算法介绍及实现——基于遗传算法改进的BP神经网络算法(附完整Python实现)
目录
一、算法介绍
1.1 遗传算法
1.2 为什么要使用遗传算法进行改进
二、算法原理
三、算法实现
3.1 算子选择
3.2 代码实现
一、算法介绍
1.1 遗传算法
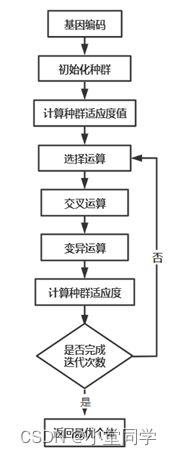
遗传算法是受启发于自然界中生物对于自然环境 “适者生存”的强大自适应能力,通过对生物演化过程模拟和抽象,构建了以自然界生物演变进化为逻辑基础的遗传算法。遗传算法包括了自然界生物在演变过程中的主要步骤,即选择、(基因)变异和(基因)交叉,对应着遗传算法中的三个运算算子。在具体的优化问题下,遗传算法会产生多个问题的可行解作为种群,然后让种群进行模拟意义上生物进化中的选择、变异、交叉等操作。在种群繁衍(迭代)一定次数之后,通过计算种群的适应度,寻找最终种群中的最优个体,该个体即代表优化问题的近似最优解。上述此即为遗传算法主要思想。其流程图如下:
1.2 为什么要使用遗传算法进行改进
BP算法原理不多赘述,可见我之前博文BP原理介绍,在BP训练过程中,很容易出现陷入局部最小值的情况,所以引入遗传算法进行优化。遗传作为一种模拟生物进化的全局寻优算法,有着优秀的全局寻优能力,能够以一个种群为基础不断的迭代进化,最后获得问题的最优解或近似最优解。BP算法和遗传算法都是人们广泛使用的算法,而且两算法具有明显的优势互补,故而很多研究者都在探索两个算法的融合方法,以期能提高算法性能、提升算法精度。
二、算法原理
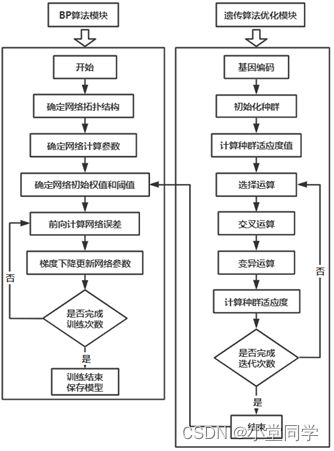
基于遗传算法改进的BP神经网络算法(GA-BP算法)的主要思想即为:通过遗传算法的全局寻优能力获得最优的BP网络的初始权值和阈值,将寻优算法获得的最优初始权值和阈值作为BP神经网络的初始权值和阈值,然后进行训练以避免陷入局部最小值。遗传算法改进后的BP神经网络权值不是随机产生的,而是遗传算法寻优模块获得的。BP算法中的初始权值和阈值作为遗传算法个体的基因值,个体长度即为BP神经网络中权值和阈值的个数,每个基因即代表一个权值或阈值,基因上的数值就是BP神经网络中连接权值或阈值的真实值,如此便组成了遗传算法中的一个染色体。一定数量的染色体作为遗传算法训练的初始种群,再经过遗传算法的选择运算、交叉运算、变异运算等迭代过程后获得一个最优个体,然后以最优个体作为BP网络的初始参数进行训练,此即为GA-BP算法的原理。流程图如下:
三、算法实现
3.1 算子选择
对于(e)所述的组织方法,是当影响因子数据和目标数据没有很强的相关性的情况下,用前一时序区间的数据作为该时序数据的影响因子来进行训练。
3.2 代码实现
实例为基于一段时序监测数据的滑坡位移预测,监测影响因子数据有:温度、降雨、风力、灌溉等,监测的目标数据是坡体的裂缝宽度数据。实验表明影响因子数据和目标数据不具有强相关性,所以选择用目标数据本身作为影响因子数据。
将整个算法分成如下模块:
chrom_code # 基因编码模块
chrom_mutate # 变异算子模块
chrom_cross # 交叉算子模块
chrom_select # 选择算子模块
chrom_fitness # 染色体适应度计算模块
data_prepare # 数据准备模块
BP_network # BPNN模块
chrom_test # 染色体检测模块
new_GA-BP # 改进算法主程序
chrom_test.py 检测生成的染色体基因有没有超限。
# 染色体检查
# 检查染色体中有没有超出基因范围的基因
def test(code_list,bound):
"""
:param code_list: code_list: 染色体个体
:param bound: 各基因的取值范围
:return: bool
"""
for i in range(len(code_list)):
if code_list[i] < bound[i][0] or code_list[i] > bound[i][1]:
return False
else:
return Truechrom_code.py 基因编码。
# 基因编码模块
import random
import numpy as np
import chrom_test
def code(chrom_len,bound):
"""
:param chrom_len: 染色体的长度,为一个数,采用实数编码即为基因的个数
:param bound: 取值范围,为一个二维数组,每个基因允许的取值范围
:return: 对应长度的编码
"""
code_list = []
count = 0
while True:
pick = random.uniform(0,1)
if pick == 0:
continue
else:
pick = round(pick,3)
temp = bound[count][0] + (bound[count][1] - bound[count][0])*pick
temp = round(temp,3)
code_list.append(temp)
count = count + 1
if count == chrom_len:
