实验1:使用Matlab工具箱进行相机标定实验
目录
-
- 1 相机标定的原理
- 2 实验过程
- 3 实验结果
-
- 3.1 检测特征点(角点)
- 3.2 本次实验平均重投影误差0.15,误差较小
- 3.3 相机外部参数(以相机为中心)
- 3.4 相机内参数和外参数
- 4 matlab生成的源码理解
- 5 矫正图片
1 相机标定的原理
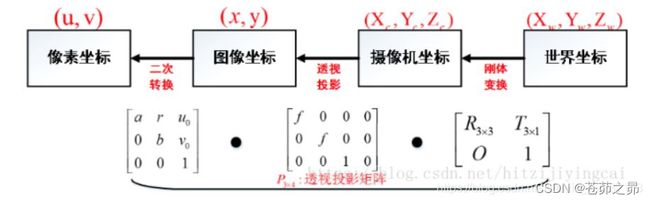
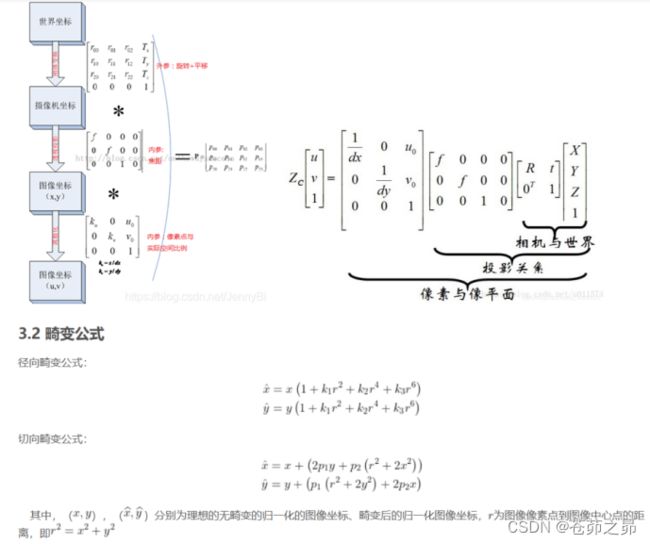
相机标定(Camera calibration)是从世界坐标系换到图像坐标系的过程,也就是求最终的投影矩阵 P的过程。在传统的相机模型中共有4种坐标系,标定的过程分为两个部分:
2 实验过程
本次实验是用matlab工具箱进行相机标定。
(1)打印一张棋盘格A4纸张(棋盘格大小为25mm),并贴在一个平板上
(2)固定相机,针对棋盘格拍摄若干张图片(本次实验用了13张图片)
(3)在图片中检测特征点(角点)
(4)解算出5个内部参数,以及6个外部参数
- 在假设透镜畸变为零的情况下,求解内外参。
- 利用非线性最小二乘极小化(Levenberg-Marquardt)同时估计包括畸变系数在内的所有参数。
- 使用第一步的解作为内、外参数的初始估计。然后将畸变系数的初始估计值设为零。
(5)根据内参校正图像
3 实验结果
3.1 检测特征点(角点)
实验的过程中,发现每张图标定后设置的X,Y和起始点是不完全一样的(原点:图1-左上,图2-右上,图3-左下),程序会根据拍摄角度自己选择坐标系。这说明图片的旋转和角度变换不会影响标定结果。
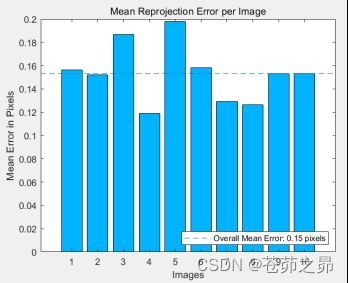
3.2 本次实验平均重投影误差0.15,误差较小
重投影误差:指的真实三维空间点在图像平面上的投影(也就是图像上的像素点)和重投影(其实是用我们的计算值得到的虚拟的像素点)的差值。
3.3 相机外部参数(以相机为中心)
3.4 相机内参数和外参数

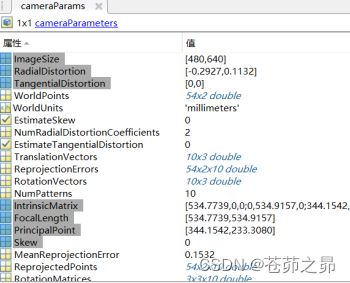
相机的内参数矩阵:

注意: 相机的内参数矩阵,5个自由度,但是还需要对matlab生成的这个矩阵进行转置!opencv不需要~
4 matlab生成的源码理解
参考:使用matlab工具箱进行相机标定实验源码理解
% Auto-generated by cameraCalibrator app on 15-Jul-2022
%-------------------------------------------------------
% Define images to process
imageFileNames = {'C:\Users\Lenovo\Desktop\相机标定图片\pic\left01.jpg',...
