与vuex的区别
去除了 mutation 选项。省去了复杂的disptach和commit流程,直接通过模块实例调用实例的actions中的方法即可触发对应action;在组件中直接可以通过模块实例的$patch修改store状态或者通过action来间接修改store状态。响应式数据原理是proxy,使得数据的增加或者删除字段都具备响应式。
安装
yarn add pinia
引入pinia
在main.ts中注册pinia插件
import {createPinia} from 'pinia' // vue3
// import {PiniaVuePlugin} from 'pinia' // vue2
const app=createApp(App)
app.use(createPinia())
app.mount('#app')
创建状态目录
在src下创建文件夹store,在store下创建文件index.ts,a.ts,b.ts。a.ts和b.ts分别是管理某个状态的模块,index.ts用来整合这些模块。
pinia模块组成
state、actions、getters。
创建pinia模块
对应选项的含义看代码注释。
1.在a.js编写如下代码
import {defineStore} from "pinia"
export default defineStore('a',{ // a是模块的命名空间,不能和其他模块的一样
state:()=>({ // state是一个函数,函数返回值为管理的状态
x:0,
y:0,
}),
})
2.在b.ts编写如下代码
import {defineStore} from "pinia"
export default defineStore('b',{
state:()=>({
name:'b',
age:18,
}),
actions:{
print(msg:string){ // 同步action
console.log(msg)
},
async setAge(newAge:number){ // 异步action
// 模拟接口
const setAgeReq=(age:T)=>new Promise((rel)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{rel(age)},1000)
})
const age=await setAgeReq(newAge)
// 在action中通过实例来直接修改状态
this.age=age
// 在action中也可以通过实例直接调用其他action
// this.print('age is be updated success')
}
},
getters:{
// 和vuex的getters一样,返回一个值就行了。和computed一样具有缓存机制
userInfo():string{
return `name:${this.name} age:${this.age}`
}
},
})
3.在index.ts中整合所有模块
import a from "./a"
import b from "./b"
export {
a,b
}
在组件中使用该状态机
pinia的api基本都在该案例中,注释和代码都很容易理解,相信小伙伴们都看的懂。如果不是很明白,可以看下一章节的api讲解,看懂的可以跳过api讲解章节。
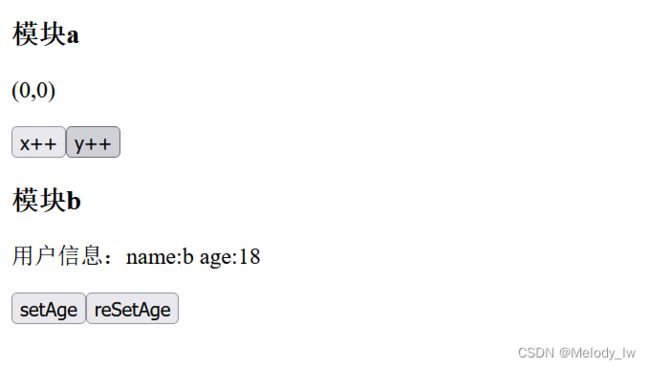
模块a
({{storeA.x}},{{storeA.y}})
模块b
用户信息:{{storeB.userInfo}}
运行结果:
pinia模块实例中的api讲解
1.获取模块实例
// 引入模块
import {a as useA ,b as useB} from "./store"
// 模块是一个函数,函数的返回值是模块的实例
const storeA=useA()
const storeB=useB()
2.提供实例修改对应模块的状态
i:直接修改
/* 通过$patch直接修改store状态,$patch方法接收一个函数,函数的参数是该模块的状态
在这个函数中我们可以直接修改store状态*/
const addx=()=>{storeA.$patch((s)=>{s.x++})}
const addy=()=>{storeA.$patch((s)=>{s.y++})}
ii:间接修改
import {storeToRefs} from "pinia"
// 如果要解构使用状态需要使用该api进行转换,否则不具备响应式
const {x,y}=storeToRefs(useA())
3.状态的解构使用
import {storeToRefs} from "pinia"
// 如果要解构使用状态需要使用该api进行转换,否则不具备响应式
const {x,y}=storeToRefs(useA())
4.监听状态的变更
// 通过 $subscribe监听状态的变更
storeB.$subscribe((c,s)=>{ // state变化时回调。有变化信息和状态两个参数
// console.log(c)
// console.log(s)
},{
detached:false, // 在组件卸载时是否继续监听
deep:true, // 是否深度监听
flush:'post', // post:组件更新后执行 ,sync:始终同步触发 ,pre:组件更新前执行
})
5.监听action的触发
// 通过$onAction监听action的调用
storeB.$onAction((c)=>{ // 当调用action时回调
// console.log(c)
// c.after(()=>{console.log('after caller')}) //after的回调在该函数中最后执行
// console.log('action')
},false) // 为true时,组件卸载时也监听该行为
6.重置状态
// 通过$reset重置对应模块的状态
const reSetAge=()=>{
storeB.$reset()
}
7.注册插件
import {createPinia} from 'pinia'
// plugin是一个函数
createPinia().use(Plugin)
状态持久化
这里需要使用到注册插件的功能。首先在src/plugins/pinia/persistence.ts中编写如下代码
import {PiniaPluginContext} from 'pinia'
import {toRaw } from 'vue'
// 封装pinia持久化插件。执行时机:store初始化时,执行次数是模块的次数
export default function(type:'localStorage' | 'sessionStorage'){
return (ctx:PiniaPluginContext)=>{
// console.log(ctx)
// const {app,options,pinia,store}=ctx
/*
app:vue应用 ;options:导出pinia模块的选项
pinia:pinia app ; store:pinia的store实例
*/
const store= ctx.store // 每次执行时的store是关于那个模块的store
const storeWay=type==='localStorage'?localStorage:sessionStorage
// console.log(store)
store.$subscribe(()=>{
// console.log(toRaw(store.$state))
storeWay.setItem('pinia_'+store.$id,JSON.stringify(toRaw(store.$state)))
},{deep:true})
// return的值为store初始状态。pinia处理过了,如果为retrun为null使用模块的初始值,
return JSON.parse(storeWay.getItem('pinia_'+store.$id) as any)
}
}
然后在mian.js编写如下代码即可。此时刷新浏览器刷新时,状态是可以保持的,不会被重置。
import { createApp} from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import {createPinia} from 'pinia'
// import {PiniaVuePlugin} from 'pinia' // vue2
import persistence from "./plugins/pinia/persistence"
const app=createApp(App)
// app.use(createPinia().use(persistence('sessionStorage'))) //sessionStorage方式持久化
app.use(createPinia().use(persistence('localStorage'))) //localStorage方式持久化
app.mount('#app')
到此这篇关于vue中使用 pinia 全局状态管理的实现的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关vue pinia 全局状态管理内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!