if chrom_test.test(code_list,bound):
break
else:
count = 0
return code_listBP_network.py 完成网络结构的构建。
# BP模块 借助PyTorch实现
import torch
# 引入了遗传算法参数的BP模型
class BP_net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_feature, n_hidden, n_output, GA_parameter):
super(BP_net, self).__init__()
# 构造隐含层和输出层
self.hidden = torch.nn.Linear(n_feature, n_hidden)
self.output = torch.nn.Linear(n_hidden, n_output)
# 给定网络训练的初始权值和偏执等
self.hidden.weight = torch.nn.Parameter(GA_parameter[0])
self.hidden.bias = torch.nn.Parameter(GA_parameter[1])
self.output.weight = torch.nn.Parameter(GA_parameter[2])
self.output.bias = torch.nn.Parameter(GA_parameter[3])
def forward(self, x):
# 前向计算
hid = torch.tanh(self.hidden(x))
out = torch.tanh(self.output(hid))
return out
# 传统的BP模型
class ini_BP_net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_feature, n_hidden, n_output):
super(ini_BP_net, self).__init__()
# 构造隐含层和输出层
self.hidden = torch.nn.Linear(n_feature, n_hidden)
self.output = torch.nn.Linear(n_hidden, n_output)
def forward(self, x):
# 前向计算
hid = torch.tanh(self.hidden(x))
out = torch.tanh(self.output(hid))
return out
def train(model, epochs, learning_rate, x_train, y_train):
"""
:param model: 模型
:param epochs: 最大迭代次数
:param learning_rate:学习率
:param x_train:训练数据(输入)
:param y_train:训练数据(输出)
:return: 最终的loss值(MSE)
"""
# path = "log.txt"
# f = open(path, 'w',encoding='UTF-8')
# f.write("train log\n------Train Action------\n"
# "Time:{}\n".format(time.ctime()))
loss_fc = torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction="sum")
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
loss_list = []
for i in range(epochs):
model.train()
# 前向计算
data = model(x_train)
# 计算误差
loss = loss_fc(data, y_train)
loss_list.append(loss)
# 更新梯度
optimizer.zero_grad()
# 方向传播
loss.backward()
# 更新参数
optimizer.step()
# print("This is {} th iteration,MSE is {}。".format(i+1,loss))
loss_ls = [loss_list[i].detach().numpy() for i in range(len(loss_list))]
return loss_ls
chrom_fitness.py 适应度计算
# 适应度计算模块
# 功能;传入一个编码,返回一个适应度值
from torchvision.transforms import transforms
import torch
import BP_network
import numpy as np
# 最小二乘思想获得两组数据的误差
def zxec_PC(X, Y):
X = np.array(X, dtype=np.float).flatten()
Y = np.array(Y, dtype=np.float).flatten()
if len(X) != len(Y):
print("Wrong!")