'C:\Users\Lenovo\Desktop\相机标定图片\pic\left02.jpg',...
'C:\Users\Lenovo\Desktop\相机标定图片\pic\left04.jpg',...
'C:\Users\Lenovo\Desktop\相机标定图片\pic\left06.jpg',...
'C:\Users\Lenovo\Desktop\相机标定图片\pic\left08.jpg',...
'C:\Users\Lenovo\Desktop\相机标定图片\pic\left09.jpg',...
'C:\Users\Lenovo\Desktop\相机标定图片\pic\left10.jpg',...
'C:\Users\Lenovo\Desktop\相机标定图片\pic\left11.jpg',...
'C:\Users\Lenovo\Desktop\相机标定图片\pic\left12.jpg',...
'C:\Users\Lenovo\Desktop\相机标定图片\pic\left13.jpg',...
};
% 角点检测和世界点生成:
% Detect checkerboards in images 在图像中检测棋盘格
% imagePoints : 矩阵(对于一个图像,大小为 M×2;对于多幅图像,大小为 M×2×图像数;对于立体图像对,大小为 M×2×图像对数×相机数。)
% imagePoints(:,:,:,1)是来自第一组图像的点,imagePoints(:,:,:,2)是来自第二组图像的点。
% 输出包含M个[x y]坐标。每个坐标表示在棋盘上检测的角点。
% boardSize:[height,width]向量,是棋盘格的高和宽,相乘并非角点数!
% imageUsed:N×1 逻辑向量,真:检测到了棋盘,假:未检测到棋盘
[imagePoints, boardSize, imagesUsed] = detectCheckerboardPoints(imageFileNames);
imageFileNames = imageFileNames(imagesUsed);
% Read the first image to obtain image size 读取第一幅图像以获得图像大小
originalImage = imread(imageFileNames{1});% imread函数从文件中加载图像并返回该图像
[mrows, ncols, ~] = size(originalImage); % mrows:行数,ncols:列数
% Generate world coordinates of the corners of the squares
squareSize = 25; % in units of 'millimeters' 棋盘格大小25mm
worldPoints = generateCheckerboardPoints(boardSize, squareSize);% 生成方格的角的世界坐标
% Calibrate the camera
% cameraParams:参数-包含内参、外参和畸变参数
% estimateCameraParameters:标定单目或多目相机
% 两个步骤:
% 1.在假设透镜畸变为零的情况下,求解内外参。
% 2.利用非线性最小二乘极小化(Levenberg-Marquardt)同时估计包括畸变系数在内的所有参数。
% 使用第一步的解作为内、外参数的初始估计。然后将畸变系数的初始估计值设为零。
[cameraParams, imagesUsed, estimationErrors] = estimateCameraParameters(imagePoints, worldPoints, ...
'EstimateSkew', false, 'EstimateTangentialDistortion', false, ... % 切向畸变:EstimateTangentialDistortion,false (default)
'NumRadialDistortionCoefficients', 2, 'WorldUnits', 'millimeters', ... % 径向畸变:NumRadialDistortionCoefficients,2 (default)
'InitialIntrinsicMatrix', [], 'InitialRadialDistortion', [], ...
'ImageSize', [mrows, ncols]);
% View reprojection errors - show重投影误差
h1=figure; showReprojectionErrors(cameraParams);
% Visualize pattern locations 查看相机外参
h2=figure; showExtrinsics(cameraParams, 'CameraCentric');
% Display parameter estimation errors
displayErrors(estimationErrors, cameraParams);
% For example, you can use the calibration data to remove effects of lens distortion.
% undistortImage():根据内参校正图像。返回校正后的图像和校正后图像相对于原有内参坐标系的原点。
% 原图像不符合小孔成像的规则,矫正完的图像符合小孔成像的规则
undistortedImage = undistortImage(originalImage, cameraParams);
% See additional examples of how to use the calibration data. At the prompt type:
% showdemo('MeasuringPlanarObjectsExample')
% showdemo('StructureFromMotionExample')
5 矫正图片
使用以上代码求出的相机参数,矫正使用本相机照出的照片
img=imread('E:\document\QQ\cap.jpg');
subplot(121),imshow(img),title('校正之前');
[correct_img,new]=undistortImage(img,cameraParams); %Matlab自带函数
subplot(122),imshow(correct_img);title('校正之后');