.rand([2,3,4]) #BCW
bn1 = nn.BatchNorm1d(3, momentum=1)
res = bn1(d1)
print(res.shape)
#二维BN(常用)
d2 = torch.rand([2,3,4,5]) #BCHW
bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(3, momentum=1) # momentum一般设置0.9
res = bn2(d2)
print(res.shape)
print(bn2.running_mean) #3个chanel均值
print(bn2.running_var) #3个chanel方差
结果:
torch.Size([2, 3, 4])
torch.Size([2, 3, 4, 5])
tensor([0.5622, 0.5005, 0.4583])
tensor([0.0914, 0.0774, 0.0840])
momentum参数:momentum参数,该参数作用于mean和variance的计算上,这里保留了历史batch里的mean和variance值,即moving mean和moving variance,借鉴优化算法里的momentum算法将历史batch里的mean和variance的作用延续到当前batch.一般momentum的值为0.9,0.99等.多个batch后,即多个0.9连乘后,最早的batch的影响会变弱。
numpy手撕实现
def batchnorm_forward(x, gamma, beta, bn_param):
"""
Forward pass for batch normalization
Input:
- x: Data of shape (N, D)
- gamma: Scale parameter of shape (D,)
- beta: Shift parameter of shape (D,)
- bn_param: Dictionary with the following keys:
- mode: 'train' or 'test'
- eps: Constant for numeric stability
- momentum: Constant for running mean / variance
- running_mean: Array of shape(D,) giving running mean of features
- running_var Array of shape(D,) giving running variance of features
Returns a tuple of:
- out: of shape (N, D)
- cache: A tuple of values needed in the backward pass
"""
mode = bn_param['mode']
eps = bn_param.get('eps', 1e-5)
momentum = bn_param.get('momentum', 0.9)
N, D = x.shape
running_mean = bn_param.get('running_mean', np.zeros(D, dtype=x.dtype))
running_var = bn_param.get('running_var', np.zeros(D, dtype=x.dtype))
out, cache = None, None
if mode == 'train':
sample_mean = np.mean(x, axis=0) #np.mean([[1,2],[3,4]])->[2,3]
sample_var = np.var(x, axis=0)
out_ = (x - sample_mean) / np.sqrt(sample_var + eps)
running_mean = momentum * running_mean + (1 - momentum) * sample_mean
running_var = momentum * running_var + (1 - momentum) * sample_var
out = gamma * out_ + beta
cache = (out_, x, sample_var, sample_mean, eps, gamma, beta)
elif mode == 'test':
# scale = gamma / np.sqrt(running_var + eps)
# out = x * scale + (beta - running_mean * scale)
x_hat = (x - running_mean) / (np.sqrt(running_var + eps))
out = gamma * x_hat + beta
else:
raise ValueError('Invalid forward batchnorm mode "%s"' % mode)
# Store the updated running means back into bn_param
bn_param['running_mean'] = running_mean
bn_param['running_var'] = running_var
return out, cache
反向传播代码:
def batchnorm_backward(dout, cache):
"""
Backward pass for batch normalization.
Inputs:
- dout: Upstream derivatives, of shape (N, D)
- cache: Variable of intermediates from batchnorm_forward.
Returns a tuple of:
- dx: Gradient with respect to inputs x, of shape (N, D)
- dgamma: Gradient with respect to scale parameter gamma, of shape (D,)
- dbeta: Gradient with respect to shift parameter beta, of shape (D,)
"""
dx, dgamma, dbeta = None, None, None
out_, x, sample_var, sample_mean, eps, gamma, beta = cache
N = x.shape[0]
dout_ = gamma * dout
dvar = np.sum(dout_ * (x - sample_mean) * -0.5 * (sample_var + eps) ** -1.5, axis=0)
dx_ = 1 / np.sqrt(sample_var + eps)
dvar_ = 2 * (x - sample_mean) / N
# intermediate for convenient calculation
di = dout_ * dx_ + dvar * dvar_
dmean = -1 * np.sum(di, axis=0)
dmean_ = np.ones_like(x) / N
dx = di + dmean * dmean_
dgamma = np.sum(dout * out_, axis=0)
dbeta = np.sum(dout, axis=0)
return dx, dgamma, dbeta
使用BN注意事项
- 训练时要将traning参数设置为True,在验证时将trainning参数设置为False。在pytorch中可通过创建 模型的model.train()和model.eval()方法控制。
- 训练时要将traning参数设置为True,在验证时将trainning参数设置为False。在pytorch中可通过创建 模型的model.train()和model.eval()方法控制。
- 一般将bn层放在卷积层(Conv)和激活层(例如Relu)之间,且卷积层不要使用偏置bias。因为使用偏置只会徒增网络的参数,导致训练起来更加的费劲。
下面我来用公式证明为什么不要使用偏置:

不难看出卷积是否使用偏置,在经过BN层之后的输出都是一样的。