n = len(X)
Wc = 0
for i in range(n):
Wc = Wc + (X[i] - Y[i]) * (X[i] - Y[i])
return Wc
def calculate_fitness(code,n_feature,n_hidden,n_output,epochs
,learning_rate,x_train,y_train):
"""
:param code: 染色体编码
:param n_feature: 输入层个数
:param n_hidden: 隐含层个数
:param n_output: 输出层个数
:param epochs: 最多迭代次数
:param learning_rate: 学习率
:param x_train: 训练(输入)数据
:param y_train: 训练(输出)数据
:return: fitness 适应度值
"""
Parameter = code[:]
# 参数提取
hidden_weight = Parameter[0:n_feature * n_hidden]
hidden_bias = Parameter[n_feature * n_hidden:
n_feature * n_hidden + n_hidden]
output_weight = Parameter[n_feature * n_hidden + n_hidden:
n_feature * n_hidden + n_hidden + n_hidden * n_output]
output_bias = Parameter[n_feature * n_hidden + n_hidden + n_hidden * n_output:
n_feature * n_hidden + n_hidden + n_hidden * n_output + n_output]
# 类型转换
tensor_tran = transforms.ToTensor()
hidden_weight = tensor_tran(np.array(hidden_weight).reshape((n_hidden, n_feature))).to(torch.float32)
hidden_bias = tensor_tran(np.array(hidden_bias).reshape((1, n_hidden))).to(torch.float32)
output_weight = tensor_tran(np.array(output_weight).reshape((n_output,n_hidden))).to(torch.float32)
output_bias = tensor_tran(np.array(output_bias).reshape((1, n_output))).to(torch.float32)
# 形装转换
hidden_weight = hidden_weight.reshape((n_hidden,n_feature))
hidden_bias = hidden_bias.reshape(n_hidden)
output_weight = output_weight.reshape((n_output,n_hidden))
output_bias = output_bias.reshape(n_output)
# 带入模型计算
GA = [hidden_weight, hidden_bias, output_weight, output_bias]
BP_model = BP_network.BP_net(n_feature,n_hidden,n_output,GA)
loss = BP_network.train(BP_model,epochs,learning_rate,x_train,y_train)
# 计算适应度
prediction = BP_model(x_train)
fitness = 10 - zxec_PC(prediction.detach().numpy(),y_train.detach().numpy())
return round(fitness,4)chrom_mutate.py 选择算子
# 变异算子
import random
def mutate(chrom_sum, size, p_mutate, chrom_len, bound, maxgen, nowgen):
"""
:param chrom_sum: 染色体群,即种群,里面为一定数量的染色体 类型为一个二维列表
:param size: 种群规模,即染色体群里面有多少个染色体 为一个数
:param p_mutate: 交叉概率 为一个浮点数
:param chrom_len: 种群长度,即一条染色体的长度,即基因的个数 为一个数
:param bound: 各基因的取值范围
:param maxgen: 最大迭代次数
:param nowgen: 当前迭代次数
:return: 变异算子后的种群
"""
count = 0
# print("\n---这是第{}次遗传迭代...".format(nowgen))
while True:
# 随机选择变异染色体
# print("{}-{}".format(nowgen,count+1))
seek = random.uniform(0,1)
while seek == 1:
seek = random.uniform(0,1)
index = int(seek * size)
# print("可能变异的染色体号数为:",index)
# 判断是否变异
flag = random.uniform(0,1)
if p_mutate >= flag:
