arm-linux 怎么使用v4l2的配置,V4L2 获取和配置摄像头
一、V4L2 获取和配置摄像头程序示例:
#include #include #include #include #include #include #include #includeint fd;
const char *input_dev = "/dev/video0";
const char *qctrl_name = NULL;
int qctrl_value = 0;
struct v4l2_capability cap;
struct v4l2_queryctrl qctrl;
static void print_qctrl(struct v4l2_queryctrl *qctrl)
{
struct v4l2_control ctrl;
ctrl.id = qctrl->id;
if (ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_G_CTRL, &ctrl) < 0)
{
perror("get ctrl failed");
ctrl.value = -999;
}
printf("%-14s : id=%08x, type=%d, minimum=%d, maximum=%d\n"
"\t\t value = %d, step=%d, default_value=%d\n",
qctrl->name, qctrl->id, qctrl->type, qctrl->minimum, qctrl->maximum,
ctrl.value, qctrl->step, qctrl->default_value);
}
static void print_menu(struct v4l2_querymenu *menu)
{
printf("\t %d : %s\n", menu->index, menu->name);
}
static int set_qctrl(struct v4l2_queryctrl *qctrl)
{
struct v4l2_control ctrl;
printf("set %s = %d\n", qctrl_name, qctrl_value);
ctrl.id = qctrl->id;
ctrl.value = qctrl_value;
return ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_S_CTRL, &ctrl);
}
static void deal_qctrl(struct v4l2_queryctrl *qctrl)
{
print_qctrl(qctrl);
if (qctrl_name && !strcmp(qctrl_name, (const char *)qctrl->name))
set_qctrl(qctrl);
}
static void qctrl_get(int id)
{
qctrl.id = id;
if (ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_QUERYCTRL, &qctrl) == 0)
{
deal_qctrl(&qctrl);
if (qctrl.type == V4L2_CTRL_TYPE_MENU)
{
int idx;
struct v4l2_querymenu menu;
for (idx = qctrl.minimum; idx <= qctrl.maximum; idx++)
{
menu.id = qctrl.id;
menu.index = idx;
if (ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_QUERYMENU, &menu)==0)
{
print_menu(&menu);
}
}
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int ret, i;
if (argc == 3)
{
qctrl_name = argv[1];
qctrl_value = atoi(argv[2]);
}
fd = open(input_dev, O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0)
{
perror("open video failed");
return -1;
}
printf("open video '%s' success\n", input_dev);
ret = ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_QUERYCAP, &cap);
if (ret < 0)
{
perror("ioctl querycap");
return -1;
}
if ((cap.capabilities & V4L2_CAP_VIDEO_CAPTURE) == 0)
{
printf("video device donot support capture\n");
return -1;
}
for (i = V4L2_CID_BASE; i < V4L2_CID_LASTP1; i++)
{
qctrl_get(i);
}
for (i = V4L2_CID_PRIVATE_BASE; i < V4L2_CID_PRIVATE_BASE+25; i++)
{
qctrl_get(i);
}
printf("close video\n");
close(fd);
}
二、
程序运行说明:
本程序是摄像头参数获取和配置的示例程序,所以系统必须带有摄像头驱动程序及摄像头传感器
程序参数说明:
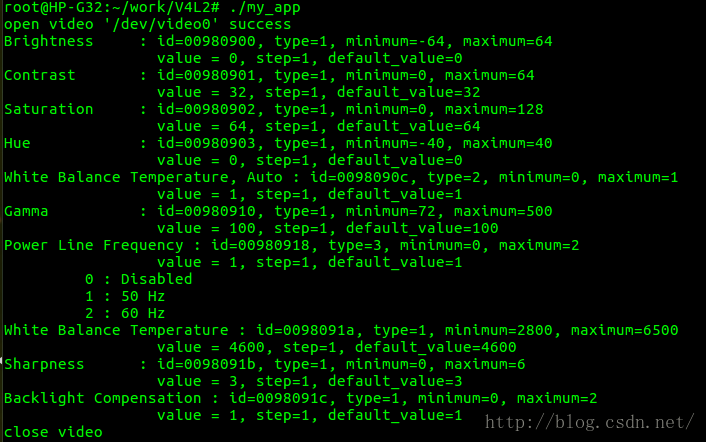
不带任何参数,则显示摄像头可配置的参数,即其当前配置值
三、带两个参数,第一个是要配置选项的名称,第二项为其对应的值。
四、程序原理说明:
本程序可简要使用如下序列说明其运行过程:
1. fd = open(input_dev, O_RDWR); 打开 /dev/video0 设备
2. ret = ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_QUERYCAP, &cap); 获取摄像头设备的能力,例如照相、输出、VBI、调频什么的。这里只需照相能力
3. ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_QUERYCTRL, &qctrl); 通过id来枚举出取摄像头的queryctrl,这个结构体用来描述摄像头的某个具体参数选项的(亮度、色度、曝光度什么的), 包括id, 名称、类型、极值和默认值。
4. ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_QUERYMENU, &menu); 如果上面获取的queryctrl类型是菜单类型的,可使用该步骤来列出所有的菜单项名称。 这一步不是必须的,只是为了让人更清除的知道queryctrl中每个值代表着什么含义。例如 "Light frequency filter" 这个选项的取值范围是 0~2, 3个菜单项说明其3个值的用途。
5. ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_S_CTRL, &ctrl) 和 ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_G_CTRL, &ctrl) 分别是设置和获取参数项当前值的接口,只需指出要配置参数项的id即可。
五、以上几个所涉及的接口体可在 /usr/include/linux/videodev2.h 文件中找到
/*
* CONTROLS
*/
struct v4l2_control {
__u32 id;
__s32 value;
};
/* Used in the VIDIOC_QUERYCTRL ioctl for querying controls */
struct v4l2_queryctrl {
__u32 id;
enum v4l2_ctrl_type type;
__u8 name[32]; /* Whatever */
__s32 minimum; /* Note signedness */
__s32 maximum;
__s32 step;
__s32 default_value;
__u32 flags;
__u32 reserved[2];
};
/* Used in the VIDIOC_QUERYMENU ioctl for querying menu items */
struct v4l2_querymenu {
__u32 id;
__u32 index;
__u8 name[32]; /* Whatever */
__u32 reserved;
};
/*
* DRIVER CAPABILITIES
*/
struct v4l2_capability {
__u8 driver[16]; /* i.e. "bttv" */
__u8 card[32]; /* i.e. "Hauppauge WinTV" */
__u8 bus_info[32]; /* "PCI:" + pci_name(pci_dev) */
__u32 version; /* should use KERNEL_VERSION() */
__u32 capabilities; /* Device capabilities */
__u32 reserved[4];
};