# 选择变异位置
# print("发生变异中...")
seek1 = random.uniform(0,1)
while seek1 == 1:
seek1 = random.uniform(0,1)
pos = int(seek1 * chrom_len)
# print("变异的基因号数为:",pos)
# 开始变异
seek3 = random.uniform(0,1)
fg = pow(seek3*(1-nowgen/maxgen),2) # 约到迭代后期,其至越接近0,变异波动就越小
# print("变异前基因为:",chrom_sum[index][pos])
if seek3 > 0.5:
chrom_sum[index][pos] = round(chrom_sum[index][pos] +
(bound[pos][1] - chrom_sum[index][pos])*fg,3)
else:
chrom_sum[index][pos] = round(chrom_sum[index][pos] -
(chrom_sum[index][pos] - bound[pos][0])*fg,3)
# print("变异后基因为:", chrom_sum[index][pos])
count = count + 1
else:
# print("未发生变异。")
count = count + 1
if count == size:
break
return chrom_sumchrom_cross.py 交叉算子
# 交叉算子
import random
import chrom_test
def cross(chrom_sum, size, p_cross, chrom_len, bound):
"""
:param chrom_sum:种群集合,为二维列表
:param size:种群总数,即染色体的个数
:param p_cross:交叉概率
:param chrom_len:染色提长度,每个染色体含基因数
:param bound:每个基因的范围
:return: 交叉后的种群集合
"""
count = 0
while True:
# 第一步 先选择要交叉的染色体
seek1 = random.uniform(0,1)
seek2 = random.uniform(0,1)
while seek1 == 0 or seek2 == 0 or seek1 == 1 or seek2 == 1:
seek1 = random.uniform(0, 1)
seek2 = random.uniform(0, 1)
# index_1(2)为选中交叉的个体在种群中的索引
index_1 = int(seek1 * size)
index_2 = int(seek2 * size)
if index_1 == index_2:
if index_2 == size - 1:
index_2 = index_2 - 1
else:
index_2 = index_2 + 1
# print("可能交叉的两个染色体为:",index_1,index_2)
# 第二步 判断是否进行交叉
flag = random.uniform(0,1)
while flag == 0:
flag = random.uniform(0,1)
if p_cross >= flag:
# 第三步 开始交叉
# print("开始交叉...")
p_pos = random.uniform(0, 1)
while p_pos == 0 or p_pos == 1:
p_pos = random.uniform(0, 1)
pos = int(p_pos * chrom_len)
# print("交叉的极影位置为:",pos)
var1 = chrom_sum[index_1][pos]
var2 = chrom_sum[index_2][pos]
pick = random.uniform(0,1)
# print("交叉前染色体为:")
# print(chrom_sum[index_1])
# print(chrom_sum[index_2])
chrom_sum[index_1][pos] = round((1-pick) * var1 + pick * var2,3)
chrom_sum[index_2][pos] = round(pick * var1 + (1-pick) * var2,3)
# print("交叉后染色体为:")
# print(chrom_sum[index_1])
# print(chrom_sum[index_2])
if chrom_test.test(chrom_sum[index_1],bound) and chrom_test.test(chrom_sum[index_2],bound):
count = count + 1
else:
continue
else:
# print("没有发生交叉。")
count = count + 1
# print("本次循环结束\n")
if count == size:
break
return chrom_sumchrom_select.py 选择算子
# 选择算子
import numpy as np
import random
def select(chrom_sum,fitness_ls):
"""
:param chrom_sum:种群
:param fitness_ls: 各染色体的适应度值
:return: 更新后的种群
"""
# print("种群适应度分别为:",fitness_ls)
fitness_ls = np.array(fitness_ls,dtype=np.float64)
sum_fitness_ls = np.sum(fitness_ls,dtype=np.float64)
P_inh = []
M = len(fitness_ls)
for i in range(M):
P_inh.append(fitness_ls[i]/sum_fitness_ls)
# 将概率累加
for i in range(len(P_inh)-1):
P_temp = P_inh[i] + P_inh[i+1]
P_inh[i+1] = round(P_temp, 2)
P_inh[-1] = 1
# 轮盘赌算法选择染色体
account = []
for i in range(M):
rand = random.random()
for j in range(len(P_inh)):
if rand <= P_inh[j]:
account.append(j)
break
else:
continue
# 根据索引号跟新种群
# print("轮盘赌的结果为:",account)
new_chrom_sum = []
for i in account:
new_chrom_sum.append(chrom_sum[i])
return new_chrom_sum
data_prepare.py 数据准备
# 数据准备
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
def Data_loader():
# 文件路径
ENU_measure_path = "18-10-25至19-3-25三方向位移数据.xlsx"
t_path = "天气数据.xls"
M_path = "data.csv"
# 三方向数据
df_1 = pd.read_excel(ENU_measure_path)
ENU_df = pd.DataFrame(df_1)
ENU_E = ENU_df["E/m"]
ENU_E = np.array(ENU_E)
ENU_N = ENU_df["N/m"]
ENU_N = np.array(ENU_N)
ENU_U = ENU_df["U/m"]
ENU_U = np.array(ENU_U)
ENU_R = ENU_df['R/m']
ENU_R = np.array(ENU_R)
df_2 = pd.read_excel(t_path)
t_df = pd.DataFrame(df_2)
# 最大温度数据
max_tem = t_df["bWendu"]
max_tem_ls = []
for i in range(len(max_tem)):
temp = str(max_tem[i])
temp = temp.replace("℃","")
max_tem_ls.append(eval(temp))
max_tem = np.array(max_tem_ls)
# 最低温度数据
min_tem = t_df["yWendu"]
min_tem_ls = []
for i in range(len(min_tem)):
temp = str(min_tem[i])
temp = temp.replace("℃","")
min_tem_ls.append(eval(temp))
min_tem =np.array(min_tem_ls)
# 天气数据
tianqi = t_df["Tian_Qi"]
tianqi = np.array(tianqi)
# 风力数据
Feng = t_df["Feng"]
Feng = np.array(Feng)
# 降雨数据
rain = t_df["rainfall"]
rain = np.array(rain)
# 灌溉数据
guangai = t_df["guangai"]
guangai = np.array(guangai)
# 获取时间数据
namels = t_df["ymd"]
name_ls = []
for i in range(len(namels)):
temp = str(namels[i])
temp = temp.replace(" 00:00:00","")
name_ls.append(str(temp))
# 读取另一文件数据,该数据为位移计和GNSS监测数据
df_3 = pd.read_csv(M_path)
M_df = pd.DataFrame(df_3)
M_data = M_df["Measurerel"]
R_data = M_df["R"]
M_data = np.array(M_data)
R_data = np.array(R_data)
return [ENU_R, M_data, R_data, ENU_U, ENU_E, ENU_N,max_tem,min_tem,name_ls]
主程序!!!!
# 改进算法主程序
import sys
import chrom_code # 基因编码模块
import chrom_mutate # 变异算子模块
import chrom_cross # 交叉算子模块
import chrom_select # 选择算子模块
import chrom_fitness # 染色体适应度计算模块
import data_prepare # 数据准备模块
import BP_network # BPNN模块
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torchvision.transforms import transforms
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import time
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# -----参数设置-----
epochs = 300 # 神经网络最大迭代次数
learning_rate = 0.01 # 学习率
n_feature = 6 # 输入层个数
n_hidden = 9 # 隐含层个数
n_output = 1 # 输出层个数
chrom_len = n_feature * n_hidden + n_hidden + n_hidden * n_output + n_output # 染色体长度
size = 15 # 种群规模
bound = np.ones((chrom_len, 2))
sz = np.array([[-1, 0], [0, 1]])
bound = np.dot(bound, sz) # 各基因取值范围
p_cross = 0.4 # 交叉概率
p_mutate = 0.01 # 变异概率
maxgen = 30 # 遗传最大迭代次数
# 数据准备
# ========================================= #
data_set = data_prepare.Data_loader()
displace = data_set[1]
name_ls = data_set[-1]
in_train_data = []
in_test_data = []
# 数目分配
train_num = 120
test_num = len(displace) - train_num - n_feature
for i in range(len(displace)):
temp = []
if i <= train_num-1: # 用于控制训练数据和预测数据的分配
temp = [round(displace[i + j], 5) for j in range(n_feature)]
in_train_data.append(temp)
else:
temp = [round(displace[i + j], 5) for j in range(n_feature)]
in_test_data.append(temp)
if i == len(displace)-n_feature-1:
break
# 格式转化
in_train_data = np.array(in_train_data)
in_test_data = np.array(in_test_data)
# 数据分割,用于建模和预测
out_train_data = displace[n_feature:train_num+n_feature]
out_test_data = displace[train_num+n_feature:len(displace)]
# 测试输出
# print(in_train_data)
# print(out_train_data)
# print(in_test_data)
# print(out_test_data)
# print(train_num)
# print(test_num)
# 数据格式转换及数据归一化
tensor_tran = transforms.ToTensor()
# 训练过程中的输入层数据
in_train_data = tensor_tran(in_train_data).to(torch.float)
in_train_data = F.normalize(in_train_data)
in_train_data = in_train_data.reshape(train_num, n_feature)
# 预测过程中的输入层数据
in_test_data = tensor_tran(in_test_data).to(torch.float)
in_test_data = F.normalize(in_test_data)
in_test_data = in_test_data.reshape(test_num, n_feature)
# 训练过程中的输出层数据
out_train_data = out_train_data.reshape(len(out_train_data), 1)
out_train_data = tensor_tran(out_train_data).to(torch.float)
un_norm1 = out_train_data[0][0]
out_train_data = F.normalize(out_train_data)
norm1 = out_train_data[0][0]
out_train_data = out_train_data.reshape(train_num, n_output)
fanshu_train = round(float(un_norm1 / norm1), 4) # 建模时,训练数据中输出数据的范数
# 预测中用于检验的输出层数据
out_test_data = out_test_data.reshape(len(out_test_data), 1)
out_test_data = tensor_tran(out_test_data).to(torch.float)
un_norm = out_test_data[0][0] # 归一化前
out_test_data = F.normalize(out_test_data)
norm = out_test_data[0][0] # 归一化后
out_test_data = out_test_data.reshape(test_num, n_output)
fanshu = round(float(un_norm / norm), 4) # 预测时,测试数据中输出数据的范数
# 建模训练数据
x_train = in_train_data
y_train = out_train_data
x_test = in_test_data
y_label = out_test_data
# ========================================== #
chrom_sum = [] # 种群,染色体集合
for i in range(size):
chrom_sum.append(chrom_code.code(chrom_len, bound))
account = 0 # 遗传迭代次数计数器
best_fitness_ls = [] # 每代最优适应度
ave_fitness_ls = [] # 每代平均适应度
best_code = [] # 迭代完成适应度最高的编码值
# 适应度计算
fitness_ls = []
for i in range(size):
fitness = chrom_fitness.calculate_fitness(chrom_sum[i], n_feature, n_hidden, n_output,
epochs, learning_rate, x_train, y_train)
fitness_ls.append(fitness)
# 收集每次迭代的最优适应值和平均适应值
fitness_array = np.array(fitness_ls).flatten()
fitness_array_sort = fitness_array.copy()
fitness_array_sort.sort()
best_fitness = fitness_array_sort[-1]
best_fitness_ls.append(best_fitness)
ave_fitness_ls.append(fitness_array.sum() / size)
while True:
# 选择算子
# print("\n这是第{}次遗传迭代。".format(account+1))
# print("平均适应度为:",fitness_array.sum()/size)
chrom_sum = chrom_select.select(chrom_sum, fitness_ls)
# 交叉算子
chrom_sum = chrom_cross.cross(chrom_sum, size, p_cross, chrom_len, bound)
# 变异算子
chrom_sum = chrom_mutate.mutate(chrom_sum, size, p_mutate, chrom_len, bound, maxgen, account + 1)
# 适应度计算
fitness_ls = []
for i in range(size):
fitness = chrom_fitness.calculate_fitness(chrom_sum[i], n_feature, n_hidden, n_output,
epochs, learning_rate, x_train, y_train)
fitness_ls.append(fitness)
# 收集每次迭代的最优适应值和平均适应值
fitness_array = np.array(fitness_ls).flatten()
fitness_array_sort = fitness_array.copy()
fitness_array_sort.sort()
best_fitness = fitness_array_sort[-1] # 获取最优适应度值
best_fitness_ls.append(best_fitness)
ave_fitness_ls.append(fitness_array.sum() / size)
# 计数器加一
account = account + 1
if account == maxgen:
index = fitness_ls.index(max(fitness_ls)) # 返回最大值的索引
best_code = chrom_sum[index] # 通过索引获得对于染色体
break
# 参数提取
hidden_weight = best_code[0:n_feature * n_hidden]
hidden_bias = best_code[n_feature * n_hidden:
n_feature * n_hidden + n_hidden]
output_weight = best_code[n_feature * n_hidden + n_hidden:
n_feature * n_hidden + n_hidden + n_hidden * n_output]
output_bias = best_code[n_feature * n_hidden + n_hidden + n_hidden * n_output:
n_feature * n_hidden + n_hidden + n_hidden * n_output + n_output]
# 类型转换
tensor_tran = transforms.ToTensor()
hidden_weight = tensor_tran(np.array(hidden_weight).reshape((n_hidden, n_feature))).to(torch.float32)
hidden_bias = tensor_tran(np.array(hidden_bias).reshape((1, n_hidden))).to(torch.float32)
output_weight = tensor_tran(np.array(output_weight).reshape((n_output, n_hidden))).to(torch.float32)
output_bias = tensor_tran(np.array(output_bias).reshape((1, n_output))).to(torch.float32)
# 形装转换
hidden_weight = hidden_weight.reshape((n_hidden, n_feature))
hidden_bias = hidden_bias.reshape(n_hidden)
output_weight = output_weight.reshape((n_output, n_hidden))
output_bias = output_bias.reshape(n_output)
GA = [hidden_weight, hidden_bias, output_weight, output_bias]
# 带入模型计算
BP_model = BP_network.BP_net(n_feature, n_hidden, n_output, GA)
ini_BP_model = BP_network.ini_BP_net(n_feature, n_hidden, n_output)
# 网络训练
loss = BP_network.train(BP_model, epochs, learning_rate, x_train, y_train)
ini_loss = BP_network.train(ini_BP_model, epochs, learning_rate, x_train, y_train)
# 建模效果
model_x = BP_model(x_train)
ini_model_x = ini_BP_model(x_train)
# 网络预测
prediction = BP_model(x_test)
ini_prediction = ini_BP_model(x_test)
# 建模数据反归一化(都换算到厘米级)
y_train = y_train.detach().numpy() * fanshu_train
model_x = model_x.detach().numpy() * fanshu_train
ini_model_x = ini_model_x.detach().numpy() * fanshu_train
# 建模绘图
train_name_ls = name_ls[6:126]
xlabel = [i for i in range(0, 120, 14)]
plt.plot(y_train, markersize=4, marker='.', label="真值", c='r')
plt.plot(model_x, markersize=4, marker='.', label="GA-BP预测值", c='b')
plt.title("GA-BP算法建模情况")
plt.ylabel("累计裂缝宽度(mm)")
plt.xticks(xlabel, [train_name_ls[i] for i in xlabel], rotation=25)
plt.grid(linestyle='-.') # 设置虚线
plt.legend()
f2 = plt.figure()
plt.plot(y_train, markersize=4, marker='.', label="真值", c='r')
plt.plot(ini_model_x, markersize=4, marker='.', label="BP预测值", c='g')
plt.title("BP算法建模情况")
plt.ylabel("累计裂缝宽度(mm)")
plt.xticks(xlabel, [train_name_ls[i] for i in xlabel], rotation=25)
plt.grid(linestyle='-.')
plt.legend()
# 预测数据格式转换(厘米级)
GABP_prediction = prediction.detach().numpy()
BP_prediction = ini_prediction.detach().numpy()
y_label = y_label.detach().numpy()
# 预测数据反归一化(厘米级)
GABP_prediction = GABP_prediction * fanshu
BP_prediction = BP_prediction * fanshu
y_label = y_label * fanshu
# 计算预测结果的SSE误差
def get_MSE(argu1, argu2):
if len(argu1) != len(argu2):
return 0
error = 0
for i in range(len(argu1)):
error = error + pow((argu1[i] - argu2[i]), 2)
error = float(error[0])
return round(error, 5)
error_BP = get_MSE(y_label, BP_prediction)
error_GA_BP = get_MSE(y_label, GABP_prediction)
print("BP算法预测MSE误差为:", error_BP)
print("GA-BP算法预测MSE误差为:", error_GA_BP)
# 将巡行情况和运行结果写入日志
f = open("log.txt",'a',encoding='UTF-8') # 追加写打开文件
f.write("运行时间:" + str(time.ctime()) + '\n')
f.write("训练数据长度为:" + str(train_num) + '\n'
+ "测试数据长度为:" + str(test_num) + '\n')
f.write("网络结构层数为:{}、{}、{}\n".format(n_feature,n_hidden,n_output))
f.write("遗传迭代所获得的最优权值为:" + str(best_code) + "\n")
f.write("======预测结果如下======\n真值数据为:" + str(y_label.flatten()) + '\n')
f.write("BP预测结果为:" + str(BP_prediction.flatten()) + "\n"
+ "GA-BP预测结果为:" + str(GABP_prediction.flatten()) + '\n')
f.write("-->>BP预测MSE误差为:" + str(error_BP) + '平方厘米\n'
+ "-->>GA-BP预测MSE误差为:" + str(error_GA_BP) + '平方厘米\n\n')
f.close()
# 预测绘图
test_name_ls = name_ls[126:152]
xlabel2 = [i for i in range(0, 26, 4)]
f3 = plt.figure()
plt.plot(y_label, markersize=4, marker='.', label="真值", c='r')
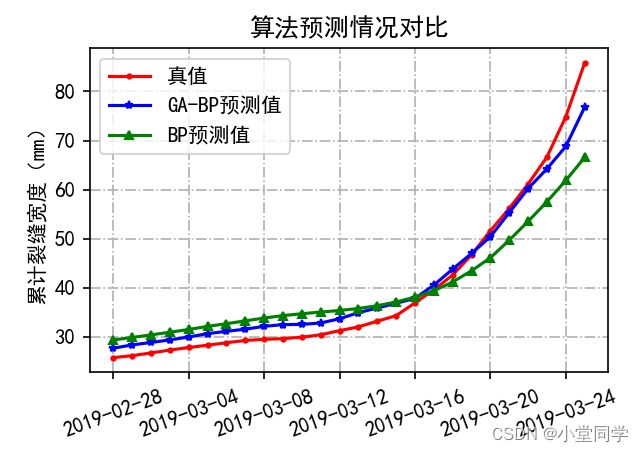
plt.plot(GABP_prediction, markersize=4, marker='*', label="GA-BP预测值", c='b')
plt.plot(BP_prediction, markersize=4, marker='^', label="BP预测值", c='g')
plt.title("算法预测情况对比")
plt.ylabel("累计裂缝宽度(mm)")
plt.xticks(xlabel2, [test_name_ls[i] for i in xlabel2], rotation=20)
plt.legend()
plt.grid(linestyle='-.')
f4 = plt.figure()
plt.plot(y_label, markersize=4, marker='.', label="真值", c='r')
plt.plot(BP_prediction, markersize=4, marker='^', label="BP预测值", c='g')
plt.title("BP算法预测情况")
plt.ylabel("累计裂缝宽度(mm)")
plt.xticks(xlabel2, [test_name_ls[i] for i in xlabel2], rotation=20)
plt.legend()
plt.grid(linestyle='-.')
f5 = plt.figure()
plt.plot(y_label, markersize=4, marker='.', label="真值", c='r')
plt.plot(GABP_prediction, markersize=4, marker='*', label="GA-BP预测值", c='b')
plt.title("GA-BP算法预测情况")
plt.ylabel("累计裂缝宽度(mm)")
plt.xticks(xlabel2, [test_name_ls[i] for i in xlabel2], rotation=20)
plt.legend()
plt.grid(linestyle='-.')
plt.show()对比结果确实有提升:
资源获取:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1pxd_69_RusYgt7iyG1UENA
提取码:tcyb
--来自百度网盘超级会员V3的分享
才疏学浅,水平有限。敬请批评指正!
共勉!